
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R058AE191MT
Shallow to Gravel (SwGr) RRU 58A-E 10-14" p.z.
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
Associated sites
| R058AE001MT |
Silty (Si) RRU 58A-E 10-14 P.Z. |
|---|---|
| R058AE004MT |
Silty-Steep (SiStp) RRU 58A-E 10-14" p.z. |
| R058AE005MT |
Clayey-Steep (CyStp) RRU 58A-E 10-14" p.z. |
| R058AE016MT |
Gravel (Gr) RRU 58A-E 10-14" p.z. |
Similar sites
| R058AE199MT |
Shallow Clay (SwC) RRU 58A-E 10-14" p.z. The Shallow Clay site differs by being clayey texture and underlain by shales. |
|---|---|
| R058AE016MT |
Gravel (Gr) RRU 58A-E 10-14" p.z. The Gravel site will be very droughty, having a water holding capacity of less than 2 inches. It is very gravelly to within 10 inches of the surface. |
| R058AE019MT |
Shallow (Sw) RRU 58A-E 10-14" p.z. The Shallow site is over hard rock or semi-consolidated beds, not gravels. |
| R058AE001MT |
Silty (Si) RRU 58A-E 10-14 P.Z. The Silty differs mainly by being over 20 inches deep to any root limiting material, including gravel. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Physiographic features
This ecological site mainly occurs on level, nearly level, and moderately steep terraces, hill slopes, stream terraces and terrace escarpments. Slopes are mainly 0 to 15 percent.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Terrace
(2) Hill (3) Plain |
|---|---|
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 1,900 – 3,500 ft |
| Slope | 15% |
| Water table depth | 60 in |
Climatic features
MLRAs 58A and 60B are considered to have a continental climate characterized by cold winters, hot summers, low humidity, light rainfall, and much sunshine. Extremes in temperature are typical. The climate is the result of this MLRA’s location in the geographic center of North America. There are few natural barriers on the northern Great Plains and the winds move freely across the plains and account for rapid changes in temperature. Seasonal precipitation is often limiting for plant growth. Annual fluctuations in species composition and total production are typical depending on the amount and timing of rainfall.
Temperatures can be very extreme in this part of Montana. Summer daytime temperatures are typically quite warm, generally averaging in the mid to upper 80º’s F for July and August. Summertime temperatures will typically reach in the 100º’s F at some point during the summer, and can reach 90º F any month between May and September. Conversely, winter temperatures can be cold, averaging in the mid teens to mid 20º’s F for December and January. There will typically be several days of below zero temperatures each winter. It is not uncommon for temperatures to reach 30–40º F below zero, or even colder, most any winter.
Spring can be windy throughout these MLRA’s, with winds averaging over 10 mph about 15 percent of the time. Speeds of 50 mph or stronger can occasionally occur as a weather system crosses this part of Montana.
MLRAs 58AE and 60BE have been divided into two distinct precipitation zones for the purpose of developing ecological site descriptions: 10–14” Mean Annual Precipitation (MAP) and 15–19” MAP.
10–14 inch zone:
The majority of the rangeland in these areas falls within the 11 to 13 inch range. During an average year, 70 to 75 percent of the annual precipitation falls between April and September, which are the primary growing season months.
Snowfall is not heavy in the area, averaging 28 total inches in the 10-14 inch MAP (Yellowstone Valley). Heavy snowfall occurs infrequently, usually late in the winter or early spring. Snow cover is typically 1 to 3 inches.
The frost free (32º F.) season averages about 105 to 145 days each year in the uplands, to nearly 170 days along the Yellowstone River Valley.
For local climate station information, refer to http://www.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/cgibin/state.pl?state=mt.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (average) | 145 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (average) | 170 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 14 in |
Influencing water features
Soil features
These soils are 10 to 20 deep over sandy gravels. Few roots penetrate deeper than 20 inches. The gravelly subsoil makes these soils moderately drougthy.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Surface texture |
(1) Gravelly silt loam (2) Very gravelly loam (3) Sandy loam |
|---|---|
| Family particle size |
(1) Sandy |
| Drainage class | Well drained to somewhat excessively drained |
| Permeability class | Moderate |
| Soil depth | 10 – 20 in |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
2 – 5 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
1 – 10% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
2 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
5 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
6.6 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
60% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
15% |
Ecological dynamics
This site developed under Northern Great Plains climatic conditions, which included the natural influence of large herbivores and occasional fire. The plant community upon which interpretations are primarily based is the Historic Climax Plant Community (HCPC). This community is described as a reference to understand the original potential of this site, and is not always considered to be the management goal for every acre of rangeland. The following descriptions should enable the landowner or manager to better understand which plant communities occupy their land, and assist with setting goals for vegetation management. It can also be useful to understand the environmental and economic values of each plant community.
