
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R032XY150WY
Sandy (Sy) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone,
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
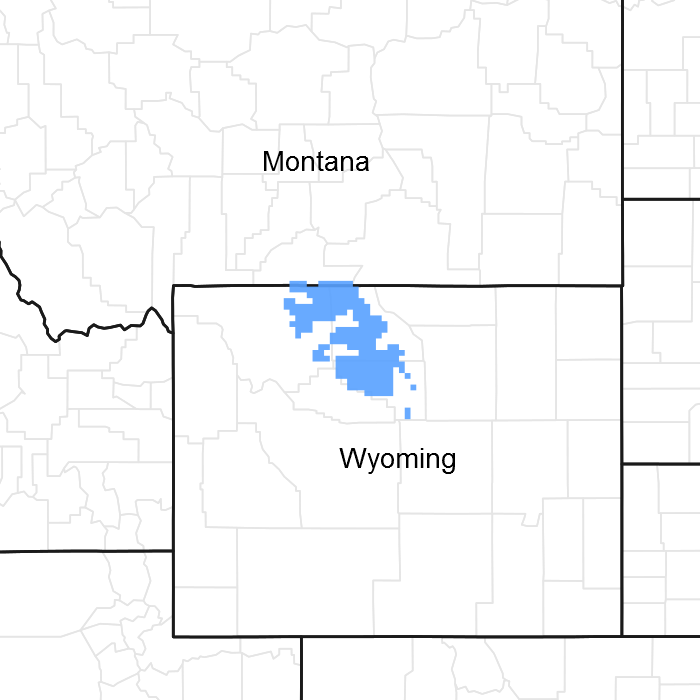
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
Associated sites
| R032XY104WY |
Clayey (Cy) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone |
|---|---|
| R032XY112WY |
Gravelly (Gr) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone |
| R032XY122WY |
Loamy (Ly) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone |
| R032XY128WY |
Lowland (LL) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone |
| R032XY166WY |
Shallow Sandy (SwSy) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone |
Similar sites
| R032XY350WY |
Sandy (Sy) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone Sandy 10-14” Foothills and Basin East P.Z. , R032XY350WY has higher production. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on nearly level to 20% slopes.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Alluvial fan
(2) Hill (3) Plateau |
|---|---|
| Flooding duration | Brief (2 to 7 days) |
| Flooding frequency | None to rare |
| Ponding duration | Very brief (4 to 48 hours) |
| Ponding frequency | None to rare |
| Elevation | 3,700 – 6,000 ft |
| Slope | 20% |
| Ponding depth |
Not specified |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
Annual precipitation ranges from 5-9 inches per year. The normal precipitation pattern shows peaks in May and June and a secondary peak in September. This amounts to about 50% of the mean annual precipitation. Much of the moisture that falls in the latter part of the summer is lost by evaporation and much of the moisture that falls during the winter is lost by sublimation. Average snowfall is about 20 inches annually. Wide fluctuations may occur in yearly precipitation and result in more dry years than those with more than normal precipitation.
Temperatures show a wide range between summer and winter and between daily maximums and minimums, due to the high elevation and dry air, which permits rapid incoming and outgoing radiation. Cold air outbreaks from Canada in winter move rapidly from northwest to southeast and account for extreme minimum temperatures. Chinook winds may occur in winter and bring rapid rises in temperature. Extreme storms may occur during the winter, but most severely affect ranch operations during late winter and spring.
High winds are generally blocked from the basin by high mountains, but can occur in conjunction with an occasional thunderstorm.
Growth of native cool-season plants begins about April 1 and continues to about July 1. Cool weather and moisture in September may produce some green up of cool season plants that will continue to late October.
The following information is from the “Emblem” climate station:
Minimum Maximum 5 yrs. out of 10 between
Frost-free period (days): 98 171 May 13 – September 19
Freeze-free period (days): 120 184 May 1 – October 5
Mean Annual Precipitation (inches): 3.22 10.97
Mean annual precipitation: 7.42 inches
Mean annual air temperature: 45.01 F (31.2 F Avg. Min. to 58.7 F Avg. Max.)
