
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R008XY005ID
South Slope Stony 12-16 PZ
Last updated: 9/23/2020
Accessed: 11/23/2024
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
Ecological site concept
This ecological site meets the NESH 2014 requirements for PROVISIONAL. A provisional ecological site is established after ecological site concepts are developed and an initial state-and-transition model is drafted. Following quality control and quality assurance reviews of the ecological site concepts, an identification number and name for the provisional ecological site are entered into ESIS. A provisional ecological site may include literature reviews, land use history information, some soils data, legacy data, ocular estimates for canopy and/or species composition by weight, and even some line-point intercept information. A provisional ecological site does not meet the NESH 2014 standards for an Approved ESD, but does provide the conceptual framework of soil-site correlation for the development of the ESD.
Associated sites
| R008XY006ID |
Shallow South Slope 12-16 PZ |
|---|
Similar sites
| R008XY006ID |
Shallow South Slope 12-16 PZ |
|---|---|
| R008XY004ID |
South Slope Loamy 12-16 PZ |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Pseudoroegneria spicata |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on moderately steep to steep south facing slopes on low plateaus and canyon walls generally greater than 30 percent. Elevations usually range from 800-2600 feet (250-800 meters).
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Canyon
|
|---|---|
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 244 – 792 m |
| Slope | 30 – 90% |
| Water table depth | 152 cm |
| Aspect | S, SW, W |
Climatic features
The elevation of MLRA 8 ranges from 1300 to 3600 feet above sea level. Average annual precipitation ranges from 12 to 17 inches, with a mean of 15 inches based on 4 long term climate stations located throughout the MLRA. In general precipitation peaks in November, December and January, with a sharp decline in July and August.
The average maximum annual temperature is 64 degrees Fahrenheit and the average minimum temperature is 41 degrees F. The frost free period can range from 160 to 186 days while the freeze free period ranges from 200 to 237 days.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (average) | 186 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (average) | 237 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 432 mm |
Figure 1. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 2. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Influencing water features
This site is not influenced by adjacent wetlands, streams, or run-on.
Soil features
The soils on this site were developed in loess, colluvium, and slope alluvium. They are stony, moderately deep, medium textured, and well drained. They have moderate permeability and a low to high available water holding capacity.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Eolian deposits
–
basalt
|
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Cobbly sandy loam |
| Family particle size |
(1) Loamy |
| Drainage class | Well drained |
| Permeability class | Moderate |
| Soil depth | 102 – 152 cm |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 5 – 10% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 12 – 20% |
| Available water capacity (0-101.6cm) |
6.86 – 13.21 cm |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-101.6cm) |
0% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-101.6cm) |
0 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-101.6cm) |
0 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-101.6cm) |
7.4 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
15 – 30% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
20 – 35% |
Ecological dynamics
The dominant visual aspect of this site is grassland with bluebunch wheatgrass dominant. Composition by weight is approximately 70-80% grass, 15-25% forbs, and T-5% shrubs.
The Reference State (State 1) moves through many phases depending on the natural and man-made forces that impact the community over time. State 1, described later, indicates some of these phases. The Reference Plant Community Phase is Phase 1.1. The plant species composition of Phase 1.1 is listed later under “Reference Plant Community Phase Plant Species Composition”.
During the last few thousand years, this site has evolved in a semi-arid climate characterized by dry summers and cold winters. Herbivory has historically occurred on this site at low levels of utilization. Herbivores include mule deer, whitetail deer, bighorn sheep, Rocky Mountain elk, lagomorphs, and small rodents.
Fire has historically occurred on the site at intervals of 20-50 years.
The Reference Plant Community Phase is dominated by bluebunch wheatgrass and Sandberg bluegrass in the understory. Subdominant species include sand dropseed, prairie junegrass, western yarrow, arrowleaf balsamroot, lupine, and buckwheat. Total annual production is 800 pounds per acre (896 kilograms per hectare) in a normal year. Production in a favorable year is 1050 pounds per acre (1175 kilograms per hectare). Production in an unfavorable year is 500 pounds per acre (560 kilograms per hectare). Structurally, cool season, deep rooted perennial grasses are dominant followed by perennial forbs followed by shallow-rooted perennial grasses while shrubs are rare.
