
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R069XY042CO
Clayey Plains
Last updated: 4/15/2025
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
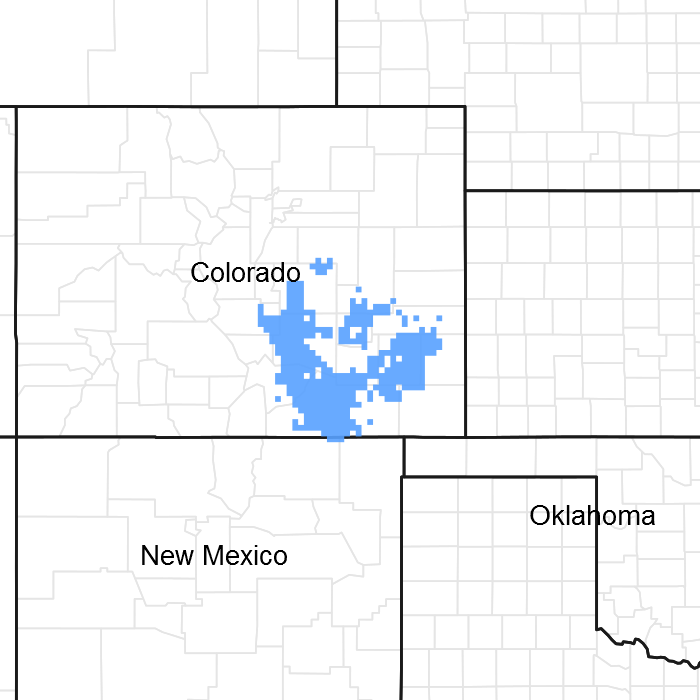
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 069X–Upper Arkansas Valley Rolling Plains
MLRA 69 is in the Arkansas Watershed of southeastern (SE)Colorado. It consists of rolling plains, river valleys, and canyonlands. The Arkansas River flows from the Rocky Mountains to Kansas. Tributaries include the Huerfano and Purgatoire Rivers. The MLRA is traversed by Interstate 25 and U.S. Highway 50, and includes the cities of Pueblo, La Junta, and Lamar. Other cities include Cañon City, and Walsenburg. Bent's Fort was once a major trading post along the Santa Fe Trail. The majority of land use is rangeland (greater than 75 percent), and 6 percent cropland. The remainder is urban, recreation, etc. Land ownership is mostly private. Federal lands include U.S. Forest Service Comanche National Grassland, Department of Defense Piñon Canyon Maneuver Site and Fort Carson. There is a minor amount of Bureau of Land Management and other federal land. State areas include Pueblo and John Martin reservoirs. Elevations MLRA-wide are 3,700 to 6,400 feet.
The "Dust Bowl" region (1930s) included SE Colorado, which is periodically affected by severe drought. Dust storms may form during drought years, in windy periods. Annual precipitation is 10 to 16 inches. Precipitation occurs mostly during the growing season, often during rapidly developing thunderstorms. Mean annual air temperature (MAAT) is 48 to 52 degrees Fahrenheit. Summer temperatures may exceed 100 degrees Fahrenheit. Evapotranspiration rates are high. Winter temperatures may be subzero. Snowfall varies from 20 to 40 inches per year. Blizzards can form quickly.
Classification relationships
MLRA 69 is in the Piedmont and Raton Sections of the Great Plains Province. The MLRA is further defined by Land Resource Units (LRUs) A, B, and C. The modal concepts of each LRU can be defined by soil properties and annual precipitation zones (PZ). Other features, such as climate, geology, landforms, and key vegetation, further refine these concepts and are described in the Ecological Site Description (ESD).
LRU A (10 to 12 inches PZ) is 2.4 million acres in the central portion of MLRA 69. There is irrigated cropland in the Arkansas Valley. Precipitation is too limited for dryland crops. Most of LRU A is rangeland, and includes the Comanche National Grassland (FS). This LRU is in portions of Bent, Crowley, Otero, and Pueblo counties. Soil Moisture Regime is Ustic Aridic. The Mean Annual Air Temperature (MAAT) is 51 to 54 degrees Fahrenheit.
LRU B (12 to 14 inches PZ) is 4.7 million acres and includes portions of Baca, Bent, Crowley, El Paso, Fremont, Kiowa, Las Animas, Lincoln, Prowers, and Pueblo counties. Most of the LRU is in rangeland. Land uses include irrigated and dry cropland, small acreage and urban ownership. Land east of Interstate 25 remains largely agricultural. Canyonlands are in the southern half and include Piñon Canyon Maneuver Site and the Picket Wire Canyon of the Comanche National Grasslands. Soil moisture regime is Ustic Aridic. The mean annual air temperature is 50 to 54 degrees Fahrenheit.