This site is considered moderately resilient to disturbance as it has only moderate soil limitations for plant growth. Changes may occur to the Historic Climax Plant Community due to management actions and/or climatic conditions. Under continued adverse impacts, a moderate decline in vegetative vigor and composition will occur. Under favorable vegetative management treatments, this site can more readily return to the Historic Climax Plant Community (HCPC).
Continual adverse impacts to the site over a period of years results in a departure from the HCPC, with a decrease of the taller, more palatable species such as bluebunch wheatgrass and little bluestem. These plants will be replaced by Western wheatgrass, needleandthread, threadleaf sedge, sand dropseed, blue grama, non-palatable forbs, and yucca. Continued deterioration results in increased amounts of green and fringed sagewort, red threeawn, and plains pricklypear.
Plants that are not a part of the climax community that are most likely to invade are Japanese brome, cheatgrass, six-weeks fescue, false buffalograss, broom snakeweed, and thistles.
State and transition model
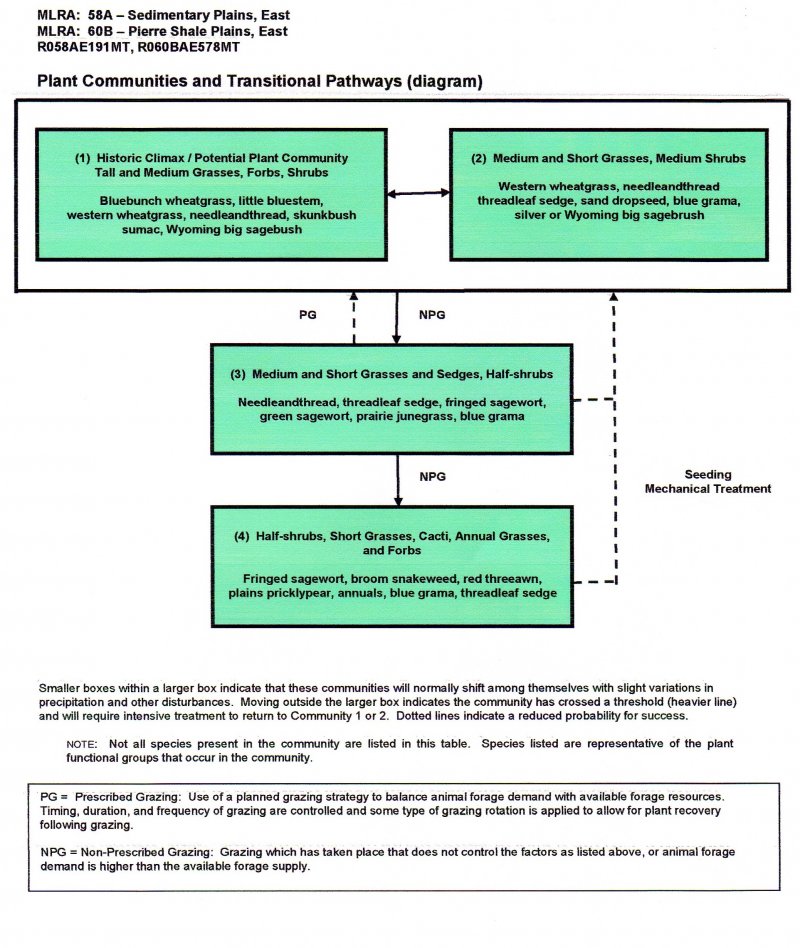
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 4 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Plant Community 1: Tall and Medium Grasses/ Forbs/ Shrubs (HCPC)
Community 1.1
Plant Community 1: Tall and Medium Grasses/ Forbs/ Shrubs (HCPC)
This plant community contains a high diversity of tall and medium height grasses bluebunch wheatgrass, little bluestem, western/thickspike wheatgrass, and needleandthread, and short grasses and sedges (plains muhly, prairie junegrass, Sandberg bluegrass, sun sedge, threadleaf sedge and blue grama). There are abundant forbs, shrubs, and half-shrubs, including skunkbush sumac, prairie rose, fringed safewort, and Wyoming big sagebrush. This plant community is well adapted to the Northern Great Plains climatic conditions. The diversity in plant species allows for high drought tolerance. Individual species can vary greatly in production depending on growing conditions (timing and amount of precipitation and temperature). Plants on this site have strong, healthy root systems that allow production to increase drastically with favorable precipitation. This plant community provides for soil stability and a functioning hydrologic cycle. Adequate plant litter is available for soil buildup and moisture retention.
