

Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R042CY902NM
Limestone Hills
Accessed: 01/18/2026
General information
Approved. An approved ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model, enough information to identify the ecological site, and full documentation for all ecosystem states contained in the state and transition model.
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 042C–Central New Mexico Highlands
To view this ESD in its most complete form refer to the PDF Version found in the New Mexico NRCS Field Office Technical Guide, section 2.
The Limestone Hills Ecological Site predominantly occurs in LRU 42.8, which is a subunit of MLRA 42 (Southern Desertic Basins, Plains, and Mountains)
MLRA Notes: LRU 42.8 was carved out of the Guadalupe Mountains portion of what used to be MLRA 70D. This Limestone Hills Ecological Site has mostly taken the place of the Limestone Hills Ecological Site that was traditionally used in MLRA 70D.
It is possible, though very rare, that the Limestone Hills Ecological Site may occur outside of this LRU boundary.
To identify locations where this ESD has been mapped, refer to the most current natural resource soil survey data on Web Soil Survey or contact your local NRCS Conservation District field office
Classification relationships
NRCS & BLM: Limestone Hills Ecological Site < LRU 42.8 Northeastern Chihuahuan Desert Hills < Major Land Resource Area 42, Southern Desertic Basins, Plains, and Mountains < Land Resource Region D, Western Range and Irrigated Region (United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006).
USFS: Limestone Hills Ecological Site < Artesia Plains Desert Grass-Shrubland Subsection < Pecos Valley Section < Southwest Plateau and Plains Dry Steppe and Shrub Province (Cleland, et al., 2007).
EPA: Limestone Hills Ecological Site<24b Chihuahuan Desert Grasslands<24 Chihuahuan Deserts (Griffith, 2006).
Ecological site concept
The soils are skeletal (greater than 35% by volume rock fragments greater than 2 mm). Soil depth is very shallow to shallow (1-50 cm). The root restrictive layer is bedrock (limestone, dolomite, sandstone). Slopes are greater than 25% and are typically around 30-60%. These are exemplified by hillsides that exist along the Guadalupe Ridge from Calsbad to White City.
Associated sites
| R042CY901NM |
Very Shallow The very shallow site has slopes < 25%, which make up hill summits adjacent to the Limestone Hills Site. |
|---|---|
| R042CY003NM |
Shallow The shallow ecological site forms on alluvial fans below the limestone hills, and has slopes < 30% |
| R042CY002NM |
Limestone Mountains The limestone hills site transitions into the cooler, limestone mountains, above 5,000 feet on north facing slopes. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Physiographic features
The Limestone Hills ecological site is on hill slopes within LRU 42.8. Elevation ranges from 3500 to 5500 feet. Soil depth can range from very shallow to shallow to limestone and dolomite bedrock. Slopes are greater than 25 percent and are generally between 30 and 60. Aspect is very important to ecological site dynamics.
The Limestone Hills ecological site occurs on slopes of hills, ridges, and mesas and is most closely associated with the Very Shallow Ecological Site, which occurs on summit positions. The Limestone Hills is also closely associated with the Shallow Ecological Site which occurs on lower alluvial fans where a shallow petrocalcic layer has formed. The Limestone Hills site includes, on average, about 15 percent rock outcrop.
Geology: The primary geologic formations that make up the parent material for the Limestone Hills Ecological Site include the Seven Rivers, Tansil, Yates, and to a lesser extent the Capitan Limestone. During Guadalupian time of the Permian Period, dynamic sedimentation of carbonate and evaproite rocks occurred around the rim of the Delaware basin creating an ideal environment for the development of a large coral reef. The rim was topographically high; the waters were shallow, well-ventilated, agitated, and warm. In this excellent marine-life environment the great Capitan Reef began to form. The Capitan Reef grew rapidly and flourished throughout Guadalupian time, surrounding the Delaware basin, controlling environments and influencing sedimentation (Kelley, 1971).
On the landward side of the reef (the backreef) the Seven Rivers, Yates, and Tansil formations developed. The first was the Seven Rivers Formation. The sediments of the Seven Rivers deposited at a time when conditions became drier, and the basin tended toward hypersalinity. The Seven Rivers contain gray to white dolomitic limestone, white to red gypsum, orange-red siltstone, and shale. Within the LRU, the Seven Rivers Formation is considered the surface layer on Azotea Mesa, Seven Rivers Hills, and West Hess Hills. The Seven Rivers Formation tends to contain more erodible sediments than the Tansil and Yates. Therefore, less bedrock is exposed where the Limestone Hills ESD occurs on the Seven Rivers Formation.
Deposited above the Seven Rivers during a quiet period within an unrestricted lagoon is the Yates Formation. The Yates is characterized by layers of very pale orange to yellowish-gray fine-grained, laminated dolomite, alternating with grayish-orange to pale yellowish-orange, calcareous quartz siltstone or very fine-grained sandstone. The Yates is the surface formation over much of Carlsbad Caverns National Park (CCNP), starting at Walnut Canyon and extending North through the Cueva Escarpment and up to Living Desert State Park.
Landward of the unrestricted lagoon was a restricted lagoon, (the Tansil Formation). Here freshwater mixed with seawater. Large amounts of sediments were carried in by streams causing a hostile environment for marine organisms. Like the Yates, the Tansil is characterized by clastic sediments such as siltstone and sandstone as well as layers of dolomite. Unlike the Yates, however, the Tansil contains many thin clay layers (Burger, 2007). The Tansil Formation is the surface layer at the Carlsbad Caverns Visitor Center.
About 15 million years ago, the ancient reef rock that had been buried by younger layers of rock began to rise, creating the Guadalupe Ridge and Mountains while exposing the Seven Rivers, Tansil, and Yates Formations. Over the years, at the hill slope positions, much of the more clastic layers of the Tansil, Yates, and Seven Rivers have eroded away, leaving the very shallow soils mixed and exposed dolomitic limestone rock outcrop which make up the Limestone Hills Ecological Site.
Ecological Site Key for LRU 42.8 and 42.9, Northeastern Chihuahuan Hills and Mountains
1. Site is within LRU 42.8, which is within the ustic-aridic soil moisture regime, and the thermic soil temperature regime. (Often contains redberry juniper)
2. Soils are loamy and not skeletal, and reside in low areas that are stream terraces and fan remnants. - Loamy Terrace ESD
2. Soils are skeletal (Greater than 35% by volume rock fragments greater than 2 mm)
3. Soils are deep to very deep. (Greater than 100 cm to root restrictive layer)
4. Site exists in an active floodplain.-Draw ESD
4. Site exists on a stream terrace or alluvial fan-Gravelly ESD
4. Site exists on steep slopes on limestone colluvium over gypsum residuum.-Limy Gyp Escarpment
3. Soils are very shallow to moderately deep (5-100 cm).
5. Root restrictive layer is a petrocalcic horizon.-Shallow ESD
5. Root restrictive layer is bedrock.
6. Slopes are less than 25%-Very Shallow ESD
6. Slopes are greater than 25%- Limestone Hills ESD
1. Site is located within LRU 42.9, and is represented by the aridic-ustic soil moisture regime, and the mesic soil temperature regime. (It often contains alligator juniper and pinon pine.)
7. Slopes are less than 25%- Shallow Limestone ESD
7. Slopes are greater than 25%- Limestone Mountains ESD
ESD Key Glossary
Glossary:
Colluvium: “Unconsolidated, unsorted earth material being transported or deposited on side slopes and/or at the base of slopes by mass movement (e.g. direct gravitational action) and by local, concentrated runoff” (Schoenberger, et al., 2012).
Petrocalcic Horizon: The petrocalcic horizon is an illuvial horizon in which secondary calcium carbonate or other carbonates have accumulated to the extent that the horizon is cemented or indurated (Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 2010).
Residuum: “Unconsolidated, weathered, or partly weathered mineral material that accumulates by disintegration of bedrock in place” (Schoenberger, et al., 2012).
Soil moisture regime: Refers to the presence or absence either of ground water or of water held at a tension of less than 1500 kPa in the soil or in specific horizons during periods of the year. Water held at a tension of 1500 kPa or more is not available to keep most mesophytic plants alive. Major differences in soil moisture are often reflected in different vegetative communities. The two major soil moisture regimes for the Guadalupe Mountains are Aridic and Ustic (Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 2010).
Soil Temperature Regime: This is the range of temperatures experienced by a soil at a depth of 50 cm. When the average temperature of a soil falls between 46 degrees F and 59 degrees, it falls into the mesic soil temperature regime. The thermic soil temperature regime falls between 59 degrees F and 72 degrees (Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 2010).
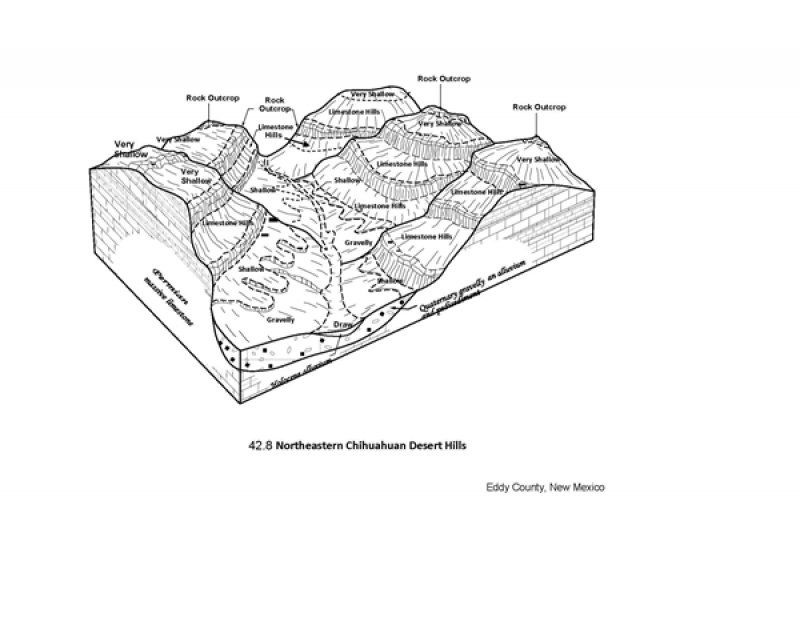
Figure 2. 42.8 Northeastern Chihuahuan Desert Hills
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Hill
(2) Escarpment |
|---|---|
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 3,500 – 5,500 ft |
| Slope | 25 – 100% |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
The mean annual precipitation is 10.4 inches to 18.3 inches, occurring mostly as high intensity, short-duration afternoon thunderstorms from July through September. Mean annual air temperature is 55 to 70 degrees F, and the frost-free season is 207 to 243 days.
Annual weather patterns, influenced by global climate events, such as El Nino and La Nina, affect and alter production and composition across the Limestone Hills Ecological Site. In general, because precipitation is minimal through the winter but increases during the summer, warm-season (C4) plants dominate the landscape. However, from year to year the production and composition can greatly shift due to variable weather patterns. The years that produce the most species richness and production are those that get slow, steady moisture through the months of May, June, and July. Late summer thunderstorms may induce heavy runoff on this site, creating flash-flooding in the draws, drainages, and canyons below.
The climate trend of the area is one toward warmer temperatures and lower precipitation. According to the Carlsbad Caverns Climate Station, during the years 2001-2011, five years received less than 10 inches of rain. Three of those years, (2003, 2005, and 2011) were below 5 inches of rain. And 2011 was both the lowest rainfall and hottest year on record. Similarly, in 1947-1957, 6 out of 11 years were below the mean low of 10.4 inches. But in that stretch, only one year, 1951, was below 5 inches. To put this in perspective, in the dry 1930’s only 2 years were below the mean low of 10.4 and none were below 5 inches. The 2001-2011 decade has been much warmer and drier than any in recorded history. In addition, during the two years of 2010 and 2011, Carlsbad Caverns National Park experienced extreme events of drought, wildfire, and flash flooding which have led to shifts in plant communities
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (average) | 243 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (average) | 263 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 18 in |
Figure 3. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 4. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Influencing water features
The Limestone Hills Ecological Site is not associated with a wetland or riparian system; it is an upland ecological site.
Soil features
Every ecological site and associated soil component has static soil properties that help define the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics that make the site unique. The following soil profile information is a description of those unique soil properties for the Limestone Hills Ecological Site. To learn about the dynamic processes of the soil component, refer to the "plant communities" section of the ESD.
The Limestone Hills Ecological Site is tied to the Lechuguilla and rock outcrop components from map units CC2, CC9, LK1, RB1, and BL1 within LRU 42.8 Northeastern Chihuahuan Hills. The CC2 and LK1 map units are very similar, and consist of complexes of components which are dominated by about 70 percent Lechuguilla, 15 percent Kimrose, and 15 percent rock outcrop. The BL1 map unit consists of about 45 percent Bogle, 20 percent Lechuguilla, and 15 percent Badlands. The Lechuguilla component has formed from mostly colluvium and residuum which has been derived from limestone and dolomite parent material. Soil depth ranges from very shallow to shallow (20-40 cm) over bedrock.
In normal years this soil is driest during the winter. It is moist in the upper part for over 90 cumulative days, but fewer than 90 consecutive days during the growing season. The soil moisture regime is aridic bordering on ustic. The mean annual soil temperature is 59 to 66 degrees F, which is classified as the thermic temperature regime.
This soil is well drained with high runoff. At the surface, the saturated hydraulic conductivity ranges from 1.0 to 10 m/second over impermeable bedrock. The Lechuguilla taxonomic class is: Loamy-skeletal mixed, superactive, calcareous, thermic Lithic Ustic Torriorthents.
Typical Pedon: Lechuguilla hill slopes; Geographic Coordinate System: 32° 7'' 12.76'''' north, 104° 33'' 54.52'''' west
A1--0 to 2.5 inches (0 to 6 cm); brown (10YR 4/3) very cobbly loam, very dark grayish brown (10YR 3/2), moist; 20 percent clay; moderate coarse granular structure; soft, very friable, slightly sticky, slightly plastic; common very fine roots and common fine roots; common fine interstitial pores; 30 percent gravel and 15 percent cobble and 5 percent stone; violently effervescent, 33 percent calcium carbonate equivalent; moderately alkaline, pH 7.9; clear smooth boundary.
A2--2.5 to 9 inches (6 to 23 cm); brown (10YR 4/3) very gravelly loam, very dark grayish brown (10YR 3/2), moist; 22 percent clay; weak medium subangular blocky structure; slightly hard, friable, slightly sticky, slightly plastic; common very fine roots and common fine roots; common fine interstitial pores; 10 percent fine gravel and 5 percent coarse gravel and 10 percent cobble and 5 percent stone; violently effervescent, 29 percent calcium carbonate equivalent; slightly alkaline, pH 7.7; clear smooth boundary.
Bk--9 to 12.5 inches (23 to 32 cm); brown (10YR 5/3) very stony loam, very dark grayish brown (10YR 3/2), moist; 23 percent clay; moderate medium subangular blocky structure; slightly hard, friable, slightly sticky, slightly plastic; few medium roots and common very fine and fine roots; common fine interstitial pores; common fine prominent irregular carbonate masses throughout and few medium prominent irregular weakly cemented carbonate nodules on bottom of rock fragments; 10 percent fine gravel and 5 percent coarse gravel and 10 percent cobble and 15 percent stone; violently effervescent, 39 percent calcium carbonate equivalent; moderately alkaline, pH 7.9; abrupt smooth boundary.
R--12.5 to 78.5 inches (32 to 200 cm); indurated limestone or dolomite bedrock.
Typical Surface Fragments <=3" (% Cover): 20-30%
Typical Surface Fragments > 3" (% Cover): 20-30%
Typical Subsurface Fragments <=3" (% Volume): 20-30%
Typical Subsurface Fragments > 3" (%% Volume): 30-50%
Typical Soil Depth: 20-40 cm
Calcium Carbonate Equivalent (percent):
A & A2 horizons-0 to 5
Bk horizon-0 to 25
Total Average Available Water Capacity (cm H2O/cm soil): 2.73 cm
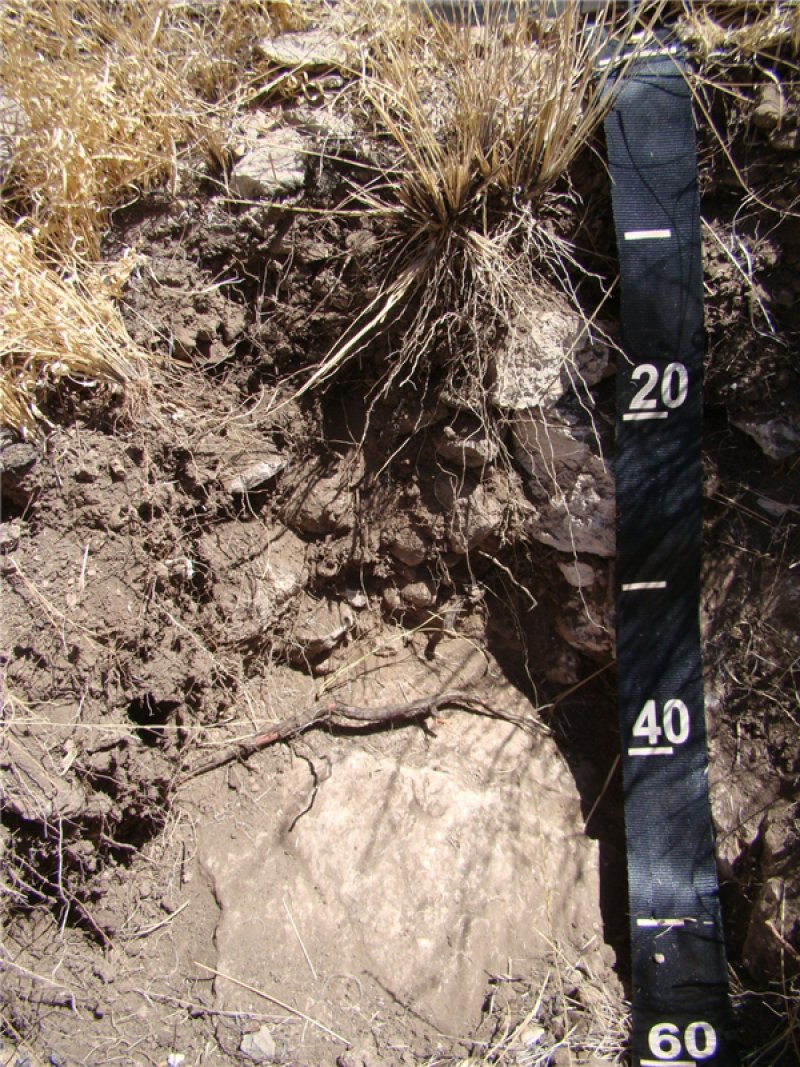

