Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site DX032X01B110
Dense Clay (DC) Big Horn Basin Rim
Last updated: 9/05/2019
Accessed: 03/13/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 032X–Northern Intermountain Desertic Basins
Major land resource area (MLRA):
032X – Northern Intermountain Desertic Basins – This MLRA is comprised of two major Basins, the Big Horn and Wind River. These two basins are distinctly different and are split by LRU’s to allow individual ESD descriptions. These warm basins are surrounded by uplifts and rimmed by mountains, creating a unique set of plant responses and communities. Unique characteristics of the geology and geomorphology single these two basins out.
Further information regarding MLRAs, refer to: United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2006. Land Resource Regions and Major Land Resource Areas of the United States, the Caribbean, and the Pacific Basin. U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook 296. Available electronically at: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/ref/?cid=nrcs142p2_053624#handbook.
LRU notes
Land Resource Unit (LRU):
32X01B (WY): This LRU is the Big Horn Basin within MLRA 32. This LRU is lower in elevation, slightly warmer and receives slightly less overall precipitation than the Wind River Basin (LRU 02). This LRU was originally divided into two LRU's - LRU A which was the core and LRU B which was the rim. With the most current standards, this LRU is divided into two Subsets. This subset is Subset B, referred to as the Rim, is a transitional band between the basin floor and the lower foothills. The subset encircles Subset A which was originally LRU A. As the LRU shifts towards the south and tracks east, changes in geology and relation to the mountain position, creates a minor shift in soil chemistry influencing the variety of ecological sites and plant interactions. The extent of soils currently correlated to this ecological site does not fit within the digitized boundary. Many of the noted soils are provisional and will be reviewed and corrected in mapping update projects. Other map units are correlated as small inclusions within other MLRA’s/LRU’s based on elevation, landform, and biological references.
Moisture Regime: Ustic Aridic – Prior to 2012, many of the soils within this group were correlated as Frigid Ustic Aridic or as Mesic Typic Aridic, with few mapped within this cross over zone. As progressive soil survey mapping continues, these “crossover” or transitional areas are being identified and corrected.
Temperature Regime: Mesic
Dominant Cover: Rangeland, with Saltbush flats the dominant vegetative cover for this LRU/ESD.
Representative Value (RV) Effective Precipitation: 10-14 inches (254 – 355 mm)
RV Frost-Free Days: 105-125 days
Classification relationships
Relationship to Other Established Classification Systems:
National Vegetation Classification System (NVC):
3 Xeromorphic Woodland, Scrub & Herb Vegetation Class
3.B Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland Subclass
3.B.1 Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland formation
3.B.1.NE Western North American Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland Division
M169 Great Basin & Intermountain Tall Sagebrush Shrubland & Steppe Macrogroup
G302 Artemisia Tridentata - Artemisia tripartita - Purshia tridentata Big Sagebrush Steppe Group
Ecoregions (EPA):
Level I: 10 North American Deserts
Level II: 10.1 Cold Deserts
Level III: 10.1.18 Wyoming Basin
Level IV: 10.1.18.g Big Horn Salt Desert Shrub Basin
Ecological site concept
• Site receives no additional water.
• Slope is <30%
• Soils are:
o Textures range from fine sandy clay loam to clay in top 4” (10 cm) of mineral soil surface
o Clay content is < 35% in top 4” (10 cm) of mineral soil surface
o All subsurface horizons in the particle size control section have a weighted average of ≥ 35% clay. (The particle size control section is the segment of the profile from either the start of an argillic horizon for 50 cm’s or from 25-100 cm’s).
