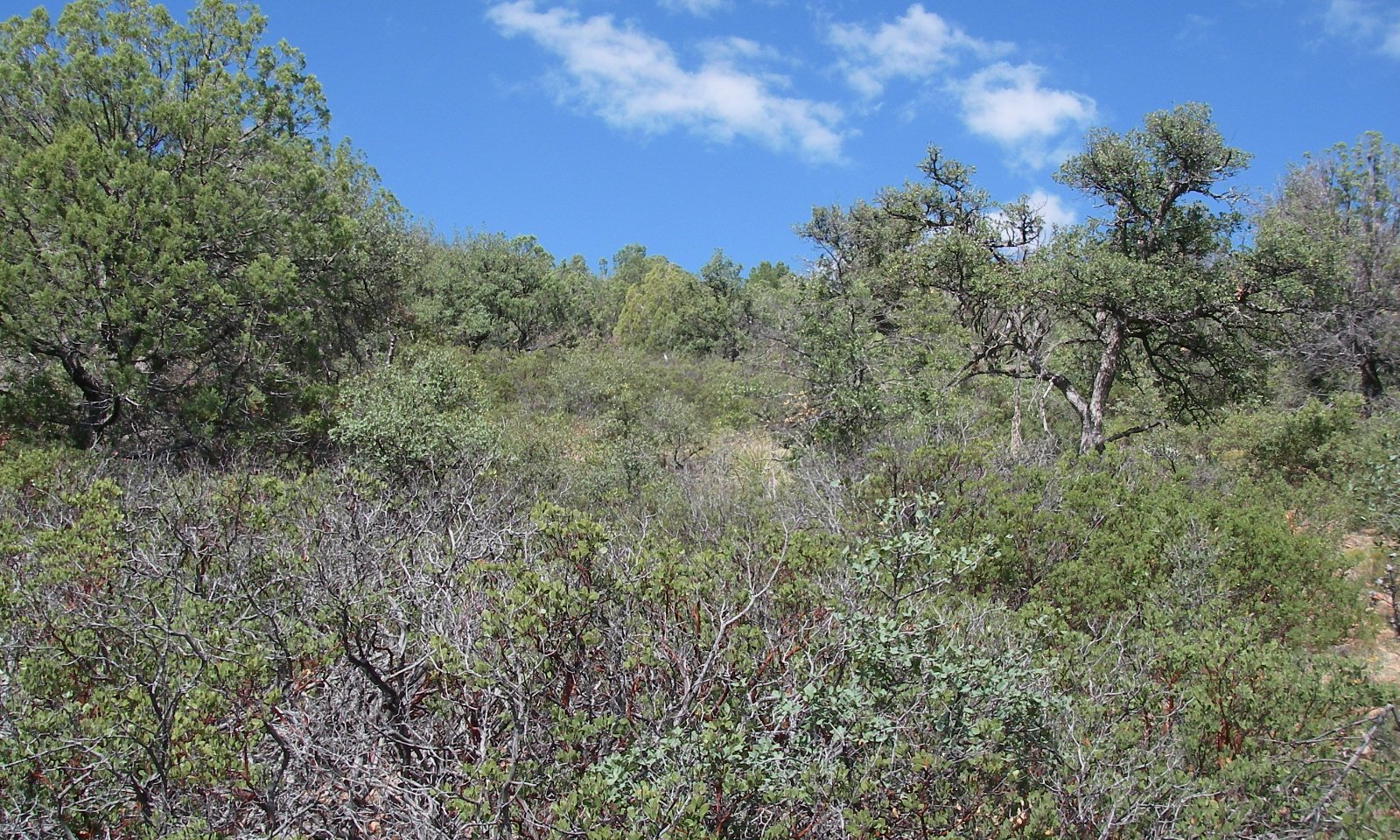
Clayey Slopes 20-24"
Scenario model
Current ecosystem state
Select a state
Management practices/drivers
Select a transition or restoration pathway
- Transition 1a More details
- Transition 1c More details
- Transition 1b More details
- Transition 2a More details
