
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R046XC507MT
Shallow to Gravel (SwGr) RRU 46-C 13-19 PZ
Last updated: 7/19/2023
Accessed: 12/22/2024
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
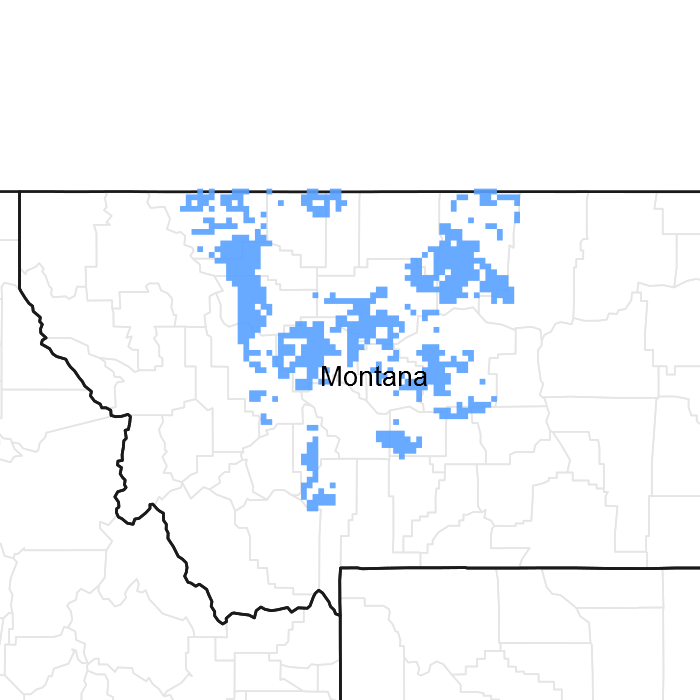
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
Associated sites
| R046XC508MT |
Silty (Si) RRU 46-C 13-19 PZ |
|---|---|
| R046XC514MT |
Gravelly (Gr) RRU 46-C 13-19 PZ |
| R046XC516MT |
Silty Steep (SiStp) RRU 46-C 13-19 PZ |
Similar sites
| R046XC508MT |
Silty (Si) RRU 46-C 13-19 PZ The Silty site differs mainly by being over 20 inches deep to any root limiting material, including gravels. |
|---|---|
| R046XC514MT |
Gravelly (Gr) RRU 46-C 13-19 PZ The Gravel site will be very droughty, having a water holding capacity of less than 2 inches. It is very gravelly to within 10 inches of the surface. |
| R046XC598MT |
Shallow Clay (SwC) RRU 46-C 13-19 PZ The Shallow Clay site differs by being clayey texture and underlain by shales instead of gravels. |
| R046XC506MT |
Shallow (Sw) RRU 46-C 13-19 PZ The Shallow site is over hard rock or semi-consolidated beds, not gravels. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Pseudoroegneria spicata |
Physiographic features
This ecological site most often occurs on level, nearly level, and moderately steep alluvial fans, knolls, stream terraces, and terrace escarpments. Slopes range from 0–15%, but can occasionally occur on slopes greater than 15%. It also occurs on nearly level valley bottoms not subject to a water table or overflow events.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Stream terrace
(2) Knoll (3) Outwash plain |
|---|---|
| Flooding frequency | None to rare |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Slope | 0 – 45% |
| Water table depth | 152 cm |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
See Climatic Data Sheet for more details (Section II of the Field Office Technical Guide) or reference the following climatic web site: http://www.wrcc.sage.dri.edu/ .
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (average) | |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (average) | |
| Precipitation total (average) | 483 mm |
Influencing water features
No influencing water features.
