Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R052XY005MT
Clayey-Steep (Cystp) Dry Grassland
Last updated: 7/09/2019
Accessed: 03/14/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
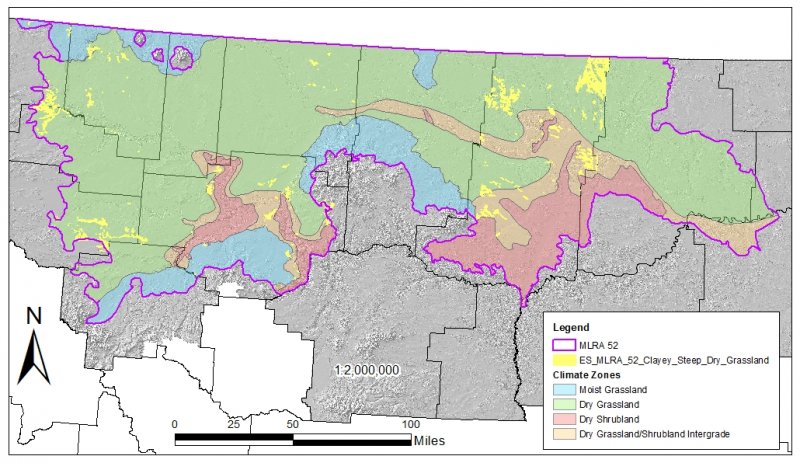
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 052X–Brown Glaciated Plains
The Brown Glaciated Plains, MLRA 52, is an expansive and agriculturally and ecologically significant area. It consists of around 14.5 million acres and stretches across 350 miles from east to west, encompassing portions of 15 counties in north-central Montana. This region represents the southwestern limit of the Laurentide Ice Sheet and is considered to be the driest and westernmost area within the vast network of glacially-derived prairie pothole landforms of the northern Great Plains. Elevation ranges from 2,000 feet (610 meters) to 4,600 feet (1,400 meters).
Soils are primarily Mollisols but Entisols, Inceptisols, Alfisols and Vertisols are also common. Till from continental glaciation is the predominant parent material, but alluvium and bedrock are also common. Till deposits are typically less than 50 feet thick, and in some areas glacially deformed bedrock occurs at or near the soil surface (Soller, 2001). Underlying the till is sedimentary bedrock largely consisting of Cretaceous shale, sandstone and mudstone (Vuke et al. 2007). It is commonly exposed on hillslopes, particularly along drainage ways. Significant alluvial deposits occur along glacial outwash channels and major drainages, including portions of the Missouri, Teton, Marias, Milk, and Frenchman Rivers. Large glacial lakes, particularly in the western half of the MLRA, deposited clayey and silty lacustrine sediments (Fullerton et al. 2013).
Much of the western portion of this MLRA was glaciated towards the end of the Wisconsin age, and the maximum glacial extent occurred approximately 20,000 years ago (Fullerton et al., 2004). The result is a geologically young landscape that is predominantly a level till plain interspersed with lake plains and dominated by soils in the Mollisol and Vertisol orders. These soils are very productive and generally are well-suited to dryland farming. Much of this area is aridic-ustic. Crop-fallow dryland wheat farming is the predominant land use. Areas of rangeland typically are on steep hillslopes along drainages.
The rangeland, much of which is native mixed grass prairie, increases in abundance in the eastern half of the MLRA. The Wisconsin-age till in the north-central part of this area typically formed large disintegration moraines with steep slopes and numerous poorly-drained potholes. A large portion of Wisconsin-age till occurring on level terrain that would typically be optimal for farming has large amounts of less-suitable sodium-affected Natrustalfs. Significant portions of Blaine, Phillips, and Valley Counties were glaciated approximately 150,000 years ago during the Illinoisan age. Due to erosion and dissection of the landscape, many of these areas have steeper slopes and more exposed bedrock than areas glaciated during the Wisconsin age (Fullerton and Colton, 1986).
