Animal community
Wildlife Interpretations
Landscape:
The MLRA 58C landscape is characterized by moderately dissected rolling plains with areas of local Badlands, buttes, and isolated hills. MLRA 58C is considered to have a continental climate with cold winters and hot summers, low humidity, light rainfall, and much sunshine. Extremes in temperature are common and characteristic of the MLRA. This area supports natural mixed-grass prairie vegetation with prairie rose, leadplant, and patches of western snowberry interspersed throughout the area. Green ash, chokecherry, and buffaloberry occur in draws and narrow valleys, creating woody riparian corridors. Complex/intermingled ecological sites create diverse grass- and shrubland habitats interspersed with varying densities linear, slope, depressional, and in-stream wetlands associated with headwater streams and tributaries to the Missouri River. These habitats provide critical life-cycle components for many wildlife species.
Historic Communities/Conditions within MLRA 58C:
The northern mixed-grass prairie was a disturbance-driven ecosystem with fire, herbivory, and climate functioning as the primary ecological drivers (either singly or often in combination). Many species of grassland birds, small mammals, insects, reptiles, amphibians, and large herds of Audubon bighorn sheep, roaming bison, elk, and pronghorn were historically among the inhabitants adapted to this semi-arid region. Bighorn sheep have been re-introduced. Roaming herbivores, as well as several small mammal and insect species, were the primary consumers linking the grassland resources to large predators (such as the wolf, mountain lion, and grizzly bear) and smaller carnivores (such as the coyote, bobcat, red fox, and raptors). The black-tailed prairie dog was once abundant and provided ecological services by manipulating the plant and soil community providing habitat for the black-footed ferret, burrowing owl, ferruginous hawk, mountain plover, swift fox, small mammals, and amphibians and reptiles. Extirpated species include free-ranging American bison, Canada lynx, common raven, grizzly bear, gray wolf, black-footed ferret, mountain plover, and peregrine falcon (breeding). Extinct from the region is the Rocky Mountain locust.
Present Communities/Conditions within MLRA 58C:
Following European influence, domestic livestock grazing, elimination of fire, energy development, and other anthropogenic factors influenced plant community composition and abundance. Transportation corridors, energy development, and Rocky Mountain juniper and ponderosa pine encroachment are the main factors contributing to habitat fragmentation, reducing habitat quality for area-sensitive species. These influences fragmented the landscape, reduced or eliminated ecological drivers (fire), and introduced exotic plant species including smooth brome, crested wheatgrass, Kentucky bluegrass, and leafy spurge further impacting plant and animal communities. The loss of the bison, reduction of black-tailed prairie dogs, and fire, as primary ecological drivers, greatly influenced the character of the remaining native plant communities and the associated wildlife moving towards a less diverse and more homogeneous landscape, lacking diverse species composition and stature.
Extensive fragmentation by annual cropping has not occurred within the MLRA. Limited fragmentation from annual cropping or tame hay production has occurred within the Little Missouri River flood plain and the higher, flat plateaus. Fragmentation east and west of MLRA 58C has funneled many species into this area in search of expansive grasslands.
Some wildlife species in this area are: mule deer, white-tailed deer, elk, bighorn sheep, pronghorn, mountain lion, coyote, red fox, bobcat, prairie rattlesnake, American badger, raccoon, North American porcupine, beaver, striped skunk, American mink, white-tailed jackrabbit, black-tailed prairie dog, Eastern and Merriam’s wild turkey, golden eagle, ferruginous hawks, sharp-tailed grouse, greater sage-grouse, black-billed magpie, and numerous species of grassland-nesting birds and pollinating insects. The highest diversity of bats in North Dakota also occurs in this MLRA, where eleven species have been documented.
Presence of wildlife species is often determined by ecological site characteristics including grass and forb species, hydrology, aspect, and other associated ecological sites. Home ranges for most species are larger than one ecological site or are dependent on more than one ecological site for annual life requisites. Ecological sites offer different habitat elements as the annual life requisites change. Habitat improvement and creation must be conducted within the mobility limits of a known population for the species.