Figure 5. Lechuguilla Hill Slope Component
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Residuum
–
dolomite
(2) Eolian deposits – limestone and sandstone |
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Gravelly loam (2) Very gravelly silt loam (3) Cobbly silty clay loam |
| Family particle size |
(1) Loamy |
| Drainage class | Moderately well drained to well drained |
| Permeability class | Slow to moderate |
| Soil depth | 2 – 20 in |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 10 – 45% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 5 – 35% |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
0.78 – 1.18 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
25% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
1 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
1 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
7 – 7.8 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
5 – 50% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
10 – 70% |
Ecological dynamics
The Limestone Hills Ecological Site contains a mix of grass, shrubs, forbs, and succulents. It is often dry due to its shallow depth, high runoff potential, and exposure to many dry, windy days. Due to the dryness, and very shallow depth of the soil, succulents such as lechuguilla, yucca, prickly pear, and sotol are very abundant on this site, sometimes causing difficulty with walking. Also, as typical with desert communities, wet springs and summers can cause swings in species richness causing an abundance of forbs to express themselves in a show of color.
There are numerous variables which influence plant communities, these variables include: elevation, aspect, percent slope, soil depth, slope shape, fracturing of bedrock, and fire frequency. The first basic variable is a combination of elevation and aspect. At the lower end of the range, (about 3500 feet on south facing slopes), the climate is warmest and driest and tends to promote more succulents and Chihuahuan desert species, such as ocotillo, mariola, tanglehead, and various cacti. As elevation increases to the upper extreme, (at about 6000 feet on south facing slopes, and 5000 on north facing slopes), grass communities change: black grama phases into curly leaf muhly, and shrub species change from mariola dominant, to redberry juniper dominant, and at the upper end, sandpaper oak dominant. Between 5000 and 5500 feet on this landform, this site transitions into the cooler, moister LRU 42.9 Limestone Mountains site.
Soil depth plays a role in determining species production and diversity. The underlying bedrock varies in depth from being exposed at the surface to a depth of 40 cm in a few places. The deeper the soil, the greater the ability for different plant species to access water and utilize other resources. Species such as blue grama and Wrights’ beebrush prefer somewhat deeper soil, while curly leaf muhly and lechuguilla prefer the very shallow soils. According to Duniway, “Cracks and fissures in the bedrock also trap water and facilitate access to water contained within the matrix of the bedrock” (Duniway, et al., 2010). Sotol can dominate where higher levels of fracturing occur.
Percent slope affects water runoff and retention, generally, the steeper the slope, the higher the runoff. In the Tansil and Yates formations, bedding plains are often exposed where dolomitic limestone resists weathering. Often these bedding plains produce a terrace like structure that collects soil and promotes productive plant communities. As water collects and travels through cracks and fissures in the bedding plain, a spring may develop, creating a very productive plant community or even a woodland cove.
Fire is a consistent disturbance regime that reduces succulents and a few shrubs while stimulating grasses and forbs. Not all fires are equal. According to Gebow, “Fire effects in the same location will vary, especially with fire timing, both seasonally and within the scheme of year-to-year moisture variation. Precipitation during seasons before and after fire has a major effect on recovery of plants. Fire researchers in the area and region suggest a 10-to-15-year fire regime is common” (Gebow, 2001).
Small and more frequent fires were more common before the mid-1800’s, with the Apache likely responsible for many small burns. Following colonization by Europeans, intervals between fires have lengthened and the average fire size has increased (Ahlstrand, 1981). Small fires are important for creating a patchy mosaic across the landscape, which provides beneficial habitat for many wildlife species.
State and transition model
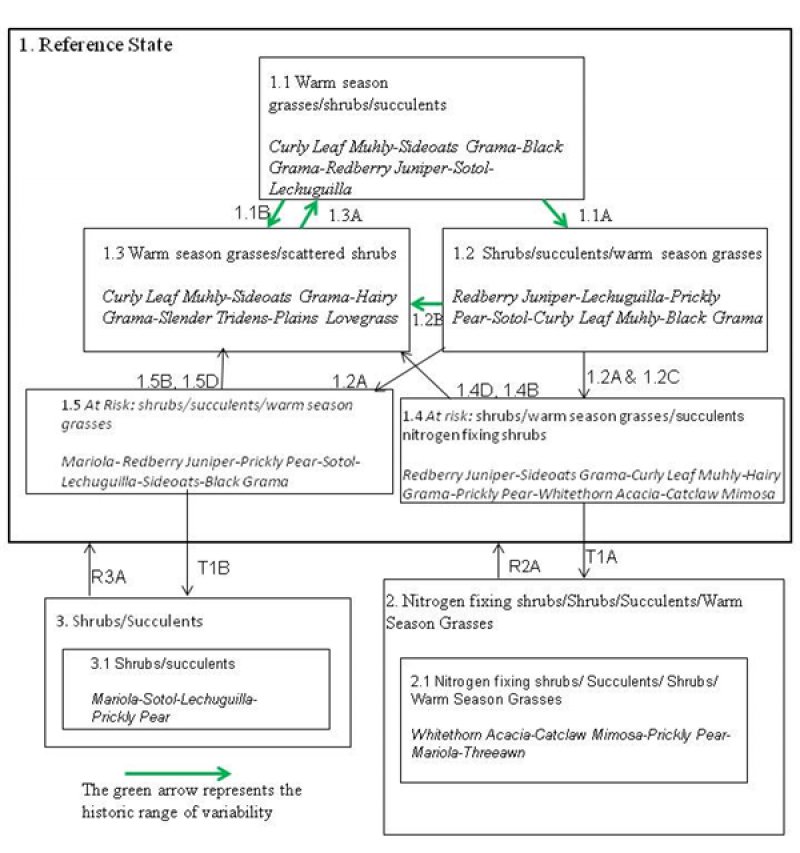
Figure 6. Limestone Hills
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Reference State
1.1 Warm season grasses/shrubs/succulents (diagnostic plant community) A mix of grasses, shrubs and succulents are present. Total foliar cover is > 65%, depending on the amount of rock outcrop. 1.1A Community Pathway: This pathway represents time between fires, during which natural processes increase shrub and succulent vigor and decrease grass production and composition. 1.1B Community Pathway: This pathway represents fire. Fire suppresses succulents and many shrubs, giving grasses a competitive advantage. 1.2 Shrubs/succulents/warm season grasses: Over time, foliar cover of shrubs and succulents increases and that of warm season grasses decreases. 1.2A Community Pathway: This pathway represents intervals between fires which are longer than the historic range of variability. Fire suppression, whether through loss of fuel load due to herbivory or from fighting natural wildfires, has increased shrub and succulent vigor and decreased grass production and percent composition. 1.2B Community Pathway: This pathway represents fire. Fire suppresses succulents and many shrubs, giving grasses a competitive advantage. 1.2C Community Pathway: This pathway represents a growing competitive advantage for nitrogen fixing shrubs due to slow changes in soil chemistry and hydrology. 1.3 Warm season grasses/scattered shrubs: This plant phase exists after fire. Grasses respond well to fire, while many shrubs and succulents decrease. 1.3A Community Pathway: This pathway represents intervals between fires, during which natural processes increase shrub and succulent vigor and decrease grass production and composition. Over time, plant community 1.3 shifts to 1.1. 1.4 At risk: shrubs/warm season grasses/succulents/nitrogen fixing shrubs: Due to gradual changes in hydrologic function and soil chemistry, succulents and shrubs increase over time. The increased abundance of native nitrogen fixing shrubs such as whitethorn and catclaw mimosa is a key indicator that this community phase is “at risk.” 1.4B Community Pathway: This pathway represents fire. Fire sets back succulents and many shrubs, giving grasses a competitive advantage. 1.4D Community Pathway: A change in livestock grazing management promotes grass vigor and decreases shrub competition. This accelerates the turnover of fine roots, causing an increase in labile carbon, acceleration in decomposition, and a resulting increase in plant available water. T1A Transition one: Slow variables: Continued encroachment by whitethorn acacia, coupled with the loss of herbaceous plant species, causes a decrease in soil organic matter, leading to a decrease in plant available water. Trigger event: A severe drought causes loss of soil organic carbon. Threshold: A hydrologic function/soil chemistry threshold is crossed. 1.5 At risk: shrubs/succulents/warm season grasses: This plant phase is the result of gradual changes in species composition to a shrub and succulent dominated community. There has been a decrease in hydrologic function as grasses are weakened in this community. This is a different plant community than 1.4, as nitrogen fixing plants are not present. 1.5B Community Pathway: This pathway represents fire. Fire sets back succulents and many shrubs, giving grasses a competitive advantage. 1.5D Community Pathway: A change in livestock grazing management to allow for decreased shrub competition, improved litter accumulation, an increase in labile carbon, and acceleration in decomposition resulting in an increase in plant available water. T1B Transition two: Slow variables: Continued decrease in grasses and overall canopy cover, causing a decrease in soil organic matter, leading to a decrease in plant available water, decomposition, and plant available nutrients. Trigger event: A severe drought, causing a loss of organic carbon. Threshold: A hydrologic function threshold was crossed. 2.0 Nitrogen fixing shrubs/succulents/shrubs/warm season grasses state 2.1 Whitethorn Acacia/succulents/shrubs/warm season grasses: Whitethorn acacia has become a prominent plant on the site. Foliar cover has decreased to < 40%. A higher Nitrogen turnover rate increases the invasiveness and stability of whitethorn. This community has a mix of shrubs, succulents, and warm season grasses. R2A Restoration Process: An increase in the competitive advantage of non-nitrogen fixing species through physical, chemical, and biological management practices. 3.0 Shrubs/succulents state 3.1 Shrubs/succulents: This plant community has crossed a threshold where shrubs and succulents dominate the canopy and grasses are very limited. Due to fire suppression and continuous herbivory a change in the hydrologic cycle has occurred. This community is very similar to 2.1 except for the presence of whitethorn and other nitrogen fixing shrubs. R3B Restoration Process: Organic matter needs to be increased in the system to stimulate decomposition, mineral cycling, and water storage. Fine root systems from grass species are important for increasing organic matter.
Community 1.1
Warm season grasses/shrubs/succulents (diagnostic plant community)
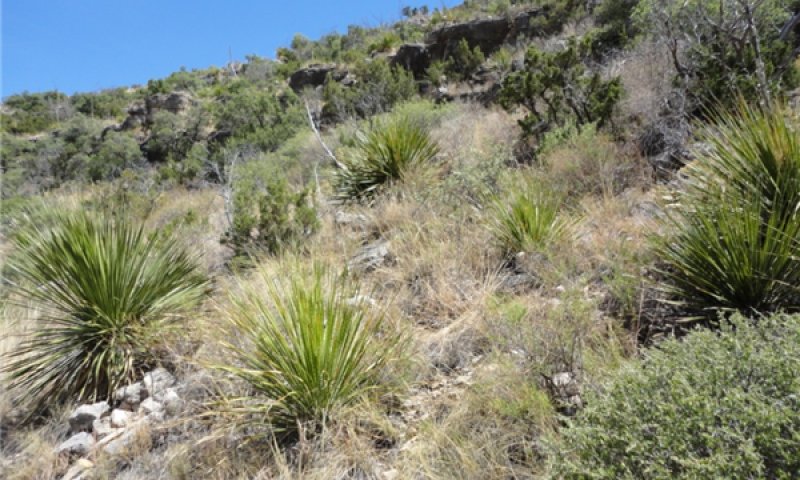