While much of the rangeland in the aridic-ustic portion of MLRA 52 is classified as belonging to the - “dry grassland” - climatic zone, sites in portions of southern MLRA 52 may belong to the -“dry shrubland” - climatic zone. The dry shrubland zone represents the northernmost extent of the big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) steppe on the Great Plains. Because similar soils occur in both southern and northern portions of the MLRA, it is currently hypothesized that climate is the primary driving factor affecting big sagebrush distribution in this area. However the precise factors are not fully understood at this time.
Sizeable tracts of largely unbroken rangeland in the eastern half of the MLRA and adjacent southern Saskatchewan are home to the Northern Montana population of greater sage grouse (Centrocercus urophasianus), and large portions of this area are considered to be a Priority Area for Conservation (PAC) by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, 2013). This population is unique among sage grouse populations because many individuals overwinter in the big sagebrush steppe (dry shrubland) in the southern portion of the MLRA and then migrate to the northern portion of the MLRA, which lacks big sagebrush (dry grassland), to live the rest of the year (Smith, 2013).
Areas of the till plain near the Bearpaw and Highwood Mountains as well as the Sweetgrass Hills and Rocky Mountain foothills are at higher elevations, receive higher amounts of precipitation, and have a typic-ustic moisture regime. These areas have significantly more rangeland production than the drier aridic-ustic portions of the MLRA and have enough moisture to produce crops annually rather than just bi-annually, as in the drier areas. Ecological sites in this higher precipitation area are classified as the moist grassland climatic zone.
Classification relationships
NRCS Soil Geography Hierarchy
• Land Resource Region: Northern Great Plains
• Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 052 Brown Glaciated Plains
• Climate Zone: Dry Grassland
National Hierarchical Framework of Ecological Units (Cleland et al. 1997, McNab et al. 2007)
• Domain: Dry
• Division: Temperate Steppe
• Province: Great Plains-Palouse Dry Steppe Province 331
• Section: Northwestern Glaciated Plains 331D
• Subsection: Montana Glaciated Plains 331Dh
• Landtype association/Landtype phase: N/A
National Vegetation Classification Standard (Federal Geographic Data Committee 2008)
• Class: Mesomorphic Shrub and Herb Vegetation Class (2)
• Subclass: Temperate and Boreal Grassland and Shrubland Subclass (2.B)
• Formation: Temperate Grassland, Meadow, and Shrubland Formation (2.B.2)
• Division: Great Plains Grassland and Shrubland Division (2.b.2.Nb)
• Macrogroup: Hesperostipa comata – Pascopyrum smithii – Festuca hallii Grassland Macrogroup (2.B.2.Nb.2)
• Group: Pascopyrum smithii - Hesperostipa comata - Schizachyrium scoparium - Bouteloua spp. Mixedgrass Prairie Group (2.B.2.Nb.2.c)
• Alliance: Pascopyrum smithii – Nassella viridula Northwestern Great Plains Herbaceous Alliance
• Association: Pascopyrum smithii - Nassella viridula Herbaceous Vegetation
EPA Ecoregions
• Level 1: Great Plains (9)
• Level 2: West-Central Semi-Arid Prairies (9.3)
• Level 3: Northwestern Glaciated Plains (42)
• Level 4: North Central Brown Glaciated Plains (42o) & Glaciated Northern Grasslands (42j)
Ecological site concept
This provisional ecological site occurs in the Dry Grassland climatic zone of MLRA 52. Figure 1 illustrates the distribution of this ecological site based on current data. This map is approximate, is not intended to be definitive, and may be subject to change. Clayey Steep Dry Grassland is a moderately extensive ecological site occurring on most landscapes in MLRA 52. This ecological site occurs on hillslopes, badlands, and bluffs where clay content of the soil is greater than 35 percent. Slopes vary from 15 to 60 percent.