Insects play an important role providing ecological services for plant community development. Insects that are scavengers or aid in decomposition provide the food chain baseline sustaining the carnivorous insects feeding upon them. Many insects provide the ecological services necessary for pollination, keeping plant communities healthy and productive. Insects provide a protein food source for numerous species including grassland nesting birds and their young.
Species unique to the MLRA:
Mountain Lions: Mountain lions were relatively common in the Badlands but disappeared from the state by the early 20th Century. Sightings resumed in the 1950’s and have subsequently increased since that time. The species has recently taken up permanent residency within the region. Mountain lions occur in of the Little Missouri Badlands and woody habitat in MLRA 58C. Rugged terrain and forest provide excellent stalking cover to hunt large mammals and other prey. Mountain lions make use of caves for escape and loafing cover.
Bighorn sheep: Bighorn sheep make use of the rugged terrain, rocky outcrops, and high plateaus of MLRA 58C along the Little Missouri River. North Dakota bighorn sheep populations are almost exclusively within MLRA 58C. Bighorn sheep were once extirpated from North Dakota but were successfully reintroduced in the mid-twentieth century. They now occur in several distinct populations within MLRA 58C. Rocky Mountain juniper encroachment degrades the limited habitat for bighorn sheep. Managers should consider bighorn sheep association with domestic sheep, since transfer of pneumonia and other diseases is known to occur.
Golden eagle: The badlands within MLRA 58C are key areas for Golden eagle nesting. Adjacent grasslands, shrublands, and black-tailed prairie dog towns are used for hunting.
Bats: MLRA 58C provides life requisites for several bat species, in part due to presence of riparian forest, wooded draws, caves, and rocky outcrops. Hibernacula of six bat species have been found in MRLA 58C; however, additional work is needed to further understand utilization of hibernacula by bats during the winter months in North Dakota.
Short-horned lizard and sagebrush lizard: This MLRA provides preferred habitat for these two species. The short-horned lizard prefers semi-arid, shortgrass prairie in rough terrain, and is uncommon to locally abundant in MLRA 58C. The rare sagebrush lizard prefers sagebrush and rocky areas provided by this MLRA and adjacent MLRA 58D.
Greater sage-grouse and Brewer’s sparrow: The extreme southwest extension of MLRA 58C have ecological sites capable of producing sufficient big sage canopy cover to provide greater sage-grouse life requisites. MLRA 58C and 58D are the only MLRAs in North Dakota that support Wyoming big sage brush (big sage) production. Research data indicates greater sage-grouse prefer big sagebrush canopy cover for nesting at ≥8% with an average height of around 16 inches. The species prefers winter cover canopy that averages 15% with an average height of around 8 inches. Soil site potential, management, climate, and other factors all play a role in the amount, if any, of big sagebrush on an ecological site. Changes in big sage canopy cover occur slowly (30-50 years) unless the site is impacted by fire or cultivation. Big sage recovery after a burn can take 30 to 100 years. Greater sage- grouse and Brewer’s sparrow habitat and populations are reduced or eliminated when big sagebrush canopy is reduced to less than 8% for greater sage-grouse and 10% cover for Brewer’s sparrow. As conifer encroachment increases, greater sage-grouse lekking activity decreases. Once conifer encroachment exceeds 4% canopy cover, no leks remain.
Species of Concern within the MLRA:
Following is a list of species considered “species of conservation priority” in the North Dakota State Wildlife Action Plan (2015); “species of greatest conservation need” in the Montana State Wildlife Action Plan (2015); and species listed as “threatened, endangered, or petitioned” under the Endangered Species Act within MLRA 58C at the time this section was developed:
Invertebrates: Dakota skipper, monarch butterfly, regal fritillary, yellow-banded bumble bee, and western bumble bee.