Figure 7. Community 1.1; Rattlesnake Trail; Carlsbad Caverns
This community phase combines a mix of warm season grasses, shrubs, and succulents. Foliar cover is between 70 and 80 percent, basal cover is between 15 and 20 percent, and bare ground is minimal due to over 55 percent of the surface covered in rock fragments. Warm season grasses make up about 45 percent foliar cover; shrubs, 14 percent; and succulents, including sotol and lechuguilla, around 14 percent. The average surface soil stability rating is a 5 under canopy and a 4.5 in the interspaces. Annual production averages around 900 lbs/ac, but can span between 600 and 1200 lbs/ac, depending on the percentage of rock outcrop, cracks and fissures in the bedrock, soil depth, slope, and annual weather patterns. This community exists approximately 5-7 years after low intensity fire. Curly leaf muhly is the dominant grass in mid to upper elevations, while “thermic” species, such as black grama, slim tridens and hairy tridens, are more dominant at lower elevations. Mariola tends to be a dominant shrub at lower to mid elevations, followed by redberry juniper at mid to upper elevations and sandpaper oak at the highest elevations. Lechuguilla is the dominant succulent and is present at all elevations, especially around rock outcrop. Sotol can be a dominant shrub in this community, especially in areas where heavy fracturing of the bedrock occurs. This plant community optimizes energy flow, hydrologic function and nutrient cycling. The diverse root systems take advantage of moisture from both close to the surface as well as deep in the rock strata. Decomposition is active, creating soil organic matter, which enhances “plant available water” needed for plant vigor.
Figure 8. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 450 | 682 | 910 |
| Shrub/Vine | 120 | 173 | 230 |
| Forb | 30 | 45 | 60 |
| Total | 600 | 900 | 1200 |
Table 6. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 1% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 25-30% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 40-50% |
| Forb foliar cover | 5-10% |
| Non-vascular plants | 1% |
| Biological crusts | 1% |
| Litter | 40-60% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 35-45% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 10-20% |
| Bedrock | 10-20% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 0-2% |
Table 7. Canopy structure (% cover)
| Height Above Ground (ft) | Tree | Shrub/Vine | Grass/ Grasslike |
Forb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | – | 1-3% | 3-7% | 1-3% |
| >0.5 <= 1 | – | 3-7% | 15-25% | 1-3% |
| >1 <= 2 | – | 6-10% | 15-25% | 1-1% |
| >2 <= 4.5 | – | 8-12% | – | – |
| >4.5 <= 13 | – | 2-6% | – | – |
| >13 <= 40 | – | – | – | – |
| >40 <= 80 | – | – | – | – |
| >80 <= 120 | – | – | – | – |
| >120 | – | – | – | – |
Figure 9. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). NM4282, Limestone Hills Reference State.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 25 | 30 | 12 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Community 1.2
Shrubs/succulents/warm season grasses
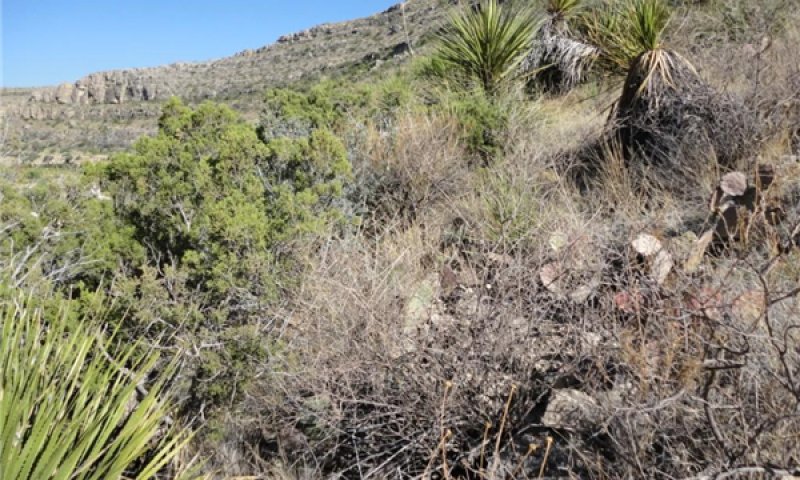

Figure 10. Community 1.2; Concave Slope; Shrub dominated; Sla
This community phase consists of a mix of shrubs, succulents, and warm season grasses. This plant community can manifest itself in two ways, either shrub dominated on concave slopes or succulent dominated on convex slopes. It is common, on the Limestone Hills Ecological Site, for the slope shape to undulate from convex to concave showing a gradient from shrub dominated to succulent dominated. There is generally less soil development on convex slopes with more exposed rock outcrop, creating a harsher environment and a competitive advantage for succulents such as lechuguilla and ocotillo. Foliar cover is between 70 and 80 percent, basal cover is between 15 and 35 percent, and bare ground is around 1 to 3 percent. Warm season grasses make up about 26 percent foliar cover; shrubs, 29 percent; succulents, 17 percent; and forbs, 4 percent. The average surface soil stability rating is 5 under canopy and 4.5 in the inter-spaces. Annual production averages around 800 lbs/ac, but can span between 500 and 1000 lbs/ac, depending on the percentage of rock outcrop, cracks and fissures in the bedrock, soil depth and annual weather patterns. This community exists approximately 14-18 years after fire. Curly leaf muhly is the dominant grass in mid to upper elevations, while “thermic” species, such as black grama, slim tridens and hairy tridens, are more dominant at lower elevations. Mariola tends to be a dominant shrub at lower to mid elevations, followed by redberry juniper at mid to upper elevations and sandpaper oak at the highest elevations. Lechuguilla is the dominant succulent and is present at all elevations, especially around rock outcrop. Sotol can be a dominant shrub in this community, especially in areas where heavy fracturing of the bedrock occurs. This plant community has developed due to an increase in shrub and succulent vigor and a decrease in grass vigor. As shrubs increase they gain a competitive advantage, primarily by out-competing the grass for water and nutrients. As grasses and fine root turnover decrease, energy flow begins to lessen due to a decrease in soil organic matter, caused by a slowdown in decomposition. Fire is the natural event that keeps mature shrub species from gaining a competitive advantage and stimulates colonization by grasses.
Figure 11. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 8. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 275 | 440 | 550 |
| Shrub/Vine | 205 | 324 | 410 |
| Forb | 20 | 36 | 40 |
| Total | 500 | 800 | 1000 |
Table 9. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 0-1% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 40-50% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 20-30% |
| Forb foliar cover | 3-5% |
| Non-vascular plants | 1% |
| Biological crusts | 1-3% |
| Litter | 40-60% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 35-45% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 10-20% |
| Bedrock | 10-20% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 1-3% |
Table 10. Canopy structure (% cover)
| Height Above Ground (ft) | Tree | Shrub/Vine | Grass/ Grasslike |
Forb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | – | 1-2% | 3-7% | 1-3% |
| >0.5 <= 1 | – | 2-4% | 15-25% | 1-3% |
| >1 <= 2 | – | 3-7% | – | – |
| >2 <= 4.5 | – | 6-10% | – | – |
| >4.5 <= 13 | 1-2% | 7-11% | – | – |
| >13 <= 40 | – | – | – | – |
| >40 <= 80 | – | – | – | – |
| >80 <= 120 | – | – | – | – |
| >120 | – | – | – | – |
Community 1.3
Warm season grasses/scattered shrubs
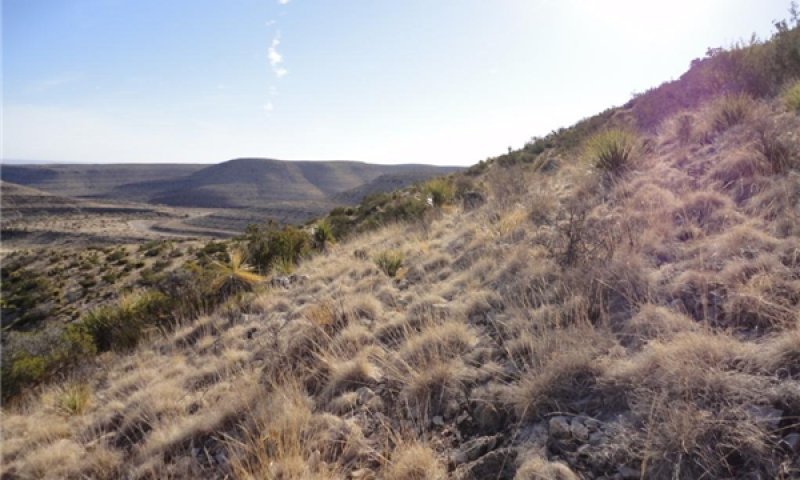

Figure 12. Community 1.3; Cueva Escarpment; 3-14-12
This community phase consists of a mix of warm season grasses, shrubs, and succulents. This plant phase exists shortly after fire has burned the site, suppressing succulents and shrubs and creating a competitive advantage for grasses. Foliar cover is between 60 and 80 percent, depending on how recent and how severe the fire had been. Also, precipitation following fire is needed for growth to resume. Basal cover is between 15 and 30 percent depending on post-fire precipitation, and bare ground is around 2 to 4 percent. Warm season grasses make up about 55 percent foliar cover; shrubs, 10 percent; and succulents, 5 percent. The average surface soil stability rating is 5 under canopy and 4.8 in the interspaces. Annual production averages around 900 lbs/ac, but can span between 600 and 1200 lbs/ac, depending on the percentage of rock outcrop, cracks and fissures in the bedrock, soil depth, and annual weather patterns. This community exists approximately 1-6 years after fire. It is a grass dominated site, with basal sprouting shrubs scattered across the site. Curly leaf muhly is the dominant grass at mid to upper elevations, while “thermic” species; such as black grama, slim tridens, and hairy tridens are more dominant at lower elevations. Mariola tends to be a dominant shrub at lower to mid elevations, followed by redberry juniper at mid to upper elevations and sandpaper oak in the highest elevations. Lechuguilla and sacahuista are the dominant succulents and are present at all elevations. This plant community is the ecological site’s response to fire within the reference state. Fire is the natural event that keeps shrub species from gaining a competitive advantage and stimulates colonization by grasses. As grasses respond with greater density following fire, decomposition speeds up, creating greater soil organic matter, infiltration, and plant available water. Over time, shrubs and succulents move back onto the site.
Figure 13. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 11. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 450 | 675 | 900 |
| Shrub/Vine | 108 | 162 | 216 |
| Forb | 42 | 63 | 84 |
| Total | 600 | 900 | 1200 |
Table 12. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 1% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 15-25% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 50-60% |
| Forb foliar cover | 3-7% |
| Non-vascular plants | 1% |
| Biological crusts | 1-3% |
| Litter | 55-75% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 35-45% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 10-20% |
| Bedrock | 10-20% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 1-3% |
Table 13. Canopy structure (% cover)
| Height Above Ground (ft) | Tree | Shrub/Vine | Grass/ Grasslike |
Forb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | – | 1-3% | 5-15% | 1-3% |
| >0.5 <= 1 | – | 4-8% | 25-35% | 2-4% |
| >1 <= 2 | – | 5-9% | 10-20% | – |
| >2 <= 4.5 | – | – | – | – |
| >4.5 <= 13 | – | – | – | – |
| >13 <= 40 | – | – | – | – |
| >40 <= 80 | – | – | – | – |
| >80 <= 120 | – | – | – | – |
| >120 | – | – | – | – |
Community 1.4
At risk: shrubs/warm season grasses/succulents/nitrogen fixing shrubs:
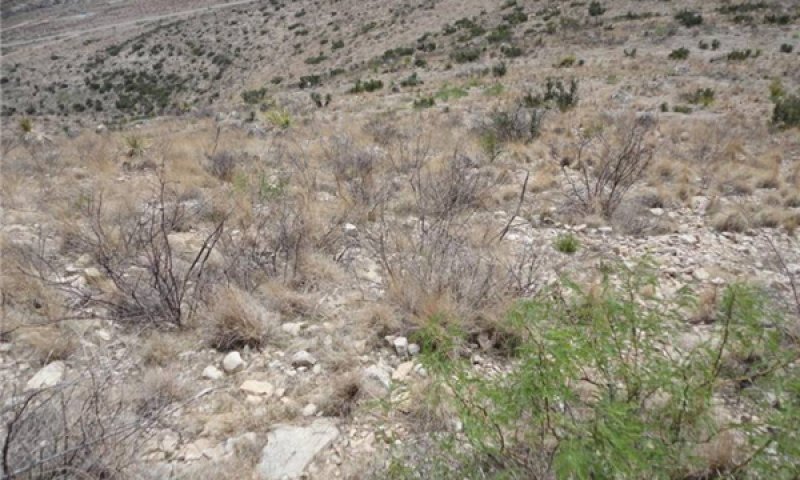

