Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R058DY027SD
Sandy Claypan
Last updated: 7/18/2024
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
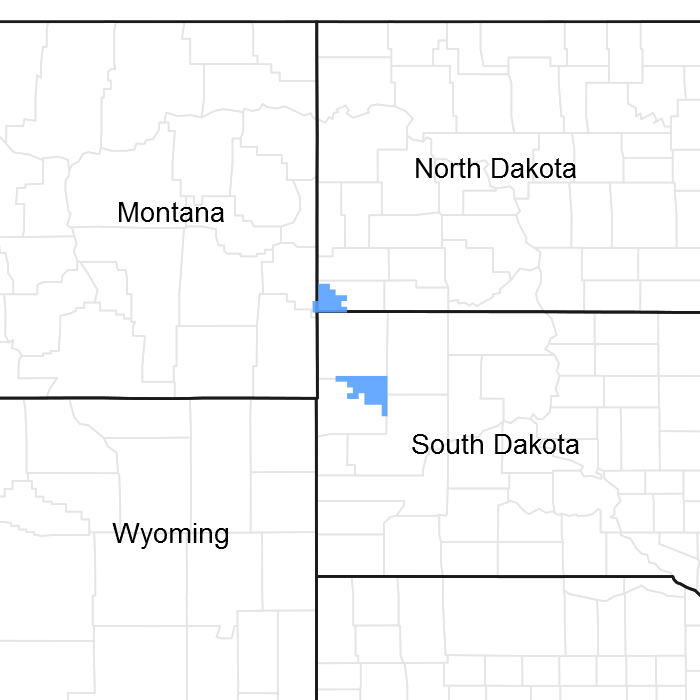
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 058D–Northern Rolling High Plains, Eastern Part
The Northern Rolling High Plains, Eastern Part (MLRA 58D) is shared between South Dakota (65 percent), Montana (21 percent), and North Dakota (14 percent). The MLRA is approximately 2,755 square miles. The small towns of Buffalo and Camp Crook, South Dakota, and Marmarth, North Dakota, are all within the boundary of this MLRA, and Baker, Montana, is on the northern most edge. Portions of the Little Missouri National Grassland and Custer National Forest are also in the MLRA. Portions of the Little Missouri River and the headwaters of major tributaries that eventually form the Grand and Moreau Rivers in South Dakota are also in this area.
The Northern Rolling High Plains, Eastern Part consists of Cretaceous marine and continental sediments of shale, siltstone, and sandstone. The continental and marine Hell Creek Formation is under approximately 85 percent of the MLRA, and the Fox Hills Sandstone forms the southern boundary of the MLRA. Tertiary deposits are in scattered areas throughout the MLRA. These deposits consist of the Paleocene Ludlow and Tongue River Formations, the Oligocene White River Group, and the Miocene Arikaree Group. These Tertiary deposits are resistant and positioned above the Cretaceous beds. Ponderosa pine growing in areas of these Tertiary formations further distinguishes these formations from the other formations in the MLRA. Pleistocene and Holocene river sand and gravel deposits are also on the valley floors and on the terraces along the larger rivers in the area. A large Quaternary eolian deposit is directly south of the town of Buffalo.
The average elevation of MLRA 58D ranges from 2,300 feet to 4,000 feet, increasing gradually from east to west. Harding Peak is the highest point at 4,019 feet. In places, flat-topped, steep-sided buttes rise sharply above the gently rolling plains below.
The dominant soil orders in this MLRA are Alfisols, Entisols, Inceptisols, and Mollisols. The soils in the area dominantly have a frigid soil temperature regime, an ustic soil moisture regime that borders on aridic, and mixed mineralogy. They are shallow to very deep, generally well drained, and loamy or clayey.
Annual precipitation is 14 to 17 inches and can fluctuate widely from year to year. Most rainfall occurs early in the growing season. Some high-intensity thunderstorms occur mid to late summer. The native vegetation in this MLRA consists primarily of grasses and forbs with a small component of trees and shrubs along streams. Ponderosa pine grow on the upper slopes and on the top of some of the higher buttes. Open grasslands are characterized by western wheatgrass, green needlegrass, blue grama, and buffalograss. Wyoming big sagebrush grows on clayey soils in the western part of the MLRA.
More than four-fifths of the MLRA is privately owned ranches running cattle, sheep, or both. Less than 5 percent of the area is federally owned. The major resource concerns are water quality, wind erosion, and water erosion (USDA, NRCS. 2006. Ag Handbook 296).
Classification relationships
USDA
Land Resource Region G—Western Great Plains Range and Irrigated Region:
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 58D—Northern Rolling High Plains, Eastern Part.
US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Level IV Ecoregions of the Conterminous United States:
Northwestern Great Plains—43:
Forested Buttes—43d.
Sagebrush Steppe—43e.
USDA Forest Service
Ecological Subregions: Sections and Subsections of Conterminous United States:
Great Plains - Palouse Dry Steppe Province—331:
Missouri Plateau Section—331M.
Sagebrush Steppe Subsection—334Mi.
Ecological site concept
The Sandy Claypan ecological site is found throughout MLRA 58D. It is located on uplands and does not receive additional moisture from runoff or overflow. Typical slopes range from 1 to 6 percent. Soils are deep (greater than 20 inches) with a fine sandy loam surface texture that is 5 to 14 inches thick. At about 5 to 14 inches below the surface, there is a hard clayey or clay loam (Btn) horizon having round-topped or “bun shaped” columnar or prismatic structure. Subsoils are high in sodium.
The vegetation in the Reference State (1.0) is dominated by cool-season grasses with short warm-season grasses being subdominant. The major grasses include needle and thread, western wheatgrass, and prairie sandreed. Forbs are common and diverse. Shrubs include, rose, fringed sagewort, and silver sagebrush.
Associated sites
| R058DY009SD |
Sandy The Sandy ecological site is be found adjacent to or upslope of the Sandy Claypan ecological site. |
|---|---|
| R058DY010SD |
Loamy The Loamy ecological site is found adjacent to or upslope of the Sandy Claypan ecological site. |
Similar sites
| R058DY009SD |
Sandy The Sandy ecological site will have more warm-season grasses; and more vegetative production than the Sandy Claypan ecological site. |
|---|---|
| R058DY010SD |
Loamy The Loamy ecological site will have more western wheatgrass; less needle and thread; and more vegetative production than the Sandy Claypan ecological site. |
| R058DY013SD |
Claypan The Claypan ecological site will have more rhizomatous wheatgrass, less prairie sandreed, more Wyoming big sagebrush, and lower vegetative production than the Sandy Claypan ecological site. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata |
Physiographic features
The Sandy Claypan ecological site occurs on nearly level to gently sloping uplands.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Fan
(2) Terrace |
|---|---|
| Runoff class | Medium to high |
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 2,300 – 4,000 ft |
| Slope | 1 – 6% |
| Water table depth | 80 in |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
The climate in MLRA 58D is typical of the drier portions of the Northern Great Plains where sagebrush steppes to the west yield to grassland to the east. Average annual precipitation ranges from 14 to 17 inches with most falling in the early growing season. Some high intensity, convective thunderstorms occur in the summer. Precipitation in winter occurs as snow. Temperatures show a wide range between summer and winter and between daily maximums and minimums. This wide range is due to the high elevation and dry air, which permit rapid incoming and outgoing radiation. Outbreaks of cold air from Canada in winter move rapidly from northwest to southeast and account for extreme minimum temperatures. Extreme storms may occur during the winter but have the most severe effect on ranching operations during late winter and in spring.
The normal average annual temperature is about 44 °F. January is the coldest month with average temperatures ranging from about 12 °F (Marmarth, North Dakota) to about 20 °F (Baker, Montana). July is the warmest month with temperatures averaging from about 70 °F (Marmarth, North Dakota) to about 76 °F (Baker, Montana). The range of normal average monthly temperatures between the coldest and warmest months is about 55 °F. Wind speeds are estimated to average about 11 miles per hour (mph) annually, ranging from about 13 mph during the spring to about 10 mph during the summer. Daytime winds are generally stronger than nighttime winds. Strong storms may bring brief periods of high winds with gusts of more than 50 mph.