Birds: American kestrel, Baird’s sparrow, bald eagle, black-billed cuckoo, bobolink, Brewer’s sparrow, burrowing owl, chestnut-collared longspur, common poorwill, eastern screech-owl ferruginous hawk, golden eagle, grasshopper sparrow, greater sage-grouse, lark bunting, loggerhead shrike, long-billed curlew, marbled godwit, McCown’s longspur, mountain plover, northern harrier, northern pintail, peregrine falcon (migration), prairie falcon, red knot (migration), red-headed woodpecker, sharp-tailed grouse, short-eared owl, Sprague’s pipit, Swainson’s hawk, upland sandpiper, western meadowlark, Wilson’s phalarope, whooping crane (migration), and willet.
Mammals: Big brown bat, black-footed ferret, black-tailed prairie dog, dwarf shrew, gray wolf, hispid pocket mouse, little brown bat, long-eared bat, long-legged bat, meadow jumping mouse, Merriam’s shrew, northern long-eared bat, porcupine, sagebrush vole, swift fox, Townsend’s big- eared bat, and western small-footed bat.
Amphibians and Reptiles: Common snapping turtle, Great Plains toad, greater short-horned lizard, milk snake, northern leopard frog, plains hognose snake, plains spadefoot, sagebrush lizard, smooth softshell, smooth green snake, and spiny softshell.
Fish and Mussels: Blue sucker, burbot, Flathead chub, northern redbelly dace, sickle-fin chub, pearl dace, shortnose gar, sturgeon chub, and sauger.
Grassland Management for Wildlife in the MLRA
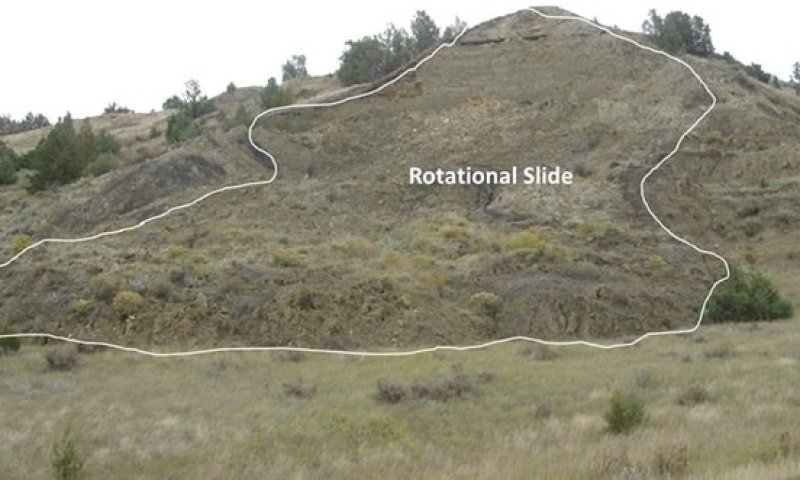
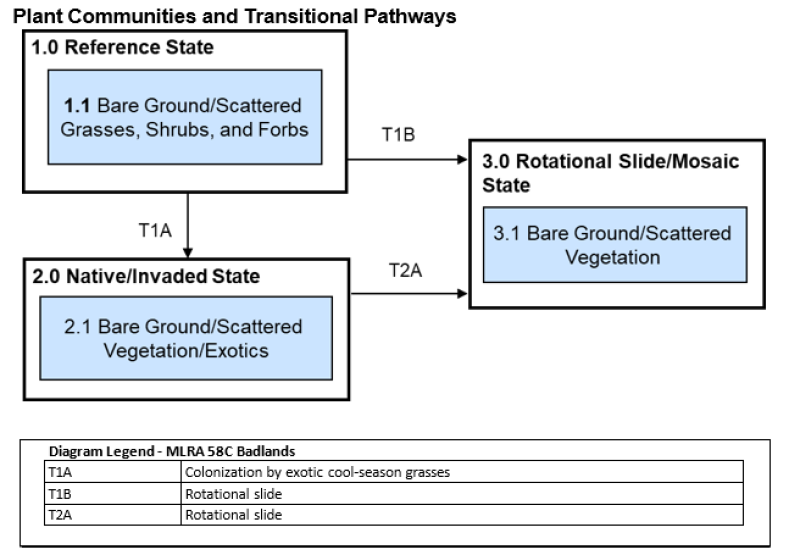
Management activities within the community phase pathways impact wildlife. Community phase, transitional, and restoration pathways are keys to long-term management within each State and between States. Significant inputs must occur to cross the threshold between States (e.g., State 3.0 to 2.0) requiring substantial economic inputs and management (mechanical, reseeding, prescribed fire, woody vegetation removal, grazing intensity, etc.). Timing, intensity, and frequency of these inputs can have dramatic positive or negative effects on local wildlife species. Ranchers and other land managers must always consider the long-term beneficial effects of management on the habitat in comparison to potential short-term negative effects to individuals.