This site is suitable for grazing by livestock in spring, early summer, and fall. The steeper slopes will limit livestock movement. Excessive trailing of livestock should be avoided to minimize terracette development and erosion on the steeper slopes. This site provides valuable wildlife food and cover for mule deer, white-tail deer, Rocky Mountain elk, Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep, raptors, and other small wildlife species.
The soils in this group are in hydrologic group C.
This site is suitable for horseback riding, hiking, hunting, plant study, and photography. It occurs between ridgetop cropland fields and other features which give aesthetic appeal. A variety of attractive flowering plants are found on this site.
Impacts on the Plant Community:
Influence of fire:
When this site burns within the normal fire frequency of 20-50 years, it has minimal effect on the plant community.
In the absence of normal fire frequency residues will build up in the crown of bluebunch wheatgrass. Plant decadence develops. When fires become more frequent than historic levels (20-50 years), vigor of the bunchgrasses will generally be reduced for a year or two. Root sprouting shrubs such as broom snakeweed and rabbitbrush will increase. With continued short fire frequency, fine leaved grasses will have their vigor reduced significantly and death may result. These species may be replaced by sixweeks fescue, cheatgrass, ventenata, and bulbous bluegrass along with a variety of annual and perennial forbs including noxious and invasive plants.
Influence of improper grazing management:
Season-long grazing and/or excessive utilization can be very detrimental to this site. This type of management leads to reduced vigor of the bunchgrasses. With reduced vigor, recruitment of these species declines. As these species decline, the plant community becomes susceptible to invasion by noxious and invasive plants.
Continued improper grazing management influences fire frequency by increasing fine fuels.
Proper grazing management that addresses frequency, duration, and intensity of grazing can also keep fine fuels from developing, thereby reducing fire frequency. A planned grazing system can be developed to intentionally accumulate fine fuels in preparation for a prescribed burn. Prescribed burns on this site need to be very carefully planned. Burns in areas without a suitable understory of perennial grasses can lead to an increase in invasive annual grasses which will lead to more frequent fire intervals.
Weather influences:
Above normal precipitation in March, April, and May can dramatically increase total annual production of the plant community. These weather patterns can also increase viable seed production of desirable species to provide for recruitment. Likewise, below normal precipitation during these spring months can significantly reduce total annual production and be detrimental to viable seed production. Overall plant composition is normally not affected when perennials have good vigor. Below normal temperatures in the spring can have an adverse impact on total production regardless of the precipitation. An early, hard freeze can occasionally kill some plants.
Prolonged drought adversely affects this plant community in several ways. Vigor, recruitment, and production are usually reduced. Mortality can occur, especially in shallow rooted species. Prolonged drought can lead to a reduction in fire frequency.
Influence of Insects and disease:
Insect and disease outbreaks can affect vegetation health. Mormon cricket and grasshopper outbreaks occur periodically. Since defoliation usually happens once during the growing season, mortality is normally low.
An outbreak of a particular insect is usually influenced by weather but no specific data for this site is available.
Influence of noxious and invasive plants:
Many of these species add to the fine-fuel component and lead to increased fire frequency. Many of the annual and perennial invasive species with deep root systems compete with desirable plants for moisture and nutrients. The result is reduced production and change in composition of the understory.
Influence of wildlife:
Big game animals use this site yearlong. Their numbers are seldom high enough to adversely affect the plant community.
Watershed:
Decreased infiltration and increased runoff occur with an increase in annual grasses and undesirable forbs. Desired understory species can be reduced. This composition change can affect nutrient and water cycles. Increased runoff also causes sheet and rill erosion. Abnormally short fire frequency also gives the same results, but to a lesser degree. The long term effect is a transition to a different state.
Plant Community and Sequence:
Transition pathways between common vegetation states and phases:
State 1.
1.1 Bluebunch wheatgrass-Sandberg bluegrass
Plant Community Phase 1.1 to 1.2 (1.1A). Develops with improper grazing management and no fire.