Growth of cool-season plants begins in early to mid-March, slowing or ceasing in late June. Warm-season plants begin growth about mid-May and continue to early or mid-September. Cool-season plants may green-up in September and October if adequate soil moisture is present.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 97-111 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | 121-129 days |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 15-17 in |
| Frost-free period (actual range) | 93-115 days |
| Freeze-free period (actual range) | 120-132 days |
| Precipitation total (actual range) | 14-17 in |
| Frost-free period (average) | 104 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | 125 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 16 in |
Figure 2. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 3. Monthly minimum temperature range
Figure 4. Monthly maximum temperature range
Figure 5. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 6. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 7. Annual average temperature pattern
Climate stations used
-
(1) BAKER 1 E [USC00240412], Baker, MT
-
(2) LADNER 9SW [USC00394671], Camp Crook, SD
-
(3) CAMP CROOK [USC00391294], Camp Crook, SD
-
(4) BUFFALO ASOS [USW00094037], Buffalo, SD
-
(5) BUFFALO 13 ESE [USW00094081], Reva, SD
-
(6) REDIG 11 NE [USC00397062], Buffalo, SD
-
(7) HOOVER [USC00393945], Newell, SD
Influencing water features
No significant water features influence the Sandy Claypan ecological site.
Soil features
Soils common to the Sandy Claypan ecological site have a fine sandy loam surface layer that is 5 to 14 inches thick. The soils are deep and formed in alluvium and residuum derived from sandstone and shale. Slopes range from 1 to 6 percent. At about 5 to 16 inches below the surface, there is a hard clayey or clay loam Btn horizon having round-topped or “bun shaped” columnar or prismatic structure. These subsoils are high in sodium. Soils are well drained and have a slow to very slow infiltration rate. Subsurface soil layers are restrictive to water movement and root penetration.
This site should show slight to no evidence of rills or wind-scoured areas. Water flow paths are broken, irregular in appearance, or discontinuous with numerous debris dams or vegetative barriers.
Major Soil correlated to the Sandy Claypan ecological site include, Ekalaka, Ladner, and Sorum.
More information can be found in the various soil survey reports. Contact the local USDA Service Center for soil survey reports that include more detail specific to your area of interest, or use the internet to access USDA’s Web Soil Survey.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Alluvium
–
sandstone and shale
(2) Residuum – sandstone and shale |
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Fine sandy loam |
| Family particle size |
(1) Loamy |
| Drainage class | Well drained |
| Permeability class | Very slow to slow |
| Soil depth | 80 in |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | Not specified |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | Not specified |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
4 – 5 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
10% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
4 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
25 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
5.6 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
Not specified |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
Not specified |
Ecological dynamics
The Sandy Claypan ecological site developed under the Northern Great Plains climatic conditions; light to severe grazing by bison and other large herbivores; sporadic, natural or human-caused wildfire (often of light intensities); and other biotic and abiotic factors that typically influence soil and site development. Changes occur in the plant communities due to short-term weather variations, effects of native and exotic plant and animal species, and management actions. Although the following plant community descriptions are typical of the transitions between communities, severe disturbances, such as periods of well below average precipitation and the introduction of non-native cool-season grasses, can cause significant shifts in plant communities and species composition.
The plant community upon which interpretations are primarily based is the Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed Plant Community (1.1). This plant community has been determined by studying rangeland relic areas, areas protected from excessive disturbance, and areas under long-term rotational grazing regimes. Trends in plant community dynamics ranging from heavily grazed to lightly grazed areas, seasonal use pastures, and historical accounts also have been used. Plant communities, states, transitional pathways, and thresholds have been determined through similar studies and experience.
Continuous grazing without adequate recovery periods following each grazing occurrence over several years causes this site to depart from the Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed Plant Community (1.1). Species such as blue grama, sedges, cudweed sagewort, hairy golden aster, prairie coneflower, scurfpea, and fringed sagewort will initially increase. Prairie sandreed, sand bluestem, western wheatgrass, green needlegrass, false gromwell, vetch, penstemon, and leadplant will decrease in frequency and production. In time, heavy continuous grazing will likely cause upland sedges and blue grama to dominate and pioneer perennials, annuals, and club moss to increase. This plant community is relatively stable, and the competitive advantage of shortgrass species prevents other species from establishing.
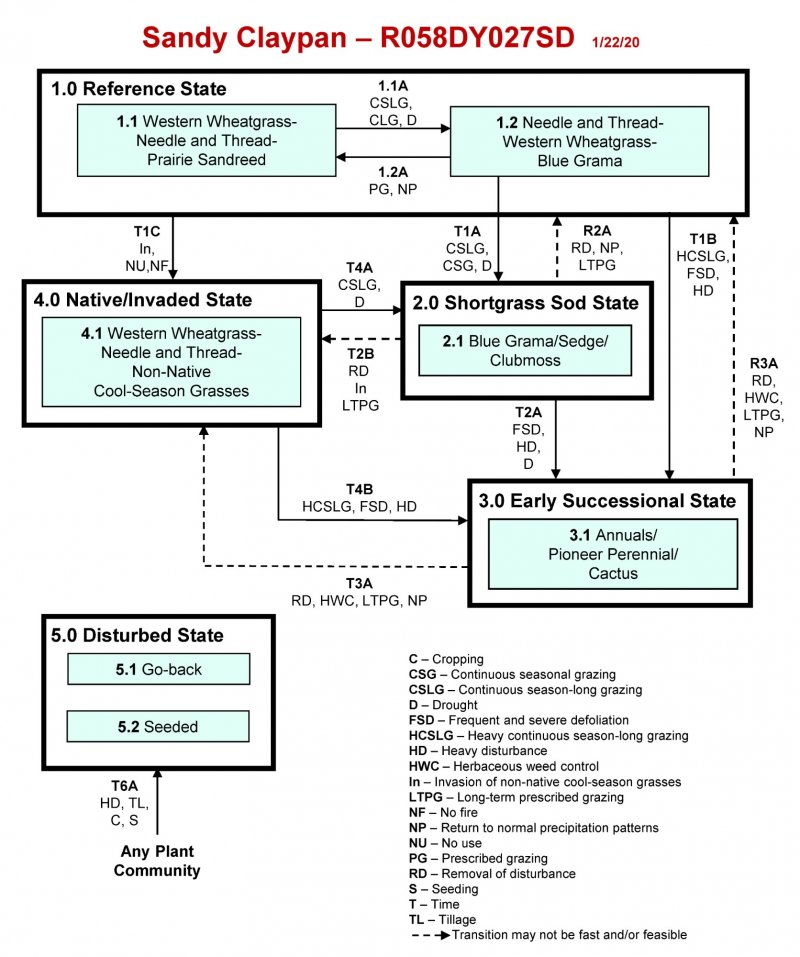
The following state-and-transition diagram illustrates the common plant communities on the site and the transition pathways between communities. The ecological processes are discussed in more detail in the plant community descriptions following the diagram.
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
Ecosystem states
States 1, 5 and 2 (additional transitions)
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 4 submodel, plant communities
State 5 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Reference State
The Reference State (1.0) represents what is believed to show the natural range of variability that dominated the dynamics of the ecological site prior to European settlement. This site in the Reference State (1.0) is dominated by cool-season grasses with warm-season grasses subdominant. In pre-European times, the primary disturbance mechanisms included frequent fire and grazing by large herding ungulates. Timing of fires and grazing coupled with weather events dictated the dynamics that occurred within the natural range of variability. Taller cool-season wheatgrasses and needlegrasses would have declined and a corresponding increase in short statured grass and grass-like species would have occurred. Today, a similar state can be found on areas that are properly managed with grazing and sometimes on areas receiving occasional short periods of rest.
Dominant plant species
-
rose (Rosa), shrub
-
prairie sagewort (Artemisia frigida), shrub
-
silver sagebrush (Artemisia cana), shrub
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
-
needle and thread (Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata), grass
-
prairie sandreed (Calamovilfa longifolia), grass
-
green needlegrass (Nassella viridula), grass
-
sand bluestem (Andropogon hallii), grass
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
prairie Junegrass (Koeleria macrantha), grass
-
sedge (Carex), grass
-
white sagebrush (Artemisia ludoviciana), other herbaceous
-
dotted blazing star (Liatris punctata), other herbaceous
-
hairy false goldenaster (Heterotheca villosa), other herbaceous
-
prairie clover (Dalea), other herbaceous
-
scurfpea (Psoralidium), other herbaceous
Community 1.1
Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed
The interpretive plant community for this site is the Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed Plant Community (1.1). This is also considered to be Reference Plant Community (1.1). This plant community can be found on areas that are properly managed with grazing and sometimes on areas receiving occasional short periods of deferment. The potential vegetation is about 85 percent grasses or grass-like plants, 10 percent forbs, 5 percent shrubs, and 0 to 1 percent mat-forming forbs. The major grasses include western wheatgrass, needle and thread, and prairie sandreed. Other grasses or grass-like species occurring on the site include green needlegrass, sand bluestem, little bluestem, blue grama, prairie Junegrass, and sedges. Significant forbs include cudweed sagewort, dotted gayfeather, hairy goldaster, prairie clover, and scurfpea. The significant shrubs that occur include rose, fringed sagewort, and silver sagebrush. This plant community is well adapted to the Northern Great Plains climatic conditions. Individual species can vary greatly in production depending on growing conditions (timing and amount of precipitation and temperature). The diversity in plant species allows for high drought tolerance. This is a healthy and sustainable plant community. Moderate or high available water capacity provides a favorable soil-water-plant relationship. Overall, the interpretive plant community has the appearance of being stable, diverse, and productive. Plant litter is properly distributed with very little movement offsite and natural plant mortality is very low.