Ecological sites occur as intermingled complexes on the landscape with gradual or sometimes abrupt transitions. Rarely do ecological sites exist in large enough acreage to manage independently. Ecological sites, supporting a dominance of herbaceous vegetation (Loamy/Limy Residual), can be located adjacent to ecological sites that support medium to tall shrubs (Loamy Overflow). Conversely, ecological sites that are dominated by short to mid statured grasses (Claypan) can be adjacent to sites with bare soil only supporting minor amounts of short grasses and forbs (Thin Claypan).
Management of these complex ecological sites can provide a heterogeneous or a homogenous landscape. Grassland bird use declines as the plant community transitions to a homogenous state. Managers need to recognize ecological sites and the complexes they occur in to properly manage the landscape. A management regime for one ecological site may negatively impact an adjacent site (e.g., alteration of a grazing regime within a Flat Bottom Wooded Draw ecological site to encourage understory growth may encourage exotic, cool-season grasses to increase or dominate an adjacent ecological site).
Life requisites and habitat deficiencies are determined for targeted species. Deficiencies need to be addressed along community phase, transitional, and restoration pathways as presented in specific state and transition models. Ecological sites should be managed and restored within the capabilities of the site to provide sustainable habitat. Managers also need to consider habitat provided by adjacent/intermingled ecological sites for species with home ranges or life requisites that cannot be provided by one ecological site.
With populations of many grassland-nesting birds in decline, it is important to maintain these ecological sites in a 1.0 Reference State or the 2.0 Native/Invaded. Plant communities, optimal for a guild of grassland species, serve as a population source where the birth rate exceeds mortality. Species may use marginal plant communities; however, these sites may function as a population sink where mortality exceeds the birth rate.
Understanding preferred vegetative stature and sensitivity to woody encroachment is necessary to manage for the specific grassland species. Various grass heights may be used for breeding, nesting, foraging, or winter habitat. While most species use varying heights, many have a preferred vegetative stature height. Please reference the provisional ESD on the North Dakota eFOTG (linked below) for a chart that provides preferred vegetative stature heights and sensitivity to woody vegetation encroachment.