Soil features
These soils are moderately deep to very deep. The soils develop on gravelly alluvium of mixed origin. Surface textures varies between silt loam, loam, sandy loam, fine sandy loam, and very fine sandy loam. Depth to sand and gravel is typically 10 to 20 inches. Few roots penetrate beyond a depth of 20 inches. The upper 10–20 inches of the soil will typically have at least 20 to 35% less gravel than the lower part of the soil profile. The Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) Equivalent is 0–15% in the upper part, generally above the gravels. There can be up to 30% CaCO3 equivalent in a "transition" layer that is immediately above the gravel layer.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Surface texture |
(1) Gravelly silt loam (2) Loam (3) Sandy loam |
|---|---|
| Drainage class | Well drained to somewhat excessively drained |
| Permeability class | Moderate |
| Soil depth | 0 – 51 cm |
| Available water capacity (0-101.6cm) |
5.08 – 10.16 cm |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-101.6cm) |
0 – 30% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-101.6cm) |
0 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-101.6cm) |
0 – 5 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-101.6cm) |
6.6 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
0 – 35% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
0 – 15% |
Ecological dynamics
This site developed under Northern Rocky Mountain foothills climatic conditions, which included the natural influence of large herbivores and occasional fire. The plant community upon which interpretations are primarily based is the Historic Climax Plant Community (HCPC). This community is described as a reference to understand the original potential of this site, and is not always considered to be the management goal for every acre of rangeland. The following descriptions should enable the landowner or manager to better understand which plant communities occupy their land, and assist with setting goals for vegetation management. It can also be useful to understand the environmental and economic values of each plant community.
This site is considered moderately resilient to disturbance as it has only moderate soil limitations for plant growth. Changes may occur to the Historic Climax Plant Community due to management actions and/or climatic conditions. Under continued adverse impacts, a moderate decline in vegetative vigor and composition will occur. Under favorable vegetative management treatments, this site can more readily return to the Historic Climax Plant Community (HCPC).
Continual adverse impacts to the site over a period of years results in a departure from the HCPC, with a decrease of the taller, more palatable species such as bluebunch wheatgrass and little bluestem. These plants will be replaced by Idaho fescue, needleandthread, Western/thickspike wheatgrass, threadleaf sedge, prairie junegrass, and non-palatable forbs. Continued deterioration results in increased amounts of green and fringed sagewort, red threeawn, and plains pricklypear.
Plants that are not a part of the climax community that are most likely to invade are Japanese brome, cheatgrass, broom snakeweed, and thistles. Noxious weeds that are likely to invade this site include spotted knapweed, leafy spurge, dalmation toadflax, and sulphur cinquefoil.
State and transition model
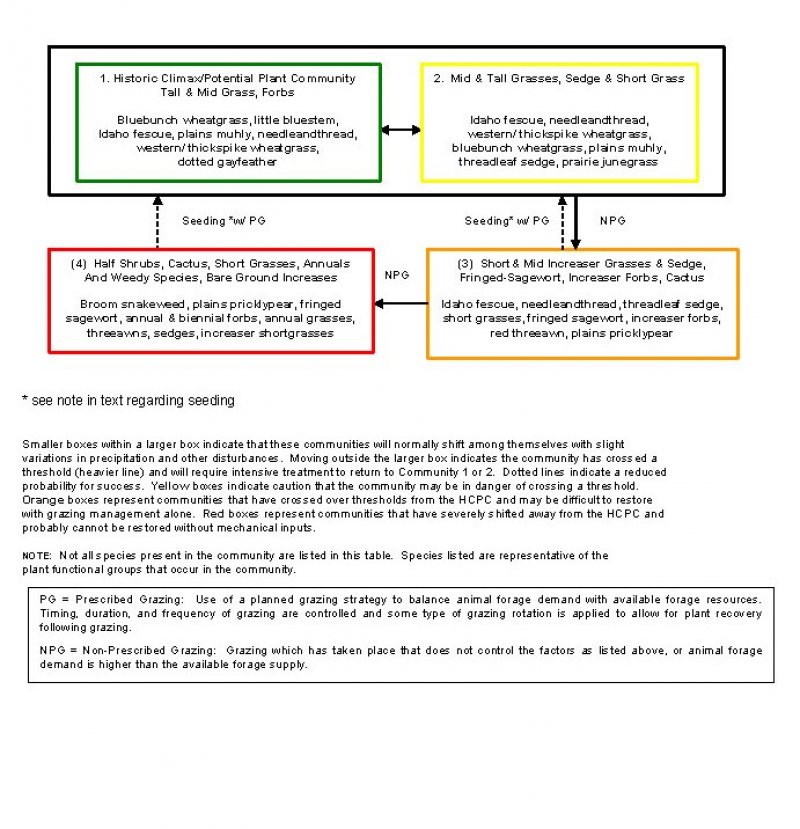
Figure 2. State and Transition Model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 4 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Tall and Medium Grasses, Forbs
Community 1.1
Tall and Medium Grasses, Forbs