For detailed information visit the Natural Resources Conservation Service National Water and Climate Center at http://www.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/ website. Other climate station(s) representative of this precipitation zone include ”Basin”, “Deaver”, “Lovell” and “Worland”.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (average) | 171 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (average) | 184 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 9 in |
Influencing water features
Soil features
The soils of this site are moderately deep (greater than 20” to bedrock) to very deep, well-drained soils that formed in alluvium or alluvium over residuum. These soils have moderately slow, moderate, moderately rapid, or rapid permeability. The surface soil will vary from 3 to 6 inches deep. Coarser topsoils may be included if underlain by finer textured subsoil. The soil characteristics having the most influence on plant community are light texture, which can affect the available moisture and amount of calcium carbonates in the profile.
Major Soil Series correlated to this site include: Apron, Griffy, Wallson, and Worland
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Surface texture |
(1) Fine sandy loam (2) Sandy loam (3) Loam |
|---|---|
| Family particle size |
(1) Loamy |
| Drainage class | Well drained to excessively drained |
| Permeability class | Moderately slow to rapid |
| Soil depth | 20 – 60 in |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | Not specified |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | Not specified |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
1.2 – 6.3 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
40% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
8 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
2 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
7.4 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
Not specified |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
Not specified |
Ecological dynamics
Potential vegetation on this site is dominated by mid cool-season perennial grasses. Other significant vegetation includes big sagebrush, and a variety of forbs. The expected potential composition for this site is about 70% grasses, 15% forbs and 15% woody plants. The composition and production will vary naturally due to historical use, fluctuating precipitation and fire frequency.
As this site deteriorates, species such as threadleaf sedge, blue grama and big sagebrush will increase. Plains pricklypear and weedy annuals will invade. Cool season grasses such as needleandthread, Indian ricegrass, and rhizomatous wheatgrasses will decrease in frequency and production.
Big sagebrush may become dominant on areas with an absence of fire and sufficient amount of precipitation. Wildfires are actively controlled in recent times and as a result old decadent stands of big sagebrush persist. Chemical control using herbicides has replaced the historic role of fire on this site. Recently, prescribed burning has regained some popularity.
Due to the amount and pattern of the precipitation, the big sagebrush component may not be resilient once it has been removed or severely reduced if a vigorous stand of grass exists and is maintained. On these areas, threadleaf sedge and blue grama may become dominant if the area is subjected to a combination of frequent and severe grazing especially yearlong grazing. As a result, a dense sod cover of threadleaf sedge and blue grama will become established.
The Historic Climax Plant Community (description follows the plant community diagram) has been determined by study of rangeland relic areas, or areas protected from excessive disturbance. Trends in plant communities going from heavily grazed areas to lightly grazed areas, seasonal use pastures, and historical accounts have also been used.