Plant Community Phase 1.1 to 1.3 (1.1B). Develops with fire.
Plant Community Phase 1.2 to 1.1 (1.2A). Develops with prescribed grazing.
Plant Community Phase 1.3 to 1.1 (1.3A). Develops with prescribed grazing and no fire.
State 1 Phase 1.2 to State 2. Develops through frequent fire and continued improper grazing management (T1B). The site crosses the threshold. It is not economically feasible to move this state back to State 1 with accelerating practices.
State 2 to unknown site. Excessive soil loss and changes in the hydrologic cycle caused by continued improper grazing management and/or frequent fire (T2.1A) cause this state to cross a threshold and retrogress to a new site with reduced potential. It is not economically feasible to move this state back to State 1 with accelerating practices.
Practice Limitations.
There are severe limitations for seeding and brush management on this site with ground moving equipment due to steep slopes and stones in the profile. Due to the scarcity of shrubs on this site, brush management would be rare. Attaining uniform utilization on the steeper slopes is difficult.
State and transition model
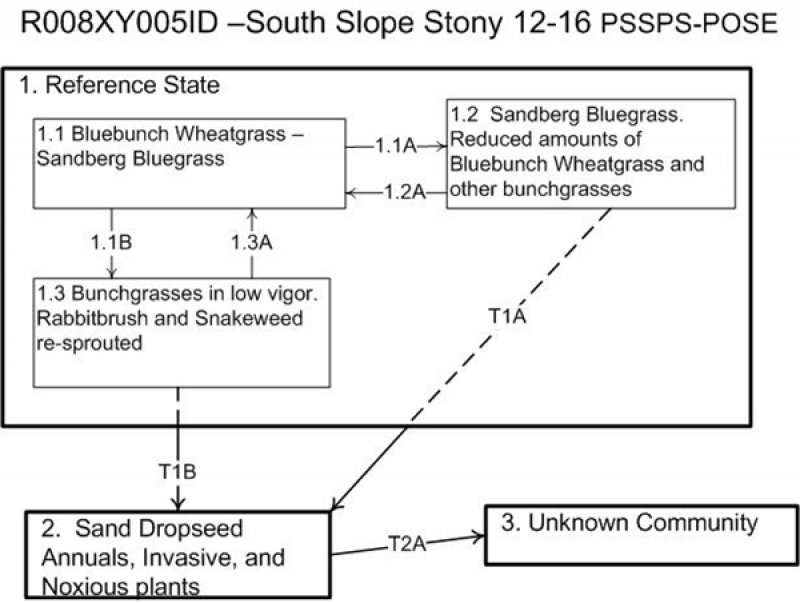
Figure 3. R008XY005ID
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
Ecosystem states
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Reference State
Community 1.1
Bluebunch Wheatgrass - Sandberg Bluegrass
State 1, Plant community phase 1.1. Reference Plant community Phase. This plant community is dominated by bluebunch wheatgrass and Sandberg bluegrass. Subdominant species include sand dropseed, prairie junegrass, western yarrow, arrowleaf balsamroot, lupine and buckwheat. Natural fire frequency is 20-50 years.
Figure 4. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 437 | 689 | 897 |
| Forb | 112 | 179 | 235 |
| Shrub/Vine | 11 | 28 | 45 |
| Total | 560 | 896 | 1177 |
Figure 5. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). ID1601, B8 ARR12/POSE. State 1, Community Phase 1.1.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 10 | 20 | 35 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Community 1.2
Sandberg Bluegrass with reduced bunchgrasses
State 1, Plant Community Phase 1.2. This plant community is dominated by Sandberg bluegrass with reduced amounts of bluebunch wheatgrass. All deep-rooted bunchgrasses are typically in low vigor. This state has developed due to improper grazing management and no fire (1.1A). Sand dropseed, forbs, and broom snakeweed are increasing. Some cheatgrass and other invasive annuals may have invaded the site.