Figure 2. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 360 | 720 | 960 |
| Forb | 68 | 135 | 180 |
| Shrub/Vine | 22 | 45 | 60 |
| Total | 450 | 900 | 1200 |
Table 6. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 5-10% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 20-30% |
| Forb foliar cover | 1-5% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0% |
| Biological crusts | 0-1% |
| Litter | 0% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 0% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 0% |
Table 7. Soil surface cover
| Tree basal cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana basal cover | 1-4% |
| Grass/grasslike basal cover | 5-10% |
| Forb basal cover | 1-4% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0% |
| Biological crusts | 0-1% |
| Litter | 20-30% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0-5% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 0% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 50-60% |
Table 8. Canopy structure (% cover)
| Height Above Ground (ft) | Tree | Shrub/Vine | Grass/ Grasslike |
Forb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.5 | – | – | – | – |
| >0.5 <= 1 | – | – | – | – |
| >1 <= 2 | – | 5-10% | 20-30% | 1-5% |
| >2 <= 4.5 | – | – | – | – |
| >4.5 <= 13 | – | – | – | – |
| >13 <= 40 | – | – | – | – |
| >40 <= 80 | – | – | – | – |
| >80 <= 120 | – | – | – | – |
| >120 | – | – | – | – |
State 2
Plant Community 2: Medium and Short Grasses/ Medium Shrubs
Community 2.1
Plant Community 2: Medium and Short Grasses/ Medium Shrubs
Slight variations in the Historic Climax plant community result in a community where the western wheatgrass and needleandthread become slightly more dominant, along with several of the short grasses. Forbs and shrubs such as silver or Wyoming big sagebrush, may also slightly increase. Grass biomass production and litter become reduced on the site as the taller grasses disappear, increasing evapotranspiration and reducing moisture retention. Additional open space in the community can result in undesirable invader species. This plant community provides for moderate soil stability.
State 3
Plant Community 3: Medium and Short Grasses and Sedges/ Half-shrubs
Community 3.1
Plant Community 3: Medium and Short Grasses and Sedges/ Half-shrubs
With continued disturbance, the community becomes dominated by needleandthread, short grasses and sedges such as threadleaf sedge, prairie junegrass, and blue grama. Forbs and half-shrubs such as green and fringed sagewort begin comprising a larger part of the plant community. This plant community is less productive than Plant Community 1 or 2. The lack of litter and short plant heights result in higher soil temperatures, poor water infiltration rates, and high evapotranspiration, which gives blue grama a competitive advantage over the cool season tall and medium grasses. This community has lost many of the attributes of a healthy rangeland, including good infiltration, minimal erosion and runoff, nutrient cycling and energy flow. This community will respond positively to improved grazing management, but significant economic inputs and time would be required to move this plant community toward a higher successional stage and a more productive plant community.
State 4
Plant Community 4: Half-shrubs/ Short Grasses/ Cacti/ Annual Grasses and Forbs
Community 4.1
Plant Community 4: Half-shrubs/ Short Grasses/ Cacti/ Annual Grasses and Forbs
If disturbance continues for a long enough period, with loss of topsoil and an increase of bare ground, the community will change to one dominated primarily by short grasses and sedges, shrubs such as silver sagebrush, half-shrubs such as broom snakeweed and fringed sagewort, and annuals and biennials. Plains prickly pear expands onto the site. Once the community has reached this condition, it is very difficult to return to a community similar to the Historic Climax plant community without some major inputs, such as reseeding. This community has extremely reduced forage value for livestock and wildlife. Significant economic inputs and time would be required to move this plant community toward a higher successional stage and a more productive plant community. The potential for using seeding or mechanical treatment to improve site health is limited due to the shallow depth to sand and gravel.