Figure 14. Community 1.4; Mosley Canyon; 3-14-12
This community phase consists of a mix of shrubs, warm season grasses, and succulents, along with an increase in nitrogen fixing shrubs. It is no longer within the “historic range of variability” as management has created an “at risk” community phase. However it is still within the reference state, meaning it has not crossed a threshold, and that intensive management (i.e., accelerating practices) is not yet required to push the system back into the historic range of variability (Bestelmeyer, et al., 2010). Foliar cover is between 40 and 70 percent, basal cover is between 15 and 25 percent, and bare ground is around 2 to 8 percent. Warm season grasses make up about 20 percent foliar cover; shrubs, 23 percent; and succulents, 7 percent. The average surface soil stability rating is 4.5 under canopy and 3.5 in the interspaces. Annual production averages around 600 lbs/ac, but can span between 300 and 900 lbs/ac, depending on the percentage of rock outcrop, cracks and fissures in the bedrock, soil depth, and annual weather patterns. This community exists due to past management and disturbance, primarily fire suppression coupled with loosely managed livestock grazing over many years. This plant community usually exists within close proximity of a livestock watering facility where continuous, season-long grazing occurs and a seed source for nitrogen fixing shrubs, such as whitethorn acacia and catclaw mimosa are available. A greater percentage of short, warm season grass species occur in this community phase along with a greater percentage of nitrogen fixing shrubs. This plant community phase has developed over time due to a number of slow ecological variables. One management practice that influences ecology is fire suppression. Shrubs gain a competitive advantage through fire suppression. Through deeper root systems, shrubs can take advantage of moisture stored in cracks and fissures in the bedrock, while grasses struggle with the slow decline of soil organic matter and the decrease of plant available water. Also, due to the decrease in soil organic matter, aggregate stability diminishes, causing a decrease in infiltration and an increase in runoff. Another factor in creating this community is the loose management of livestock over many years. Livestock contribute to the distribution of nitrogen fixing plant seed and can lessen plant vigor and soil organic matter through continuous grazing and over-utilization. As the vigor of grasses and some shrubs decreases, nitrogen fixing plants start to increase and begin to change the chemistry and hydrology of the site. This site is “at risk” of crossing a threshold into state two.
Figure 15. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 14. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 165 | 330 | 495 |
| Shrub/Vine | 120 | 240 | 360 |
| Forb | 15 | 30 | 45 |
| Total | 300 | 600 | 900 |
Table 15. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 1% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 25-35% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 15-25% |
| Forb foliar cover | 3-7% |
| Non-vascular plants | 1% |
| Biological crusts | 1-3% |
| Litter | 20-50% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 35-45% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 10-20% |
| Bedrock | 10-20% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 3-5% |
Table 16. Canopy structure (% cover)
| Height Above Ground (ft) | Tree | Shrub/Vine | Grass/ Grasslike |
Forb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | 1-1% | 2-6% | 5-15% | 1-3% |
| >0.5 <= 1 | – | 5-9% | 6-10% | 2-4% |
| >1 <= 2 | – | 7-12% | 1-3% | – |
| >2 <= 4.5 | – | 8-9% | – | – |
| >4.5 <= 13 | – | 2-4% | – | – |
| >13 <= 40 | – | – | – | – |
| >40 <= 80 | – | – | – | – |
| >80 <= 120 | – | – | – | – |
| >120 | – | – | – | – |
Community 1.5
At risk: shrubs/succulents/warm season grasses
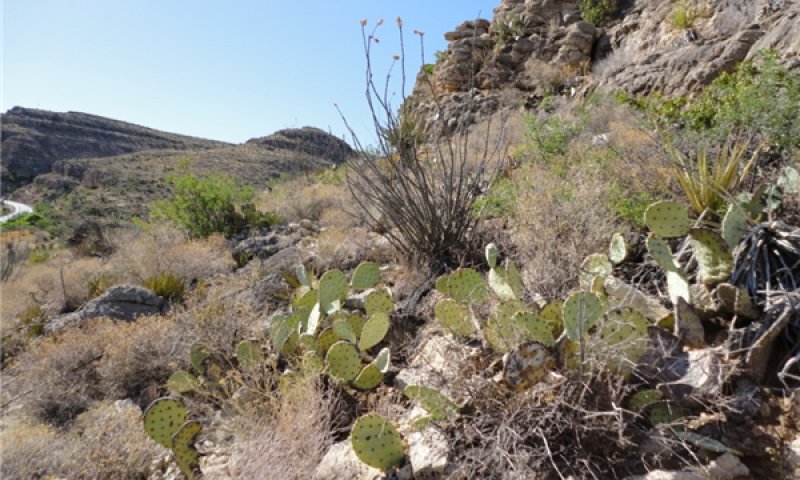

Figure 16. Community 1.5; Mariola-succulent dominated; Walnut
This community phase consists of a mix of shrubs, succulents, and warm season grasses. This plant community is much like 1.4, except it does not contain the presence of nitrogen fixing shrubs. It is an “at risk” plant community because it is no longer within the historical range of variability, mainly due to long years of fire suppression. This plant community, much like 1.2, can manifest itself in different ways, depending on elevation, aspect, and slope shape. Shrubs become dominant in cooler positions, with deeper soils. Succulents become dominant along warmer aspects with thinner soils. There is generally less soil development on convex slopes with more exposed rock outcrop, creating a harsher environment and a competitive advantage for succulents such as prickly pear, lechuguilla, and ocotillo. Thus, one can observe a gradient from shrub-dominated to succulent-dominated as slopes transition from concave to convex. Foliar cover is between 40 and 80 percent, basal cover is between 10 and 30 percent, and bare ground is around 2 to 8 percent. Warm season grasses make up about 18 percent foliar cover; shrubs, 25 percent; succulents, 14 percent; and forbs, 4 percent. The average surface soil stability rating is 4.5 under canopy and 3.5 in the interspaces. Annual production averages around 600 lbs/ac, but can span between 400 and 800 lbs/ac, depending on the percentage of rock outcrop, cracks and fissures in the bedrock, soil depth, and annual weather patterns. This community exists after about 20 years of fire suppression. Curly leaf muhly is the dominant grass in mid to upper elevations while “thermic” species such as black grama, slim tridens, and hairy tridens are more dominant at lower elevations. Mariola tends to be a dominant shrub at lower to mid elevations, followed by redberry juniper at mid to upper elevations and sandpaper oak at the highest elevations. Lechuguilla and prickly pear are the dominant succulents present, especially around rock outcrop. Sotol can be a dominant shrub in this community, especially in areas where heavy fracturing of the bedrock occurs. This plant community has developed due to an increase in shrub and succulent vigor and a decrease in grass vigor. As shrubs increase they gain a competitive advantage, primarily by out-competing the grass for water and plant available nutrients. As grasses decrease, energy flow begins to lessen due to a decrease in soil organic matter, caused by a slowdown in decomposition. Fire is the natural event that keeps mature shrub species from gaining a competitive advantage and stimulates colonization by grasses.
Figure 17. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 17. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrub/Vine | 200 | 300 | 400 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 180 | 270 | 360 |
| Forb | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| Total | 400 | 600 | 800 |
Table 18. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 1% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 35-45% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 15-25% |
| Forb foliar cover | 2-6% |
| Non-vascular plants | 1% |
| Biological crusts | 1-3% |
| Litter | 40-60% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 35-45% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 10-20% |
| Bedrock | 10-20% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 3-7% |
Table 19. Canopy structure (% cover)
| Height Above Ground (ft) | Tree | Shrub/Vine | Grass/ Grasslike |
Forb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | – | 3-7% | 2-6% | 1-3% |
| >0.5 <= 1 | – | 6-10% | 5-9% | 1-3% |
| >1 <= 2 | – | 7-11% | 5-9% | – |
| >2 <= 4.5 | – | 7-11% | – | – |
| >4.5 <= 13 | – | 3-7% | – | – |
| >13 <= 40 | – | – | – | – |
| >40 <= 80 | – | – | – | – |
| >80 <= 120 | – | – | – | – |
| >120 | – | – | – | – |
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2


This pathway is the slow movement, over time from Community 1.1 to Community 1.2. This pathway represents time between fires within the natural range of variability, as it will take 10 to 14 years, after fire, for shrubs and succulents to achieve foliar cover > 25 percent. Shrub and succulent vigor increase as grass vigor decreases due to various ecological processes. The first is through direct competition for resources. Shrubs have greater access to nutrients and moisture deep in cracks and fissures within the bedrock strata. The second is a slow decrease in labile carbon, thus decreasing organic matter which leads to a decrease in water-holding capacity and a resulting decrease in grass vigor.
Pathway 1.1B
Community 1.1 to 1.3


This pathway represents a single fire event driving plant Community 1.1 to 1.3. Grasses respond fairly quickly after fire, while shrubs and succulents are suppressed. This pathway occurs within the range of historic variability. Many shrubs and succulents take a while to respond after a fire event. They must re-grow from below ground root systems or from seed. Grasses can colonize quickly, through tillering, especially when precipitation follows closely after fire. Note: This species list reflects the model concept of the diagnostic plant phase. Inventory data from multiple plots and sources were used to compile this list. Note: Ranges reflect variability based on soils, temperature and moisture caused by factors such as elevation, aspect, and slope shape based on average moisture year conditions. Note: Species annual production is given in pounds per acre. Note: A zero in the species production column indicates that the species does not occur at the high or low elevation range of the ecological site. (I.e. tanglehead does not occur at 5500 feet)
Pathway 1.2B
Community 1.2 to 1.3


This pathway represents a single fire event driving plant Community 1.2 to 1.3. Grasses respond fairly quickly after fire, while shrubs and succulents are suppressed. This pathway occurs within the range of historic variability. Many shrubs and succulents take a while to respond after a fire event. They must re-grow from below ground root systems or come back from seed. Grasses can colonize quickly, through tillering after a fire event, especially when precipitation follows closely after fire.
Pathway 1.2C
Community 1.2 to 1.4


This pathway represents a growing competitive advantage from nitrogen fixing shrubs due to slow changes in soil chemistry and hydrology. Nitrogen fixing shrubs such as whitethorn acacia, catclaw acacia, and catclaw mimosa will start to increase in vigor, creating immediate competition with grasses and eventually other shrubs.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.4


This pathway is the slow movement, over time from Community 1.2 to Community 1.4 or 1.5. This pathway represents time between fires, which are longer than the historic range of variability. Fire suppression, whether through loss of fuel load due to herbivory or from fighting natural wildfires, has increased shrub and succulent vigor and decreased grass production and composition. Shrub and succulent vigor increases as grass vigor decreases due to various ecological processes. One such process is direct competition for resources. Shrubs have greater access to nutrients and moisture deep in cracks and fissures within the bedrock strata. Another process is the slow decrease in labile carbon, thus decreasing organic matter. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in water-holding capacity and a consequential decrease in grass vigor.
Pathway 1.3A
Community 1.3 to 1.1


This pathway is the slow movement from Community 1.3 to Community 1.1. This pathway represents intervals between fires during which natural processes increase shrub and succulent vigor and decrease grass production and grass species composition. Shrub and succulent vigor increases as grass vigor decreases due to various ecological processes. The first of these is direct competition for resources. Shrubs have greater access to moisture and nutrients deep in cracks and fissures within the bedrock strata. The second is a slow decrease in labile carbon, thus decreasing soil organic matter which leads to a decrease in grass vigor.
Pathway 1.4B
Community 1.4 to 1.3


pathway represents a single fire event driving plant Community 1.4 to 1.3. Grasses respond fairly quickly after fire, while shrubs and succulents are suppressed. This pathway coupled with a change in livestock grazing will lead back to the historic range of variability.
Pathway 1.4D
Community 1.4 to 1.3


A change in livestock grazing management promotes grass vigor and decreases shrub competition. This accelerates the turnover of fine roots, causing an increase in labile carbon, acceleration in decomposition, and an increase in plant available water.
Pathway 1.5B
Community 1.5 to 1.3


This pathway represents a single fire event driving plant Community 1.5 to 1.3. Grasses respond fairly quickly after fire, while shrubs and succulents are suppressed. This pathway will lead back to the historic range of variability
Pathway 1.5D
Community 1.5 to 1.3


A change in livestock grazing management promotes grass vigor and decreases shrub competition. This accelerates the turnover of fine roots, causing an increase in labile carbon, acceleration in decomposition, and an increase in plant available water.
State 2
Nitrogen fixing shrubs/succulents/shrubs/warm season grasses state
Whitethorn acacia has become a prominent plant on the site. Foliar cover has decreased to < 40%. A higher Nitrogen turnover rate increases the invasiveness and stability of whitethorn. This community has a mix of shrubs, succulents, and warm season grasses.
Community 2.1
Whitethorn Acacia/succulents/shrubs/warm season grasses

Figure 18. Community 2.1; Seven Rivers Hills; 4-16-12
This community phase consists of a mix of shrubs, succulents, and warm season grasses along with an increase in nitrogen fixing shrubs, especially whitethorn acacia. It is no longer within the reference state, as the site has crossed a threshold into a degraded state. Because the site has crossed a threshold, intensive management (i.e., accelerating practices) is required to restore the system. Foliar cover is between 30 and 50 percent, basal cover is between 3 and 12 percent, and bare ground is around 5 to 15 percent. Warm season grasses make up about 10 percent foliar cover; shrubs, 20 percent; and succulents, 8 percent. The average surface soil stability rating is 3.5 under canopy and 3 in the interspaces. Annual production averages around 300 lbs/ac, but can span between 150 and 450 lbs/ac, depending on the percentage of rock outcrop, cracks and fissures in the bedrock, soil depth and annual weather patterns. This community exists due to past management and disturbance, primarily fire suppression coupled with grazing management that decreases grass competition. After many years of slow retrogression, a trigger event such as a severe drought could cause this site to cross a threshold where ecological processes and soil properties keep it in a degraded state. With fire suppression, shrubs gain a competitive advantage due to deeper root systems, which take advantage of moisture stored in cracks and fissures in the bedrock, while grasses struggle with the slow decline of soil organic matter and the decrease of plant available water. Also, due to the decrease in soil organic matter, aggregate stability diminishes, creating a decrease in infiltration and an increase in runoff. Livestock may contribute to the distribution of shrub seed and can lessen grass vigor and soil organic matter through continuous grazing and over-stocking. As grass vigor decreases, shrubs gain a competitive advantage. As nitrogen fixing shrubs, especially whitethorn, increase a change in the chemistry and hydrology of the system occurs. This site suffers from low labile carbon and high nitrogen turnover, ultimately slowing the nutrient cycle and reducing plant available water. Over time, without a change in management, it is possible for this plant community to degrade further where only whitethorn, a few scattered shrubs, and fluffgrass exist.
Figure 19. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 20. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrub/Vine | 82 | 165 | 247 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 60 | 120 | 180 |
| Forb | 8 | 15 | 23 |
| Total | 150 | 300 | 450 |
Table 21. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 1% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 25-35% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 5-15% |
| Forb foliar cover | 2-4% |
| Non-vascular plants | 1% |
| Biological crusts | 2-6% |
| Litter | 25-35% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 35-45% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 10-20% |
| Bedrock | 10-20% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 4-12% |
Table 22. Canopy structure (% cover)
| Height Above Ground (ft) | Tree | Shrub/Vine | Grass/ Grasslike |
Forb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | 1-1% | 2-4% | 6-10% | 1-3% |
| >0.5 <= 1 | – | 4-8% | 1-3% | 1-2% |
| >1 <= 2 | – | 7-11% | – | – |
| >2 <= 4.5 | – | 4-8% | – | – |
| >4.5 <= 13 | – | 2-4% | – | – |
| >13 <= 40 | – | – | – | – |
| >40 <= 80 | – | – | – | – |
| >80 <= 120 | – | – | – | – |
| >120 | – | – | – | – |
State 3
Shrubs/succulents state
This plant community in this state has crossed a threshold where shrubs and succulents dominate the canopy and grasses are very limited. Due to fire suppression and continuous herbivory a change in the hydrologic cycle has occurred. This community is very similar to 2.1 except for the presence of whitethorn and other nitrogen fixing shrubs.
Community 3.1
Shrubs/succulents