- Restoration pathway 3a More details
- Restoration pathway 4a More details
-
No transition or restoration pathway between the selected states has been described
Target ecosystem state
Select a state
Description
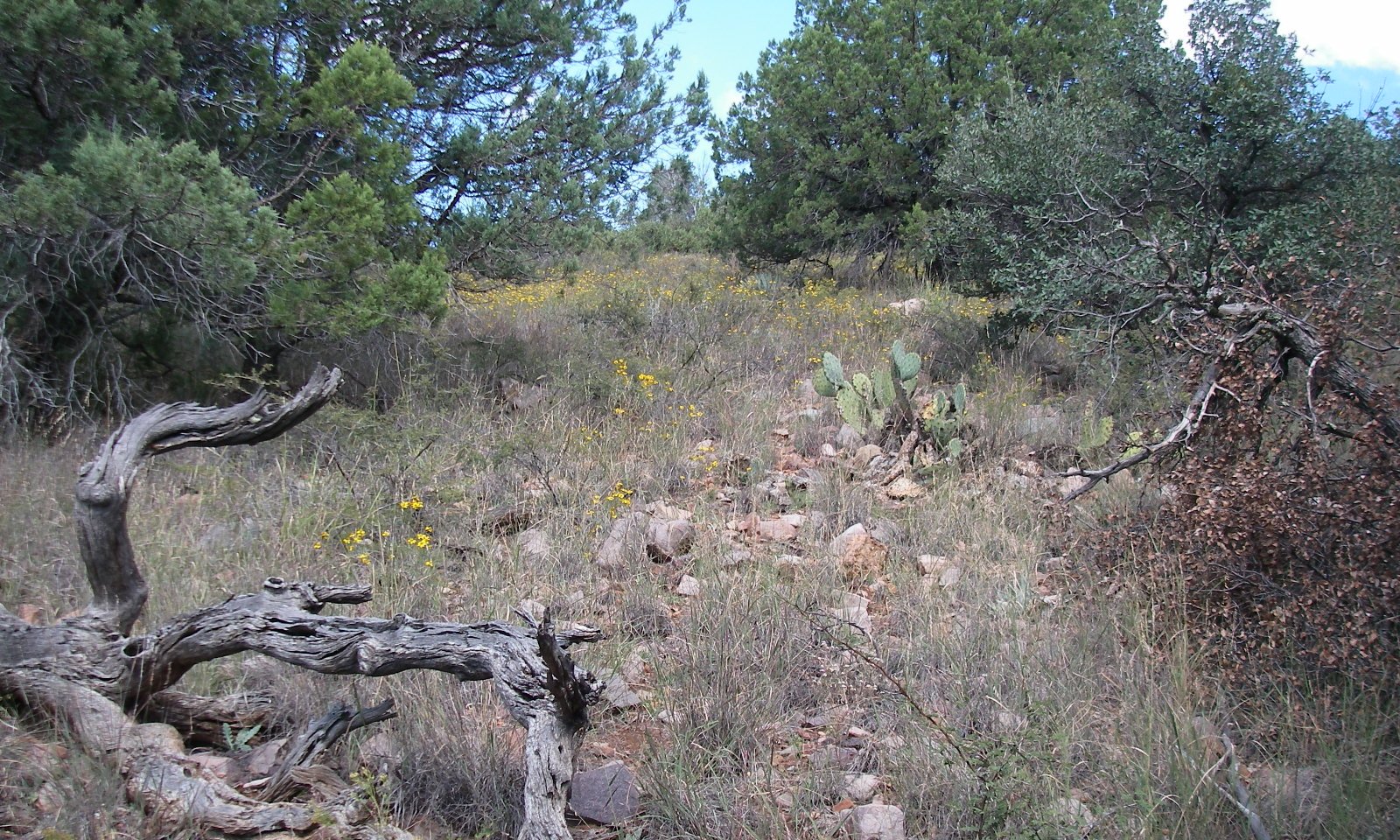
Grass, shrubs, and trees are all represented in the plant community.