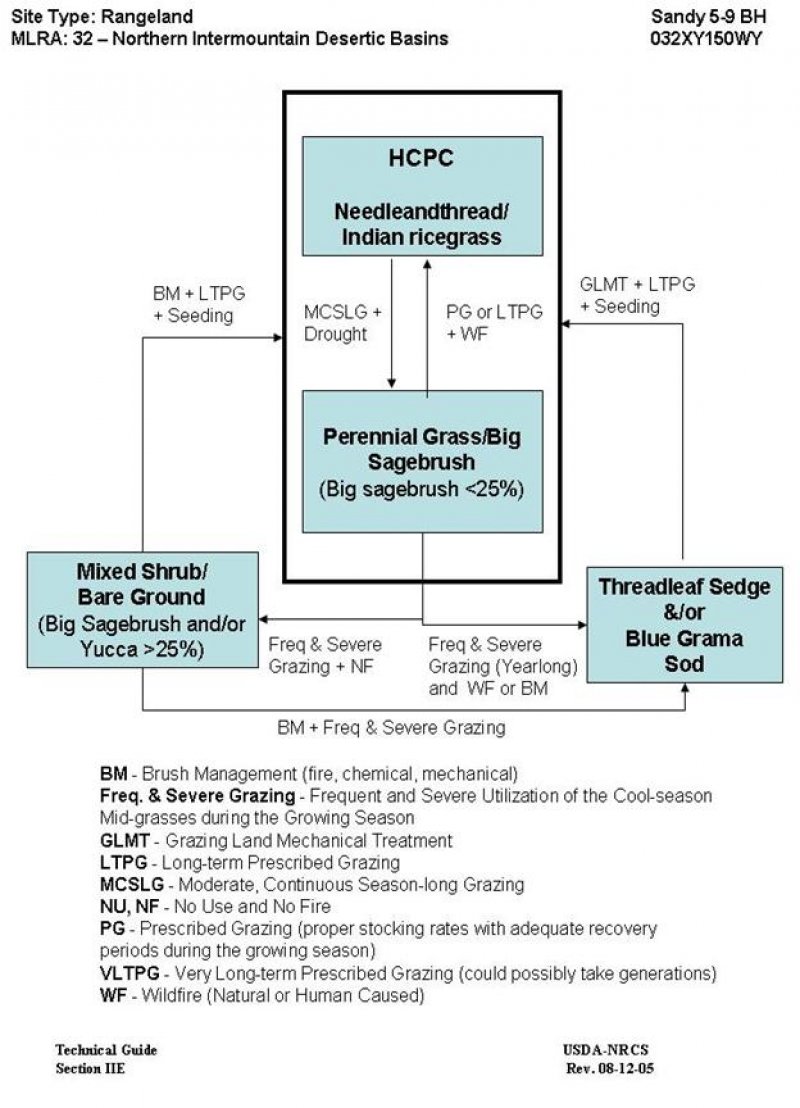
The following is a State and Transition Model Diagram that illustrates the common plant communities (states) that can occur on the site and the transitions between these communities. The ecological processes will be discussed in more detail in the plant community narratives following the diagram.
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 4 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Needleandthread/Indian Ricegrass Plant Community
Community 1.1
Needleandthread/Indian Ricegrass Plant Community
The interpretive plant community for this site is the Historic Climax Plant Community. This state evolved with grazing by large herbivores and periodic fires. The cyclical nature of the fire regime in this community prevented big sagebrush from being the dominant landscape. This plant community can be found on areas that are properly managed with grazing and/or prescribed burning, and on areas receiving occasional short periods of rest. The state is mostly cool season mid-grasses and a variety of forbs and woody species. Potential vegetation is about 70% grasses or grass-like plants, 15% forbs, and 15% woody plants. The major grasses include needleandthread, Indian ricegrass and rhizomatous wheatgrasses. Other grasses occurring in the state include Sandberg bluegrass, blue grama, threadleaf sedge, and threeawns. Big sagebrush is a conspicuous component of this state. A variety of forbs also occurs in this state and plant diversity is high (see Plant Composition Table). The total annual production (air-dry weight) of this state is about 400 lbs. /acre, but it can range from about 225 lbs. /acre in unfavorable years to about 600 lbs. /acre in above average years. The state is stable and well adapted to the Northern Intermountain Desertic Basins climatic conditions. The diversity in plant species allows for high drought resistance. This is a sustainable plant community (site/soil stability, watershed function, and biologic integrity). Transitions or pathways leading to other plant communities are as follows: • Moderate, Continuous Season-Long grazing will convert the plant community to the Perennial Grass/Big Sagebrush Plant Community. Prolonged drought will exacerbate this transition.