Figure 20. Community 3.1; Mariola dominated community; Walnut
This community phase combines a mix of shrubs, succulents and some warm season grasses. It is no longer within the reference state as the site has crossed a threshold into a degraded state. Because the site has crossed a threshold, intensive management (i.e., accelerating practices) are required to restore the system. Foliar cover is between 30 and 70 percent, basal cover is between 5 and 20 percent, and bare ground is around 5 to 15 percent. Warm season grasses make up about 10 percent foliar cover; shrubs, 30 percent; and succulents, 8 percent. The average surface soil stability rating is 4.0 under canopy and 3.5 in the interspaces. Annual production averages around 400 lbs/ac, but can span between 200 and 600 lbs/ac, depending on the percentage of rock outcrop, cracks and fissures in the bedrock, soil depth and annual weather patterns. This community exists due to past management and disturbance, primarily fire suppression coupled with grazing management that decreases grass competition. After many years of slow retrogression a trigger event such as a severe drought could cause this site to cross a threshold where ecological processes and soil properties keep it in a degraded state. This state is different than state two due to the scarcity or absence of nitrogen fixing shrubs. With fire suppression, shrubs gain a competitive advantage due to deeper root systems, which take advantage of moisture stored in cracks and fissures in the bedrock, while grasses struggle with the slow decline of soil organic matter and the decrease of plant available water. Also, due to the decrease in soil organic matter, aggregate stability diminishes leading to a decrease in infiltration and an increase in runoff. Livestock may contribute to the degradation of this site as they can lessen plant vigor and soil organic matter through continuous grazing and over-stocking. As grass vigor decreases, shrubs gain a competitive advantage. This site suffers from low labile carbon and soil organic matter, ultimately slowing the nutrient cycle and reducing plant available water. Over time, without a change in management, it is possible for this plant community to degrade further.
Figure 21. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 23. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrub/Vine | 110 | 220 | 330 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 80 | 160 | 240 |
| Forb | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Total | 200 | 400 | 600 |
Table 24. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 1% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 35-45% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 8-12% |
| Forb foliar cover | 1-5% |
| Non-vascular plants | 1% |
| Biological crusts | 2-6% |
| Litter | 25-35% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 34-45% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 10-20% |
| Bedrock | 10-20% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 4-12% |
Table 25. Canopy structure (% cover)
| Height Above Ground (ft) | Tree | Shrub/Vine | Grass/ Grasslike |
Forb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | – | 3-7% | 6-10% | 1-3% |
| >0.5 <= 1 | – | 7-11% | 1-3% | 1-2% |
| >1 <= 2 | – | 9-13% | – | – |
| >2 <= 4.5 | – | 7-11% | – | – |
| >4.5 <= 13 | – | 2-6% | – | – |
| >13 <= 40 | – | – | – | – |
| >40 <= 80 | – | – | – | – |
| >80 <= 120 | – | – | – | – |
| >120 | – | – | – | – |
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
This transition moves the site across a threshold to state two. Slow variables: Continued encroachment by whitethorn acacia, and catclaw mimosa, coupled with the loss of the herbaceous plant community. Both chemical and hydrological shifts occur as the C:N decreases creating an increase in the nitrogen turnover rate and creating an on-going competitive advantage for nitrogen fixing shrubs. Trigger event: A severe drought, causing a loss of organic carbon. Threshold: A hydrologic function/soil chemistry threshold is crossed.
Transition T1B
State 1 to 3
This transition moves the site across a threshold to state three. Slow variables: A continued competitive advantage and increase of shrubs and succulents, coupled with the loss of the herbaceous plant community. A hydrological shift occurs as shrubs and succulents out-compete herbaceous plants for water resources. Trigger event: A severe drought, causing a loss of organic carbon. Threshold: A hydrologic function threshold is crossed.
Restoration pathway R2A
State 2 to 1
An increase in the competitive advantage of non-nitrogen fixing species through physical, chemical, and biological management practices. Various facilitating and management practices can be used to restore this ecological site back to reference. Chemical, mechanical, and biological practices can all be used to suppress whitethorn and other leguminous thorny plants in the plant community. Also, range seeding, winter feeding, browsing, and high intensity-short duration livestock grazing can help bring grass seed and organic matter back into the system and start restoring soil carbon and microbial levels. Eventually, prescribed burning will also help reduce shrub competition and improve grass vigor, once fuel loads can carry fire. Monitoring foliar cover by species will help inform the land manager if plant composition is responding to management.
Restoration pathway R3A
State 3 to 1
An increase in the competitive advantage of herbaceous species through prescribed burning and grazing management practices. Various facilitating and management practices can be used to restore this ecological site back to reference. Prescribed burning is important to help reduce shrub competition for nutrients and water resources. Chemical, mechanical, and biological practices can also be used to suppress shrub competition. Also, range seeding, winter feeding, browsing, and high intensity-short duration livestock grazing can help bring grass seed and organic matter back into the system and start restoring soil carbon and microbial levels. Monitoring foliar cover by species will help inform the land manager if plant composition is responding to management.
Additional community tables
Table 26. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Warm Season Tallgrasses | 20–70 | ||||
| cane bluestem | BOBA3 | Bothriochloa barbinodis | 9–45 | 1–3 | ||
| silver beardgrass | BOLA2 | Bothriochloa laguroides | 9–27 | 1–2 | ||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | Warm Season Midgrasses | 350–450 | ||||
| curlyleaf muhly | MUSE | Muhlenbergia setifolia | 90–198 | 2–18 | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 63–99 | 4–6 | ||
| purple threeawn | ARPU9 | Aristida purpurea | 54–72 | 3–5 | ||
| slim tridens | TRMU | Tridens muticus | 27–63 | 2–4 | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 9–45 | 1–5 | ||
| tanglehead | HETER6 | Heteropogon | 0–36 | 1–4 | ||
| green sprangletop | LEDU | Leptochloa dubia | 9–27 | 1–2 | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 5–14 | 1 | ||
| bullgrass | MUEM | Muhlenbergia emersleyi | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 3 | Warm Season Shortgrasses | 200–250 | ||||
| black grama | BOER4 | Bouteloua eriopoda | 18–108 | 1–9 | ||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 45–81 | 4–8 | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 9–45 | 1–4 | ||
| hairy woollygrass | ERPI5 | Erioneuron pilosum | 5–32 | 1–2 | ||
| Hall's panicgrass | PAHA | Panicum hallii | 5–32 | 1–2 | ||
| red grama | BOTR2 | Bouteloua trifida | 0–18 | 0–2 | ||
| sand muhly | MUAR2 | Muhlenbergia arenicola | 0–18 | 0–2 | ||
| common wolfstail | LYPH | Lycurus phleoides | 5–14 | 1 | ||
| streambed bristlegrass | SELE6 | Setaria leucopila | 5–14 | 1 | ||
| tobosagrass | PLMU3 | Pleuraphis mutica | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| low woollygrass | DAPU7 | Dasyochloa pulchella | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Carolina crabgrass | DIPU9 | Digitaria pubiflora | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nineawn pappusgrass | ENDE | Enneapogon desvauxii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 4 | Cool Season Tallgrasses | 0–36 | ||||
| New Mexico feathergrass | HENE5 | Hesperostipa neomexicana | 0–36 | 0–2 | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 5 | Perennial Forbs | 20–70 | ||||
| threadleaf phlox | PHME2 | Phlox mesoleuca | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| croton | CROTO | Croton | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| hawkweed buckwheat | ERHI3 | Eriogonum hieraciifolium | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| Davis Mountain mock vervain | GLBIC | Glandularia bipinnatifida var. ciliata | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| hairy false goldenaster | HEVI4 | Heterotheca villosa | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Fendler's bladderpod | LEFE | Lesquerella fendleri | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Lewis flax | LILE3 | Linum lewisii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| plains blackfoot | MELE2 | Melampodium leucanthum | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| James' nailwort | PAJA | Paronychia jamesii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| ivyleaf groundcherry | PHHE4 | Physalis hederifolia | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| cryptantha | CRYPT | Cryptantha | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| silver prairie clover | DABIA | Dalea bicolor var. argyrea | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Wright's prairie clover | DAWR | Dalea wrightii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| spreading fleabane | ERDI4 | Erigeron divergens | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nodding onion | ALCE2 | Allium cernuum | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Hartweg's sundrops | CAHA14 | Calylophus hartwegii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| wholeleaf Indian paintbrush | CAIN14 | Castilleja integra | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| twinleaf senna | SEBA3 | Senna bauhinioides | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Douglas' ragwort | SEFLD | Senecio flaccidus var. douglasii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| resurrection plant | SEPI | Selaginella pilifera | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| early shaggytuft | STBA | Stenandrium barbatum | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| stemmy four-nerve daisy | TESC2 | Tetraneuris scaposa | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 6 | Annual Forbs | 0–1 | ||||
| 12 | Fern | 5–14 | ||||
| Cochise scaly cloakfern | ASCO42 | Astrolepis cochisensis | 5–14 | 0–1 | ||
| star cloak fern | NOST | Notholaena standleyi | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 7 | Shrubs | 75–125 | ||||
| Pinchot's juniper | JUPI | Juniperus pinchotii | 9–45 | 2–6 | ||
| pungent oak | QUPU | Quercus pungens | 0–36 | 0–6 | ||
| mariola | PAIN2 | Parthenium incanum | 5–32 | 1–5 | ||
| resinbush | VIST | Viguiera stenoloba | 9–27 | 1–3 | ||
| littleleaf ratany | KRER | Krameria erecta | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| algerita | MATR3 | Mahonia trifoliolata | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| Wright's beebrush | ALWR | Aloysia wrightii | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| javelina bush | COER5 | Condalia ericoides | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| featherplume | DAFO | Dalea formosa | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| longleaf jointfir | EPTR | Ephedra trifurca | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| desert myrtlecroton | BEOB | Bernardia obovata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| creosote bush | LATR2 | Larrea tridentata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| catclaw acacia | ACGR | Acacia greggii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| roundflower catclaw | ACRO | Acacia roemeriana | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| lotebush | ZIOB | Ziziphus obtusifolia | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| prairie sumac | RHLA3 | Rhus lanceolata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| skunkbush sumac | RHTRT | Rhus trilobata var. trilobata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| evergreen sumac | RHVI3 | Rhus virens | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 8 | Half Shrubs | 15–25 | ||||
| dyssodia | DYSSO | Dyssodia | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| rough menodora | MESC | Menodora scabra | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| fiveneedle pricklyleaf | THPEP | Thymophylla pentachaeta var. pentachaeta | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| hairy crinklemat | TIHI | Tiquilia hispidissima | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| desert zinnia | ZIAC | Zinnia acerosa | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| damianita | CHME3 | Chrysactinia mexicana | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 9 | Cactus | 15–25 | ||||
| purple pricklypear | OPMAM | Opuntia macrocentra var. macrocentra | 14–23 | 1–3 | ||
| tulip pricklypear | OPPH | Opuntia phaeacantha | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| tree cholla | CYIMI | Cylindropuntia imbricata var. imbricata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| pitaya | ECEN2 | Echinocereus enneacanthus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| devilshead | ECHO | Echinocactus horizonthalonius | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| rainbow cactus | ECPE | Echinocereus pectinatus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| horse crippler | ECTE | Echinocactus texensis | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| kingcup cactus | ECTR | Echinocereus triglochidiatus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nylon hedgehog cactus | ECVI2 | Echinocereus viridiflorus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| ocotillo | FOSP2 | Fouquieria splendens | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 10 | Yucca | 0–1 | ||||
| soaptree yucca | YUEL | Yucca elata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Torrey's yucca | YUTO | Yucca torreyi | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 11 | Yucca-Like Plants | 40–50 | ||||
| green sotol | DALE2 | Dasylirion leiophyllum | 18–36 | 3–9 | ||
| lechuguilla | AGLE | Agave lechuguilla | 5–14 | 3–5 | ||
| Texas sacahuista | NOTE | Nolina texana | 5–14 | 1–3 | ||
|
Tree
|
||||||
| 13 | Tree | 0–1 | ||||
| Texas madrone | ARXA80 | Arbutus xalapensis | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
Table 27. Community 1.2 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Warm Season Tallgrasses | 20–40 | ||||
| cane bluestem | BOBA3 | Bothriochloa barbinodis | 8–24 | 1–2 | ||
| silver beardgrass | BOLA2 | Bothriochloa laguroides | 8–24 | 1–2 | ||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | Warm Season Midgrasses | 145–290 | ||||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 64–96 | 3–5 | ||
| curlyleaf muhly | MUSE | Muhlenbergia setifolia | 16–96 | 1 | ||
| purple threeawn | ARPU9 | Aristida purpurea | 32–48 | 1–3 | ||
| slim tridens | TRMU | Tridens muticus | 24–40 | 1–3 | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 4–28 | 1–2 | ||
| tanglehead | HETER6 | Heteropogon | 0–16 | 0–2 | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 4–12 | 1 | ||
| bullgrass | MUEM | Muhlenbergia emersleyi | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 3 | Warm Season Shortgrasses | 100–200 | ||||
| black grama | BOER4 | Bouteloua eriopoda | 16–96 | 1–5 | ||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 24–56 | 1–3 | ||
| hairy woollygrass | ERPI5 | Erioneuron pilosum | 8–56 | 1–3 | ||