Submodel
Description
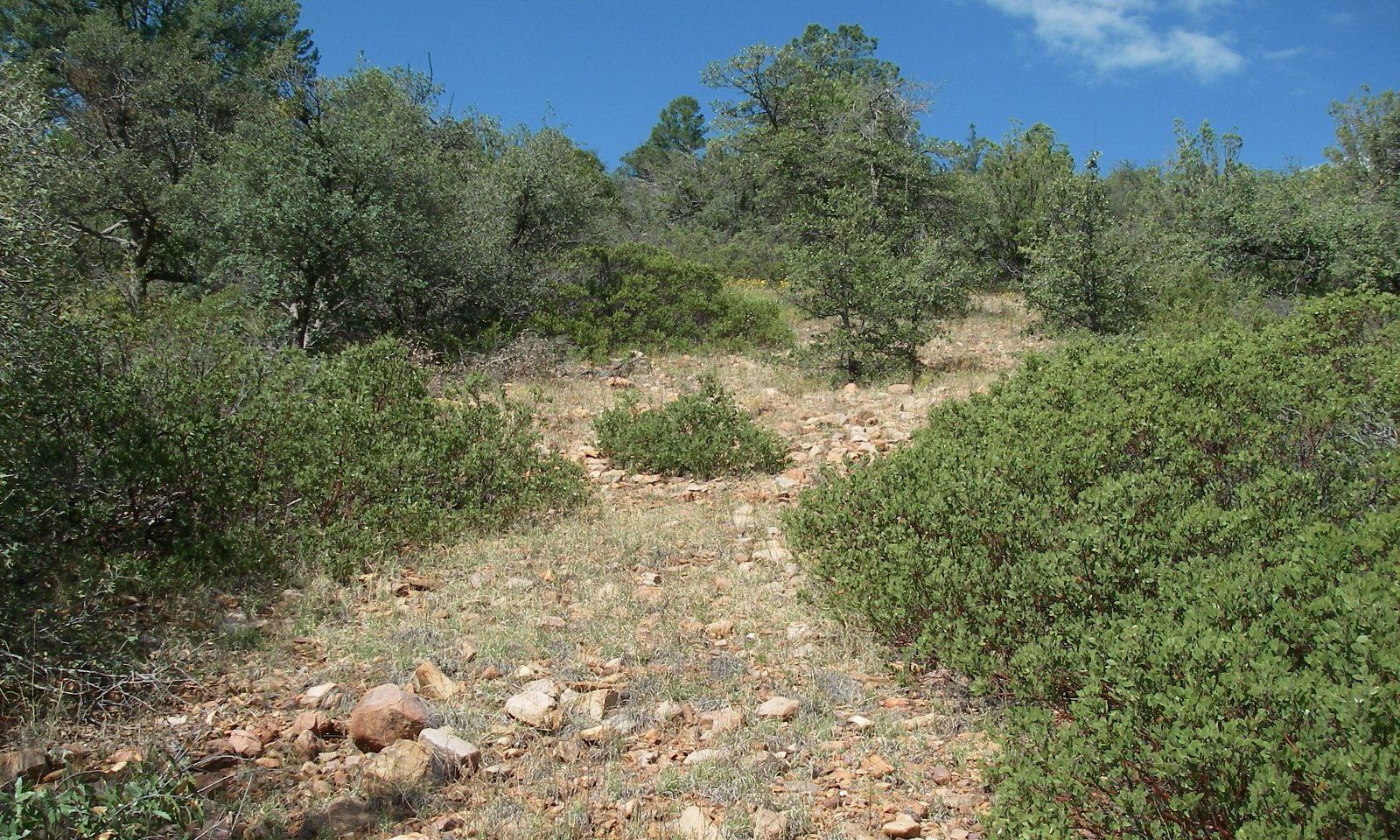
Blue grama is the dominant herbaceous plant in the plant community.
