Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F003XN946WA
Southern Washington Cascades Moist Low Cryic Coniferous Forest
Last updated: 1/30/2025
Accessed: 04/08/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 003X–Olympic and Cascade Mountains
Steep mountains and narrow to broad, gently sloping valleys characterize this MLRA. A triple junction of two oceanic plates and one continental plate is directly offshore from Puget Sound. Subduction of the oceanic plates under the westerly and northwesterly moving continental plate contributes to volcanic activity in the Cascade Mountains. Movement among these plates has resulted in major earthquakes and the formation of large stratovolcanoes. The Cascade Mountains consist primarily of volcanic crystalline rock and some associated metasedimentary rock. The mean annual precipitation is dominantly 60 to 100 inches, but it is 30 to 60 inches on the east side of the Cascade Mountains.
The soil orders in this MLRA are dominantly Andisols, Spodosols, and Inceptisols and minor areas of Entisols and Histosols. The soils are dominantly in the frigid or cryic temperature regime and the udic moisture regime. The soils generally are shallow to very deep, well drained, ashy to medial, and loamy or sandy. They are on mountain slopes and ridges.
Ecological site concept
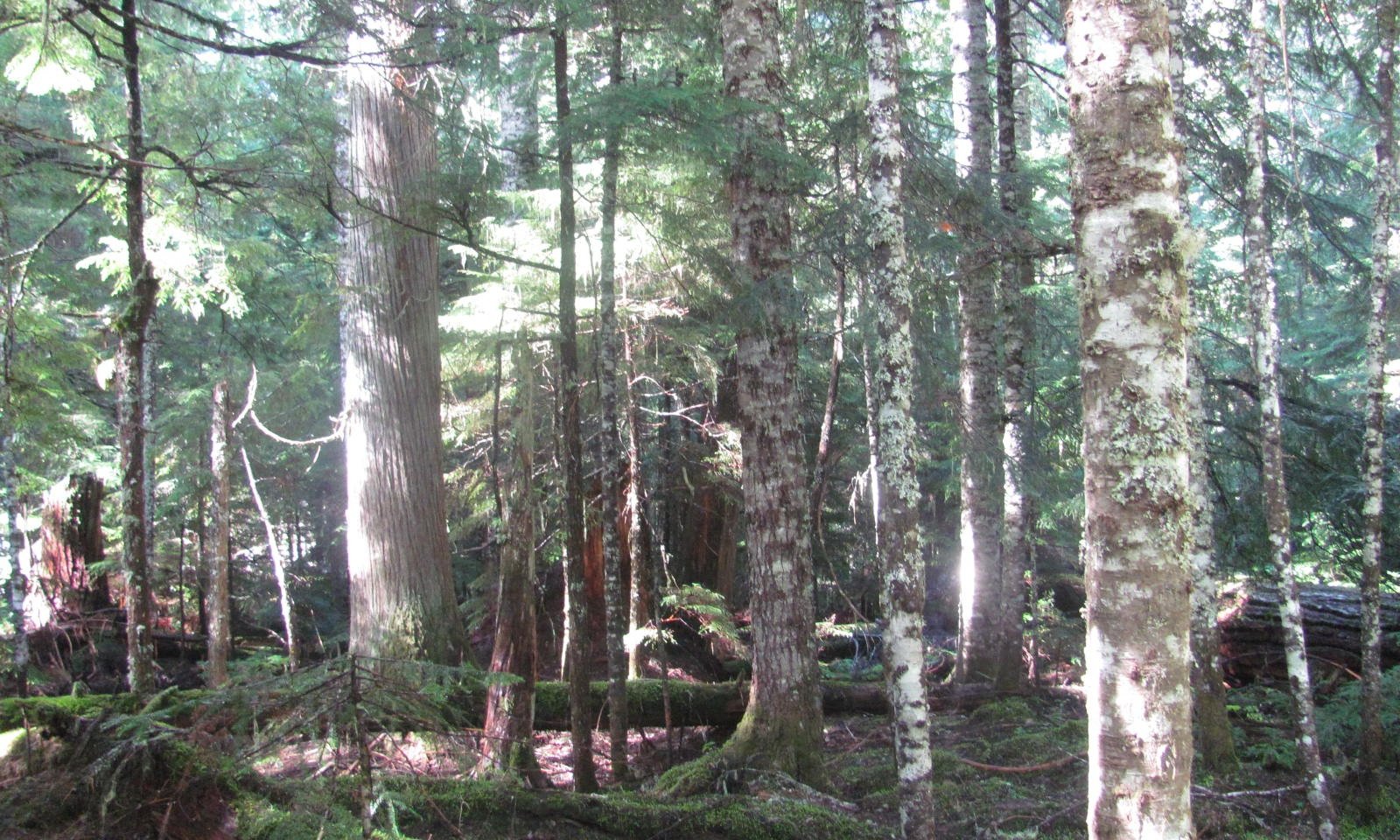
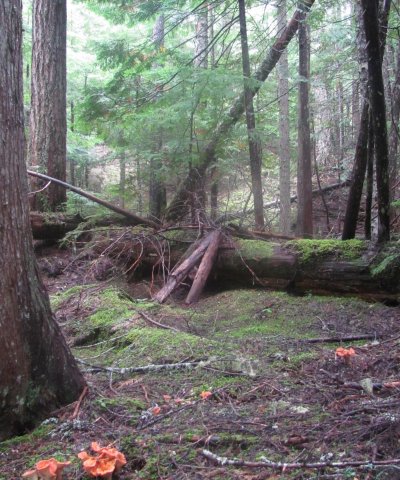
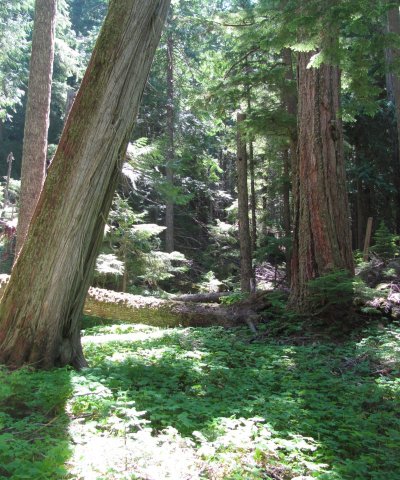
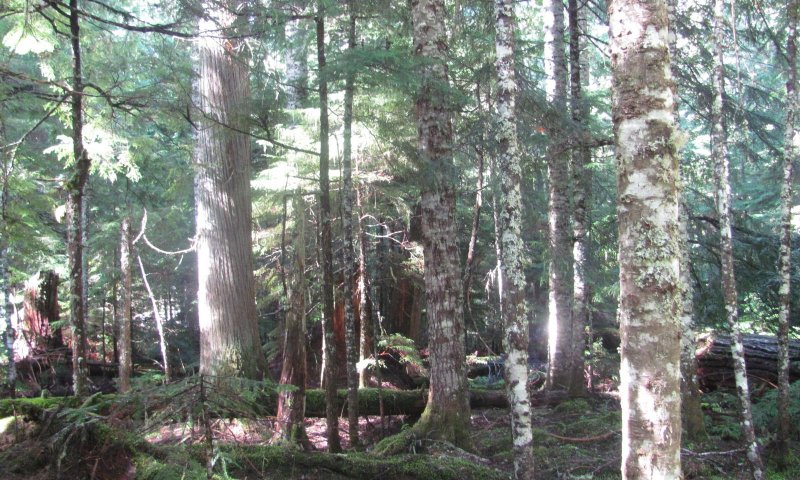
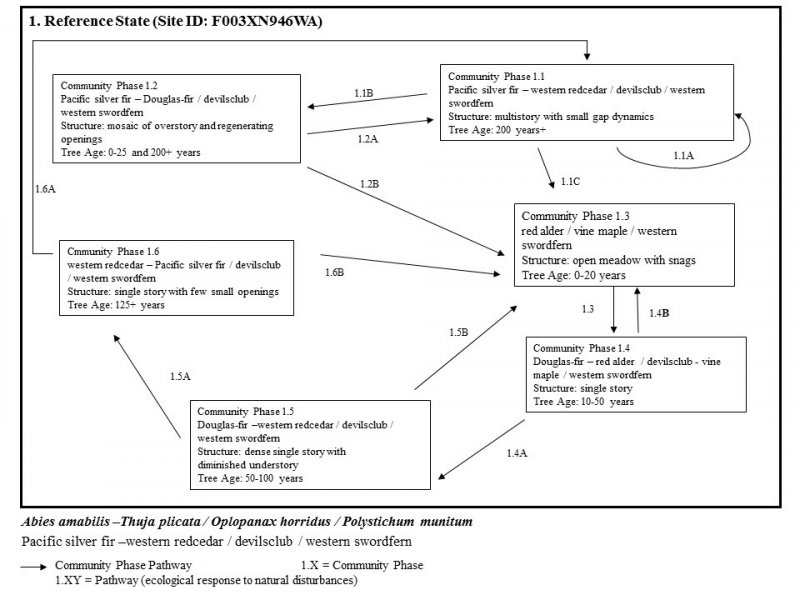