| Hall's panicgrass | PAHA | Panicum hallii | 8–40 | 1–2 | ||
| common wolfstail | LYPH | Lycurus phleoides | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| tobosagrass | PLMU3 | Pleuraphis mutica | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nineawn pappusgrass | ENDE | Enneapogon desvauxii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 4 | Cool-season Tallgrasses | 0–16 | ||||
| New Mexico feathergrass | HENE5 | Hesperostipa neomexicana | 0–16 | 0–2 | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 5 | Perennial Forbs | 20–40 | ||||
| threadleaf phlox | PHME2 | Phlox mesoleuca | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| Davis Mountain mock vervain | GLBIC | Glandularia bipinnatifida var. ciliata | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| hairy false goldenaster | HEVI4 | Heterotheca villosa | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| Hartweg's sundrops | CAHA14 | Calylophus hartwegii | 1 | 1–2 | ||
| wholeleaf Indian paintbrush | CAIN14 | Castilleja integra | 1 | 1–2 | ||
| croton | CROTO | Croton | 1 | 1–2 | ||
| Havard's buckwheat | ERHA | Eriogonum havardii | 1 | 1–2 | ||
| hawkweed buckwheat | ERHI3 | Eriogonum hieraciifolium | 1 | 1–2 | ||
| early shaggytuft | STBA | Stenandrium barbatum | 1 | 1–2 | ||
| nodding onion | ALCE2 | Allium cernuum | 1 | 1–2 | ||
| twinleaf senna | SEBA3 | Senna bauhinioides | 1 | 1 | ||
| spreading fleabane | ERDI4 | Erigeron divergens | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| James' nailwort | PAJA | Paronychia jamesii | 1 | 1 | ||
| ivyleaf groundcherry | PHHE4 | Physalis hederifolia | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 6 | Annual Forbs | 1 | ||||
| 12 | Fern | 4–12 | ||||
| Cochise scaly cloakfern | ASCO42 | Astrolepis cochisensis | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| star cloak fern | NOST | Notholaena standleyi | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 7 | Shrubs | 135–270 | ||||
| mariola | PAIN2 | Parthenium incanum | 40–120 | 2–8 | ||
| Pinchot's juniper | JUPI | Juniperus pinchotii | 0–96 | 1–9 | ||
| pungent oak | QUPU | Quercus pungens | 0–48 | 0–4 | ||
| featherplume | DAFO | Dalea formosa | 1–48 | 1–3 | ||
| skunkbush sumac | RHTRT | Rhus trilobata var. trilobata | 0–32 | 0–2 | ||
| resinbush | VIST | Viguiera stenoloba | 8–24 | 1–3 | ||
| Wright's beebrush | ALWR | Aloysia wrightii | 1–16 | 1–3 | ||
| roundflower catclaw | ACRO | Acacia roemeriana | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| littleleaf ratany | KRER | Krameria erecta | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| algerita | MATR3 | Mahonia trifoliolata | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| catclaw mimosa | MIACB | Mimosa aculeaticarpa var. biuncifera | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| javelina bush | COER5 | Condalia ericoides | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| prairie sumac | RHLA3 | Rhus lanceolata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| desert myrtlecroton | BEOB | Bernardia obovata | 1 | 1 | ||
| longleaf jointfir | EPTR | Ephedra trifurca | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| whitethorn acacia | ACCO2 | Acacia constricta | 1 | 1 | ||
| catclaw acacia | ACGR | Acacia greggii | 1 | 1 | ||
| 8 | Half-Shrubs | 15–35 | ||||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 1–32 | 2–4 | ||
| desert zinnia | ZIAC | Zinnia acerosa | 1–31 | 1 | ||
| dyssodia | DYSSO | Dyssodia | 4–12 | 1 | ||
| hairy crinklemat | TIHI | Tiquilia hispidissima | 1 | 1 | ||
| damianita | CHME3 | Chrysactinia mexicana | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 9 | Cactus | 20–40 | ||||
| purple pricklypear | OPMAM | Opuntia macrocentra var. macrocentra | 8–24 | 2–4 | ||
| ocotillo | FOSP2 | Fouquieria splendens | 0–16 | 0–2 | ||
| tulip pricklypear | OPPH | Opuntia phaeacantha | 4–12 | 1–3 | ||
| tree cholla | CYIMI | Cylindropuntia imbricata var. imbricata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| rainbow cactus | ECPE | Echinocereus pectinatus | 1 | 1 | ||
| horse crippler | ECTE | Echinocactus texensis | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| kingcup cactus | ECTR | Echinocereus triglochidiatus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nylon hedgehog cactus | ECVI2 | Echinocereus viridiflorus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 10 | Yucca | 5–12 | ||||
| Torrey's yucca | YUTO | Yucca torreyi | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| soaptree yucca | YUEL | Yucca elata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 11 | Yucca-like plants | 30–60 | ||||
| lechuguilla | AGLE | Agave lechuguilla | 8–24 | 1–7 | ||
| green sotol | DALE2 | Dasylirion leiophyllum | 8–24 | 2–6 | ||
| Texas sacahuista | NOTE | Nolina texana | 8–24 | 1–5 | ||
Table 28. Community 1.3 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Warm Season Tallgrasses | 24–48 | ||||
| cane bluestem | BOBA3 | Bothriochloa barbinodis | 9–27 | 1–3 | ||
| silver beardgrass | BOLA2 | Bothriochloa laguroides | 9–27 | 1–3 | ||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | Warm Season Midgrasses | 270–540 | ||||
| curlyleaf muhly | MUSE | Muhlenbergia setifolia | 45–261 | 4–24 | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 81–117 | 6–8 | ||
| purple threeawn | ARPU9 | Aristida purpurea | 45–81 | 1–5 | ||
| slim tridens | TRMU | Tridens muticus | 32–48 | 2–4 | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 9–45 | 1–3 | ||
| tanglehead | HETER6 | Heteropogon | 0–36 | 1–4 | ||
| green sprangletop | LEDU | Leptochloa dubia | 8–24 | 1–2 | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 5–14 | 1 | ||
| 3 | Warm Season Shortgrasses | 150–300 | ||||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 54–108 | 5–9 | ||
| black grama | BOER4 | Bouteloua eriopoda | 27–81 | 2–10 | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 9–27 | 1–3 | ||
| hairy woollygrass | ERPI5 | Erioneuron pilosum | 9–27 | 1–3 | ||
| Hall's panicgrass | PAHA | Panicum hallii | 9–27 | 1–3 | ||
| red grama | BOTR2 | Bouteloua trifida | 0–18 | 0–1 | ||
| sand muhly | MUAR2 | Muhlenbergia arenicola | 0–18 | 0–1 | ||
| streambed bristlegrass | SELE6 | Setaria leucopila | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| common wolfstail | LYPH | Lycurus phleoides | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| low woollygrass | DAPU7 | Dasyochloa pulchella | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Carolina crabgrass | DIPU9 | Digitaria pubiflora | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nineawn pappusgrass | ENDE | Enneapogon desvauxii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 4 | Cool-season Tallgrasses | 0–18 | ||||
| New Mexico feathergrass | HENE5 | Hesperostipa neomexicana | 0–18 | 0–3 | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 5 | Perennial Forbs | 24–48 | ||||
| Davis Mountain mock vervain | GLBIC | Glandularia bipinnatifida var. ciliata | 9–27 | 1–3 | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| spreading fleabane | ERDI4 | Erigeron divergens | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| threadleaf phlox | PHME2 | Phlox mesoleuca | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| polygala | POLYG | Polygala | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Douglas' ragwort | SEFLD | Senecio flaccidus var. douglasii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| early shaggytuft | STBA | Stenandrium barbatum | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Havard's buckwheat | ERHA | Eriogonum havardii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| croton | CROTO | Croton | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| James' nailwort | PAJA | Paronychia jamesii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nodding onion | ALCE2 | Allium cernuum | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 6 | Annual Forbs | 2–14 | ||||
| common sunflower | HEAN3 | Helianthus annuus | 2–14 | 1–3 | ||
| 12 | Fern | 0–1 | ||||
| Cochise scaly cloakfern | ASCO42 | Astrolepis cochisensis | 0–1 | 1 | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 7 | Shrubs | 78–156 | ||||
| Pinchot's juniper | JUPI | Juniperus pinchotii | 0–54 | 0–5 | ||
| mariola | PAIN2 | Parthenium incanum | 9–45 | 1–3 | ||
| pungent oak | QUPU | Quercus pungens | 0–27 | 0–3 | ||
| featherplume | DAFO | Dalea formosa | 9–27 | 1–2 | ||
| resinbush | VIST | Viguiera stenoloba | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| javelina bush | COER5 | Condalia ericoides | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| lotebush | ZIOB | Ziziphus obtusifolia | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| skunkbush sumac | RHTRT | Rhus trilobata var. trilobata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| longleaf jointfir | EPTR | Ephedra trifurca | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| littleleaf ratany | KRER | Krameria erecta | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| algerita | MATR3 | Mahonia trifoliolata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| catclaw mimosa | MIACB | Mimosa aculeaticarpa var. biuncifera | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| catclaw acacia | ACGR | Acacia greggii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| roundflower catclaw | ACRO | Acacia roemeriana | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| Wright's beebrush | ALWR | Aloysia wrightii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 8 | Half-Shrubs | 18–36 | ||||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 9–27 | 1–3 | ||
| dyssodia | DYSSO | Dyssodia | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| rough menodora | MESC | Menodora scabra | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| fiveneedle pricklyleaf | THPEP | Thymophylla pentachaeta var. pentachaeta | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| hairy crinklemat | TIHI | Tiquilia hispidissima | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| desert zinnia | ZIAC | Zinnia acerosa | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 9 | Cactus | 5–14 | ||||
| purple pricklypear | OPMAM | Opuntia macrocentra var. macrocentra | 5–14 | 1–3 | ||
| tulip pricklypear | OPPH | Opuntia phaeacantha | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| tree cholla | CYIMI | Cylindropuntia imbricata var. imbricata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| devilshead | ECHO | Echinocactus horizonthalonius | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| horse crippler | ECTE | Echinocactus texensis | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| kingcup cactus | ECTR | Echinocereus triglochidiatus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nylon hedgehog cactus | ECVI2 | Echinocereus viridiflorus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| ocotillo | FOSP2 | Fouquieria splendens | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| cactus apple | OPEN3 | Opuntia engelmannii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 10 | Yucca | 5–14 | ||||
| Torrey's yucca | YUTO | Yucca torreyi | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| soaptree yucca | YUEL | Yucca elata | 0–1 | 1 | ||
| 11 | Yucca-like-plants | 5–14 | ||||
| lechuguilla | AGLE | Agave lechuguilla | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| Texas sacahuista | NOTE | Nolina texana | 5–14 | 1–2 | ||
| green sotol | DALE2 | Dasylirion leiophyllum | 0–1 | 1 | ||
Table 29. Community 1.4 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Warm Season Tallgrasses | 6–18 | ||||
| cane bluestem | BOBA3 | Bothriochloa barbinodis | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| 2 | Warm Season Midgrasses | 78–234 | ||||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 54–78 | 2–5 | ||
| curlyleaf muhly | MUSE | Muhlenbergia setifolia | 12–60 | 1–3 | ||
| slim tridens | TRMU | Tridens muticus | 18–30 | 1–2 | ||
| purple threeawn | ARPU9 | Aristida purpurea | 12–24 | 1–2 | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| 3 | Warm Season Shortgrasses | 72–216 | ||||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 42–66 | 2–5 | ||
| black grama | BOER4 | Bouteloua eriopoda | 6–54 | 1–3 | ||
| nineawn pappusgrass | ENDE | Enneapogon desvauxii | 3–21 | 1–2 | ||
| hairy woollygrass | ERPI5 | Erioneuron pilosum | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| Hall's panicgrass | PAHA | Panicum hallii | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| common wolfstail | LYPH | Lycurus phleoides | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| streambed bristlegrass | SELE6 | Setaria leucopila | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| low woollygrass | DAPU7 | Dasyochloa pulchella | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| Carolina crabgrass | DIPU9 | Digitaria pubiflora | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 4 | Cool-season Tallgrasses | 3–9 | ||||
| New Mexico feathergrass | HENE5 | Hesperostipa neomexicana | 3–9 | 1 | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 5 | Perennial Forbs | 15–45 | ||||
| croton | CROTO | Croton | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| hawkweed buckwheat | ERHI3 | Eriogonum hieraciifolium | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| Davis Mountain mock vervain | GLBIC | Glandularia bipinnatifida var. ciliata | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| James' nailwort | PAJA | Paronychia jamesii | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| threadleaf phlox | PHME2 | Phlox mesoleuca | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| polygala | POLYG | Polygala | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| resurrection plant | SEPI | Selaginella pilifera | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| spreading fleabane | ERDI4 | Erigeron divergens | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| whitemargin sandmat | CHAL11 | Chamaesyce albomarginata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 6 | Annual Forbs | 3–9 | ||||
| common sunflower | HEAN3 | Helianthus annuus | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| 12 | Fern | 3–9 | ||||
| Cochise scaly cloakfern | ASCO42 | Astrolepis cochisensis | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 7 | Shrubs | 81–243 | ||||
| mariola | PAIN2 | Parthenium incanum | 12–48 | 1–7 | ||
| Pinchot's juniper | JUPI | Juniperus pinchotii | 0–48 | 1–5 | ||
| pungent oak | QUPU | Quercus pungens | 0–36 | 0–4 | ||
| featherplume | DAFO | Dalea formosa | 6–30 | 1–3 | ||
| whitethorn acacia | ACCO2 | Acacia constricta | 6–30 | 1–3 | ||
| catclaw acacia | ACGR | Acacia greggii | 6–18 | 1–3 | ||
| catclaw mimosa | MIACB | Mimosa aculeaticarpa var. biuncifera | 6–18 | 1–3 | ||
| resinbush | VIST | Viguiera stenoloba | 6–18 | 1–3 | ||
| algerita | MATR3 | Mahonia trifoliolata | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| roundflower catclaw | ACRO | Acacia roemeriana | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| javelina bush | COER5 | Condalia ericoides | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| longleaf jointfir | EPTR | Ephedra trifurca | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| littleleaf sumac | RHMI3 | Rhus microphylla | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 8 | Half-Shrubs | 9–27 | ||||
| dyssodia | DYSSO | Dyssodia | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| rough menodora | MESC | Menodora scabra | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| fiveneedle pricklyleaf | THPEP | Thymophylla pentachaeta var. pentachaeta | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| hairy crinklemat | TIHI | Tiquilia hispidissima | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 9 | Cactus | 12–36 | ||||
| purple pricklypear | OPMAM | Opuntia macrocentra var. macrocentra | 6–18 | 2–4 | ||