Figure 6. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). ID1601, B8 ARR12/POSE. State 1, Community Phase 1.1.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 10 | 20 | 35 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Community 1.3
Sprouting Shrubs low vigor bunchgrasses
State 1, Plant community Phase 1.3. This plant community is dominated by bluebunch wheatgrass and Sandberg bluegrass with reduced vigor. Forbs remain about in the same proportion as Plant Community 1.1. Rabbitbrush and broom snakeweed have resprouted from fire. Some cheatgrass may have invaded the site. This plant community is the result of wildfire (1.1B).
Figure 7. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). ID1601, B8 ARR12/POSE. State 1, Community Phase 1.1.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 10 | 20 | 35 | 25 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
State 2
Annuals
Community 2.1
Sand Dropseed - Annuals
State 2. This plant community is dominated by sand dropseed, cheatgrass, and other annuals. Root sprouting shrubs such as rabbitbrush and broom snakeweed can be present, dependent upon, how frequent, fire has occurred. Some soil loss has occurred. This state has developed due to frequent fires and improper grazing management (T1B) from plant community phase 1.2, State 1 or as a result of frequent fires and/or improper grazing management (T1A) from plant community phase 1.3. The site has crossed the threshold. It is not economically feasible to move this state back to State 1 with accelerating practices.
Figure 8. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). ID1602, B8 BRTE-Annuals. State 2.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 10 | 30 | 40 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
State 3
Unknown
Community 3.1
Unknown Community
Additional community tables
Table 6. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | 437–897 | |||||
| bluebunch wheatgrass | PSSP6 | Pseudoroegneria spicata | 336–673 | – | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 0–90 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 0–56 | – | ||
| Sandberg bluegrass | POSE | Poa secunda | 28–56 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 2 | 112–235 | |||||
| common yarrow | ACMI2 | Achillea millefolium | 28–56 | – | ||
| lupine | LUPIN | Lupinus | 0–45 | – | ||
| plains pricklypear | OPPO | Opuntia polyacantha | 0–34 | – | ||
| balsamroot | BALSA | Balsamorhiza | 17–34 | – | ||
| buckwheat | ERIOG | Eriogonum | 0–28 | – | ||
| fleabane | ERIGE2 | Erigeron | 0–22 | – | ||
| desertparsley | LOMAT | Lomatium | 0–17 | – | ||
| phlox | PHLOX | Phlox | 0–17 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 3 | Shrubs | 11–45 | ||||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 0–28 | – | ||
| yellow rabbitbrush | CHVI8 | Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus | 0–22 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Wildlife Interpretations.
Animal Community – Wildlife Interpretations
This rangeland ecological site provides diverse habitat for many native wildlife species. The plant community is dominated by herbaceous vegetation which provides year-round forage for large herbivores. Important seasonal habitat is provided for resident and migratory animals including western toad, western rattlesnake, shrews, jackrabbits, ground squirrels, mice, coyote, red fox, badger, northern harrier, red-tailed hawk, horned lark, and western meadowlark. Area sensitive species include Woodhouse’s toad, ring-necked snake, grasshopper sparrow, and Merriam’s shrew. Areas of noxious and invasive plant species (cheatgrass, bulbous bluegrass, ventenata, yellow-star thistle, and rush skeletonweed) can replace native plant species which provide critical feed, brood-rearing, and nesting cover for a variety of native wildlife. Water features are sparse, provided by seasonal runoff, artificial water catchments, and springs.
State 1 Phase 1.1 - Bluebunch Wheatgrass/ Sandberg Bluegrass Reference Plant Community (RPC): This plant community provides a diversity of grasses and forbs, used by native insect communities that assist in pollination. Flowering forbs and shrubs including yarrow, arrowleaf balsamroot, phlox, biscuitroot, buckwheat, and rabbitbrush provide spring through fall habitat for pollinators. The reptile and amphibian community is represented by western rattlesnake, northern alligator lizard, ring-necked snake, pygmy short-horned lizard, western toad, Woodhouse’s toad, tiger salamander, Columbia spotted frog, and northern leopard frog. Amphibians are associated with springs and isolated water bodies adjacent to this plant community. Spring developments that capture all available water would preclude the use of this site by amphibians. The plant community supports a variety of migratory and resident avian species that prefer grassland plant communities for food, brood-rearing, and nesting cover. They may include savannah sparrow, lark sparrow, grasshopper sparrow, Say’s phoebe, western kingbird, horned lark, and western meadowlark. Wild turkey may frequent the site for brood-rearing in the spring and summer. The plant community provides spring, fall, and winter forage for mule deer and elk. Bluebunch wheatgrass and arrowleaf balsamroot are desirable forage species for elk and mule deer. The grazing management will determine the quality and amount of forage available for mule deer and elk. A small mammal population including Preble’s shrew, mountain cottontail, white-tailed jackrabbit, Merriam’s shrew, western jumping mouse, and deer mouse may utilize this site.
