Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R029XY186CA
Sandy Slope 10-12" p.z.
Last updated: 2/20/2025
Accessed: 03/04/2026
General information
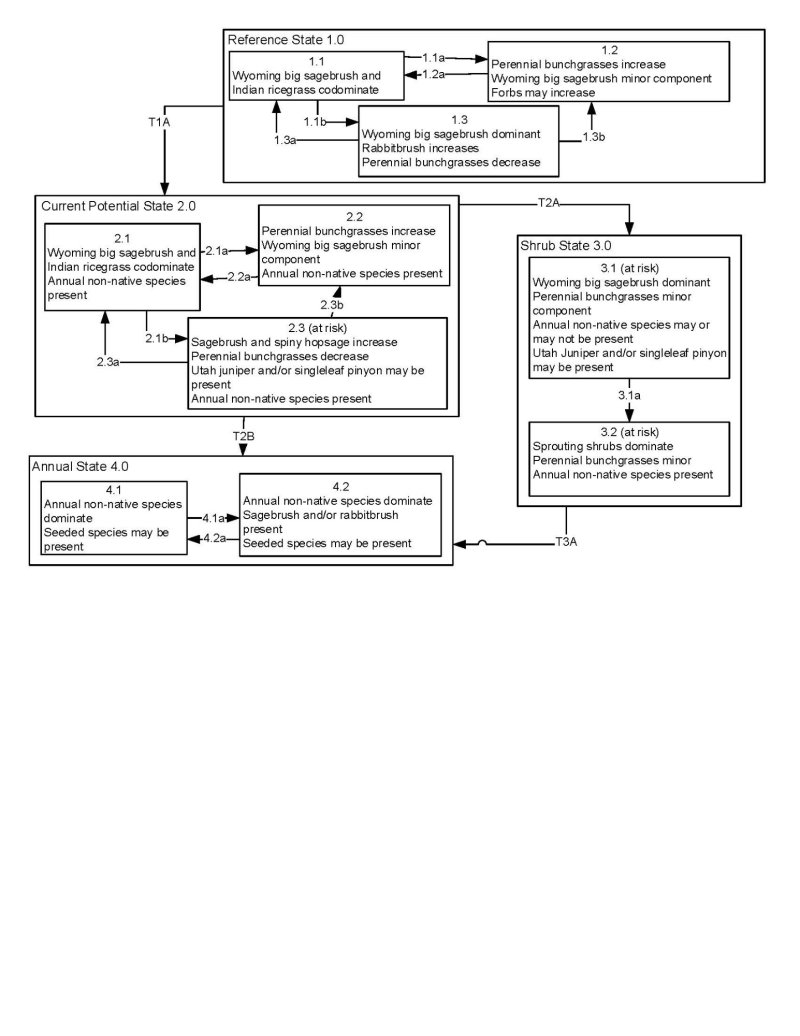
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 029X–Southern Nevada Basin and Range
The Southern Nevada Basin and Range MLRA (29) represents the transition from the Mojave Desert to the Great Basin. It is cooler and wetter than the Mojave. It is warmer and typically receives more summer precipitation than the Great Basin. This area is in Nevada (73 percent), California (25 percent), and Utah (2 percent). It makes up about 26,295 square miles (68,140 square kilometers). Numerous national forests occur in the area, including the San Bernardino, Angeles, Sequoia, Inyo, Humboldt-Toiyabe, and Dixie National Forests. Portions of Death Valley National Monument, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s Nevada Test Site, the Hawthorne Ammunition Depot, and the Nellis Air Force Range in Nevada and the China Lake Naval Weapons Center in California also are in this MLRA. The northeast part of the Paiute Indian Reservation and the southern third of the Walker River Indian Reservation are in the part of this MLRA in Nevada, and the Lone Pine, Fort Independence, and Big Pine Indian Reservations are in the part in California.
Physiography:
The entire area is in the Great Basin Section of the Basin and Range Province of the Intermontane Plateaus. The area of broad, nearly level, aggraded desert basins and valleys between a series of mountain ranges trending north to south. The basins are bordered by sloping fans and pluvial lake terraces. The mountains are uplifted fault blocks with steep side slopes and not well dissected due to limited annual precipitation. Most of the valleys in this MLRA are closed basins or bolsons containing sinks or playa lakes.
Geology:
The mountains are dominated by Pliocene and Miocene andesite and basalt rocks, Paleozoic and Precambrian carbonate rocks prominent in some areas. Scattered outcrops of older Tertiary intrusives and very young tuffaceous sediments (Pliocene and Miocene) are in the western and eastern thirds of this MLRA. The valleys consist mostly of alluvial fill and playa deposits at the lowest elevations in the closed basins.
Climate:
The average annual precipitation is 3 to 12 inches (75 to 305 millimeters) in most of this area. It may be as high as 29 inches (735 millimeters), on the higher mountain slopes. Most of the rainfall occurs as high-intensity, convective thunderstorms during the growing season. Summers are dry, but sporadic storms are common in July and August.
Water Resources:
Water resources are scarce. Ground water and surface water sources are limited. Streams are small and intermittent. Quality of surface water in naturally degraded as streams cross area of valley fill effected by dissolved salts. Irrigation water may raise the levels of dissolved salts and suspended sediments causing contamination.
Soils:
Dominant soil orders include Entisols and Aridisols.