Figure 2. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Figure 3. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). WY0501, 5-9BH Upland sites. Monthly percentages of total annual growth for all upland sites with dominantly C3 Cool season plants..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 15 | 50 | 20 | 5 | 10 |
State 2
Perennial Grass/Big Sagebrush Plant Community
Community 2.1
Perennial Grass/Big Sagebrush Plant Community
Historically, this plant community evolved under grazing and a low fire frequency. Currently, it is found under moderate, season-long grazing by livestock and will be exacerbated by prolonged drought conditions. In addition, the fire regime for this site has been modified and extended periods without fire is now common. This plant community is still dominated by cool-season grasses, while short grasses/grasslikes and miscellaneous forbs account for the balance of the understory. Wyoming big sagebrush is now a conspicuous part of the overall production and accounts for the majority of the overstory. The understory of grass and grass-like plants includes needleandthread, rhizomatous wheatgrasses, blue grama, threadleaf sedge, and Sandberg bluegrass. Forbs commonly found in this plant community include scarlet globemallow, fringed sagewort, lemon scurfpea, sulfur buckwheat, hairy goldaster, and phlox. Sagebrush can make up to 25% of the annual production. The overstory of sagebrush and understory of grass and forbs provide a diverse plant community. When compared to the Historic Climax Plant Community, needleandthread, Indian ricegrass, and winterfat have decreased. Indian ricegrass may occur in only trace amounts under the sagebrush canopy or within the patches of pricklypear. Threadleaf sedge, blue grama and big sagebrush have increased. Plains pricklypear cactus will also have increased, but occurs only in small patches. The total annual production (air-dry weight) of this state is about 320 pounds per acre, but it can range from about 180 lbs. /acre in unfavorable years to about 480 lbs. /acre in above average years. This plant community is resistant to change. The herbaceous species present are well adapted to grazing; however, species composition can be altered through long-term overgrazing. The herbaceous component is mostly intact and plant vigor and replacement capabilities are sufficient. Water flow patterns and litter movement may be occurring but only on steeper slopes. Incidence of pedestalling is minimal. Soils are mostly stable and the surface shows minimum soil loss. The watershed is functioning and the biotic community is intact. Transitional pathways leading to other plant communities are as follows: • Prescribed grazing or possibly long-term prescribed grazing, will convert this plant community to the HCPC. The probability of this occurring is high especially if rotational grazing along with short deferred grazing is implemented as part of the prescribed method of use. In addition, the removal of fire suppression will allow a somewhat natural fire regime to reoccur to more easily transition between this plant community and the HCPC. A prescribed fire treatment can be useful to hasten this transition if desired. • Frequent and severe grazing plus no fire will convert this plant community to the Mixed Shrub/Bare Ground Plant Community. The probability of this occurring is high. This is especially evident on areas with historically higher precipitation and the sagebrush stand is not adversely impacted by drought or heavy browsing. • Frequent and severe grazing (yearlong grazing), will convert the plant community to the Threadleaf Sedge and/or Blue Grama Sod Plant Community. The probability of this occurring is high especially if the sagebrush stand has been severely affected by drought or heavy browsing or has been removed by wildfire or brush management.
Figure 4. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). WY0501, 5-9BH Upland sites. Monthly percentages of total annual growth for all upland sites with dominantly C3 Cool season plants..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 15 | 50 | 20 | 5 | 10 |
State 3
Mixed Shrub/Bare Ground Plant Community
Community 3.1
Mixed Shrub/Bare Ground Plant Community