This is the interpretive plant community and is considered to be the Historic Climax Plant Community (HCPC) for this site. This plant community contains a high diversity of tall and medium height, cool and warm season grasses (bluebunch wheatgrass, little bluestem, western or thickspike wheatgrass, and plains muhly), and short grasses and sedges (Idaho fescue, prairie junegrass, Sandberg bluegrass, plains reedgrass, threadleaf and needleleaf sedge). There are abundant forbs (dotted gayfeather) which occur in smaller percentages. Shrubs such as silver sagebrush can also be present. This plant community is well adapted to the Northern Rocky Mountain foothills climatic conditions. The diversity in plant species allows for drought tolerance. Individual species can vary greatly in production depending on growing conditions (timing and amount of precipitation, and temperature). This plant community is well suited to managed livestock grazing and provides diverse habitat for many wildlife species. Plants on this site have strong, healthy root systems that allow production to increase significantly with favorable moisture conditions. This plant community provides for soil stability and a properly functioning hydrologic cycle. Abundant plant litter is available for soil building and moisture retention. Plant litter is properly distributed with very little movement off-site and natural plant mortality is very low. The soils associated with this site provide a moderately limited soil-water-plant relationship.
Figure 3. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 986 | 1255 | 1524 |
| Shrub/Vine | 62 | 118 | 191 |
| Forb | 62 | 118 | 191 |
| Total | 1110 | 1491 | 1906 |
Table 6. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 5-10% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 20-40% |
| Forb foliar cover | 1-5% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0-1% |
| Biological crusts | 0% |
| Litter | 0% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 0% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 0% |
Table 7. Soil surface cover
| Tree basal cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana basal cover | 0-2% |
| Grass/grasslike basal cover | 14-21% |
| Forb basal cover | 1-2% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0-1% |
| Biological crusts | 0% |
| Litter | 50-60% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 5-15% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 10-20% |
State 2
Medium and Short Grasses, Sedge, and Increaser Forbs
Community 2.1
Medium and Short Grasses, Sedge, and Increaser Forbs
Early stages of degradation, including non-prescribed grazing, will tend to change the HCPC to a community dominated by medium and short grasses and sedges such as Idaho fescue, needleandthread, western / thickspike wheatgrass, threadleaf sedge, prairie junegrass, and Sandberg bluegrass. Most of the taller and more palatable plants (bluebunch wheatgrass, little bluestem) will still be present but in smaller amounts. There may be an increase in the amount of some shrubs, such as silver sagebrush. Palatable and nutritious forbs will be replaced by less desirable and more aggressive species such as pussytoes and western yarrow. Biomass production and litter become slightly reduced on the site with Community 2 as the taller grasses become replaced by shorter ones. Evapotranspiration tends to increase, moisture retention is reduced, and soil surface temperatures increase. Some natural ecological processes will be altered. These plant communities provide for moderate soil stability. Increased amounts of bare ground can result in undesirable species invading. Common invaders can include spotted knapweed, leafy spurge, dalmation toadflax, and sulphur cinquefoil. This plant community will readily respond to improved grazing management, but a significant amount of time can be necessary to move it toward a higher successional stage and a more productive plant community similar to community 1.