State 1 Phase 1.2 - Sandberg Bluegrass Plant Community: This phase has developed due to improper grazing management and little to no fire. The reduced vigor and production of herbaceous vegetation will reduce the quality of the habitat for insects. The reptile and amphibian community is represented by western rattlesnake, gophersnake, terrestrial gartersnake, and western toad. Amphibians are associated with springs adjacent to the site. Spring developments that capture all available water would preclude the use of the area by amphibians. Quality of cover habitat for ground-nesting birds is reduced due to improper grazing, resulting in sparse herbaceous vegetation. The reduced vigor of plants and improper grazing management of the herbaceous plant community provides a shorter grazing season for mule deer, white-tailed deer and elk. Quality of winter forage for large herbivores is reduced due to poor grazing management and a loss of native deep-rooted bunchgrasses. The small mammal community would be similar to the State 1 Phase 1.1 small mammal community.
State 1 Phase 1.3 - Bluebunch Wheatgrass/ Sandberg Bluegrass/ Rabbitbrush/ Brome /Snakeweed Plant Community: This plant community is the result of fire. The forb community would be similar to that in State 1 Phase 1.1. Insect diversity would be similar to State 1 Phase 1.1 insect community. The reptile community would also be similar to the State 1 Phase 1.1 reptile community. Quality of cover habitat for ground-nesting birds is reduced due to improper grazing, resulting in sparse herbaceous vegetation. Deep-rooted bunchgrasses are reduced in vigor and production, resulting in a shorter grazing season for mule deer, white-tailed deer, and elk. The small mammal community would be similar to the State 1 Phase 1.1 small mammal community. An increase in woody vegetation may increase the quality of cover habitat for small mammals.
State 2 –Sand Dropseed/ Annuals/ Invasives/ Noxious Weeds Plant Community: This state has developed due to frequent fires and improper grazing management from State 1 Phase 1.2. It also occurs with frequent fire or improper grazing management from State 1 Phase 1.3. The plant community supports harmful insects, such as grasshoppers due to improved breeding conditions. The plant community would support a very limited population of pollinators, supported by noxious weeds. Most reptilian species are not supported with food, water, or cover. The diversity of grassland avian species is reduced due to poor cover and food conditions. Birds of prey including hawks and falcons may range throughout these areas looking for prey species. Large herbivores may utilize the herbaceous vegetation in the early part of the year when the invasive annuals (cheatgrass) are more palatable. At other times of the year large herbivores would not regularly utilize these areas due to poor forage and cover conditions. The populations of small mammals would be reduced due to poor cover and food habitat. Large blocks of this plant community would fragment the reference plant community and reduce the quality of the habitat for animal species that historically used the site.
Grazing Interpretations.
This site is suitable for grazing by livestock in spring, early summer, and fall. The steeper slopes will limit livestock movement. Excessive trailing of livestock should be avoided to minimize terracette development and erosion on the steeper slopes.
Estimated initial stocking rate will be determined with the landowner or decision-maker. They will be based on the inventory which includes species, composition, similarity index, production, past use history, season of use, and seasonal preference.
Hydrological functions
The soils in this group are in hydrologic group C.
Recreational uses
This site is suitable for horseback riding, hiking, hunting, plant study and photography. It occurs between ridgetop cropland fields and other features which give aesthetic appeal. A variety of attractive flowering plants are found on this site.