This ecological site is at middle to high elevations (1,800 to 5,700 feet) in Mount Rainier National Park. Climate is key in the succession of the forest dynamics. The cold, wet winters and dry, cool summers impact the species composition and site productivity. This ecological site is in swales and on terraces and debris aprons of glacial-valley walls.
The soils that support this site are in the cryic soil temperature regime and the aquic soil moisture regime. They are somewhat poorly drained and very deep. They have a seasonal high water table in March through June. The most common natural disturbance is windthrow due to the seasonal high water table. Soil moisture is not a limiting factor for forest growth because of the abundance of precipitation and the inherent water-holding properties of soils influenced by volcanic ash. A thin organic horizon consisting of decomposing twigs, needles, and litter is on the soil surface. This horizon helps to protect the soil from wind and water erosion.
Pacific silver fir (Abies amabilis) and western redcedar (Thuja plicata) are the most common overstory species. Bigleaf maple (Acer macrophyllum), western hemlock (Tsuga heterophylla), Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii), and red alder (Alnus rubra) may be codominant. Devilsclub (Oplopanax horridus), vine maple (Acer circinatum), salmonberry (Rubus spectabilis), and thimbleberry (Rubus parviflorus) make up the dense subcanopy.
Associated sites
| F003XN942WA |
Southern Washington Cascades Moist Frigid Coniferous Forest Ecological site F003NX946WA is located at higher elevations compared to F003XN942WA. The presence of Pacific silver fir is a good indicator for F003XN946WA. |
|---|---|
| F003XN950WA |