State 3
Short and Mid Increaser Grasses and Sedge, Fringed Sagewort, Increaser Forbs, Cactus
Community 3.1
Short and Mid Increaser Grasses and Sedge, Fringed Sagewort, Increaser Forbs, Cactus
With continued heavy disturbance, the site will become dominated by short and medium increaser grasses such as Sandberg bluegrass, plains reedgrass, prairie junegrass, western or thickspike wheatgrass, and Idaho fescue, fringed sagewort, and increaser forbs such as pussytoes and western yarrow. There may still be remnant amounts of some of the late-seral species such as bluebunch wheatgrass and little bluestem present. The taller grasses will occur only occasionally. Palatable forbs will be mostly absent. Undesirable species such as red threeawn, plains pricklypear cactus and broom snakeweed may become common. Annuals and weedy species may begin to be apparent. This plant community is the result of long-term, heavy, continuous grazing and/or annual, early spring seasonal grazing. Repeated spring grazing depletes stored carbohydrates, resulting in weakening and eventual death of the cool season tall and medium grasses. This plant community can occur throughout the pasture, on spot grazed areas, and around water sources where season-long grazing patterns occur. This community will respond positively to improved grazing management, but significant economic inputs along with a significant amount of time and extended rest are usually required to move it toward a higher successional stage and a more productive plant community. There are limitations to using seeding and/or mechanical treatments on this site due to the shallow soils
State 4
Half Shrubs, Cactus, Annuals and Weedy Species, Short Grasses, Bare Ground
Community 4.1
Half Shrubs, Cactus, Annuals and Weedy Species, Short Grasses, Bare Ground
Further deterioration of community 3 results in a plant community dominated by undesirable plants such as broom snakeweed, plains pricklypear cactus, fringed sagewort, weedy forbs (e.g., pussytoes and thistles), annuals and biennials such as cheatgrass and Japanese bromes and curlycup gumweed, and red threeawn. Many increaser sedges and short grasses such as threadleaf sedge, prairie junegrass, Sandberg bluegrass and plains reedgrass will be abundant. Most of the climax species such as bluebunch wheatgrass will be gone. Plant communities 3 & 4 produce less usable forage for wildlife and livestock than the others described. The continuation of the downward trend and degradation of this site has resulted in higher soil surface temperatures, reduced water infiltration, and higher evapotranspiration. This has resulted in plant species that are more adapted to drier conditions, including cactus. Most of the attributes of a healthy rangeland, including good infiltration, minimal erosion and runoff, nutrient cycling and energy flow, have been lost. Community 4 can respond positively to improved grazing management but it will take several years along with significant additional inputs and extended rest to move it towards communities similar in production and composition to others that have been described. The potential for using seeding or mechanical treatment to improve site health is limited due to the shallow depth to sand and gravel.