This plant community is the result of frequent and severe grazing and protection from fire. Sagebrush eventually dominates this plant community, as the annual production of sagebrush will exceed 25%. Yucca on coarser soils can also be a major part of this plant community. These shrub species are a significant component of the plant community and the preferred cool season grasses have been eliminated or greatly reduced. The dominant grasses are Sandberg bluegrass, threadleaf sedge, and blue grama. Weedy annual species such as cheatgrass may occupy the site if a seed source is available. Patches of pricklypear cactus can be noticeable. Noxious weeds such as Russian knapweed, leafy spurge, or Canada thistle may invade the site if a seed source is available. The interspaces between plants have expanded leaving the amount of bare ground more prevalent. As compared with the HCPC or the Perennial Grass/Big Sagebrush Plant Communities, the annual production is similar, as the shrub production compensates for the decline in the herbaceous production. The total annual production (air-dry weight) of this state is about 300 pounds per acre, but it can range from about 150 lbs. /acre in unfavorable years to about 400 lbs. /acre in above average years. This plant community is resistant to change as the stand becomes more decadent. These areas may actually be more resistant to fire as less fine fuels are available and the bare ground between the sagebrush plants is increased. Continued frequent and severe grazing or the removal of grazing does not seem to affect the composition or structure of the plant community. Plant diversity is moderate to poor. The plant vigor is diminished and replacement capabilities are limited due to the reduced number of cool-season grasses. Plant litter is noticeably less when compared to the HCPC. Soil erosion has accelerated because of increased bare ground. Water flow patterns and pedestalling are obvious. Infiltration is reduced and runoff has increased. Rill channels may be noticeable in the interspaces and gullies may be establishing where rills have concentrated down slope. Transitions or pathways leading to other plant communities are as follows: • Brush management, followed by prescribed grazing and possible reseeding will return this plant community at or near the HCPC. If prescribed fire is used as a means to reduce or remove the shrubs, sufficient fine fuels will need to be present. This may require deferment from grazing prior to treatment. Post management is critical to ensure success. This can range from two or more years of rest to partial growing season deferment, depending on the condition of the understory at the time of treatment and the growing conditions following treatment. In the case of an intense wildfire that occurs when desirable plants are not completely dormant the length of time required to reach the HCPC may be increased and seeding of natives is recommended. • Brush management, followed by frequent and severe grazing, will convert the plant community to the Threadleaf Sedge and/or Blue Grama Sod Plant Community.
Figure 5. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). WY0501, 5-9BH Upland sites. Monthly percentages of total annual growth for all upland sites with dominantly C3 Cool season plants..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 15 | 50 | 20 | 5 | 10 |
State 4
Threadleaf Sedge and/or Blue Grama Sod Plant Community
Community 4.1
Threadleaf Sedge and/or Blue Grama Sod Plant Community
This plant community is the result of frequent and severe yearlong grazing. A sod of threadleaf sedge and blue grama dominate the site. Pricklypear cactus can become dense enough in patches so that livestock cannot graze forage growing within the cactus clumps. Big sagebrush has been reduced and in some cases removed. When the historic climax community is replaced by sod forming communities, grass production as well as total production is significantly reduced. All cool-season mid-grasses and forbs have been greatly reduced or removed. Plant diversity is extremely low. The total annual production (air-dry weight) of this state is about 100 pounds per acre, but it can range from about 55 lbs. /acre in unfavorable years to about 150 lbs. /acre in above average years. This sod is extremely resistant to change and continued frequent and severe grazing or the removal of grazing does not seem to affect the plant composition or structure of the plant community. The biotic integrity of this state is not functional and plant diversity is extremely low. Plant vigor is significantly weakened and replacement capabilities are limited due to the reduced number of cool-season grasses. The biotic integrity of this plant community is not intact. This sod bound plant community is very resistant to water infiltration. While this sod protects the site itself, off-site areas are affected by excessive runoff that can cause rills and gully erosion. Water flow patterns are obvious in the bare ground areas and pedestalling is apparent along the sod edges. Rill channels are noticeable in the interspaces and gullies may be establishing where rills have concentrated down slope. The watershed may or may not be functioning, as runoff may affect adjoining sites. Transitional pathways leading to other plant communities are as follows: • Grazing land mechanical treatment (chiseling, etc.) and reseeding and pricklypear cactus control (if needed), followed by prescribed grazing, will return this plant community to near Historic Climax Plant Community condition.