The distinguishing characteristics of this site are moderately steep to very steep slopes, a relatively well developed soil profile, and clayey textures in the upper 4 inches of soil. Soils are typically moderately deep to very deep (between 20 to 60 inches to bedrock), are derived from shale residuum or clayey till, and typically have an ochric epipedon. Textures in the upper 4 inches of soil are in the fine textural family and contains greater than 35 percent, but not more than 45 percent, clay. Sometimes the underlying horizons exhibit shrink swell characteristics such as slickensides. This site is typically nonacid, with pH values greater than 5.6 throughout the soil profile. In general, plant production is relatively good on this site and species diversity can be high. Characteristic vegetation is western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii) and green needlegrass (Nassella viridula). Thickspike wheatgrass (Elymus lanceolatus) becomes more common in the northern extent of MLRA 52. The principal shrub on this site is silver sagebrush (Artemisia cana), which typically comprises 5 percent canopy cover or less.
Preliminary studies indicate that there may also be an acid variant of this site. This variant appears to exhibit retarded shrub growth, reduced cover of cool season bunchgrasses, and increased cover of creeping juniper and prairie sandreed. At this time, this variant cannot be consistently identified as a separate ecological site concept and further investigation is required.
Associated sites
| R052XY001MT |
Clayey (Cy) Dry Grassland Clayey Dry Grassland is adjacent to Clayey Steep on slopes of less than 15 percent. It typically occupies a summit position upslope from the Clayey Steep Dry Grassland ecological site. |
|---|---|
| R052XY131MT |
Shallow Clay (Swc) Dry Grassland Shallow Clay Dry Grassland is adjacent to Clayey Steep where bedrock occurs near the soil surface. It typically occupies a backslope position similar to the Clayey Steep Dry Grassland ecological site. |
| R052XY007MT |
Coarse Clay (Coc) Dry Grassland This site occurs on moderate to steeply sloping hillslopes adjacent to the Clayey Steep Dry grassland site. It is commonly in the same landscape positions but has different soil structure. |
Similar sites
| R052XY703MT |
Clayey-Steep (Cystp) Dry Shrubland This site differs from Clayey Steep Dry Grassland in that annual temperatures are slightly warmer and it supports big sagebrush rather than silver sagebrush. |
|---|---|
| R052XY131MT |
Shallow Clay (Swc) Dry Grassland This site differs from Clayey Steep Dry Grassland in that depth to bedrock is less than 20 inches. |
| R052XY007MT |
Coarse Clay (Coc) Dry Grassland This site differs from Clayey Steep Dry Grassland in that the soil structure in the surface horizon is coarse granular rather than fine. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
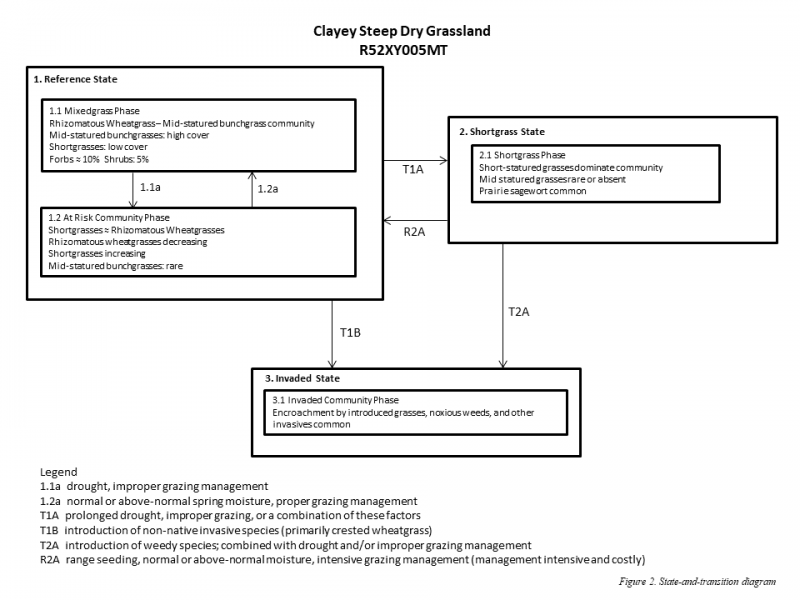
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.