Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site FX053A99X062
Swale (Se)
Last updated: 4/25/2025
Accessed: 02/11/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 053A–Northern Dark Brown Glaciated Plains
The Northern Dark Brown Glaciated Plains, MLRA 53A, is a large, agriculturally and ecologically significant area. It consists of approximately 6.1 million acres and stretches 140 miles from east to west and 120 miles from north to south, encompassing portions of 8 counties in northeastern Montana and northwestern North Dakota. This region represents part of the southern edge of the Laurentide Ice Sheet during maximum glaciation. It is one of the driest and westernmost areas within the vast network of glacially derived prairie pothole landforms of the Northern Great Plains and falls roughly between the Missouri Coteau to the east and the Brown Glaciated Plains to the west. Elevation ranges from 1,800 feet (550 meters) to 3,300 feet (1,005 meters).
Soils are primarily Mollisols, but Inceptisols and Entisols are also common. Till from continental glaciation is the predominant parent material, but alluvium and bedrock are also common. Till deposits are typically less than 50 feet thick (Soller, 2001). Underlying the till is sedimentary bedrock largely consisting of Cretaceous shale, sandstone, and mudstone (Vuke et al., 2007). The bedrock is commonly exposed on hillslopes, particularly along drainageways. Significant alluvial deposits occur in glacial outwash channels and along major drainages, including portions of the Missouri, Poplar, and Big Muddy Rivers. Large eolian deposits of sand occur in the vicinity of the ancestral Missouri River channel east of Medicine Lake (Fullerton et al., 2004). The northwestern portion of the MLRA contains a large unglaciated area containing paleoterraces and large deposits of sand and gravel known as the Flaxville gravel.
Much of this MLRA was glaciated towards the end of the Wisconsin age, and the maximum glacial extent occurred approximately 20,000 years ago (Fullerton and Colton, 1986; Fullerton et al., 2004). Subsequent erosion from major stream and river systems has created numerous drainageways throughout much of the MLRA. The result is a geologically young landscape that is predominantly a dissected till plain interspersed with alluvial deposits and dominated by soils in the Mollisol and Inceptisol orders. Much of this area is typic ustic, making these soils very productive and generally well suited to production agriculture.
Dryland farming is the predominant land use, and approximately 50 percent of the land area is used for cultivated crops. Winter, spring, and durum varieties of wheat are the major crops, with over 48 million bushels produced annually (USDA-NASS, 2017). Areas of rangeland typically are on steep hillslopes along drainages. The rangeland is mostly native mixed-grass prairie similar the Stipa-Agropyron, Stipa-Bouteloua-Agropyron, and Stipa-Bouteloua faciations (Coupland, 1950, 1961). Cool-season grasses dominate and include rhizomatous wheatgrasses, needle and thread, western porcupine grass, and green needlegrass. Woody species are generally rare; however, many of the steeper drainages support stands of trees and shrubs such as green ash and chokecherry. Seasonally ponded, prairie pothole wetlands may occur throughout the MLRA, but the greatest concentrations are in the east and northeast where receding glaciers stagnated and formed disintegration moraines with hummocky topography and numerous areas of poorly drained soils.
Classification relationships
NRCS Soil Geography Hierarchy
• Land Resource Region: Northern Great Plains
• Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 053A Northern Dark Brown Glaciated Plains
National Hierarchical Framework of Ecological Units (Cleland et al., 1997; McNab et al., 2007)
• Domain: Dry
• Division: Temperate Steppe
• Province: Great Plains-Palouse Dry Steppe Province 331
• Section: Glaciated Northern Grasslands Section 331L
• Subsection: Glaciated Northern Grasslands Subsection 331La
• Landtype association/Landtype phase: N/A
National Vegetation Classification Standard (Federal Geographic Data Committee, 2008)
• Class: Mesomorphic Shrub and Herb Vegetation Class (2)
• Subclass: Temperate and Boreal Grassland and Shrubland Subclass (2.B)
• Formation: Temperate Grassland and Shrubland Formation (2.B.2)
• Division: Central North American and Shrubland Division (2.B.2.Nb)