Figure 8. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 950 | 1352 | 1850 |
| Forb | 75 | 120 | 165 |
| Shrub/Vine | 75 | 120 | 165 |
| Moss | 0 | 8 | 20 |
| Total | 1100 | 1600 | 2200 |
Figure 9. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD5802, Northern Rolling High Plains, cool-season dominant, warm-season subdominant. Cool-season dominant, warm-season subdominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 23 | 34 | 15 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Community 1.2
Needle and Thread-Western Wheatgrass-Blue Grama
This plant community develops under continuous season-long grazing or continuous seasonal grazing (grazing at the same time of year every year). The potential vegetation is made up of approximately 85 percent grasses and grass-like species, 10 percent forbs, 5 percent shrubs, and 0 to 3 percent mat-forming forbs. The dominant grasses include needle and thread, western wheatgrass, blue grama, sedge, and little bluestem. Other grasses or grass-like species may include prairie sandreed, sand dropseed, and prairie Junegrass. Significant forbs include cudweed sagewort, green sagewort, scurfpea, western yarrow, and white prairie aster. The dominant shrubs that occur include silver sagebrush, cactus, rose, and fringed sagewort. Compared to the Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed Plant Community (1.1), species such as needle and thread, blue grama, little bluestem, and threadleaf sedge have increased. Prairie sandreed, western wheatgrass, sand bluestem, and big bluestem have decreased in composition. Annual bromes, bluegrass, sweetclover, and other annual grasses and forbs can invade the site. This plant community can occur in a mosaic with patchy, slightly used areas occurring adjacent to and intermingled with this plant community. This plant community is not resistant to change. Changes in grazing management can result in a shift to another plant community. This community is fairly resilient following normal disturbances because of the high diversity of plant species and the high amount of litter. Soil erosion is low. The water cycle is functioning due to the litter cover on the soil surface. Infiltration is high because of the soil texture and surface litter.
Figure 10. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 6. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 690 | 1002 | 1300 |
| Forb | 55 | 90 | 125 |
| Shrub/Vine | 55 | 90 | 125 |
| Moss | 0 | 18 | 40 |
| Total | 800 | 1200 | 1590 |
Figure 11. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD5802, Northern Rolling High Plains, cool-season dominant, warm-season subdominant. Cool-season dominant, warm-season subdominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 23 | 34 | 15 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2
Continuous seasonal grazing; continuous season-long grazing, grazing for extended periods of time during the actively growing period of the dominant grasses without adequate recovery periods; or heavy grazing in combination with drought will lead to the Reference Plant Community (1.1) to the Needle and Thread-Western Wheatgrass-Blue Grama Plant Community (1.2).
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1
Prescribed grazing with proper stocking rate, change in season of use, and adequate time for plant recovery; and a return to normal precipitation patterns following drought will convert the Needle and Thread-Western Wheatgrass-Blue Grama Plant Community (1.2) to the Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed Plant Community (1.1).
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Grazing |
|---|
State 2
Shortgrass Sod State
The Shortgrass Sod State is dominated by shortgrass species, upland sedges and clubmoss. This State is the result of grazing management that did not provide adequate recovery time for cool-season wheatgrasses and needlegrass. The hydrologic function of this state is dramatically altered. Runoff is high and infiltration is low. This State is very resistant to change through grazing management alone.
Dominant plant species
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
sedge (Carex), grass
-
Sandberg bluegrass (Poa secunda), grass
-
purple threeawn (Aristida purpurea), grass
-
needle and thread (Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata), grass
-
prairie Junegrass (Koeleria macrantha), grass
-
clubmoss (Lycopodiella), other herbaceous
-
white sagebrush (Artemisia ludoviciana), other herbaceous
-
tarragon (Artemisia dracunculus), other herbaceous
-
goldenrod (Solidago), other herbaceous
-
white prairie aster (Symphyotrichum falcatum), other herbaceous
-
scurfpea (Psoralidium), other herbaceous
Community 2.1
Blue Grama/Sedge/Clubmoss
This plant community can develop from the adverse effects of long-term continuous season-long grazing; long-term early spring seasonal grazing; or heavy grazing in combination with drought. Annual grazing too early in the spring depletes stored carbohydrates, resulting in weakening and eventual death of the cool-season mid-grasses. Short grasses and grass-likes and forbs increase to dominate the site and annual production decreases dramatically. Lack of litter and reduced plant vigor result in higher soil temperatures, poor water infiltration rates, and high evapotranspiration, which gives blue grama and sedges a competitive advantage over cool-season mid-grasses. This plant community can occur throughout the pasture, on spot grazed areas, and around water sources where season-long grazing patterns occur. Blue grama and sedge are the dominant species. Clubmoss is not dominant by weight but occupies a significant amount of the surface cover of the plant community. Other grasses that may be present include Sandberg bluegrass, red threeawn, needle and thread, prairie Junegrass, and annual grasses. Forbs such as cudweed sagewort, green sagewort, goldenrod, white prairie aster, and scurfpea may also be present. There is usually less than 10 percent bare ground. This plant community is relatively stable. The thick sod and competitive advantage of shortgrass species prevent other species from establishing. This plant community is less productive than the Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed Plant Community (1.1). Runoff increases and infiltration will decrease. Soil erosion will be minimal due to the sod forming habit of blue grama.
Figure 12. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 7. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 415 | 728 | 1045 |
| Forb | 40 | 77 | 110 |
| Shrub/Vine | 40 | 68 | 95 |
| Moss | 5 | 27 | 50 |
| Total | 500 | 900 | 1300 |
Figure 13. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD5803, Northern Rolling High Plains, cool-season/warm-season co-dominant.. Cool-season, warm-season co-dominant, uplands..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 20 | 28 | 21 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
State 3
Early Successional State
The Early Successional State (3.0) is dominated by weedy annuals, threeawn, wheatgrass, and pricklypear cactus. This State is the result of heavy disturbance such as frequent and severe defoliation, heavy livestock concentrations coupled with grazing management that does not provide adequate recovery time for cool-season wheatgrasses and needlegrasses. The hydrologic function is also likely to be dramatically altered. Runoff is high and infiltration is low. This State is very resistant to change through grazing management alone.
Dominant plant species
-
threeawn (Aristida), grass
-
field brome (Bromus arvensis), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
sedge (Carex), grass
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
-
sixweeks fescue (Vulpia octoflora), grass
-
prairie sagewort (Artemisia frigida), other herbaceous
-
fetid marigold (Dyssodia papposa), other herbaceous
-
Cuman ragweed (Ambrosia psilostachya), other herbaceous
-
pussytoes (Antennaria), other herbaceous
-
prostrate verbena (Verbena officinalis var. prostrata), other herbaceous
Community 3.1
Annuals/Pioneer Perennial/Cactus
This plant community develops under heavy, continuous season-long grazing; frequent and severe defoliation; or under heavy disturbance such as livestock feeding areas. The potential plant community is made up of approximately 70 percent grasses and grass-like species, 25 percent forbs, and 5 percent shrubs. The dominant grasses include threeawn and annual brome grasses. Other grasses may include blue grama, sedges, western wheatgrass, and sixweeks fescue. The dominant forbs include fringed sagewort, fetid marigold, western ragweed, pussytoes, prostrate verbena, and other annual invader-like species. Other plant species from adjacent ecological sites can become minor components of this plant community. This plant community is susceptible to invasion of Canada thistle and other non-native species because of the relatively high percentage of bare ground. Compared to the Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed Plant Community (1.1), red threeawn, annual brome grasses, cactus, and the percentage of bare ground has increased. Wheatgrasses, needlegrasses, and other cool-season grasses and grass-like species have decreased, as have the many of the warm-season grasses. Many annual and perennial forbs, including native and non-native species, have invaded the site. This plant community is resistant to a change back to a higher successional plant community because of the loss of plant diversity and overall soil disturbance. It is very susceptible to invasion of non-native plant species. The potential for soil erosion is very high because of the bare ground and shallow-rooted herbaceous plant community. Water runoff will increase, and infiltration will decrease due to animal-related soil compaction and loss of root mass due to low plant diversity and vigor. This plant community will require significant economic inputs and time to move toward another plant community. This movement is highly variable in its succession.