Southern Washington Cascades Moist High Cryic Coniferous Forest Ecological site F003NX950WA is located at higher elevations compared to F003XN946WA. The presence of mountain hemlock, Alaska cedar, and Cascade azalea are a good indicators for F003XN950WA. |
Similar sites
| F003XN947WA |
Southern Washington Cascades Low Cryic Coniferous Forest Ecological F003XN946WA, Southern Washington Cascades Moist Low Cryic Coniferous Forest, has features similar to those of site F003XN947WA, Washington Cascades Low Cryic Coniferous Forest. The soils of site F003XN947WA are well drained. Species adapted to the drier conditions, such as Pacific silver fir, western hemlock, and black mountain huckleberry, are common. |
|---|---|
| F003XN945WA |
Southern Washington Cascades Wet Low Cryic Coniferous Forest Ecological F003XN945WA, Southern Washington Cascades Wet Low Cryic Coniferous Forest, has features similar to those of site F003XN946WA, Washington Cascades Moist Low Cryic Coniferous Forest. Ecological site F003XN945WA is wetter than site F003XN946WA. It is prone to frequent periods of ponding and it has a higher seasonal water table. As a result, site F003XN945WA supports species adapted to wetness, such as western redcedar, red alder, and American skunkcabbage. Ecological F003XN946WA is drier, and it supports species such as Pacific silver fir, western redcedar, and devilsclub. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Abies amabilis |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Oplopanax horridus |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Polystichum munitum |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.