| ocotillo | FOSP2 | Fouquieria splendens | 3–9 | 0–4 | ||
| tulip pricklypear | OPPH | Opuntia phaeacantha | 3–9 | 1–3 | ||
| tree cholla | CYIMI | Cylindropuntia imbricata var. imbricata | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| horse crippler | ECTE | Echinocactus texensis | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| kingcup cactus | ECTR | Echinocereus triglochidiatus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nylon hedgehog cactus | ECVI2 | Echinocereus viridiflorus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| cactus apple | OPEN3 | Opuntia engelmannii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 10 | Yucca | 3–9 | ||||
| Torrey's yucca | YUTO | Yucca torreyi | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| soaptree yucca | YUEL | Yucca elata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 11 | Yucca-like plants | 15–45 | ||||
| lechuguilla | AGLE | Agave lechuguilla | 6–30 | 1–3 | ||
| green sotol | DALE2 | Dasylirion leiophyllum | 6–18 | 1–3 | ||
| Texas sacahuista | NOTE | Nolina texana | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
Table 30. Community 1.5 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Warm Season Tallgrasses | 3–9 | ||||
| cane bluestem | BOBA3 | Bothriochloa barbinodis | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| 2 | Warm Season Midgrasses | 80–160 | ||||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 30–54 | 2–4 | ||
| slim tridens | TRMU | Tridens muticus | 24–36 | 1–2 | ||
| curlyleaf muhly | MUSE | Muhlenbergia setifolia | 6–30 | 1–2 | ||
| purple threeawn | ARPU9 | Aristida purpurea | 12–24 | 1–2 | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 0–12 | 1 | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| 3 | Warm Season Shortgrasses | 92–184 | ||||
| black grama | BOER4 | Bouteloua eriopoda | 12–72 | 1–5 | ||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 6–42 | 1–2 | ||
| low woollygrass | DAPU7 | Dasyochloa pulchella | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| hairy woollygrass | ERPI5 | Erioneuron pilosum | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| common wolfstail | LYPH | Lycurus phleoides | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| Hall's panicgrass | PAHA | Panicum hallii | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| streambed bristlegrass | SELE6 | Setaria leucopila | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| nineawn pappusgrass | ENDE | Enneapogon desvauxii | 0–12 | 0–1 | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| Carolina crabgrass | DIPU9 | Digitaria pubiflora | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 4 | Cool-season Tallgrasses | 0–12 | ||||
| New Mexico feathergrass | HENE5 | Hesperostipa neomexicana | 0–12 | 1–2 | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 5 | Perennial Forbs | 16–32 | ||||
| croton | CROTO | Croton | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| hawkweed buckwheat | ERHI3 | Eriogonum hieraciifolium | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| Davis Mountain mock vervain | GLBIC | Glandularia bipinnatifida var. ciliata | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| threadleaf phlox | PHME2 | Phlox mesoleuca | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| polygala | POLYG | Polygala | 1 | 1 | ||
| resurrection plant | SEPI | Selaginella pilifera | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| James' nailwort | PAJA | Paronychia jamesii | 1 | 1 | ||
| spreading fleabane | ERDI4 | Erigeron divergens | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| whitemargin sandmat | CHAL11 | Chamaesyce albomarginata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 6 | Annual Forbs | 3–9 | ||||
| common sunflower | HEAN3 | Helianthus annuus | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| 12 | Fern | 3–9 | ||||
| Cochise scaly cloakfern | ASCO42 | Astrolepis cochisensis | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| star cloak fern | NOST | Notholaena standleyi | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 7 | Shrubs | 108–216 | ||||
| mariola | PAIN2 | Parthenium incanum | 18–54 | 2–10 | ||
| Pinchot's juniper | JUPI | Juniperus pinchotii | 6–54 | 1–9 | ||
| pungent oak | QUPU | Quercus pungens | 0–48 | 0–8 | ||
| featherplume | DAFO | Dalea formosa | 12–24 | 1–3 | ||
| resinbush | VIST | Viguiera stenoloba | 6–18 | 1–3 | ||
| algerita | MATR3 | Mahonia trifoliolata | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| javelina bush | COER5 | Condalia ericoides | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| littleleaf ratany | KRER | Krameria erecta | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| Wright's beebrush | ALWR | Aloysia wrightii | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| desert myrtlecroton | BEOB | Bernardia obovata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| longleaf jointfir | EPTR | Ephedra trifurca | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| whitethorn acacia | ACCO2 | Acacia constricta | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| catclaw acacia | ACGR | Acacia greggii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| roundflower catclaw | ACRO | Acacia roemeriana | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| catclaw mimosa | MIACB | Mimosa aculeaticarpa var. biuncifera | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| littleleaf sumac | RHMI3 | Rhus microphylla | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 8 | Half-Shrubs | 12–24 | ||||
| dyssodia | DYSSO | Dyssodia | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| rough menodora | MESC | Menodora scabra | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| fiveneedle pricklyleaf | THPEP | Thymophylla pentachaeta var. pentachaeta | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| hairy crinklemat | TIHI | Tiquilia hispidissima | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 9 | Cactus | 32–64 | ||||
| purple pricklypear | OPMAM | Opuntia macrocentra var. macrocentra | 6–18 | 1–3 | ||
| tulip pricklypear | OPPH | Opuntia phaeacantha | 6–18 | 1–3 | ||
| ocotillo | FOSP2 | Fouquieria splendens | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| tree cholla | CYIMI | Cylindropuntia imbricata var. imbricata | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| horse crippler | ECTE | Echinocactus texensis | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| kingcup cactus | ECTR | Echinocereus triglochidiatus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nylon hedgehog cactus | ECVI2 | Echinocereus viridiflorus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| cactus apple | OPEN3 | Opuntia engelmannii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 10 | Yucca | 3–9 | ||||
| Torrey's yucca | YUTO | Yucca torreyi | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| soaptree yucca | YUEL | Yucca elata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 11 | Yucca-like plants | 36–72 | ||||
| green sotol | DALE2 | Dasylirion leiophyllum | 6–42 | 1–11 | ||
| lechuguilla | AGLE | Agave lechuguilla | 6–30 | 1–3 | ||
| Texas sacahuista | NOTE | Nolina texana | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
Table 31. Community 2.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Warm Season Midgrasses | 22–68 | ||||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 12–18 | 1–3 | ||
| purple threeawn | ARPU9 | Aristida purpurea | 6–12 | 1–2 | ||
| slim tridens | TRMU | Tridens muticus | 6–12 | 1–2 | ||
| curlyleaf muhly | MUSE | Muhlenbergia setifolia | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 0–1 | 1 | ||
| 2 | Warm Season Shortgrasses | 37–113 | ||||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 12–24 | 2–5 | ||
| black grama | BOER4 | Bouteloua eriopoda | 3–21 | 1–3 | ||
| hairy woollygrass | ERPI5 | Erioneuron pilosum | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| Hall's panicgrass | PAHA | Panicum hallii | 6–18 | 1–2 | ||
| low woollygrass | DAPU7 | Dasyochloa pulchella | 6–18 | 1 | ||
| Carolina crabgrass | DIPU9 | Digitaria pubiflora | 3–9 | 1 | ||
| red grama | BOTR2 | Bouteloua trifida | 2–5 | 1 | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 3 | Perennial Forbs | 6–18 | ||||
| scarlet beeblossom | GACO5 | Gaura coccinea | 2–5 | 1 | ||
| hawkweed buckwheat | ERHI3 | Eriogonum hieraciifolium | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 4 | Annual Forbs | 3–8 | ||||
| common sunflower | HEAN3 | Helianthus annuus | 3–8 | 1 | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 5 | Shrubs | 60–180 | ||||
| whitethorn acacia | ACCO2 | Acacia constricta | 15–75 | 4–16 | ||
| catclaw mimosa | MIACB | Mimosa aculeaticarpa var. biuncifera | 9–51 | 1–6 | ||
| mariola | PAIN2 | Parthenium incanum | 6–18 | 1–3 | ||
| Pinchot's juniper | JUPI | Juniperus pinchotii | 6–12 | 1–3 | ||
| roundflower catclaw | ACRO | Acacia roemeriana | 6–12 | 1–3 | ||
| resinbush | VIST | Viguiera stenoloba | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| javelina bush | COER5 | Condalia ericoides | 2–5 | 1–2 | ||
| featherplume | DAFO | Dalea formosa | 2–5 | 1–2 | ||
| algerita | MATR3 | Mahonia trifoliolata | 2–5 | 1 | ||
| 6 | Half-Shrubs | 0–1 | ||||
| dyssodia | DYSSO | Dyssodia | 0–1 | 1 | ||
| 7 | Cactus | 15–45 | ||||
| purple pricklypear | OPMAM | Opuntia macrocentra var. macrocentra | 6–12 | 1–2 | ||
| tulip pricklypear | OPPH | Opuntia phaeacantha | 6–12 | 1–2 | ||
| cactus apple | OPEN3 | Opuntia engelmannii | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| tree cholla | CYIMI | Cylindropuntia imbricata var. imbricata | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
| ocotillo | FOSP2 | Fouquieria splendens | 0–1 | 1 | ||
| 8 | Yucca-like plants | 7–20 | ||||
| lechuguilla | AGLE | Agave lechuguilla | 6–12 | 1–3 | ||
| green sotol | DALE2 | Dasylirion leiophyllum | 3–9 | 1–2 | ||
Table 32. Community 3.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Warm Season Midgrasses | 30–90 | ||||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 12–28 | 1–3 | ||
| purple threeawn | ARPU9 | Aristida purpurea | 8–20 | 1–2 | ||
| slim tridens | TRMU | Tridens muticus | 8–20 | 1–2 | ||
| curlyleaf muhly | MUSE | Muhlenbergia setifolia | 4–16 | 1–2 | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 2 | Warm Season Shortgrasses | 50–150 | ||||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 8–40 | 1–3 | ||
| black grama | BOER4 | Bouteloua eriopoda | 4–28 | 1–2 | ||
| hairy woollygrass | ERPI5 | Erioneuron pilosum | 4–28 | 1–2 | ||
| Hall's panicgrass | PAHA | Panicum hallii | 8–28 | 1–2 | ||
| low woollygrass | DAPU7 | Dasyochloa pulchella | 4–28 | 1 | ||
| red grama | BOTR2 | Bouteloua trifida | 0–16 | 0–1 | ||
| Carolina crabgrass | DIPU9 | Digitaria pubiflora | 4–12 | 1 | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 3 | Perennial Forbs | 8–24 | ||||
| scarlet beeblossom | GACO5 | Gaura coccinea | 2–6 | 1 | ||
| hawkweed buckwheat | ERHI3 | Eriogonum hieraciifolium | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 4 | Annual Forbs | 2–6 | ||||
| common sunflower | HEAN3 | Helianthus annuus | 2–6 | 1 | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 5 | Shrubs | 70–210 | ||||
| mariola | PAIN2 | Parthenium incanum | 20–68 | 3–13 | ||
| Pinchot's juniper | JUPI | Juniperus pinchotii | 4–60 | 1–11 | ||
| pungent oak | QUPU | Quercus pungens | 0–56 | 0–10 | ||
| featherplume | DAFO | Dalea formosa | 4–20 | 1–3 | ||
| algerita | MATR3 | Mahonia trifoliolata | 2–14 | 1–3 | ||
| javelina bush | COER5 | Condalia ericoides | 2–14 | 1–3 | ||
| resinbush | VIST | Viguiera stenoloba | 4–12 | 1–3 | ||
| Wright's beebrush | ALWR | Aloysia wrightii | 2–6 | 1–2 | ||
| desert myrtlecroton | BEOB | Bernardia obovata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| longleaf jointfir | EPTR | Ephedra trifurca | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| whitethorn acacia | ACCO2 | Acacia constricta | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| roundflower catclaw | ACRO | Acacia roemeriana | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| littleleaf sumac | RHMI3 | Rhus microphylla | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 6 | Half-Shrubs | 10–30 | ||||
| dyssodia | DYSSO | Dyssodia | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| rough menodora | MESC | Menodora scabra | 2–6 | 1 | ||
| fiveneedle pricklyleaf | THPEP | Thymophylla pentachaeta var. pentachaeta | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| hairy crinklemat | TIHI | Tiquilia hispidissima | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 7 | Cactus | 12–36 | ||||
| purple pricklypear | OPMAM | Opuntia macrocentra var. macrocentra | 4–12 | 1–3 | ||
| tulip pricklypear | OPPH | Opuntia phaeacantha | 4–12 | 1–2 | ||
| ocotillo | FOSP2 | Fouquieria splendens | 2–6 | 1–2 | ||
| tree cholla | CYIMI | Cylindropuntia imbricata var. imbricata | 2–6 | 1 | ||
| horse crippler | ECTE | Echinocactus texensis | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| kingcup cactus | ECTR | Echinocereus triglochidiatus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| nylon hedgehog cactus | ECVI2 | Echinocereus viridiflorus | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| cactus apple | OPEN3 | Opuntia engelmannii | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 8 | Yucca | 2–6 | ||||
| Torrey's yucca | YUTO | Yucca torreyi | 2–6 | 1–2 | ||
| soaptree yucca | YUEL | Yucca elata | 0–1 | 0–1 | ||
| 9 | Yucca-like plants | 14–52 | ||||
| green sotol | DALE2 | Dasylirion leiophyllum | 4–28 | 1–6 | ||
| lechuguilla | AGLE | Agave lechuguilla | 4–20 | 1–3 | ||
| Texas sacahuista | NOTE | Nolina texana | 2–6 | 1–2 | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Part 1: Wildlife
The Limestone Hills ecological site lies at the northern extent of the Chihuahuan Desert and provides habitat for many different wildlife species.
Species of special interest:
These are species of special interest that have habitat needs associated with the Limestone Hills ecological site.
Guadalupe Mountains Tiger Beetle: This beetle is endemic to the Guadalupe Ridge and Mountains and is tightly associated with limestone outcroppings (SWCA Environmental Consultants, 2007). Adults feed on just about anything they can see and catch, including invertebrates that may be larger than themselves. Their vision seems acute, as any movement (even by a human at a distance) causes them to turn and face the source of the motion. Beetles, flies, caterpillars, ants, grasshopper nymphs, and spiders are just a few of the invertebrates reported as tiger beetle prey. Although most tiger beetles are wary and not easily approached, they are also preyed upon. Predators of tiger beetles include dragonflies, robber flies, other tiger beetles, birds, and small vertebrates. Mites are also known to parasitize tiger beetles ( Spomer, Hoback, Golick, Higley, 2006).
Rock Rattlesnake: The rare mottled rock rattlesnake is found only in New Mexico, Texas, and Chihuahua, Mexico. In New Mexico, the rattlesnake is limited to the southern Guadalupe Mountains and exists within all canyons throughout the Guadalupe Ridge. It is the most frequently encountered rattlesnake in CCNP and is found around exposed bedrock where it feeds on lizards, snakes, and small mammals (SWCA Environmental Consultants, 2007).
Texas Horned Lizard: Horned lizards have habitat needs that require healthy harvester ant communities. Harvester ants are the preferred food of horned lizards and when this food resource declines due to shifts to a degraded plant community, or through infrastructure development, lizard numbers will also decline ( Henke and Fair, 1998). Feeding may occur at nest entrances or on ant foraging trails and mature lizards are capable of eating 70 to 100 ants per day. Although ants comprise a majority of the diet, Texas horned lizards are opportunistic predators and will consume crickets, grasshoppers, beetles, centipedes, bees and caterpillars. The diagnostic plant community phase (1.1) is best for providing a wide range of plant and insect species needed for Texas horned lizard habitat.