• Macrogroup: Hesperostipa comata - Pascopyrum smithii - Festuca hallii Grassland Macrogroup (2.B.2.Nb.2)
o Group: Pascopyrum smithii - Hesperostipa comata - Schizachyrium scoparium Mixedgrass Prairie Group (2.B.2.Nb.2.c)
Alliance: Pascopyrum smithii - Nassella viridula Northwestern Great Plains Grassland Alliance
Association: Pascopyrum smithii - Nassella viridula Grassland
o Group: Hesperostipa comata - Bouteloua gracilis Dry Mixedgrass Prairie Group (2.B.2.Nb.2.c)
Alliance: Hesperostipa curtiseta - Elymus lanceolatus Grassland Alliance
Association: Hesperostipa curtiseta - Elymus lanceolatus Grassland
EPA Ecoregions
• Level 1: Great Plains (9)
• Level 2: West-Central Semi-Arid Prairies (9.3)
• Level 3: Northwestern Glaciated Plains (42)
• Level 4: Glaciated Dark Brown Prairie (42i)
Glaciated Northern Grasslands (42j)
Ecological site concept
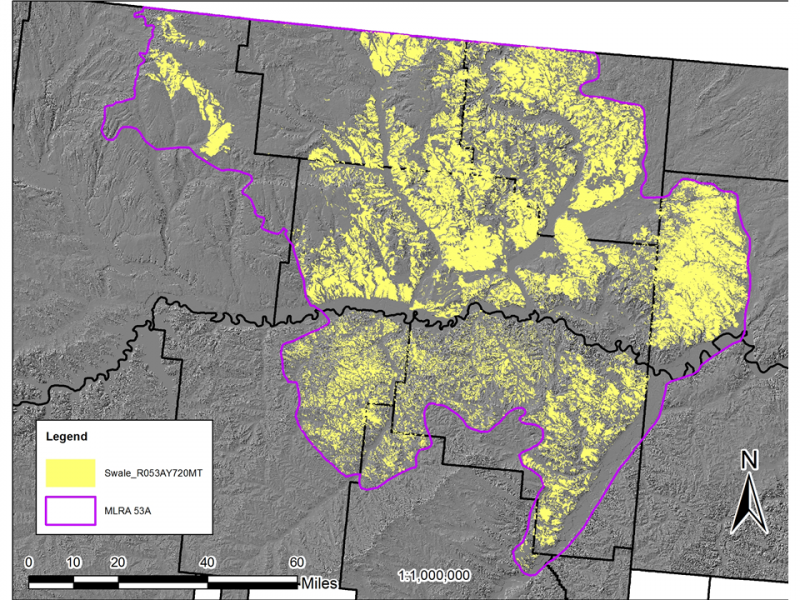
This provisional ecological site is common throughout MLRA 53A. Figure 2 illustrates the distribution of this ecological site based on current data. Many map units contain minor components with this ecological site; these minor components typically make up less than 10 percent of the map unit composition. The map in Figure 1 is approximate, is not intended to be definitive, and may be subject to change. Swale is an extensive ecological site occurring on swale micro-features within nearly level to gently sloping landscapes. The distinguishing characteristic of this site is that it receives additional moisture via surface runoff from adjacent sites. Soils for this ecological site are typically very deep (more than 60 inches) with a thick (16 inches or more) mollic epipedon. Characteristic vegetation is green needlegrass (Nassella viridula), rhizomatous wheatgrasses, and needlegrass (Hesperostipa spp).
Associated sites
| FX053A99X032 |
Loamy (Lo) The Loamy ecological site is found on slopes of less than 15 percent on moraines and till plains upslope from and commonly surrounding the Swale Moist Grassland ecological site. The upper 4 inches of soil contains 18 to 35 percent clay. |
|---|---|
| FX053A99X040 |
Loamy Steep (LoStp) The Loamy Steep ecological site is found on slopes of 15 percent or greater upslope from the Swale ecological site. It occurs on hillslopes whereas Swale ecological site occurs on swale microfeatures where surface runoff is concentrated. |
| FX053A99X029 |
Limy Steep (LyStp) The Limy Steep ecological site is found on slopes of 15 percent or greater upslope from the Swale ecological site. It occurs on convex hillslopes whereas the Swale ecological site occurs on swale microfeatures where surface runoff is concentrated. |
| FX053A99X030 |
Limy (Ly) The Limy ecological site occurs upslope from the Swale ecological site. It is generally on shoulders or crests whereas Swale ecological site occurs on swale microfeatures where surface runoff is concentrated. |
Similar sites
| FX053A99X756 |
Woody Draw (WD) This site differs from the Swale ecological site in that it is dominated by woody species. It typically occurs in steep, V-shaped drainages whereas Swale occurs in broad U-shaped swales. |
|---|---|
| FX053A99X060 |
Overflow (Ov) This site differs from the Swale ecological site in that it is on flood plains rather than upland swales. It generally is on stream terraces adjacent to a losing stream reach and in some areas has a water table greater than 40 inches below the soil surface. |
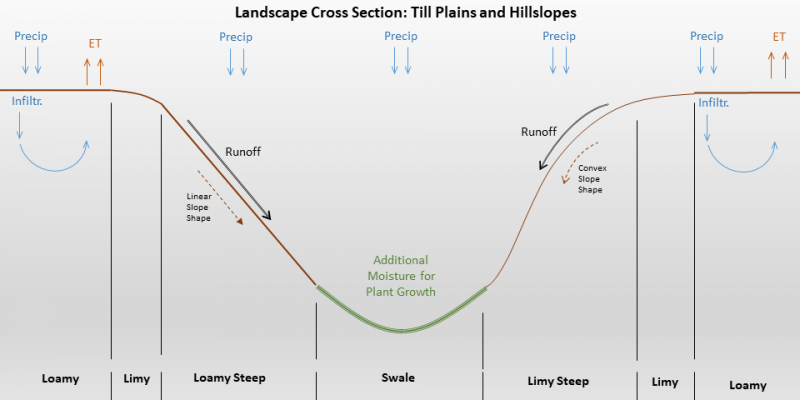
Figure 1. Similar and associated sites diagram.
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Symphoricarpos occidentalis |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Nassella viridula |
Legacy ID
R053AY720MT
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Introduction of non-native grass species, such as Kentucky bluegrass, smooth brome, and crested wheatgrass. |
|---|---|---|
| T2A | - | Displacement of native species by non-native invasive species (Kentucky bluegrass, noxious weeds, etc.) |
| T2B | - | Conversion to cropland |
| T3A | - | Conversion to cropland |
| T4A | - | Cessation of annual cropping |
| T5A | - | Conversion to cropland |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
| 2.1A | - | Drought, improper grazing management |
|---|---|---|
| 2.2A | - | Return to normal or above average precipitation, proper grazing management |
| 2.2B | - | Prolonged drought, improper grazing management, or a combination of these factors. |
| 2.3A | - | Normal or above-normal spring moisture, proper grazing management. |