Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R044BP807MT
Saline-Sodic Grassland
Last updated: 3/08/2024
Accessed: 03/14/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
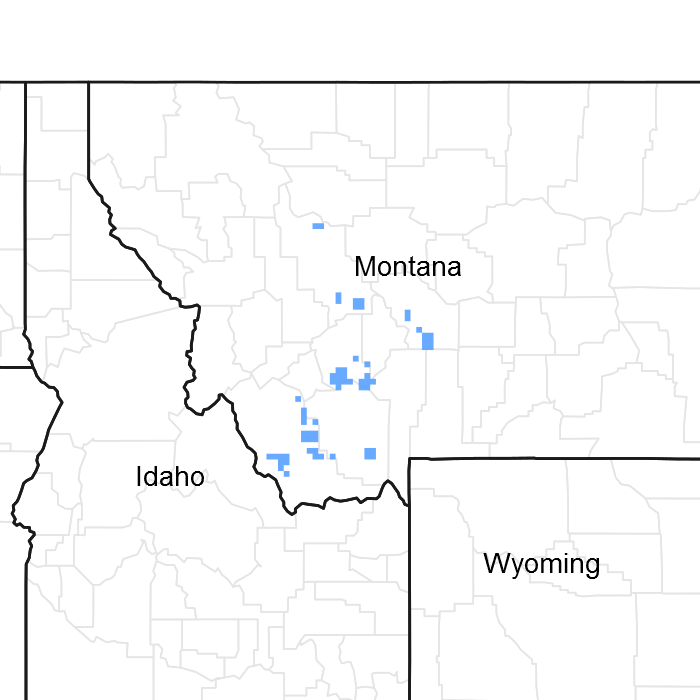
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 044B–Central Rocky Mountain Valleys
44B Central Rocky Mountain Valleys
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 44B, Central Rocky Mountain Valleys, is nearly 3.7 million acres of Southwest Montana. This MLRA borders 2 MLRAs: 43B Central Rocky Mountains and Foothills, and MLRA 46 Northern and Central Rocky Mountain Foothills.
The major watersheds of this MLRA are the Missouri and Yellowstone Rivers along with their associated headwaters such as the Beaverhead, Big Hole, Jefferson, Ruby, Madison, Gallatin, and Shields Rivers. Limited portions of the MLRA are west of the Continental Divide along the Clark Fork River. These waters allow for extensive irrigation for crop production in an area that would generally be only compatible with rangeland and grazing. The Missouri River and its headwaters are contained behind several reservoirs used for irrigation water, hydroelectric power, and municipal water.
The primary land use of this MLRA is production agriculture (grazing, small grain production, and hay) with limited mining. Urban Development is also high.
MRLA 44B consists of 7 Climate based Land Resource Units (LRUs). Annual precipitation ranges from a low of 9” to a high near 24”. The driest areas tend to be in the valley bottoms of southwest Montana in the rain shadow of the mountains. The wettest areas tend to be near the edges of the MLRA where it borders with MLRA 43B. Frost Free periods also vary greatly with from less than 30 days in the Big Hole Valley to approximately 110 days in the warm valleys along the Yellowstone River and Missouri River Headwaters.
MLRA 44B’s plant communities are highly variable however are dominated by a cool season grass and shrub steppe community on the rangeland and a mixed coniferous forest in the mountains. Warm season grasses occupy an extremely limited extent in this MLRA. Most subspecies of Big Sagebrush are present, to some extent, across the MLRA.
Ecological site concept
44B Central Rocky Mountain Valleys
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 44B, Central Rocky Mountain Valleys, is nearly 3.7 million acres of Southwest Montana. This MLRA borders 2 MLRAs: 43B Central Rocky Mountains and Foothills, and MLRA 46 Northern and Central Rocky Mountain Foothills.
The major watersheds of this MLRA are the Missouri and Yellowstone Rivers along with their associated headwaters such as the Beaverhead, Big Hole, Jefferson, Ruby, Madison, Gallatin, and Shields Rivers. Limited portions of the MLRA are west of the Continental Divide along the Clark Fork River. These waters allow for extensive irrigation for crop production in an area that would generally be only compatible with rangeland and grazing. The Missouri River and its headwaters are contained behind several reservoirs used for irrigation water, hydroelectric power, and municipal water.
The primary land use of this MLRA is production agriculture (grazing, small grain production, and hay) with limited mining. Urban Development is also high.
MRLA 44B consists of 7 Climate based Land Resource Units (LRUs). Annual precipitation ranges from a low of 9” to a high near 24”. The driest areas tend to be in the valley bottoms of southwest Montana in the rain shadow of the mountains. The wettest areas tend to be near the edges of the MLRA where it borders with MLRA 43B. Frost Free periods also vary greatly with from less than 30 days in the Big Hole Valley to approximately 110 days in the warm valleys along the Yellowstone River and Missouri River Headwaters.
MLRA 44B’s plant communities are highly variable however are dominated by a cool season grass and shrub steppe community on the rangeland and a mixed coniferous forest in the mountains. Warm season grasses occupy an extremely limited extent in this MLRA. Most subspecies of Big Sagebrush are present, to some extent, across the MLRA.
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Pseudoroegneria spicata |
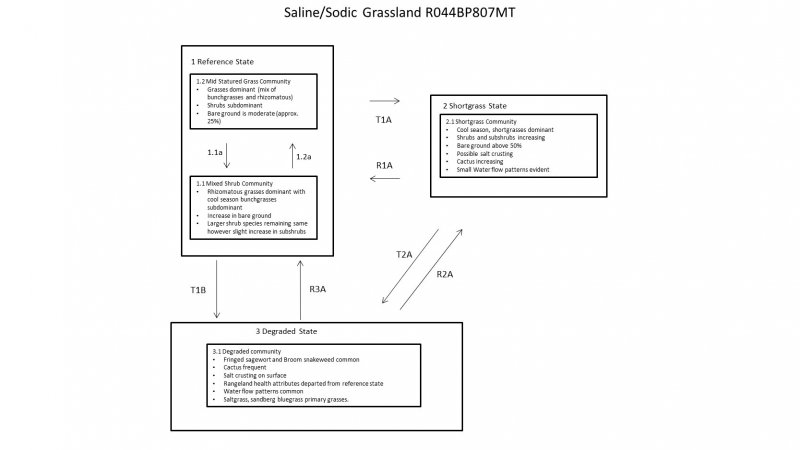
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.