Figure 6. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). WY0501, 5-9BH Upland sites. Monthly percentages of total annual growth for all upland sites with dominantly C3 Cool season plants..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 15 | 50 | 20 | 5 | 10 |
Additional community tables
Table 5. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | 20–60 | |||||
| thickspike wheatgrass | ELLA3 | Elymus lanceolatus | 20–60 | – | ||
| thickspike wheatgrass | ELLAL | Elymus lanceolatus ssp. lanceolatus | 20–60 | – | ||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 20–60 | – | ||
| 2 | 120–200 | |||||
| needle and thread | HECO26 | Hesperostipa comata | 120–200 | – | ||
| 3 | 40–80 | |||||
| Indian ricegrass | ACHY | Achnatherum hymenoides | 40–80 | – | ||
| 4 | 20–40 | |||||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 20–40 | – | ||
| 5 | 20–40 | |||||
| bluebunch wheatgrass | PSSP6 | Pseudoroegneria spicata | 20–40 | – | ||
| 6 | 0–40 | |||||
| Grass, perennial | 2GP | Grass, perennial | 0–20 | – | ||
| threeawn | ARIST | Aristida | 0–20 | – | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 0–20 | – | ||
| threadleaf sedge | CAFI | Carex filifolia | 0–20 | – | ||
| Sandberg bluegrass | POSE | Poa secunda | 0–20 | – | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 0–20 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 7 | 20–60 | |||||
| Forb, perennial | 2FP | Forb, perennial | 0–20 | – | ||
| textile onion | ALTE | Allium textile | 0–20 | – | ||
| fleabane | ERIGE2 | Erigeron | 0–20 | – | ||
| desertparsley | LOMAT | Lomatium | 0–20 | – | ||
| phlox | PHLOX | Phlox | 0–20 | – | ||
| scarlet globemallow | SPCO | Sphaeralcea coccinea | 0–20 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 8 | 20–60 | |||||
| big sagebrush | ARTR2 | Artemisia tridentata | 20–60 | – | ||
| 9 | 0–40 | |||||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–20 | – | ||
| yellow rabbitbrush | CHVI8 | Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus | 0–20 | – | ||
| rubber rabbitbrush | ERNA10 | Ericameria nauseosa | 0–20 | – | ||
| spiny hopsage | GRSP | Grayia spinosa | 0–20 | – | ||
| winterfat | KRLA2 | Krascheninnikovia lanata | 0–20 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Animal Community – Wildlife Interpretations
Historic Climax Plant Community: The predominance of grasses in this plant community favors grazers and mixed-feeders, such as bison, elk, and antelope. Suitable thermal and escape cover for deer may be limited due to the low quantities of woody plants. However, topographical variations could provide some escape cover. When found adjacent to sagebrush dominated states, this plant community may provide brood rearing/foraging areas for sage grouse, as well as lek sites. Other birds that would frequent this plant community include western meadowlarks, horned larks, and golden eagles. Many grassland obligate small mammals would occur here.
Perennial Grass/Big Sagebrush Plant Community: The combination of an overstory of sagebrush and an understory of grasses and forbs provide a very diverse plant community for wildlife. The crowns of sagebrush tend to break up hard crusted snow on winter ranges, so mule deer and antelope may use this state for foraging and cover year-round, as would cottontail and jack rabbits. It provides important winter, nesting, brood-rearing, and foraging habitat for sage grouse. Brewer’s sparrows’ nest in big sagebrush plants and hosts of other nesting birds utilize stands in the 20-30% cover range.
Mixed Shrub/Bare Ground Plant Community: This plant community can provide important winter foraging for elk, mule deer and antelope, as sagebrush can approach 15% protein and 40-60% digestibility during that time. This community provides excellent escape and thermal cover for large ungulates, as well as nesting habitat for upland game birds. However, it provides little foraging opportunities for upland game birds, as fewer forbs are available. Many grassland obligate small mammals would occur here.
Threadleaf Sedge and/or Blue Grama Sod Plant Community: These communities provide limited foraging for antelope and other grazers. They may be used as a foraging site by sage grouse if proximal to woody cover and if the Historic Climax Plant Community or the Perennial Grass/Big Sagebrush Plant Community is limited. Generally, these are not target plant communities for wildlife habitat management.