Additional community tables
Table 8. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 0 | Shrubs and Half-shrubs | 62–191 | ||||
| Shrub, broadleaf | 2SB | Shrub, broadleaf | 0–95 | – | ||
| silver sagebrush | ARCAV2 | Artemisia cana ssp. viscidula | 0–95 | – | ||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 0–95 | – | ||
| skunkbush sumac | RHTR | Rhus trilobata | 0–95 | – | ||
| prairie rose | ROARS | Rosa arkansana var. suffulta | 0–95 | – | ||
| common snowberry | SYAL | Symphoricarpos albus | 0–95 | – | ||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 0–1 | – | ||
| plains pricklypear | OPPO | Opuntia polyacantha | 0–1 | – | ||
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 0 | Grasses and Sedges | 986–1524 | ||||
| bluebunch wheatgrass | PSSP6 | Pseudoroegneria spicata | 493–1334 | – | ||
| little bluestem | SCSCD | Schizachyrium scoparium var. divergens | 0–572 | – | ||
| Idaho fescue | FEID | Festuca idahoensis | 0–286 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 62–191 | – | ||
| plains muhly | MUCU3 | Muhlenbergia cuspidata | 0–191 | – | ||
| Sandberg bluegrass | POSE | Poa secunda | 62–95 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 62–95 | – | ||
| Grass, perennial | 2GP | Grass, perennial | 0–95 | – | ||
| needleleaf sedge | CADU6 | Carex duriuscula | 62–95 | – | ||
| threadleaf sedge | CAFI | Carex filifolia | 62–95 | – | ||
| plains reedgrass | CAMO | Calamagrostis montanensis | 62–95 | – | ||
| thickspike wheatgrass | ELLAL | Elymus lanceolatus ssp. lanceolatus | 0–48 | – | ||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 0–48 | – | ||
| purple threeawn | ARPU9 | Aristida purpurea | 0–1 | – | ||
| Fendler's threeawn | ARPUF | Aristida purpurea var. fendleriana | 0–1 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 0 | Forbs | 62–191 | ||||
| Forb, perennial | 2FP | Forb, perennial | 0–95 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 0–95 | – | ||
| pussytoes | ANTEN | Antennaria | 0–95 | – | ||
| hairy false goldenaster | HEVI4 | Heterotheca villosa | 0–95 | – | ||
| bitter root | LERE7 | Lewisia rediviva | 0–95 | – | ||
| dotted blazing star | LIPU | Liatris punctata | 12–95 | – | ||
| desertparsley | LOMAT | Lomatium | 0–95 | – | ||
| lupine | LUPIN | Lupinus | 0–1 | – | ||
| deathcamas | ZIGAD | Zigadenus | 0–1 | – | ||
| little larkspur | DEBIC | Delphinium bicolor ssp. calcicola | 0–1 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Livestock Grazing Interpretations: Managed livestock grazing is suitable on this site as it has the potential to produce a limited amount of high quality forage. Grazing must be managed carefully on this site to be sure livestock drift onto the better, more productive sites is not excessive. Management objectives should include maintenance or improvement of the plant community.
Using shorter grazing periods and providing for adequate re-growth after grazing are recommended for plant maintenance, health, and recovery. Continual over stocking and season-long use of this site can be detrimental and will alter the plant composition and production over time. The result will be plant communities that resemble numbers 3 and 4, depending on how long this grazing management is used as well as other circumstances such as weather conditions and fire frequency.
Whenever Plant Community 2 (medium and short grasses) occurs, grazing management strategies that will prevent further degradation need to be implemented. This community is still stable, productive, and healthy provided it receives proper management. It will respond fairly quickly to improved grazing management, including increased growing season rest of key forage plants. Grazing management alone can usually move this back towards the potential / historic climax community.
Plant community 3 is the result of long-term, heavy, continuous grazing and/or annual, early spring seasonal grazing. Repeated heavy early spring grazing, especially during stem elongation (generally mid May through mid June), can also have detrimental affects on the taller, key forage species. Repeated spring grazing depletes stored carbohydrates, resulting in weakening and eventual death of the cool season tall and medium grasses. This plant community can occur throughout the pasture, on spot grazed areas, and around water sources where season-long grazing patterns occur.
Plant Communities 3 and 4 have a high percentage of aggressive, less-desirable species. Once these have become established, it is significantly more difficult using grazing management alone to restore the site to one that resembles the HCPC. It becomes critical at this point to implement a grazing strategy that will restore the stability and health of the site. Rest, usually for a number of years, can sometimes help with re-establishment of the desired species, depending on the amount of desirable species remaining. There are limitations to using seeding and/or mechanical treatment on this site due to the shallow soils.
Calculating Safe Stocking Rates: Proper stocking rates should be incorporated into a grazing
management strategy that protects the resource, maintains or improves rangeland health, and is consistent with management objectives. Safe stocking rates will be based on useable forage production, and should consider ecological condition and trend of the site, and past grazing use history.