Additional community tables
Table 9. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Native grasses | 355–840 | ||||
| bluebunch wheatgrass | PSSP6 | Pseudoroegneria spicata | 68–480 | – | ||
| little bluestem | SCSCS | Schizachyrium scoparium var. scoparium | 22–180 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 22–180 | – | ||
| plains muhly | MUCU3 | Muhlenbergia cuspidata | 22–120 | – | ||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 22–120 | – | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 22–120 | – | ||
| tufted wheatgrass | ELMA7 | Elymus macrourus | 22–120 | – | ||
| 2 | Native grasses and sedges | 4–120 | ||||
| Grass, perennial | 2GP | Grass, perennial | 4–60 | – | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 4–60 | – | ||
| threadleaf sedge | CAFI | Carex filifolia | 4–60 | – | ||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 4–60 | – | ||
| prairie sandreed | CALO | Calamovilfa longifolia | 4–60 | – | ||
| plains reedgrass | CAMO | Calamagrostis montanensis | 4–60 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 4–60 | – | ||
| Sandberg bluegrass | POSE | Poa secunda | 4–60 | – | ||
| 3 | Native grasses | 1–2 | ||||
| Fendler threeawn | ARPUL | Aristida purpurea var. longiseta | 1–2 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 4 | Native forbs | 68–180 | ||||
| Forb, perennial | 2FP | Forb, perennial | 4–60 | – | ||
| onion | ALLIU | Allium | 4–60 | – | ||
| tarragon | ARDR4 | Artemisia dracunculus | 4–60 | – | ||
| milkvetch | ASTRA | Astragalus | 4–60 | – | ||
| white prairie clover | DACA7 | Dalea candida | 4–60 | – | ||
| purple prairie clover | DAPU5 | Dalea purpurea | 4–60 | – | ||
| blacksamson echinacea | ECAN2 | Echinacea angustifolia | 4–60 | – | ||
| American licorice | GLLE3 | Glycyrrhiza lepidota | 4–60 | – | ||
| hairy false goldenaster | HEVI4 | Heterotheca villosa | 4–60 | – | ||
| dotted blazing star | LIPU | Liatris punctata | 4–60 | – | ||
| spiny phlox | PHHO | Phlox hoodii | 4–60 | – | ||
| white milkwort | POAL4 | Polygala alba | 4–60 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 4–60 | – | ||
| American vetch | VIAM | Vicia americana | 4–60 | – | ||
| 5 | Native forbs | 1–2 | ||||
| deathcamas | ZIGAD | Zigadenus | 1–2 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 6 | Native shrubs and half-shrubs | 22–60 | ||||
| Shrub, broadleaf | 2SB | Shrub, broadleaf | 4–60 | – | ||
| silver sagebrush | ARCA13 | Artemisia cana | 4–60 | – | ||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 4–60 | – | ||
| Wyoming big sagebrush | ARTRW8 | Artemisia tridentata ssp. wyomingensis | 4–60 | – | ||
| yellow rabbitbrush | CHVI8 | Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus | 4–60 | – | ||
| rubber rabbitbrush | ERNAN5 | Ericameria nauseosa ssp. nauseosa var. nauseosa | 4–60 | – | ||
| creeping juniper | JUHO2 | Juniperus horizontalis | 4–60 | – | ||
| skunkbush sumac | RHTR | Rhus trilobata | 4–60 | – | ||
| prairie rose | ROAR3 | Rosa arkansana | 4–60 | – | ||
| soapweed yucca | YUGL | Yucca glauca | 4–60 | – | ||
| 7 | Native shrubs and half-shrubs | 1–2 | ||||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 1–2 | – | ||
| plains pricklypear | OPPO | Opuntia polyacantha | 1–2 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Livestock Grazing Interpretations:
Managed livestock grazing is suitable on this site as it has the potential to produce a moderate amount of high quality forage. Forage production may be somewhat limited on sites with steep slopes where the potential for runoff is high, reducing the effectiveness of the precipitation received for plant growth. The steeper slopes may also limit livestock travel and result in poor grazing distribution, especially in areas away from water. Management objectives should include maintenance or improvement of the plant community. Shorter grazing periods and adequate re-growth after grazing are recommended for plant maintenance and recovery. Heavy stocking and season long use of this site can be detrimental and will alter the plant community composition and production over time.