Figure 14. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD5804, Northern Rolling High Plains, warm-season dominant, cool-season sub-dominant.. Warm-season dominant, cool-season sub-dominant, uplands..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 18 | 24 | 25 | 15 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
State 4
Native/Invaded State
This State is dominated by western wheatgrass, needle and thread, and non-native cool-season annual and perennial grasses. The Native/Invaded State (4.0) can resemble the Reference State (1.0) in species composition and vegetative production except that it is invaded by non-native cool-season grasses.
Dominant plant species
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
-
needle and thread (Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata), grass
-
field brome (Bromus arvensis), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis), grass
-
crested wheatgrass (Agropyron cristatum), grass
-
white sagebrush (Artemisia ludoviciana), other herbaceous
-
scarlet globemallow (Sphaeralcea coccinea), other herbaceous
-
common yarrow (Achillea millefolium), other herbaceous
-
scurfpea (Psoralidium), other herbaceous
Community 4.1
Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Non-Native Cool-Season Grasses
This plant community will look much like the Reference Plant Community (1.1), other than the non-native cool-season annual and perennial grasses that have invaded the plant community. Smooth brome, cheatgrass, field brome, or crested wheatgrass can make up to 15 percent (by air-dry weight) of the species composition. Cool-season mid-grasses will make up approximately 85 percent of the plant community, 10 percent forbs, and 5 percent shrubs. The dominant grasses include western wheatgrass, needle and thread, annual bromegrass, and blue grama. Under long-term non-use, Kentucky bluegrass and crested wheatgrass may become the dominant grass species. Forbs commonly found on this plant community include cudweed sagewort, scarlet globemallow, common yarrow, and scurfpea. Production in wet years may be very similar or slightly higher than the Reference Plant Community (1.1), but in dry years will be much lower. Under proper management, this plant community is productive and stable. The soil erosion is low to moderate. Infiltration and runoff are moderate.
Figure 15. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD5801, Northern Rolling High Plains, cool-season dominant.. Cool-season dominant, uplands..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 4 | 12 | 25 | 36 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
State 5
Disturbed State
Any plant community can transition to the Disturbed State (5.0). The two separate vegetative plant communities found in this State are highly variable in nature. They are derived through different management scenarios and are not related successionally. Infiltration, runoff, and soil erosion vary depending upon the vegetation present on the site.
Dominant plant species
-
broom snakeweed (Gutierrezia sarothrae), shrub
-
threeawn (Aristida), grass
-
dropseed (Sporobolus), grass
-
field brome (Bromus arvensis), grass
-
crested wheatgrass (Agropyron cristatum), grass
-
smooth brome (Bromus inermis), grass
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
-
foxtail barley (Hordeum jubatum), grass
-
sweetclover (Melilotus), other herbaceous
-
mountain deathcamas (Zigadenus elegans), other herbaceous
-
prickly lettuce (Lactuca serriola), other herbaceous
-
Canadian horseweed (Conyza canadensis), other herbaceous
-
forage kochia (Bassia prostrata), other herbaceous
-
common sunflower (Helianthus annuus), other herbaceous
Community 5.1
Go-back
The Go-back plant community can be reached whenever severe mechanical disturbance occurs (e.g., tilled and abandoned cropland). During the early successional stages, the species that mainly dominate are annual grasses and forbs, later replaced by both native and introduced perennials. The vegetation in this plant community can vary greatly, sometimes it is dominated by threeawn, dropseed, annual brome, crested wheatgrass, smooth brome, broom snakeweed, sweetclover, and non-native thistles. Other plants that commonly occur on the site can include western wheatgrass, deathcamas, prickly lettuce, mare’s tail, kochia, squirreltail, foxtail, and annual sunflower. Bare ground is prevalent due to the loss of organic matter and lower overall soil health.
Community 5.2
Seeded
The Seeded Plant Community normally includes those areas seeded to pubescent or intermediate wheatgrass, crested wheatgrass, alfalfa, or other forage species. For adapted species, refer to the USDA-NRCS e-FOTG for the appropriate Forage Suitability Group description.
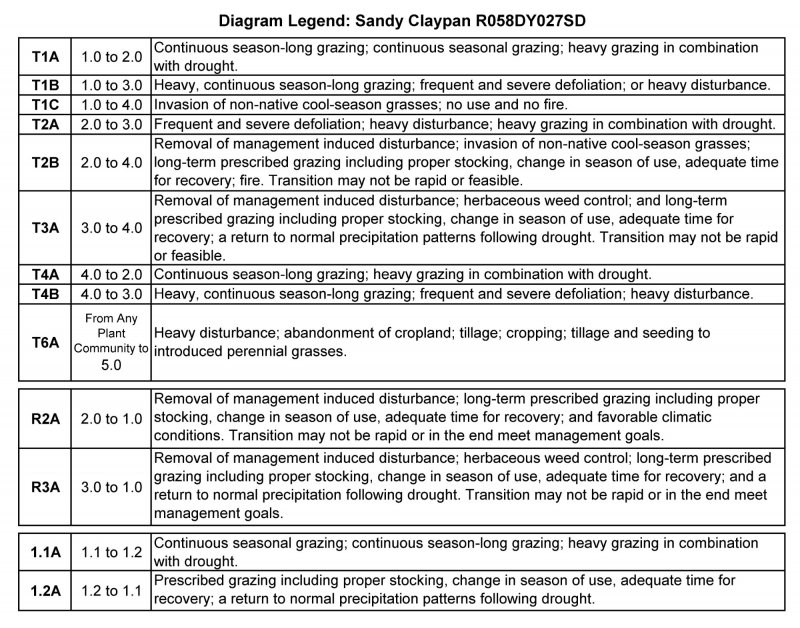
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
Continuous season-long grazing; continuous seasonal grazing (early spring); or heavy grazing in combination with drought will transition the Reference State (1.0) to the Shortgrass Sod State (2.0). This transition is most likely to occur from the Needle and Thread-Western Wheatgrass-Blue Grama Plant Community (1.2).
Transition T1B
State 1 to 3
Heavy, continuous season-long grazing; frequent and severe defoliation; or heavy disturbance including livestock feeding areas will transition the Reference State (1.0) to the Early Successional State (3.0).
Transition T1C
State 1 to 4
Invasion of non-native cool-season annual and perennial grasses and possibly long-term no use and no fire will transition the Reference State (1.0) is State to the Native/Invaded State (4.0).
Transition T6A
State 1 to 5
Heavy disturbance including tillage, abandonment of cropland, seeding to improved pasture species, will result in a transition to the Disturbed State (5.0). This transition can occur from any plant community on this site.
Restoration pathway R2A
State 2 to 1
Removal of the grazing disturbance coupled with long-term prescribed grazing, and favorable climatic conditions, which allow for adequate plant recovery periods, may cause a shift the Shortgrass Sod State (2.0) to the Reference State (1.0). This transition may not be rapid or in the end meet management goals.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Grazing |
|---|
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
Frequent and severe defoliation, or heavy disturbance such as livestock or wildlife concentration areas, and extended periods of drought will move the Shortgrass Sod State (2.0) to the Early Successional State (3.0).
Transition T2B
State 2 to 4
Removal of grazing disturbances; invasion on non-native cool-season grasses; long-term prescribed grazing, and favorable climatic conditions, which allow for adequate plant recovery periods, may cause the Shortgrass Sod State (2.0) to shift to the Native/Invaded State (4.0). This transition my not be rapid or feasible.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Grazing |
|---|
Transition T6A
State 2 to 5
Heavy disturbance including tillage, abandonment of cropland, seeding to improved pasture species, will result in a transition to the Disturbed State (5.0). This transition can occur from any plant community on this site.