Calculations used to determine a safe stocking rate are based on the amount of useable forage available,
taking into account the harvest efficiency of the animal and the grazing strategy to be implemented. Average annual production must be measured or estimated to properly assess useable forage production and stocking rates.
The following is an example of how to calculate the recommended stocking rate. This example does not use production estimates from this specific ecological site. You will need to adjust the annual production values and run the calculations using total annual production values from the ecological sites encountered on each individual ranch/pasture. Before making specific recommendations, an on-site evaluation must be made.
Example of total annual production amounts by type of year:
Favorable years = 2200 lbs/acre
Normal years = 1480 lbs/acre
Unfavorable years = 1200 lbs/acre
It is recommended that on slopes of 30% or less, stocking rate should be derived from the total annual production pounds minus 500 pounds for residual dry matter and 25% harvest efficiency. On slopes over 30%, stocking rate is derived from total annual production pounds minus 800 pounds for residual dry matter and 25% harvest efficiency. Refer to the NRCS National Range and Pasture Handbook for a list of Animal Unit Equivalents.
Sample Calculations using Favorable Year production amounts:
< 30% slopes: AUM/AC = [(2200-500)(0.25)]/915 lbs/month for one AU = 0.46 AUM/AC
AC/AUM = (1.0 AU)/(0.46AUM/AC) = 2.2 AC/AUM
> 30% slopes: AUM/AC = [(2200-800)(0.25)]/915 lbs/month for one AU = 0.38 AUM/AC
AC/AUM = (1.0 AU)/(0.38 AU! M/AC) = 2.6 AC/AUM
NOTE: 915 lbs/month for one Animal Unit is used as the baseline for maintenance requirements. This equates to 30 lbs/day of air-dry forage (1200 lb cow at 2.5% of body weight).
Hydrological functions
The soils associated with this ecological site are generally in Hydrologic Soil Group B. The infiltration rates for these soils will normally be moderate. The runoff potential for this site is moderate, depending on slope and ground cover/health. Runoff curve numbers generally range from 76 to 94.
Good hydrologic conditions exist on rangelands if plant cover (grass, litter, and brush canopy) is greater than 70%. Fair conditions exist when cover is between 30 and 70%, and poor conditions exist when cover is less than 30%. Sites in high similarity to HCPC (Plant Communities 1 and 2) generally have enough plant cover and litter to optimize infiltration, minimize runoff and erosion, and have a good hydrologic condition. The deep root systems of the potential vegetation help maintain or increase infiltration rates and reduce runoff.
Sites in low similarity (Plant Communities 3 and 4) are generally considered to be in poor hydrologic condition as the majority of plant cover is from shallow-rooted species such as prairie junegrass, annuals, and half-shrubs.
Erosion is minor for sites in high similarity. Rills and gullies should not be present. Water flow patterns, if present, will be barely observable. Plant pedestals are essentially non-existent. Plant litter remains in place and is not moved by erosion. Soil surfaces should not be compacted or crusted. Plant cover and litter helps retain soil moisture for use by the plants. Maintaining a healthy stand of perennial vegetation will optimize the amount of precipitation that is received. (Reference: Engineering Field Manual, Chapter 2 and Montana Supplement 4).
Recreational uses
This site provides some recreational opportunities for hiking, horseback riding, big game and upland bird hunting. The forbs have flowers that appeal to photographers. This site provides valuable open space and visual aesthetics. Caution should be used during wet weather periods.
Wood products
None
Supporting information
Contributors
Matt Ricketts
Robert L. Ross
Robert Leinard; Barbara Gibbons; Loretta Metz; Peter Husby, Jon Siddoway, Matt Ricketts
Approval
Kirt Walstad, 7/19/2023
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | |
| Date | 12/22/2024 |
| Approved by | Kirt Walstad |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
-
Presence of water flow patterns:
-
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
-
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
-
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
-
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
-
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
-
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
-
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
-
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
-
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
-
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Sub-dominant:
Other:
Additional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
-
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
-
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
-
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
-
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.