Whenever Plant Community 2 (medium and short grasses) occurs, grazing management strategies need to be implemented to avoid further deterioration. This community is still stable, productive, and healthy provided it receives proper management. This community will respond fairly quickly to improved grazing management including increased growing season rest of key forage plants. Grazing management alone can usually move this community back to one more similar to potential if a good seed source of the taller grasses still exists.
Plant Community 3 or 4 have extremely reduced forage value for livestock and wildlife. Once this site is occupied by these communities, it will be more difficult to restore it to a community that resembles the potential with grazing management alone. Additional growing season rest is often necessary for re-establishment of the desired species and to restore the stability and health of the site.
The potential for using seeding and/or mechanical treatment to improve site health is limited due to the shallow depth to sand and gravel.
Wildlife Interpretations:
The following is a description of habitat values for the different plant communities that may occupy the site:
Plant Community 1: Tall and Medium Grasses/ Forbs/ Shrubs (HCPC):
The predominance of grasses plus a diversity of forbs, shrubs and half-shrubs in this community favors grazers and mixed feeders such as bison, pronghorn and elk. Warm season grasses extend the availability of nutritious forage for grazers. Large animal nutrition levels are relatively high yearlong because of the diversity of plant life forms and seasonality. Complex plant structural diversity provides habitat for a variety of small mammals (mainly seedeaters, i.e. deer mice) and neotropical migratory birds. The diversity of grass life forms and heights, along with scattered shrubs and a variety of forbs, provides habitat for many bird species including the long-billed curlew, vesper sparrow, and western meadowlark. Residual grass and litter cover provide nesting habitat for a number of bird species, particularly those favoring somewhat sparser cover than is available on deep soils.
Plant Community 2: Medium and Short Grasses/ Medium Shrubs:
Some loss of litter and residual grass cover degrades ground-nesting bird habitat somewhat. A more open ground cover may provide lek sites for sage grouse, if large expanses of sagebrush-grassland are nearby. The loss of warm season grasses shortens the green feed period for grazers and mixed feeders. Pronghorn and mule deer may forage on abundant forbs and shrubs/half-shrubs.
Plant Community 3: Medium and Short Grasses and Sedges/ Half-shrubs:
A general loss of plant species diversity, litter and residual cover reduce wildlife habitat value considerably. Ground-nesting bird habitat suffers from a lack of cover. Sage grouse may find lek sites here if the community is adjacent to large blocks of sagebrush-grassland. Other bird species such as mountain plovers and long-billed curlews may nest in the sparse cover. Small mammal species composition is simplified, mainly consisting of deer mice. Selective feeders, such as mule deer and pronghorn forage on forbs and shrubs/half-shrubs.
Plant Community 4: Half-shrubs/ Short Grasses/ Cacti/ Annuals:
Wildlife habitat value is generally quite low. Bird species favoring sparse cover, including mountain plovers and McCown’s longspurs may nest in this community. Seed production from annuals and scattered perennial grasses and forbs will support some deer mice.
Hydrological functions
The soils associated with this ecological site are generally in Hydrologic Soil Group B. The infiltration rates for these soils will normally be moderate. The runoff potential for this site is moderate, depending on slope and ground cover/health. Runoff curve numbers generally range from 76 to 94.
Good hydrologic conditions exist on rangelands if plant cover (grass, litter, and brush canopy) is greater than 70%. Fair conditions exist when cover is between 30 and 70%, and poor conditions exist when cover is less than 30%. Sites in high similarity to HCPC (Plant Communities 1 and 2) generally have enough plant cover and litter to optimize infiltration, minimize runoff and erosion, and have a good hydrologic condition. The deep root systems of the potential vegetation help maintain or increase infiltration rates and reduce runoff.
Sites in low similarity (Plant Communities 3 and 4) are generally considered to be in poor hydrologic condition as the majority of plant cover is from shallow-rooted species such as blue grama and annual grasses, and half-shrubs.
Erosion is minor for sites in high similarity. Rills and gullies should not be present. Water flow patterns, if present, will be barely observable. Plant pedestals are essentially non-existent. Plant litter remains in place and is not moved by erosion. Soil surfaces should not be compacted or crusted. Plant cover and litter helps retain soil moisture for use by the plants. Maintaining a healthy stand of perennial vegetation will optimize the amount of precipitation that is received. (Reference: Engineering Field Manual, Chapter 2 and Montana Supplement 4).