Restoration pathway R3A
State 3 to 1
Removal of grazing disturbance, and herbaceous weed control to address annual bromes and cactus followed with long-term prescribed grazing that incorporates proper stocking, change in season of use, and periodic deferment will potentially transition the Early Successional State (3.0) to the Reference State (1.0). A return to normal or above normal precipitation will help with this transition. This transition my not occur or meet management objectives.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Grazing | |
|---|---|
| Herbaceous Weed Control |
Transition T3A
State 3 to 4
Removal of the grazing disturbance; invasion on non-native cool-season grasses; herbaceous weed control; long-term prescribed grazing, and favorable climatic conditions, which allow for adequate plant recovery periods, may shift the Early Successional State (3.0) to the Native/Invaded State (4.0). This transition may not be rapid or feasible.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Grazing | |
|---|---|
| Herbaceous Weed Control |
Transition T6A
State 3 to 5
Heavy disturbance including tillage, abandonment of cropland, seeding to improved pasture species, will result in a transition to the Disturbed State (5.0). This transition can occur from any plant community on this site.
Transition T4A
State 4 to 2
Continuous season-long grazing or heavy grazing in combination with drought will transition the Native/Invaded State (4.0) to the Shortgrass Sod State (2.0).
Transition T4B
State 4 to 3
Heavy, continuous season-long grazing, or frequent and severe defoliation, or heavy disturbance including livestock or wildlife concentration areas, will transition the Native/Invaded State (4.0) to the Early Successional State (3.0).
Transition T6A
State 4 to 5
Heavy disturbance including tillage, abandonment of cropland, seeding to improved pasture species, will result in a transition to the Disturbed State (5.0). This transition can occur from any plant community on this site.
Additional community tables
Table 8. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Rhizomatous Wheatgrass | 320–480 | ||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 320–480 | – | ||
| thickspike wheatgrass | ELLAL | Elymus lanceolatus ssp. lanceolatus | 0–80 | – | ||
| 2 | Cool-Season Bunchgrass | 160–400 | ||||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 160–400 | – | ||
| green needlegrass | NAVI4 | Nassella viridula | 0–80 | – | ||
| 3 | Tall Warm-Season Grasses | 80–320 | ||||
| prairie sandreed | CALO | Calamovilfa longifolia | 80–240 | – | ||
| sand bluestem | ANHA | Andropogon hallii | 0–80 | – | ||
| big bluestem | ANGE | Andropogon gerardii | 0–48 | – | ||
| 4 | Short-Warm Season Grasses | 16–80 | ||||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 16–80 | – | ||
| saltgrass | DISP | Distichlis spicata | 0–16 | – | ||
| Fendler threeawn | ARPUL | Aristida purpurea var. longiseta | 0–16 | – | ||
| 5 | Warm-Season Bunchgrasses | 16–80 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 0–80 | – | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 0–32 | – | ||
| 6 | Other Native Grasses | 32–112 | ||||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 16–80 | – | ||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 16–48 | – | ||
| Sandberg bluegrass | POSE | Poa secunda | 0–32 | – | ||
| sixweeks fescue | VUOC | Vulpia octoflora | 0–16 | – | ||
| 7 | Grass-Likes | 16–80 | ||||
| threadleaf sedge | CAFI | Carex filifolia | 16–80 | – | ||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 0–48 | – | ||
| Grass-like (not a true grass) | 2GL | Grass-like (not a true grass) | 0–48 | – | ||
| 8 | Non-Native Cool-Season Grasses | 0 | ||||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 9 | Forbs | 80–160 | ||||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 16–48 | – | ||
| Forb, native | 2FN | Forb, native | 0–48 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 16–32 | – | ||
| white prairie aster | SYFA | Symphyotrichum falcatum | 16–32 | – | ||
| woolly plantain | PLPA2 | Plantago patagonica | 16–32 | – | ||
| dotted blazing star | LIPU | Liatris punctata | 16–32 | – | ||
| hairy false goldenaster | HEVI4 | Heterotheca villosa | 16–32 | – | ||
| prairie clover | DALEA | Dalea | 16–32 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 16–32 | – | ||
| stiff sunflower | HEPA19 | Helianthus pauciflorus | 0–32 | – | ||
| longbract spiderwort | TRBR | Tradescantia bracteata | 16–32 | – | ||
| cinquefoil | POTEN | Potentilla | 0–16 | – | ||
| wavyleaf thistle | CIUN | Cirsium undulatum | 0–16 | – | ||
| western wallflower | ERAS2 | Erysimum asperum | 0–16 | – | ||
| spiny phlox | PHHO | Phlox hoodii | 0–16 | – | ||
| upright prairie coneflower | RACO3 | Ratibida columnifera | 0–16 | – | ||
| rush skeletonplant | LYJU | Lygodesmia juncea | 0–16 | – | ||
| scarlet beeblossom | GACO5 | Gaura coccinea | 0–16 | – | ||
| scarlet globemallow | SPCO | Sphaeralcea coccinea | 0–16 | – | ||
| purple locoweed | OXLA3 | Oxytropis lambertii | 0–16 | – | ||
| Missouri goldenrod | SOMI2 | Solidago missouriensis | 0–16 | – | ||
| beardtongue | PENST | Penstemon | 0–16 | – | ||
| western marbleseed | ONBEO | Onosmodium bejariense var. occidentale | 0–16 | – | ||
| field sagewort | ARCA12 | Artemisia campestris | 0–16 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 10 | Shrubs | 80–160 | ||||
| silver sagebrush | ARCA13 | Artemisia cana | 16–80 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–80 | – | ||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 16–48 | – | ||
| Wyoming big sagebrush | ARTRW8 | Artemisia tridentata ssp. wyomingensis | 0–48 | – | ||
| prairie rose | ROAR3 | Rosa arkansana | 16–48 | – | ||
| plains pricklypear | OPPO | Opuntia polyacantha | 16–32 | – | ||
| brittle pricklypear | OPFR | Opuntia fragilis | 0–16 | – | ||
|
Moss
|
||||||
| 11 | Mat-Forming Forbs | 0–16 | ||||
| lesser spikemoss | SEDE2 | Selaginella densa | 0–16 | – | ||
Table 9. Community 1.2 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Rhizomatous Wheatgrass | 60–240 | ||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 60–240 | – | ||
| thickspike wheatgrass | ELLAL | Elymus lanceolatus ssp. lanceolatus | 0–60 | – | ||
| 2 | Cool-Season Bunchgrass | 180–360 | ||||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 180–360 | – | ||
| green needlegrass | NAVI4 | Nassella viridula | 0–12 | – | ||
| 3 | Tall Warm-Season Grasses | 0–60 | ||||
| prairie sandreed | CALO | Calamovilfa longifolia | 0–60 | – | ||
| sand bluestem | ANHA | Andropogon hallii | 0–12 | – | ||
| 4 | Short-Warm Season Grasses | 60–180 | ||||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 60–180 | – | ||
| saltgrass | DISP | Distichlis spicata | 0–36 | – | ||
| Fendler threeawn | ARPUL | Aristida purpurea var. longiseta | 0–36 | – | ||
| 5 | Warm-Season Bunchgrasses | 12–96 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 12–96 | – | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 0–60 | – | ||
| 6 | Other Native Grasses | 24–84 | ||||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 12–48 | – | ||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 12–36 | – | ||
| Sandberg bluegrass | POSE | Poa secunda | 0–24 | – | ||
| sixweeks fescue | VUOC | Vulpia octoflora | 0–12 | – | ||
| 7 | Grass-Likes | 24–120 | ||||
| threadleaf sedge | CAFI | Carex filifolia | 24–120 | – | ||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 0–60 | – | ||
| Grass-like (not a true grass) | 2GL | Grass-like (not a true grass) | 0–60 | – | ||
| 8 | Non-Native Cool-Season Grasses | 12–60 | ||||
| cheatgrass | BRTE | Bromus tectorum | 12–60 | – | ||
| crested wheatgrass | AGCR | Agropyron cristatum | 0–48 | – | ||
| Kentucky bluegrass | POPR | Poa pratensis | 0–48 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 9 | Forbs | 60–120 | ||||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 12–60 | – | ||
| field sagewort | ARCA12 | Artemisia campestris | 12–36 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 12–36 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 12–36 | – | ||
| white prairie aster | SYFA | Symphyotrichum falcatum | 12–36 | – | ||
| Forb, native | 2FN | Forb, native | 0–36 | – | ||