o Moderately deep to very deep (20-80+ in. (50-200+ cm)
o Not skeletal (<35% rock fragments) within 20” (50 cm) of mineral soil surface
o None to Slightly effervescent throughout top 20” (50 cm) of mineral soil surface
o Non-saline, sodic, or saline-sodic
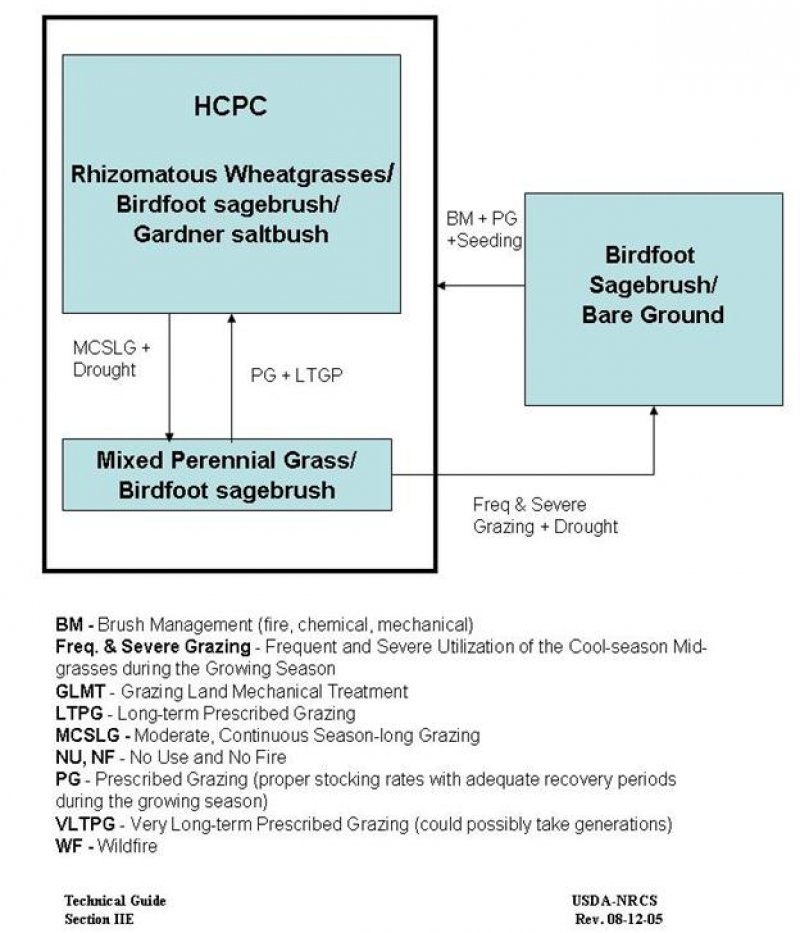
Site drafted from historic range site: R032XY118WY. Based on heavy clay soils that develop large cracks at the surface when dry. Site has a thin cap of coarser soils on the surface. This community is dominated by birdfoot sagebrush and generally lacks Wyoming big sagebrush.
Associated sites
| R032XY104WY |
Clayey (Cy) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone Dense clay will occur in small swales or side slopes with the clayey site. Sit is both associated and similar. |
|---|---|
| R032XY138WY |
Saline Lowland (SL) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone Saline Lowland is found in association with Dense Clay in perennial or intermittent stream channels. Saline Lowland is a step below Dense clay where the water table has an influence on the vegetation. Dense Clay will be a riser or step above the water table in depressions or along a drainage system. |
| R032XY144WY |
Saline Upland (SU) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone Saline Upland sites will occur in close proximity with Dense Clay. Dense Clay will be higher on the landform with lower affect by salt accumulations. Site is both associated and similar. |
Similar sites
| R032XY118WY |
Impervious Clay (IC) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone Clayey site is similar to Dense Clay but is lacking the coarser surface textures and Clayey supports Wyoming Big Sagebrush more than birdfoot sagebrush, and has a greater composition of mid-stature cool-season grasses. Overall, production is greater on a clayey site. |
|---|---|
| R032XY344WY |
Saline Upland (SU) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone Saline Upland may be similar in production with a shift in species. Saline Upland is Gardner's saltbush dominated (significant salts - sodic, saline, gypsic, saline-sodic) while Dense Clay is birdfoot sagebrush dominated (minimal to no salt accumulations). |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Artemisia pedatifida |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Pascopyrum smithii |
Legacy ID
R032XB110WY
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.