Gray Vireo: The gray vireo is found in the desert Southwest. Over 80 percent of the Gray Vireo territories in New Mexico are found in 12 sites, with the largest site being found in the Guadalupe Mountains (Pierce, 2007). The Gray Vireo appears to not winter in New Mexico but move down to the Big Bend area where it is associated with various shrubs and cacti. Summer habitat in the Guadalupe’s seems to be linked to juniper and oak plant communities at the upper end of the limestone hills ecological site (above 4300 feet). During breeding season, (April-July) the Gray Vireo are insectivorous, taking grasshoppers, stinkbugs, crickets, moths, and caterpillars for food. In New Mexico, nests are primarily in Juniper trees (Pierce, 2007). Plant communities within the historic range of variability are important for the Gray Vireo to find nesting, breeding, and brood-rearing cover. The birds will find nesting cover in plant communities 1.1 and 1.2, while moving to community phase 1.3 to find food.
Peregrine Falcon: The Peregrine Falcon is a species of concern that occurs throughout the west. According to experts at the “Living Desert Zoo and Gardens State park” in Carlsbad New Mexico, the peregrine falcon has only been spotted on a rare occasion in the fall or winter.
Common hog-nosed skunk: Hog-nosed skunks are distinguished from striped skunks primarily by the pelage, with a characteristic broad white marking beginning at the top of the head and extending down the back and tail. They make their dens in rocky areas within the Limestone Hills. They are omnivorous, and they eat differently according to the season. They mainly eat insects and grubs but also eat fruit, small mammals, snakes and carrion. Because rattlesnakes react to skunk musk with an alarm reaction, it is believed that skunks may feed extensively on rattlesnakes. In search of food, this skunk that roots can turn over large areas of earth with its bare nose and front claws as it searches for food (Buie, 2003).
Mountain Lion: The mountain lion is an excellent stalk-and-ambush predator, pursuing a wide variety prey. Deer make up its primary food source, but they will also hunt species as small as insects and rodents. The mountain lion stalks through shrubs and across ledges before delivering a powerful leap onto the back of its prey with a suffocating neck bite. The mountain lion is capable of breaking the neck of its prey with a strong bite and momentum bearing the animal to the ground. Kills are generally estimated at around one large ungulate every two weeks. This period shrinks for females raising young, and may be as short as one kill every three days when cubs are nearly mature at around 15 months.
Only females are involved in parenting. Females are fiercely protective of their cubs, and have been seen to successfully fight off animals as large as black bears in their defense. Caves and other alcoves that offer protection are used as litter dens (Cougar, 2013).
The Very Shallow and Limestone Hills ecological sites provide excellent habitat for the mountain lion life cycle. The abundance of shrubs in plant community 1.2 is ideal for lions to hide and stalk prey. Mountain lions can work the edge of hill summits and position themselves above prey where they can pounce with a killing blow.
Eastern White-throated Wood Rat: This large rat is often called a packrat because of the large nest of sticks and other material that it incorporates into nests. The nocturnal rat feeds on a wide variety of plants and finds shelter around dense stands of cacti such as cholla and prickly pear. Plant communities 1.1 and 1.2 are ideal for nesting white-throated wood rats.
Other species associated with the limestone hills ecological site:
Birds:
Turkey Vulture
Mississippi Kite
Red-tailed Hawk
American Kestrel
Great Horned Owl
Spotted Towhee
Canyon Towhee
Cassin’s Sparrow
Brewer’s Sparrow
Black-throated Sparrow
White-crowned Sparrow
Dark-eyed Junco
Scaled Quail
White-winged Dove
Mourning Dove
Eurasian Collared Dove (introduced)
Lesser Nighthawk
Common Nighthawk
Black-chinned Hummingbird
Ladder-backed Woodpecker
Western Kingbird
Cliff Swallow
Barn Swallow
Verdin
Cactus Wren
Rock Wren
Northern Mockingbird
Curved-billed Thrasher
House Finch
House Sparrow
Mammals:
Mexican Ground Squirrel
Yellow-faced Pocket Gopher
Merriam’s Kangaroo Rat
Merriam’s Pocket Mouse
Western Harvest Mouse
Southern Plains Woodrat
Cactus Mouse
White-footed Mouse
White-ankled Mouse
Hispid Cotton Rat
North American Porcupine
Black-tailed Jackrabbit
Desert Cottontail
American Badger
Striped Skunk
Grey Fox
Coyote
Bobcat
Mule Deer
Barbary Sheep (introduced)
Ringtail
Reptiles:
Green Toad
Red-spotted toad
Rio-Grande Leopard Frog
Eastern Collared Lizard
Greater Earless Lizard
Round Tailed Horned Lizard
Crevice Spiny Lizard
Prairie Lizard
Common Side-blotched Lizard
Texas Banded Gecko
Chihuahuan Spotted Whiptail
Common Checkered Whiptail
Ring-necked Snake
Striped Whip Snake
Western Ground Snake
Note: This species list was composed with help from the Living Desert Zoo and Gardens State Park, Carlsbad, New Mexico.
Desert Bighorn and Barbary sheep: By 1946 the desert bighorn was extirpated from the Guadalupe Mountains. Illegal hunting and excessive competition from livestock are the major culprits. Disease from livestock played a role as well.
Currently, there is an estimated 400-770 Barbary sheep in the Guadalupe Mountains. This species fills the niche that desert bighorn once held. There has been consideration given to re-introducing the desert bighorn, but this will most likely not happen unless the population of Barbary sheep can be reduced.
Barbary sheep are native to North Africa, and were released in the Hondo Valley, Largo Canyon, and the Canadian River drainage between 1955 and 1970. Viable populations have become established in historic bighorn habitat in the Guadalupe and Sacramento Mountains. They compete with desert bighorn due to their higher rate of increase, ability to subsist on lower quality forage, and preference for habitat similar to that of bighorn. Barbary sheep are socially aggressive when they encounter bighorn and may disrupt the rut (Goldstein and Rominger, 2003).
Part II Livestock:
The Limestone Hills Ecological Site has traditionally been grazed by all kinds and classes of livestock, during all seasons of the year. In the early part of the 20th century, goats and sheep were used extensively along the Guadalupe Ridge, taking advantage of browse species. Currently, though, there are very few goat and sheep operations in the area due to many market factors. Cattle numbers are in decline due to drought and extensive wildfire from 2001-2011.
With a planned livestock grazing and browsing system, the limestone hills ecological site could be managed for sustained agriculture while maintaining the historic range of variability. Prescribed fire may be used as a management tool to hold the plant communities within the historic range of variability.
Hydrological functions
The Lechuguilla soil component is in hydrologic group “D”; as are all soils that have a depth to impenetrable layer of less than 50 cm. Runoff from this site is common, especially during heavy rainstorms, because the soil is shallow and well drained. During heavy rain, once the soil is saturated, surface sheet flow is common. The severity of sheet flow depends on the plant community and the amount of gravel armoring. As the plant community changes from the historic range of variability to the “at risk” plant community, surface sheet flow increases due to a lack of vegetation and a decrease in soil aggregate stability.
Fire can temporarily change the soil surface chemistry, making it hydrophobic for a time and causing more sediment to move off site. It is important for vegetation to re-establish and provide structure for infiltration and organic matter for water storage.
Limestone has low permeability, but plant communities depend on deep cracks and fissures to hold soil, nutrients, and organic matter. In these deep cracks, organic matter acts like a sponge, storing water and keeping plants alive through dry periods. Deep cracks within bedding plains also act as conduits, moving water to plants rooted on a limestone terrace. Sometimes springs occur where bedding plains are exposed on hill sides.
Recreational uses
The Limestone Hills Ecological Site provides limited recreational use due to its lack of drinking water. Hiking is limited to day trips and should not be attempted without adequate water and a large hat. Hunting is common on this site, especially for mule deer.
Other information
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Data was collected during the years of 2011 and 2012. For all tier one data points, ocular methods were used to collect estimates of production, ground cover, and canopy cover. The Doman-Krajina method was used for canopy cover estimates. Soil pits were dug for verification on many tier one plots. Tier two and three protocols always were verified and analyzed with soil pits. Other methods used were line-point-intercept (LPI), double-sampling (DS), canopy gap (CG), and soil stability (SS). This ecological site had a number of tier one and tier two plots, with one tier three at the diagnostic plant community. Historic data from BLM monitoring points were used as well.
Type locality
| Location 1: Eddy County, NM | |
|---|---|
| UTM zone | N |
| UTM northing | 3560227 |
| UTM easting | 546367 |
| General legal description | The tier 3 sample data was collected on BLM land along Dark Canyon Road. |
Other references
Coauthors:
Aaron Miller-MLRA 70 Project Leader, NRCS
Logan Peterson-MLRA 70 Soil Scientist, NRCS
Special Contributors:
Steve Daly-Soil/Range Conservationist, Carlsbad Field Office, BLM
Herman Garcia-Ecological Site Inventory Specialist, Southwest Region 8, NRCS
Tracy Hughes-Range Conservation Technician, Carlsbad Field Office, NRCS
Darren James-Researcher, USDA, Jornada ARS
Reviewers:
Steve Daly-Soil Conservationist, Carlsbad Field Office, BLM
Herman Garcia-Ecological Site Inventory Specialist, Southwest Region 8, NRCS
Mark Moseley-Ecological Site Inventory Specialist, Texas Region 9, NRCS
Richard Strait-State Soil Scientist, New Mexico NRCS
John Tunberg-State Rangeland Management Specialist, New Mexico NRCS
Renee West-Biologist, Carlsbad Caverns National Park
ESD Workgroup:
Lu Burger-Natural Resource Specialist, State Office, BLM
Steve Daly-Soil Conservationist, Carlsbad Field Office, BLM
Samuel Denman-Cultural Resource Specialist, Carlsbad Caverns National Park
Garth Grizzle, District Conservationist, Area Range Conservationist, NRCS, retired
Charles Hibner-MLRA 70 SS Leader, NRCS, retired
Tracy Hughes-Range Conservation Technician, Carlsbad, NRCS
Laurie Kincaid-Rancher, Carlsbad
Michael McGee- Hydrologist, Roswell Field Office, BLM
Aaron Miller-MLRA 70 Project Leader, NRCS
Susan Norman-GIS Specialist, Carlsbad Caverns National Park
Logan Peterson-MLRA 70 Soil Scientist, NRCS
Mark Sando-Rangeland Management Specialist, Guadalupe District, USFS
Kent Schwartzkopf-Chief, Stewardship and Science Div., Carlsbad Caverns National Park
Renee West-Biologist, Carlsbad Caverns National Park
Pete Biggam-Soils Program Manager, National Park Service, Lakewood Colorado
References:
Ahlstrand, G., 1981. Ecology of fire in the Guadalupe Mountains and adjacent Chihuahuan Desert. Carlsbad(New Mexico): Carlsbad Caverns and Guadalupe Mountains National Park.
Bestelmeyer, Moseley, Shaver, Sanchez, Briske, and Fernandez-Gimenez, 2010. Practical Guidance for Developing State-and-Transition Models. Rangelands, p. 26.
Buie, L., 2003. Hog-nosed skunk. [Online]
Available at: http://itech.pensacolastate.edu/sctag/hn_skunk/index.htm
[Accessed 26 10 2012].
Burger, P., 2007. Walking Guide to the Geology of Carlsbad Cavern. Carlsbad, NM: Carlsbad Caverns and Guadalupe Mountains Association.
Burkett, B. a. T., Version 1.1. A Field Guide to Pedoderm and Pattern Classes, Las Cruces, New Mexico: USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range.
Cleland, D. T. et al., 2007. Ecological Subregions: Sections and Subsections of the Conterminiuos United States.. s.l.:United States Forest Service.
Cougar. (2013, September 8). In Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved 21:37, September 19, 2013, from http://http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Cougar&oldid=571991990
Duniway, Bestelmeyer, Tugel, 2010. Soil Processes and Properties That Distinguish Ecological Sites and States. Rangelands, pp. 9-15.
Gebow, B. S., 2001. Search, Compile, and Analyze Fire Literature and Research Associated with Chihuahuan Desert Uplands, Tuscon: The University of Arizona.
Goldstein and Rominger, 2003. Plan for the Recovery of Desert Bighorn Sheep in New Mexico, Santa Fe: New MExico Department of Game and Fish.
Henke and Fair, 1998. Management of Texas Horned Lizards, Kingsville, Tx.: Caesar Kleberg WIldlife Research Institute.
Herrick, et al., 2001. Soil aggregate stability kit for field-based soil quality and rangeland health evalutations.. s.l.:s.n.
Kayser, D. W., 2010. Prehistory: SHort and Seet. "Different peoples over a long period of time vistied, used the abundant resoruces or lived here at CASVE.", s.l.: s.n.
Kelley, V., 1971. Geology of the Pecos Country, Southeastern New Mexico. s.l.:New Mexico bureau of Mines and Mineral Resources.
Keys to Soil Taxonomy; United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation District; Eleventh Edition; 2010
New Mexico Game and Fish, n.d. Wildlife Notes-Ringtail, s.l.: New Mexico Game and Fish.
Pellant, Pyke, Shaver, Herrick, 2005. Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health. Version 4 ed. Denver(CO.): United States Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Managment, National science and Technology Center, Division of Science Integration.
Pierce, L. J., 2007. Gray Vireo (Vireo vicinior) Recovery Plan, Santa Fe, NM: New Mexico Department of Game and Fish.
Schoeneberger, P.J., and Wysocki, D.A. 2012. Geomorphic Description System, Version 4.2. Natural Resources Conservation Service, National Soil Survey Center, Lincoln, NE.
Spomer, Hoback, Golick, Higley, 2006. Biology, Lifecycle, and Behavior. [Online]
Available at: http://drshigley.com/lgh/netigers/index.htm
[Accessed 26 10 2012].
SWCA Environmental Consultants, 2007. Carlsbad Caverns National Park, Environmental Assessment, s.l.: U.S. Department of Interior.
United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006. Land Resource Regions and Major Land Resource Areas of the United States, the caribbean, and the Pacific Basin. s.l.:s.n.
Contributors
Scott Woodall
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | |
| Date | |
| Approved by | |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
-
Presence of water flow patterns:
-
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
-
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
-
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
-
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
-
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
-
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
-
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
-
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
-
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
-
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Sub-dominant:
Other:
Additional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
-
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
-
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
-
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
-
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.