Recreational uses
This site provides recreational opportunities for big game and upland bird hunting, and hiking. The forbs have flowers that appeal to photographers. This site provides valuable open space and visual aesthetics.
Other information
The following is an example of how to calculate the recommended stocking rate. This example does not use production estimates from this specific ecological site. You will need to adjust the annual production values and run the calculations using total annual production values from the ecological sites encountered on each individual ranch/pasture. Before making specific recommendations, an on-site evaluation must be made.
Example of total annual production amounts by type of year:
Favorable years = 2200 lbs/acre
Normal years = 1480 lbs/acre
Unfavorable years = 1200 lbs/acre
It is recommended that on slopes of 30% or less, stocking rate should be derived from the total annual production pounds minus 500 pounds for residual dry matter and 25% harvest efficiency. On slopes over 30%, stocking rate is derived from total annual production pounds minus 800 pounds for residual dry matter and 25% harvest efficiency. Refer to the NRCS National Range and Pasture Handbook for a list of Animal Unit Equivalents.
Sample Calculations using Favorable Year production amounts:
< 30% slopes: AUM/AC = [(2200-500)(0.25)]/915 lbs/month for one AU = 0.46 AUM/AC
AC/AUM = (1.0 AU)/(0.46AUM/AC) = 2.2 AC/AUM
> 30% slopes: AUM/AC = [(2200-800)(0.25)]/915 lbs/month for one AU = 0.38 AUM/AC
AC/AUM = (1.0 AU)/(0.38 AUM/AC) = 2.6 AC/AUM
NOTE: 915 lbs/month for one Animal Unit is used as the baseline for maintenance requirements. This equates to 30 lbs/day of air-dry forage (1200 lb cow at 2.5% of body weight).
Supporting information
Inventory data references
NRCS-Production & Composition Record for Native Grazing Lands (Range-417): 13
BLM-Soil & Vegetation Inventory Method (SVIM) Data: 6
NRCS-Range Condition Record (ECS-2): 30
NRCS-Range/Soil Correlation Observations & Soil 232 notes: 14
Contributors
Bob Leinard
JVF, REL, RSN, MJR, SKW, SVF, POH
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | T. DeCock; R Kilian |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | Tammy DeCock |
| Date | 06/11/2014 |
| Approved by | Jon Siddoway |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
None. -
Presence of water flow patterns:
None on slopes less than 25%. On slopes 25 – 40% water flow patterns may be 2-3 feet long and 4 inches wide. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
Not evident on slopes < 20%. On slopes greater than 20% erosional pedestals up to .5 inches high may be present with terracettes present at debris dams. -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
Bare ground is < 50%. Bare ground will occur as small areas less than 5 inches in diameter. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
Active gullies should not be present. Existing gullies should be “healed” with a good vegetative cover. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
None. -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Plant litter remains in place and is not moved by erosional forces on slopes less than 25%. Herbaceous litter may move up to 4 inches on slopes > 25%. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Surface Soil Aggregate Stability under plant canopy should typically be 5. Surface Soil Aggregate Stability not under plant canopy should typically be 4 slightly less. -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
Use soil survey series description. -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
A combination of shallow and deep rooted species have a positive effect on infiltration rate. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
No compaction layer or soil surface crusting should be evident. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Cool season, mid-stature, bunch grassesSub-dominant:
Warm season, mid-stature, bunch grasses > forbs > Cool season, mid-stature, rhizomatous grasses = Cool season, short-stature, bunch grasses and sedgesOther:
Minor components: Warm season, mid-stature, rhizomatous grasses > Warm season, short-stature, rhizomatous grasses = Warm season, tall stature, rhizomatous grasses = Cool season, short-stature, rhizomatous grasses and sedges = shrubs and half shrubsAdditional:
(Blue grama should be grouped with warm season, short-stature, rhizomatous grasses due to its growth form) -
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Very low. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Litter cover is in contact with soil surface. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
1050 to 1200 #/acre (13 to 14 inch precip. Zone) 450 to 900 #/ac (10 to 12 inch precip. Zone). -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
Knapweeds, whitetop, Dalmatian toadflax, St. Johnswort, perennial pepperweed. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
All species are capable of reproducing.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.