Animal Community – Grazing Interpretations
The following table lists suggested stocking rates for cattle under continuous season-long grazing under normal growing conditions. These are conservative estimates that should be used only as guidelines in the initial stages of the conservation planning process. Often, the current plant composition does not entirely match any particular plant community (as described in this ecological site description). Because of this, a field visit is recommended, in all cases, to document plant composition and production. More precise carrying capacity estimates should eventually be calculated using this information along with animal preference data, particularly when grazers other than cattle are involved. Under more intensive grazing management, improved harvest efficiencies can result in an increased carrying capacity. If distribution problems occur, stocking rates must be reduced to maintain plant health and vigor.
Plant Community Production Carrying Capacity*
(lb. /ac) (AUM/ac)
Historical Climax Plant Community 225-600 .20
Perennial Grass/Big Sagebrush 180-480 .16
Mixed Shrub/Bare Ground 150-400 .10
Threadleaf Sedge and/or Blue Grama Sod 55-150 .05
* - Continuous, season-long grazing by cattle under average growing conditions.
Grazing by domestic livestock is one of the major income-producing industries in the area. Rangeland in this area may provide yearlong forage for cattle, sheep, or horses. During the dormant period, the forage for livestock use needs to be supplemented with protein because the quality does not meet minimum livestock requirements.
Hydrological functions
Water is the principal factor limiting forage production on this site. This site is dominated by soils in hydrologic group B, with localized areas in hydrologic group C. Infiltration potential for this site varies from moderately rapid to rapid depending on soil hydrologic group and ground cover. Runoff varies from low to moderate. In many cases, areas with greater than 75% ground cover have the greatest potential for high infiltration and lower runoff. An example of an exception would be where short-grasses form a strong sod and dominate the site. Areas where ground cover is less than 50% have the greatest potential to have reduced infiltration and higher runoff (refer to Part 630, NRCS National Engineering Handbook for detailed hydrology information).
Rills and gullies should not typically be present. Water flow patterns should be barely distinguishable if at all present. Pedestals are only slightly present in association with bunchgrasses. Litter typically falls in place, and signs of movement are not common. Chemical and physical crusts are rare to non-existent. Cryptogamic crusts are present, but only cover 1-2% of the soil surface.
Recreational uses
This site provides hunting opportunities for upland game species. The wide varieties of plants which bloom from spring until fall have an esthetic value that appeals to visitors.
Wood products
No appreciable wood products are present on the site.
Other products
None noted.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented here has been derived from NRCS inventory data. Field observations from range trained personnel were also used. Other sources used as references include: USDA NRCS Water and Climate Center, USDA NRCS National Range and Pasture Handbook, and USDA NRCS Soil Surveys from various counties.
Inventory Data References
Data Source Number of Records Sample Period State County
SCS-RANGE-417 19 1965-1986 WY Park & others
Contributors
Ray Gullion
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | Ray Gullion |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | ray.gullion@wy.usda.gov |
| Date | 05/02/2008 |
| Approved by | E. Bainter |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
Rills should not be present -
Presence of water flow patterns:
Barely observable -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
Essentially non-existent -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
Bare ground is 25-35% occurring in small areas throughout site -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
Active gullies should not be present -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
None -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Little to no plant litter movement. Plant litter remains in place and is not moved by erosional forces. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Plant cover and litter is at 60% or greater of soil surface and maintains soil surface integrity. Soil Stability class is anticipated to be 4 or greater. -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
Use Soil Series description for depth and color of A-horizon -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
Grass canopy and basal cover should reduce raindrop impact and slow overland flow providing increased time for infiltration to occur. Healthy deep rooted native grasses enhance infiltration and reduce runoff. Infiltration is Moderately Rapid to Rapid. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
No compaction layer or soil surface crusting should be present. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Mid stature Bunch Grasses > Shrubs > Forbs > Mid Stature Rhizomatous Grasses > Short stature Grasses/GrasslikeSub-dominant:
Other:
Additional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Very Low -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Average litter cover is 20-30% with depths of 0.1 to 0.25 inches -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
400 lbs/ac -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
Threadleaf sedge, Blue grama, Big sagebrush, Yucca, Prickly Pear, Cheatgrass and other annuals, Exotics, and Species found on Noxious Weed List -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
All species are capable of reproducing
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.