Wood products
None.
Other products
None.
Other information
Field Offices
Lewiston, ID
Moscow, ID
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented here has been derived from NRCS clipping and other inventory data. Also, field knowledge of range-trained personnel was used. Those involved in developing this site description include:
Dave Franzen, co-owner, Intermountain Rangeland Consultants, LLC
Jacy Gibbs, co-owner, Intermountain Rangeland Consultants, LLC
Jim Cornwell, Range Management Specialist, IASCD
Brendan Brazee, State Rangeland Management Specialist, NRCS, Idaho
Lee Brooks, Range Management Specialist, IASCD
Bruce Knapp, Resource Soil Scientist, NRCS, Idaho
Other references
Hironaka, M., M.A. Fosberg, A. H. Winward. 1983. Sagebrush-Grass Habitat Types of Southern Idaho. University of Idaho, Moscow, Idaho. Bulletin Number “35”.
USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station. 2004. Restoring Western Ranges and Wildlands. General Technical Report RMRS-GTR-136-vols. 1-3.
USDA, NRCS.2001. The PLANTS Database, Version 3.1 (http://plants.usda.gov.). National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA 70874-4490 USA.
USDA, Forest Service, Fire Effects Information Database. 2004. www.fs.fed.us/database.
USDI Bureau of land Management, US Geological Survey; USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, Agricultural Research Service; Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health. Technical Reference 1734-6; Version 4-2005.
Contributors
BB
Dave Franzen And Jacy Gibbs
Approval
Kendra Moseley, 9/23/2020
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | Dave Franzen and Jacy Gibbs Intermountain Range Consultants 17700 Fargo Rd. Wilder, ID 83676 |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | Brendan Brazee, State Rangeland Management Specialist USDA-NRCS 9173 W. Barnes Drive, Suite C, Boise, ID 83709 |
| Date | 03/19/2009 |
| Approved by | Kendra Moseley |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
Rills can occur on this site. If rills are present they are likely to occur on the steeper slopes and immediately following wildfire. Cobbles and stones on the surface reduce erosion. -
Presence of water flow patterns:
Water-flow patterns can occur on this site. When they occur, they are short and disrupted by cool season grasses, cobbles, and stones and are not extensive. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
Both occur on this site but are not extensive. In areas where flow patterns and/or rills are present, a few pedestals may be expected. Terracettes occur on the site uphill from large bunchgrasses. -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
Data is not available. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
Do not occur on this site. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
Are usually not present. Immediately following wildfire some soil movement may occur on lighter textured soils. -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Fine litter in the interspaces may move up to 3 feet following a significant run-off event. Coarse litter generally does not move except on the steeper slopes. Litter is also moved mechanically by hoof/ foot traffic. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Values should range from 4 to 6 . -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
The surface horizon is very dark brown and typically 3 to 7 inches thick. Structure is weak fine granular and soil organic matter ranges from 2 to 4 percent. -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
Bunchgrasses, especially deep-rooted perennials, slow run-off and increase infiltration. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
Is not present. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Deep rooted perennials with fibrous root systems are needed for soil stability.
season deep rooted perennial bunchgrassesSub-dominant:
perennial forbsOther:
shallow-rooted bunchgrassesAdditional:
shrubs -
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Decadence in the larger bunchgrasses can occur on this site near the end of the fire cycle. This is usually indicated by a build-up of old residues in the crown. Mortality can occur following extended drought. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Additional litter cover data is needed but is expected to be 25-35 percent to a depth of <0.1 inches. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
Is 800 pounds per acre (888 kilograms per hectare) in a year with normal temperatures and precipitation. Perennial grasses produce 75-80 percent of the total production, forbs 15-25 percent and shrubs T-5 percent. -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
Includes cheatgrass, soft chess, ventenata, bulbous bluegrass, medusahead, red threeawn, tarweed, curlycup gumweed, spotted and diffuse knapweed, dalmation toadflax, Mediterranean sage, Scotch thistle, Rush skeletonweed, and yellow star-thistle. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
All functional groups have the potential to reproduce in most years.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.