https://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/references/public/ND/58C_Badland_Narrative_FINAL.pdf
Badland Wildlife Habitat Interpretation:
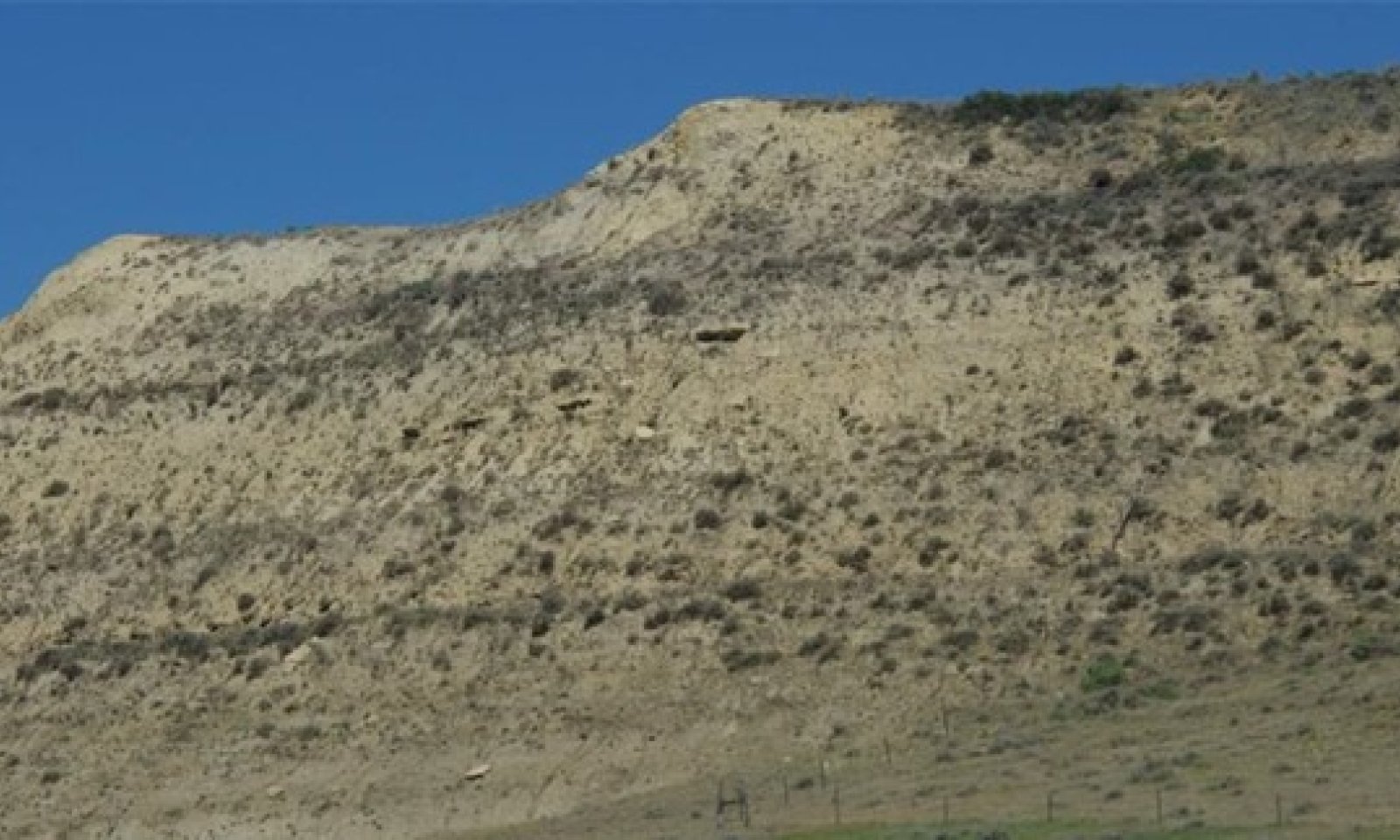
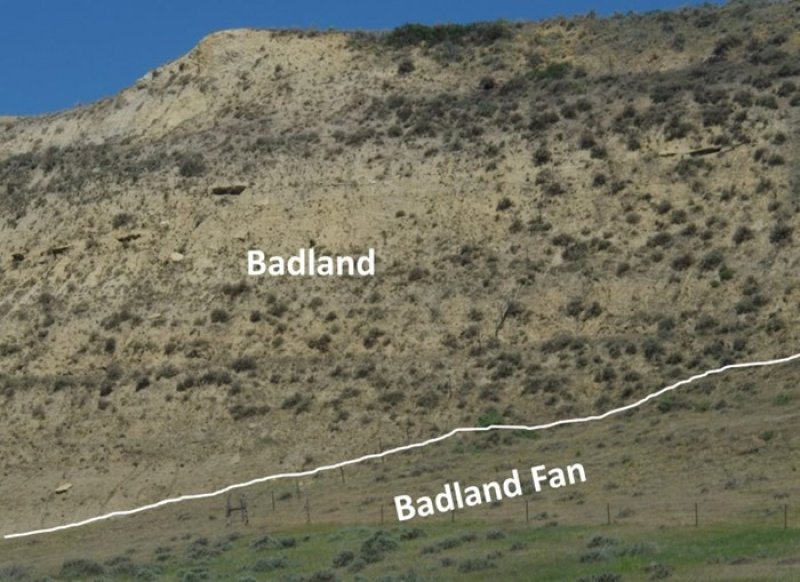
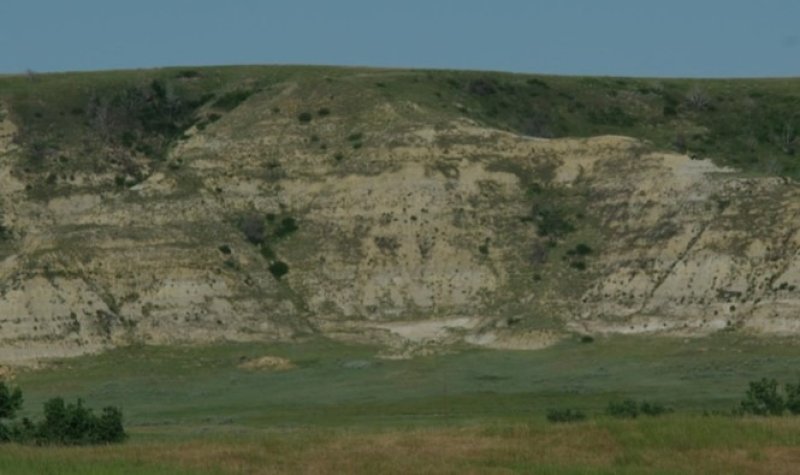
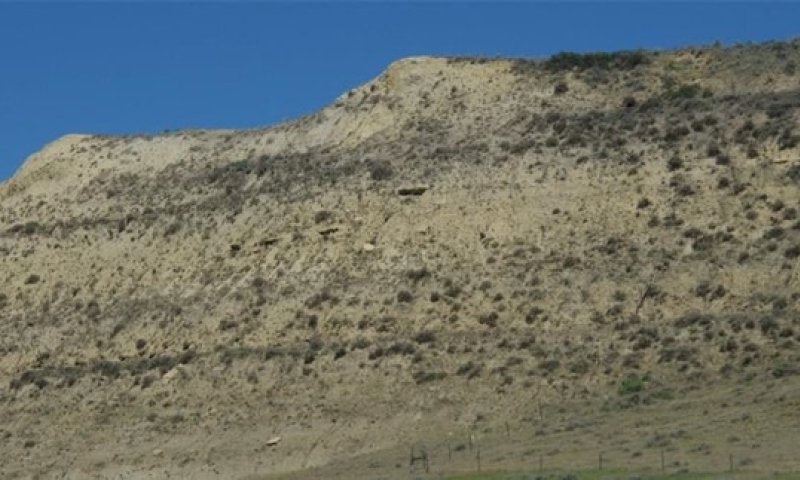
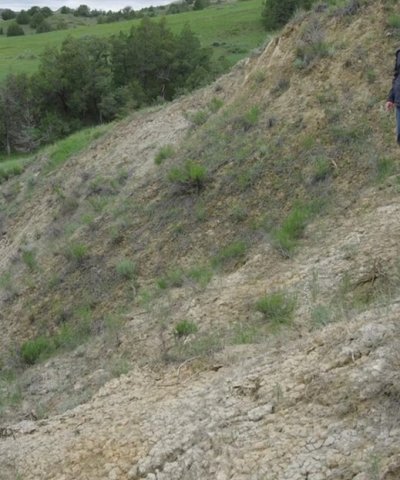
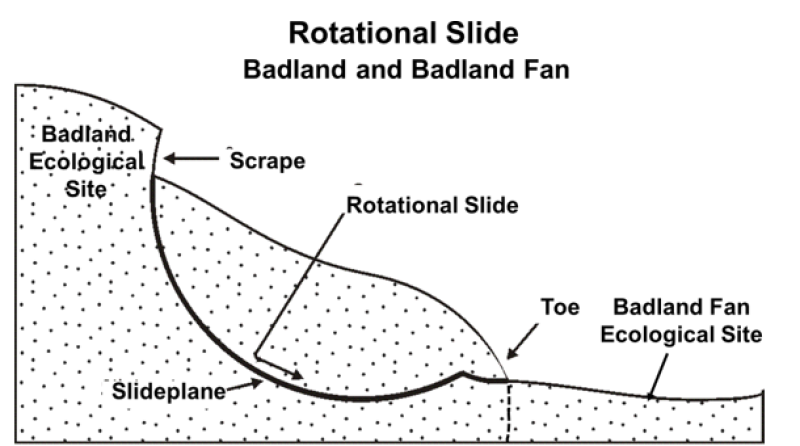
Badland ecological sites consist of bare, eroding exposures of soft siltstone and shale bedrock on steep-sided buttes, escarpments, knobs, ridges, and in deeply entrenched, steep-sided- drainageways. The exposed bedrock makes up about 80 percent of any given area and supports little or no vegetation. Associated ecological sites include Badland Fan, Limy Residual, Very Shallow, and Shallow Loamy.
Badland ecological sites are steep with limited grasses, forbs, or shrubs. Bare ground and exposed bedrock dominate the site providing limited food and cover for wildlife. Steep slopes limit ground dwelling mammals and grazing herbivores. Badland ecological sites provide excellent habitat for bighorn sheep using these sites for