Submodel
Description
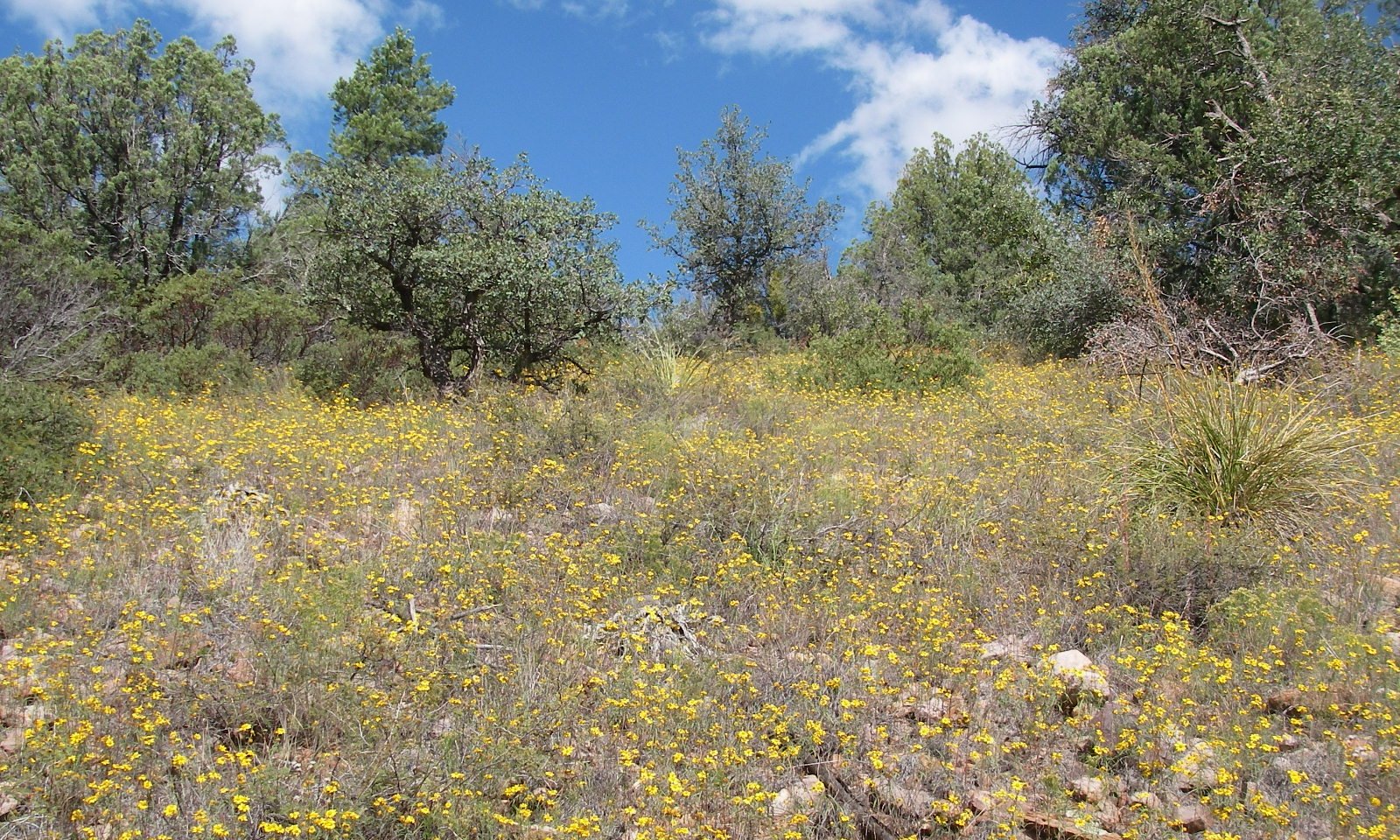
Basal area of short grasses is significantly reduced and annuals become dominant.
Submodel
Description
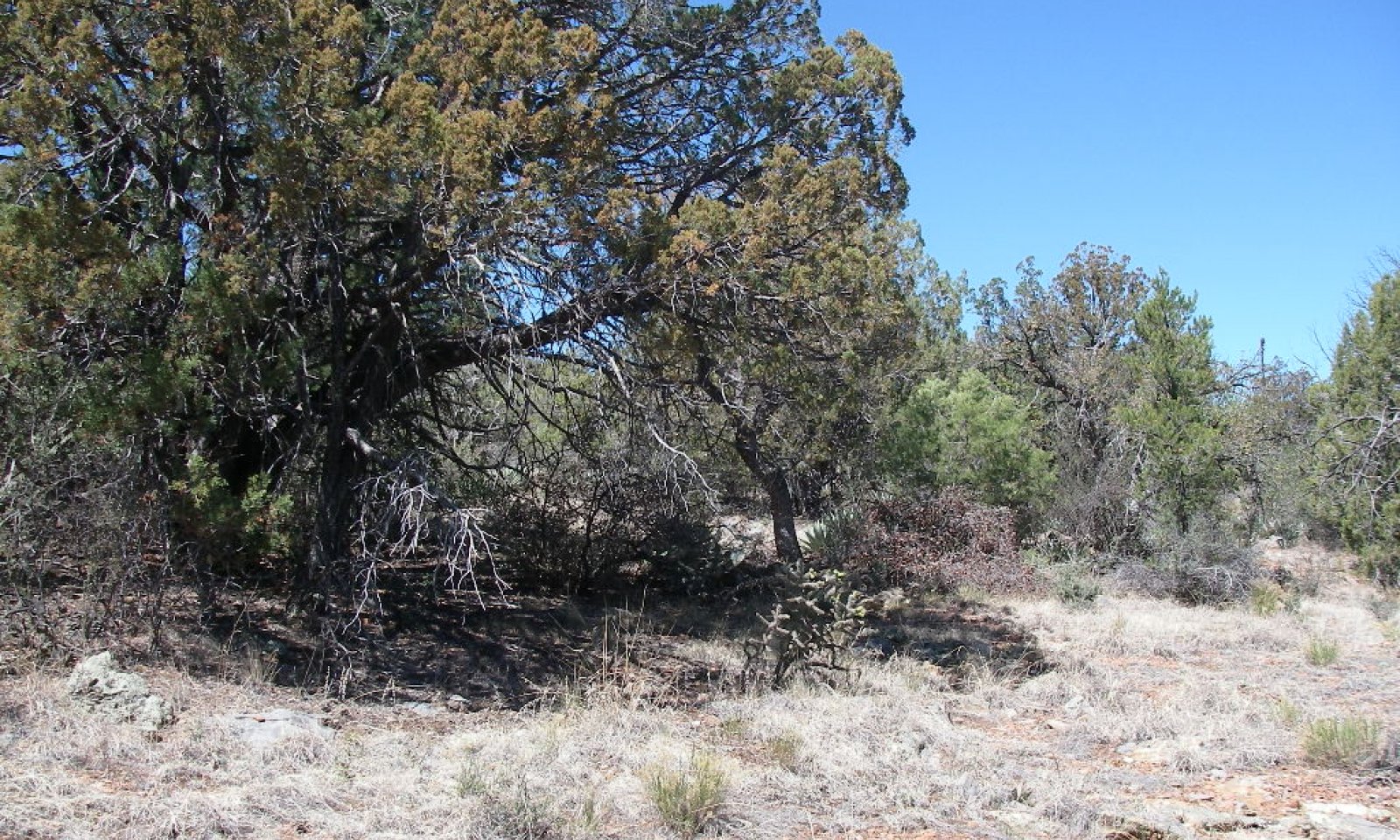
Tree regeneration increases in size and trees dominate the site.
Submodel
Mechanism
High intensity continuous herbivory by livestock or wildlife reduces the vigor and abundance of sideoats grama and increases the abundance of short grasses like blue grama on cool aspects or hairy grama and curly mesquite on warm aspects. Horses being more apt to use steeper slopes can have equally detrimental effects.
Mechanism
Absence of fires for very long periods allows tree regeneration to grow to maturity and increase in size on the site.
Mechanism
Exact mechanism is uncertain. However, fire intervals are likely greater than the historic 7-10 years of adjacent ponderosa pine forests, which the herbaceous species of the Reference Plant Community are capable of supporting. Fire intervals are likely of sufficient length that existing manzanita plants become sexually mature and able to produce seed as suggested by Pase and Granfelt (1977) which is scarified in future fires.
Mechanism
Continuous high intensity herbivory reduces the vigor and basal area of short grasses and opens the community up to increased abundance of annual species like goldeneye.
Mechanism
Unknown. Prescribed grazing of remnant plants with range planting to increase the abundance of desirable species. Aerial application of seed is the only practical method of seeding.
Model keys
Briefcase
Add ecological sites and Major Land Resource Areas to your briefcase by clicking on the briefcase (![]() ) icon wherever it occurs. Drag and drop items to reorder. Cookies are used to store briefcase items between browsing sessions. Because of this, the number of items that can be added to your briefcase is limited, and briefcase items added on one device and browser cannot be accessed from another device or browser. Users who do not wish to place cookies on their devices should not use the briefcase tool. Briefcase cookies serve no other purpose than described here and are deleted whenever browsing history is cleared.
) icon wherever it occurs. Drag and drop items to reorder. Cookies are used to store briefcase items between browsing sessions. Because of this, the number of items that can be added to your briefcase is limited, and briefcase items added on one device and browser cannot be accessed from another device or browser. Users who do not wish to place cookies on their devices should not use the briefcase tool. Briefcase cookies serve no other purpose than described here and are deleted whenever browsing history is cleared.
Ecological sites
Major Land Resource Areas
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.