Ecological site concept
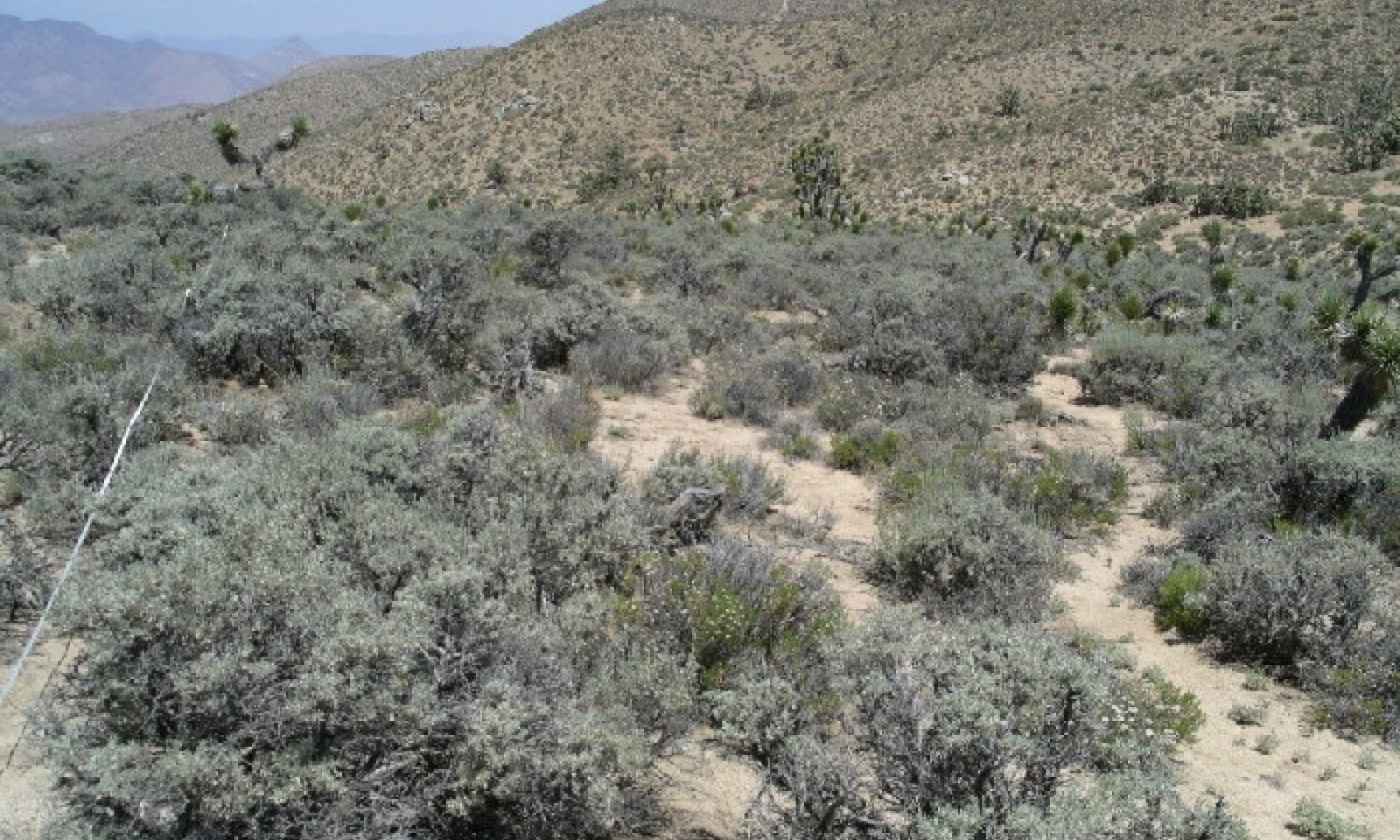
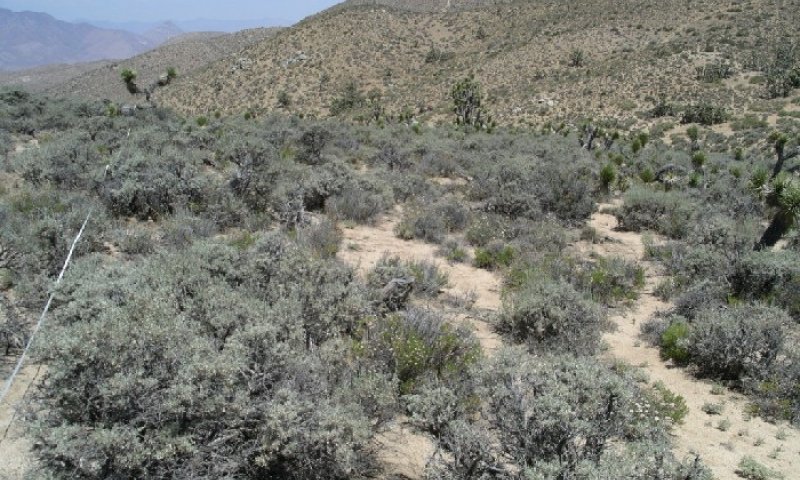
The Sandy Slope 10-12" p.z. Ecological Site is on mountains. It is on backslopes that typically have a north-facing aspect, but may be on slopes with an east-facing aspect. Slopes range from 15 to 60 percent, but are typically between 30 and 60 percent. The soils are formed from colluvium and residuum derived and weathered from granite. Soils are very deep and sandy throughout the profile with no soil development.
Associated sites
| F029XY001CA |
Shallow Sandy Slope This a woodland community found at higher elevations on upper backslopes of mountains. It is typically found on north and east-facing slopes. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Artemisia tridentata ssp. vaseyana |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Poa secunda |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.