escape, loafing, and lambing areas. Steep slopes provide excellent visibility to detect predators while the associated ecological sites provide foraging opportunities. These associated sites commonly support grassland nesting birds and forage, escape, and thermal cover for small herbivores. The short statured vegetation of these associated sites is preferred by short-grass nesting birds.
Grazing Interpretations
Due to site conditions, (e.g., steep slopes, limited forage production, etc.), grazing on this site is limited. Therefore, grazing management efforts should be concentrated on adjacent sites and should be applied that enhances the competitive advantage of native grass and forb species. This may include: (1) grazing when exotic cool-season grasses are actively growing and native cool-season grasses are dormant; (2) applying proper deferment periods allowing native grasses to recover and maintain or improve vigor; (3) adjusting overall grazing intensity to reduce excessive plant litter (above that needed for rangeland health indicator #14 – see Rangeland Health Reference Worksheet); (4) incorporating early heavy spring utilization which focuses grazing pressure on exotic cool-season grasses and reduces plant litter, provided that livestock are moved when grazing selection shifts from exotic cool-season grasses to native grasses.
Grazing levels are noted within the plant community narratives and pathways in reference to grazing management on adjacent sites. “Degree of utilization” is defined as the proportion of the current years forage production that is consumed and/or destroyed by grazing animals (may refer to a single plant species or a portion or all the vegetation). “Grazing utilization” is classified as slight, moderate, full, close, and severe (see the following table for description of each grazing use category). The following utilization levels are also described in the Ranchers Guide to Grassland Management IV. Utilization levels are determined by using the landscape appearance method as outlined in the Interagency Technical Reference “Utilization Studies and Residual Measurements” 1734-3.
Utilization Level:
Slight (Light) 0-20% Appears practically undisturbed when viewed obliquely. Only choice areas and forage utilized.