| Forb, introduced | 2FI | Forb, introduced | 0–36 | – | ||
| woolly plantain | PLPA2 | Plantago patagonica | 12–24 | – | ||
| field cottonrose | LOAR5 | Logfia arvensis | 0–24 | – | ||
| scarlet globemallow | SPCO | Sphaeralcea coccinea | 12–24 | – | ||
| Missouri goldenrod | SOMI2 | Solidago missouriensis | 12–24 | – | ||
| prairie clover | DALEA | Dalea | 0–12 | – | ||
| upright prairie coneflower | RACO3 | Ratibida columnifera | 0–12 | – | ||
| rush skeletonplant | LYJU | Lygodesmia juncea | 0–12 | – | ||
| dotted blazing star | LIPU | Liatris punctata | 0–12 | – | ||
| longbract spiderwort | TRBR | Tradescantia bracteata | 0–12 | – | ||
| hairy false goldenaster | HEVI4 | Heterotheca villosa | 0–12 | – | ||
| purple locoweed | OXLA3 | Oxytropis lambertii | 0–12 | – | ||
| spiny phlox | PHHO | Phlox hoodii | 0–12 | – | ||
| wavyleaf thistle | CIUN | Cirsium undulatum | 0–12 | – | ||
| western wallflower | ERAS2 | Erysimum asperum | 0–12 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 10 | Shrubs | 60–120 | ||||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 12–60 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–60 | – | ||
| silver sagebrush | ARCA13 | Artemisia cana | 12–48 | – | ||
| plains pricklypear | OPPO | Opuntia polyacantha | 12–24 | – | ||
| prairie rose | ROAR3 | Rosa arkansana | 12–24 | – | ||
| Wyoming big sagebrush | ARTRW8 | Artemisia tridentata ssp. wyomingensis | 0–24 | – | ||
| brittle pricklypear | OPFR | Opuntia fragilis | 0–24 | – | ||
|
Moss
|
||||||
| 11 | Mat-Forming Forbs | 0–36 | ||||
| lesser spikemoss | SEDE2 | Selaginella densa | 0–36 | – | ||
Table 10. Community 2.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Rhizomatous Wheatgrass | 0–72 | ||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 0–72 | – | ||
| thickspike wheatgrass | ELLAL | Elymus lanceolatus ssp. lanceolatus | 0–27 | – | ||
| 2 | Cool-Season Bunchgrass | 0–90 | ||||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 0–90 | – | ||
| 4 | Short-Warm Season Grasses | 180–315 | ||||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 135–270 | – | ||
| Fendler threeawn | ARPUL | Aristida purpurea var. longiseta | 9–72 | – | ||
| saltgrass | DISP | Distichlis spicata | 0–45 | – | ||
| 5 | Warm-Season Bunchgrass | 9–63 | ||||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 9–63 | – | ||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 0–18 | – | ||
| 6 | Other Native Grasses | 18–45 | ||||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 9–27 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 9–27 | – | ||
| Sandberg bluegrass | POSE | Poa secunda | 0–18 | – | ||
| sixweeks fescue | VUOC | Vulpia octoflora | 0–9 | – | ||
| 7 | Grass-Likes | 90–225 | ||||
| threadleaf sedge | CAFI | Carex filifolia | 45–180 | – | ||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 9–90 | – | ||
| Grass-like (not a true grass) | 2GL | Grass-like (not a true grass) | 9–90 | – | ||
| 8 | Non-Native Coo-Season Grasses | 9–45 | ||||
| cheatgrass | BRTE | Bromus tectorum | 9–45 | – | ||
| crested wheatgrass | AGCR | Agropyron cristatum | 0–36 | – | ||
| Kentucky bluegrass | POPR | Poa pratensis | 0–36 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 9 | Forbs | 45–108 | ||||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 9–63 | – | ||
| field sagewort | ARCA12 | Artemisia campestris | 9–45 | – | ||
| field cottonrose | LOAR5 | Logfia arvensis | 0–36 | – | ||
| Forb, introduced | 2FI | Forb, introduced | 0–36 | – | ||
| Forb, native | 2FN | Forb, native | 0–27 | – | ||
| white prairie aster | SYFA | Symphyotrichum falcatum | 9–27 | – | ||
| Missouri goldenrod | SOMI2 | Solidago missouriensis | 9–27 | – | ||
| scarlet globemallow | SPCO | Sphaeralcea coccinea | 9–18 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 9–18 | – | ||
| woolly plantain | PLPA2 | Plantago patagonica | 9–18 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 9–18 | – | ||
| spiny phlox | PHHO | Phlox hoodii | 0–9 | – | ||
| rush skeletonplant | LYJU | Lygodesmia juncea | 0–9 | – | ||
| purple locoweed | OXLA3 | Oxytropis lambertii | 0–9 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 10 | Shrubs | 45–90 | ||||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 9–63 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–45 | – | ||
| silver sagebrush | ARCA13 | Artemisia cana | 9–27 | – | ||
| brittle pricklypear | OPFR | Opuntia fragilis | 0–27 | – | ||
| plains pricklypear | OPPO | Opuntia polyacantha | 9–18 | – | ||
| prairie rose | ROAR3 | Rosa arkansana | 9–18 | – | ||
| Wyoming big sagebrush | ARTRW8 | Artemisia tridentata ssp. wyomingensis | 0–9 | – | ||
|
Moss
|
||||||
| 11 | Mat-Forming Forbs | 9–45 | ||||
| lesser spikemoss | SEDE2 | Selaginella densa | 9–45 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Wildlife Interpretations
MLRA 58D lies within the drier portion of the northern mixed-grass prairie ecosystem where sagebrush steppes to the west yield to grassland steppes to the east. Prior to European settlement, this area consisted of diverse grass- and shrubland habitats interspersed with varying densities of depressional instream wetlands and woody riparian corridors. These habitats provided critical life cycle components for many users. Many species of grassland birds, small mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and herds of roaming bison, elk, and pronghorn were among the inhabitants adapted to this semi-arid region. Roaming herbivores, as well as several small mammal and insect species, were the primary consumers linking the grassland resources to predators such as the gray wolf, mountain lion, and grizzly bear, and smaller carnivores such as the coyote, bobcat, fox, and raptors. The prairie dog was once abundant; however, the species remains a keystone species within its range. The black-footed ferret, burrowing owl, ferruginous hawk, mountain plover, and swift fox were associated with prairie dog complexes.
Historically, the northern mixed-grass prairie was a disturbance-driven ecosystem with fire, herbivory, and climate functioning as the primary disturbance factors either singly or in combination. Following European settlement, livestock grazing, cropland conversion, elimination of fire, energy development, and other anthropogenic factors influenced species composition and abundance. Introduced and invasive species further impacted plant and animal communities. The bison was a historical keystone species but had been extirpated in this area as a free-ranging herbivore. The loss of the bison and reduction of prairie dog populations and fire as ecological drivers greatly influenced the character of the remaining native plant communities and altered wildlife habitats. Human development has reduced habitat quality for area-sensitive species.
Within MLRA 58D, the Sandy Claypan ecological site provides upland grassland cover with an associated forb component. It was typically part of an expansive grassland landscape that included combinations of Loamy, Shallow Loamy, Shallow Clayey, Thin Loamy, Sandy, Claypan, Sands, Clayey, and Thin Claypan ecological sites.
This site provided habitat for species requiring unfragmented grassland. Important habitat features and components found commonly or exclusively on this site may include greater sage-grouse and sharp-tailed grouse leks; upland nesting habitat for grassland birds, forbs and insects for brood habitat; and a forage source for small and large herbivores. Many grassland and shrub steppe nesting bird populations are declining. Extirpated species include free-ranging bison, grizzly bear, gray wolf, black-footed ferret, mountain plover, Rocky Mountain locust, and swift fox.
The majority of the Sandy Claypan ecological site has remains intact and provides increasingly important habitat for grassland and shrub steppe nesting birds, small rodents, coyote, and a variety of reptiles, amphibians, and insects. Invasive species such as annual bromegrasses and crested wheat have impacted the biological integrity of the site for some grassland birds such as greater sage-grouse. Changes in historic fire regime and domestic grazing have impacted the forb/shrub/grass percentages. Greater sage-grouse and Brewer’s sparrow benefit when sagebrush increases.
Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed (1.1): The predominance of grasses plus high diversity of forbs and shrubs in this community favors grazers and mixed-feeders, such as deer and pronghorn. Insects, such as pollinators, play a large role in maintaining the forb community and provide a forage base for grassland birds and other species. The complex plant structural diversity provides habitat for a wide array of migratory and resident birds. Grasshopper sparrow, lark bunting, western meadowlark, and sharp-tailed grouse are common and benefit from the structure and composition this plant community provides. Brewer’s sparrow and greater sage-grouse may be present depending on the frequency and distribution of big sagebrush. Diverse prey populations are available for grassland raptors such as ferruginous hawk, Swainson’s hawk, golden eagle, and prairie falcon.
The diversity of grasses, forbs, and shrubs provide high nutrition levels for small and large herbivores including voles, mice, thirteen-lined ground squirrel, white-tailed jackrabbit, and deer. This ES provides excellent wintering habitat for pronghorn. The higher stature of this plant community provides thermal, protective, and escape cover for herbivores and grassland birds. Predators utilizing this plant community include coyote, American badger, red fox, and long-tailed weasel. This plant community provides habitat for herptiles such as the spade foot toad, bull snake, and western rattlesnake.
Needle and Thread-Western Wheatgrass-Blue Grama (1.2): The predominance of grasses plus high diversity of forbs and shrubs in this community favors grazers and mixed-feeders, such as deer and pronghorn. Insects, such as pollinators, play a large role in maintaining the forb community and provide a forage base for grassland birds and other species. The plant structural diversity provides habitat for a wide array of migratory and resident birds. Grasshopper sparrow, lark bunting, western meadowlark, and sharp-tailed grouse are common and benefit from the mid- to short structure and composition this plant community provides. This site provides limited nesting and brood rearing habitat for greater sage-grouse. Diverse prey populations are available for grassland raptors such as ferruginous hawk, Swainson’s hawk, golden eagle, and prairie falcon.
The diversity of grasses, forbs, and shrubs provide high nutrition levels for small and large herbivores including voles, mice, thirteen-lined ground squirrel, white-tailed jackrabbit, and deer. The moderate stature of this plant community provides suitable thermal, protective, and escape cover for small herbivores and grassland birds. Predators utilizing this plant community include coyote, American badger, red fox, and long-tailed weasel. This plant community provides habitat for spade foot toad, Great Plains toad, bull snake, and western rattlesnake.
Blue Grama/Sedge/Clubmoss (2.1): This plant community develops under continuous seasonal grazing; continuous season-long grazing; or from over utilization during extended drought periods. Blue grama, sedge, and clubmoss will dominate. The forb diversity has decreased. A shift to short plant structure will favor prairie dog expansion with prairie dog town sites and associate species such as ferruginous hawk and burrowing owl. Species such as horned lark, long-billed curlew, upland sandpiper, and white-tailed jackrabbit will increase due to the loss of big sagebrush. Species such as Brewer’s sparrow, greater sage-grouse, as well as, desert cottontail will rarely use this site.
The short stature of this plant community limits suitable thermal, protective, and escape cover. Prey populations are reduced and are more vulnerable to raptor and mammalian predation. Predators utilizing this plant community include the coyote, American badger, red fox, and long-tailed weasel.
Extreme impairment of the ecological processes impacts offsite aquatic habitats through excessive runoff, nutrient, and sediment loads. Elevated surface temperatures resulting from reduced cover and litter will greatly reduce habitat for most amphibian species, grassland birds, and mammals.
Annual/Pioneer Perennial/Cactus (3.1): This plant community develops under severe disturbance or excessive defoliation. The dominant vegetation includes pioneer annual grasses, forbs, invaders, and early successional biennial and perennial species. Plant species from adjacent ecological sites may become minor components of this plant community. The community is susceptible to invasion of annual bromegrasses, crested wheatgrass, and other nonnative species due to severe soil disturbances and relatively high percent of bare ground.
Soil erosion is potentially high, impacting offsite aquatic habitats through increased runoff, nutrient, and sediment loads. Reduced surface cover, low plant density, low plant vigor, loss of root biomass, and soil compaction, all contribute to decreased wildlife abundance and diversity.
Since secondary succession is highly variable plant and wildlife species will vary. This plant community provides habitat for generalist or early successional species.
Grazing Interpretations
The following list suggests annual, initial stocking rates for average growing conditions. These estimates are conservative and should be used only as guidelines in the initial stages of conservation planning. Commonly, the current plant composition does not entirely match any particular plant community (as described in this ecological site description). Therefore, a resource inventory is necessary to document plant composition and production. More accurate estimates of carrying capacity should eventually be calculated using the following stocking rate information along with animal preference data and actual stocking records, particularly when grazers other than cattle are involved. In consultation with the land manager, a more intensive grazing management program that results in improved harvest efficiencies and increased carrying capacity may be developed.
The following suggested initial stocking rates are based on 912 lb/acre (air-dry weight) per animal-unit-month (AUM) with a 25 percent harvest efficiency of preferred and desirable forage species (refer to USDA-NRCS, National Range and Pasture Handbook). An AUM is defined as the equivalent amount of forage required by a 1,000-pound cow, with or without calf, for one month.
Plant Community: Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Prairie Sandreed (1.1)
Average Production (lb/acre, air-dry): 1,600
Stocking Rate (AUM/acre): 0.44
Plant Community: Needle and Thread-Western Wheatgrass-Blue Grama (1.2)
Average Production (lb/acre, air-dry): 1,200
Stocking Rate (AUM/acre): 0.33
Plant Community: Blue Grama/Sedge/Clubmoss (2.1)
Average Production (lb/acre, air-dry): 900*
Stocking Rate (AUM/acre): 0.25*
Plant Community: Western Wheatgrass-Needle and Thread-Non-Native Cool-Season Grasses (4.1)
Average Production (lb/acre, air-dry): 1,400*
Stocking Rate (AUM/acre): 0.38*
Plant Community: All other plant communities identified in this document have variable annual production values and require onsite sampling to determine initial stocking rates.
* Total annual production and stocking rates are highly variable and require onsite sampling.
Total onsite annual production may contain vegetation deemed undesirable or untargeted by the grazing animal. Therefore, AUM values may need to be reduced to reflect only preferred or desirable forage species.
Grazing by domestic livestock is one of the major income-producing industries in the area. Rangeland in this area may provide yearlong forage for livestock. During the dormant period, the forage for livestock likely has insufficient protein to meet livestock requirements. Added protein allows ruminants to better utilize the energy stored in grazed plant materials. A forage quality test (either directly or through fecal sampling) should be used to determine the level of supplementation needed.
Hydrological functions
Water is the principal factor limiting forage production on this site. This site is dominated by soils in hydrologic group B. Infiltration and runoff potential for this site varies from moderate to high depending on soil hydrologic group, slope, and ground cover. In many cases, areas with greater than 75 percent ground cover have the greatest potential for high infiltration and lower runoff. An example of an exception would be where shortgrasses form a strong sod and dominate the site. Normally areas where ground cover is less than 50 percent have the greatest potential to have reduced infiltration and higher runoff. Refer to the USDA-NRCS National Engineering Handbook, Part 630, for hydrologic soil groups, runoff quantities, and hydrologic curves.
Recreational uses
This site provides opportunities for hunting upland game species. The wide variety of plants that bloom from spring until fall have aesthetic value that appeals to visitors.
Wood products
No appreciable wood products are typically present on this site.
Other products
Harvesting the seeds of native plants can provide additional income on this site.
Other information
Revision Notes: “Previously Approved” Provisional
This provisional ecological site description (ESD) has passed quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) to ensure it meets the 2014 NESH standards for a “Provisional” ecological site description.
This ecological site description (ESD) is an updated “Previously Approved” ESD that represented a first-generation tier of documentation that met all requirements as an “Approved” ESD as laid out in the 1997 National Range and Pasture Handbook (NRPH). The requirements for approved status changed with the release of the 2014 National Ecological Site Handbook (NESH). The previously approved document fully described the reference state and community phases in the state-and-transition model. All other alternative states were at least described in narrative form. The “Previously Approved” ESD has been field-tested for a minimum of five years and is a proven functional document for conservation planning. The “Previously Approved” ESD may not contain all tabular and narrative entries as required in the current “Approved” level of documentation, but it is expected this ESD will continue refinement toward the current “Approved” status.
Site Development and Testing Plan
Future work, as described in an official project plan, is necessary to validate the information in this provisional ecological site description. The plan will include field activities for low-, medium-, and high-intensity sampling, soil correlations, and analysis of the data. Annual field reviews should be done by soil scientists and vegetation specialists. Final field review, peer review, quality control, and quality assurance reviews are required to produce the final document.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented here has been derived from NRCS clipping data and other inventory data. Field observations from range-trained personnel were also used. Those involved in developing this site description include: Ryan Beer, Range Management Specialist (RMS), NRCS; Chuck Berdan, Biologist, Bureau of Land Management (BLM); Stan Boltz, RMS, NRCS; Dave Dewald, Wildlife BIO, NRCS; Mitch Faulkner, RMS, NRCS; Jody Forman, RMS, NRCS; Dennis Froemke, RMS, NRCS; Tom Juntti, BIO, United States Forest Service (USFS); Cheryl Nielsen, RMS, NRCS; Jeff Printz, RMS, NRCS; Mike Stirling, RMS, NRCS; Dan Svingen, BIO, USFS; Darrell Vanderbusch, Soil Scientist, NRCS; Cindy Zachmeier, BIO, NRCS; and Tim Zachmeier, BIO, BLM.
Other references
Beck, J.L., J.W. Connelly, C.L. Wambolt. 2010. Consequences of treating Wyoming big sagebrush to enhance wildlife habitats; Rangeland Ecology and Management 65:444–455, September 2012
Cleland, D.T., J.A. Freeouf, J.E. Keys, G.J. Nowacki, C.A. Carpenter, and W.H McNab. 2007. Ecological subregions: Sections and subsections of the conterminous United States. USDA Forest Service, General Technical Report WO-76D. https://www.fs.fed.us/research/publications/misc/73326-wo-gtr-76d-cleland2007.pdf (accessed 31 January 2019).
Cooper, S.V., P. Lesica, G.M. Kudray. 2001. Post-fire recovery of Wyoming big sagebrush steppe in central and southeastern Montana; Natural Resources and Environmental Issues, Volume 16; Shrublands: Wildlands and Wildlife Habitats, Article 12.
Cowardin, L.M., V. Carter, F.C. Golet, and E.T. LaRoe. 1979. Classification of wetlands and deep-water habitats of the United States. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service FWS/OBS-79/31.
High Plains Regional Climate Center, University of Nebraska. 2018. http://www.hprcc.unl.edu/ (accessed 6 April 2018).
Innes, Robin J. 2019. Artemisia tridentata subsp. wyomingensis, Wyoming big sagebrush. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Missoula Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Available: https://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/shrub/arttriw/all.html (accessed 9 December 2019).
Larson, G.E. and J.R. Johnson. 1999. Plants of the Black Hills and Bear Lodge Mountains. South Dakota State University, College of Agriculture and Biological Sciences and Agriculture Experiment Station, Bulletin 732, Brookings, SD.
Toledo, D., M. Sanderson, K. Spaeth, J. Hendrickson, and J. Printz. 2014. Extent of Kentucky bluegrass and its effect on native plant species diversity and ecosystem services in the Northern Great Plains of the United States. Invasive Plant Science and Management. 7(4):543–522. Weed Science Society of America.
Soil Survey Staff. 2018. Official soil series descriptions. USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/home/?cid=nrcs142p2_053587 (accessed 20 December 2018).
Soil Survey Staff. 2018. Web Soil Survey. USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. https://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/WebSoilSurvey.aspx (accessed 20 December 2018).
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 1997. National range and pasture handbook, rev. 1, 2003. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/stelprdb1043055.pdf (accessed 7 January 2018).
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2006. Land resource regions and major land resource areas of the United States, the Caribbean, and the Pacific Basin. Agriculture Handbook 296. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_050898.pdf (accessed 17 January 2018).
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2007. National engineering handbook, part 654. Rosgen Stream Classification Technique – Supplemental Materials, Technical Supplement 3E. https://directives.sc.egov.usda.gov/OpenNonWebContent.aspx?content=17833.wba (accessed 4 March 2019).
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2012. National engineering handbook, part 630. Hydrology chapters from e-Directives. https://directives.sc.egov.usda.gov/viewerFS.aspx?hid=21422 (accessed 17 January 2018).
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2014. National ecological site handbook, 1st ed. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/ref/?cid=nrcseprd1291232 (accessed 27 January 2018).
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2018. Climate data. National Water and Climate Center. http://www.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/ (accessed 2 December 2018).
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2018. Electronic field office technical guide. https://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov (accessed 24 September 2018).
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2018. National Soil Information System, Information Technology Center. http://nasis.nrcs.usda.gov (accessed 25 May 2018.
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2018. PLANTS database. National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC. http://plants.usda.gov (accessed 27 December 2018).
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2018. EPA level III and level IV ecoregions of the conterminous United States. https://www.epa.gov/eco-research/level-iii-and-iv-ecoregions- conterminous-united-states (accessed 26 April 2018).
Contributors
Stan Boltz
Travis Patient
Rick L. Peterson
Approval
Suzanne Mayne-Kinney, 7/18/2024
Acknowledgments
This ecological site description was updated by Rick L. Peterson on January 22, 2020.
The ESDs were available for QC review by Mark Hayek, Emily Helms, Ryan Beer, and Mitch Faulkner.
All ecological sites were then reviewed and approved at the Provisional Level by David Kraft, Regional ESS, Salina, KS in September 2020.
Non-Discrimination Statement
In accordance with Federal civil rights law and U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) civil rights regulations and policies, the USDA, its Agencies, offices, and employees, and institutions participating in or administering USDA programs are prohibited from discriminating based on race, color, national origin, religion, sex, gender identity (including gender expression), sexual orientation, disability, age, marital status, family/parental status, income derived from a public assistance program, political beliefs, or reprisal or retaliation for prior civil rights activity, in any program or activity conducted or funded by USDA (not all bases apply to all programs). Remedies and complaint filing deadlines vary by program or incident.
Persons with disabilities who require alternative means of communication for program information (e.g., Braille, large print, audiotape, American Sign Language, etc.) should contact the responsible Agency or USDA's TARGET Center at (202) 720-2600 (voice and TTY) or contact USDA through the Federal Relay Service at (800) 877-8339. Additionally, program information may be made available in languages other than English.
To file a program discrimination complaint, complete the USDA Program Discrimination Complaint Form, AD-3027, available online at https://www.ascr.usda.gov/filing-program-discrimination-complaint-usda-customer and at any USDA office, or write a letter addressed to USDA and provide in the letter all of the information requested in the form. To request a copy of the complaint form, call (866) 632-9992. Submit your completed form or letter to USDA by:
(1) mail: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Avenue, SW, Washington, D.C. 20250-9410;
(2) fax: (202) 690-7442; or
(3) email: program.intake@usda.gov.
USDA is an equal opportunity provider, employer, and lender.
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | Stan Boltz |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | stanley.boltz@sd.usda.gov, 605-352-1236 |
| Date | 05/07/2010 |
| Approved by | Suzanne Mayne-Kinney |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
None. -
Presence of water flow patterns:
None, or barely visible and discontinuous. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
None. -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
5 to 25 percent is typical. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
None should be present. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
None. -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Litter should fall in place. Slight amount of movement of smallest size class litter is possible, but not normal. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Soil aggregate stability ratings should typically be 5 to 6, normally 6. Surface organic matter adheres to the soil surface. Soil surface fragments will typically retain structure indefinitely when dipped in distilled water. -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
A-horizon should be 2 to 5 inches thick with mollic (dark) colors when moist. Structure typically is medium to fine granular at least in the upper A-horizon. -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
Combination of shallow and deep rooted species (mid & tall rhizomatous and tufted perennial cool-season grasses) with fine and coarse roots positively influences infiltration. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
None – natural pan appears at roughly 5 to 15 inches with “biscuit-top” appearance at top of pan. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Mid cool-season rhizomatous grasses > Mid/tall cool-season bunchgrasses >Sub-dominant:
Tall warm-season grasses > Forbs = Shrubs >Other:
Short warm-season grasses = Mid warm-season bunchgrasses = Grass-likesAdditional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Very little evidence of decadence or mortality. Bunch grasses have strong, healthy centers and shrubs are vigorous. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
-
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
Production ranges from 1,100-2,200 lbs./acre (air-dry weight). Reference value production is 1,600 lbs./acre (air-dry weight). -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
State and local noxious weeds -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
All species exhibit high vigor relative to climatic conditions. Do not rate based solely on seed production. Perennial grasses should have vigorous rhizomes or tillers.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.