Moderate 20-40% Almost all of accessible range shows grazing. Little or no use of poor forage. Little evidence of trailing to grazing.
Full 40-60% All fully accessible areas are grazed. The major sites have key forage species properly utilized (about half taken, half left). Points of concentration with overuse limited to 5 to 10 percent of accessible area.
Close (Heavy) 60-80% All accessible range plainly shows use and major sections closely cropped. Livestock forced to use less desirable forage, considering seasonal preference.
Severe > 80% Key forage species completely used. Low-value forages are dominant.
Recreational uses
The largest acreage of public land available for recreation in the MLRA is owned and managed by the United States Forest Service (USFS) within the Little Missouri National Grasslands in North Dakota (525,211 acres). These areas are available for hunting, fishing, hiking, camping, horse and bike riding, nature viewing, etc. In addition, the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) manages 30,895 acres in North Dakota and Montana with the same recreational opportunities as the USFS lands. North Dakota and Montana Department of Trust Lands (80,220 acres) provide hunting, bird watching, hiking, and other outdoor recreation opportunities. North Dakota Wildlife Management Areas (3,447 acres) of land managed by the states for wildlife habitat in MLRA 58C.
MLRA 58C is home to the North and South Units of Theodore Roosevelt National Park. The Park encompasses approximately 70,000 acres and welcomes approximately 900,000 visitors annually. 29,920 acres of the park is designated Wilderness Area. The south unit of the park has a 48-mile scenic drive while the north unit has a 28-mile scenic drive. The Badland and associated ecological sites provide the main scenery attraction.
Bird watching: Public and private grasslands within MLRA 58C provide essential habitat for prairie-dependent bird species (such as Sprague's pipits, western meadowlark, and Baird's sparrow) along with some of the larger, showy members of the upland prairie including marbled godwits, upland sandpipers, and willets. The abundance of publicly owned lands (such as Theodore Roosevelt National Park, USFS, North Dakota Department of Trust Lands, BLM, etc.) provide excellent birding opportunities. MLRA 58C is in the Central Flyway.
Hunting/Fishing: MLRA 58C is a fall destination for upland game bird hunters, especially sharp-tailed grouse. This MLRA also provides excellent white-tailed deer, mule deer, pronghorn, elk, coyote, and mountain lion hunting opportunities along with the only bighorn sheep hunting units in the North Dakota. The North Dakota Game and Fish Department manages three man-made fishing lakes within the MLRA. Available species include rainbow and brown trout, bluegill, and largemouth and smallmouth bass.
Camping: Many camping opportunities exist in the MLRA. Modern and primitive camping is available at the Theodore Roosevelt National Park, Sully’s Creek State Park, Little Missouri State Park, Buffalo Gap Campground, BLM land, and the Dakota Prairie National Grasslands. The Sully’s Creek and Little Missouri State Parks are designated horse parks.
Hiking/Biking: Over 150 miles of the May-Daah-Hey Trail provide some of the best single-track trails in the world for biking, hiking, or horseback riding. The International Mountain Biking Association (IMBA) has designated the hiking, biking, and horseback riding trail as EPIC - meaning it’s one of the top mountain biking trails in the United States. The trail has nine fenced campgrounds, each accessible by gravel surfaced roads; they include camping spurs, potable water, hitching rails, picnic tables, fire rings, and accessible toilets. They are spaced about every 20 miles along the trail. The North and South Units of the Theodore Roosevelt National Park provide 38.9 and 49.6 miles, respectively, of hiking trails for walkers, bikers, or horseback riders. The Little Missouri State Park has 45 miles of trails that run through the North Dakota Badlands.
Canoeing: Traversing 274 miles through MLRA 58C, the Little Missouri River provides early spring canoeing and kayaking. The Little Missouri River is the only designated State Scenic River in the MLRA. The river passes through Sully Creek State Park, the Little Missouri National Grassland, and Theodore Roosevelt National Park.