The Clayey Plains Ecological Site, LRUs A and B, was developed from an earlier version of the Clayey Ecological Site (2004, re-named Clayey Plains in 2007). This earlier version of the Clayey Ecological Site (2004) was based on input from Natural Resources Conservation Service (formerly Soil Conservation Service) and historical information obtained from the Clayey Range Site descriptions (new in 2004). This ESD meets the Provisional requirements of the National Ecological Site Handbook (NESH). This ESD will continue refinement towards an Approved status according to the NESH.
Ecological site concept
The Clayey Plains Ecological Site is a run-off site with slopes of less than 10 percent. The soils have surface textures of silty clay, clay loam, and silty clay loam, and greater than 35 percent clay in the particle control section.
Associated sites
| R069XY046CO |
Shaly Plains The Shaly Plains Ecological Site is commonly adjacent. |
|---|---|
| R069XY047CO |
Alkaline Plains The Alkaline Plains is Ecological Site is commonly adjacent. |
| R069XY006CO |
Loamy Plains The Loamy Plains Ecological Site is commonly adjacent. |
| R069XY037CO |
Saline Overflow The Saline Overflow is Ecological Site is commonly adjacent. |
Similar sites
| R069XY047CO |
Alkaline Plains The soils of the Alkaline Plains Ecological Site contain salts. |
|---|---|
| R069XY006CO |
Loamy Plains The surface texture of the Loamy Plains Ecological Site includes loam and silt loam, and has less than 35 percent clay in the particle size control section. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Atriplex canescens |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Bouteloua gracilis |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on plains.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Interfluve
(2) Fan remnant (3) Ridge (4) Hillslope (5) Terrace (6) Drainageway |
|---|---|
| Runoff class | Medium to high |
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 3,700 – 6,400 ft |
| Slope | 15% |
| Ponding depth |
Not specified |
| Water table depth | 60 in |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
Approximately 75 percent of the annual precipitation occurs during the growing season from mid-April to late September. Snowfall can vary greatly from year to year and can range from 20 to 40 inches per year. Winds are estimated to average 6 to 7 miles per hour annually. Daytime winds are generally stronger than nighttime winds. Occasional strong storms may bring brief periods of high winds with gusts to more than 60 miles per hour. The average length of the freeze-free period (28 °F) is 168 days. The average last freeze in the spring is April 22nd, and the average date of first freeze in fall is October 7th. The average length of the frost-free period (32 °F) is 149 days. The last frost in the spring is May 5th, and the average date for first frost in the fall (32 °F), is October 1. July is the hottest month, and January is the coldest. It is not uncommon for temperature to exceed 100 degrees Fahrenheit during the summer. Summer humidity is low and evaporation is high. The winters are characterized with frequent northerly winds, producing severe cold and temperatures dropping to -30 degrees Fahrenheit.
LRU A, in the Arkansas River Valley, is the hottest and driest portion of the MLRA. Mean Annual Precipitation (MAP) is 10 to 12 inches, and Mean Annual Air Temperature (MAAT) is 51 to 54 degrees Fahrenheit. LRU B is the largest extent. MAP is 12-14 inches, and MAAT is 50 to 54 degrees Fahrenheit
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 127-134 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | 149-161 days |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 12-14 in |
| Frost-free period (actual range) | 121-135 days |
| Freeze-free period (actual range) | 141-164 days |
| Precipitation total (actual range) | 11-16 in |
| Frost-free period (average) | 129 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | 153 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 13 in |
Figure 2. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 3. Monthly minimum temperature range
Figure 4. Monthly maximum temperature range
Figure 5. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 6. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 7. Annual average temperature pattern
Climate stations used
-
(1) CHERAW 1 N [USC00051539], La Junta, CO
-
(2) ORDWAY 21 N [USC00056136], Ordway, CO
-
(3) PUEBLO MEM AP [USW00093058], Pueblo, CO
-
(4) ORDWAY 2 ENE [USC00056131], Ordway, CO
-
(5) TACONY 13 SE [USC00058157], Boone, CO
-
(6) LA JUNTA 20 S [USC00054726], La Junta, CO
-
(7) PUEBLO RSVR [USC00056765], Pueblo, CO
-
(8) ROCKY FORD 2 SE [USC00057167], Rocky Ford, CO
-
(9) EADS [USC00052446], Eads, CO
Influencing water features
There is no influential water table or wetland associated with this site.
Wetland description
N/A
Soil features
The soils of this site are moderately deep or very deep. They are well drained with moderately slow or slow permeability. The surface layer thickness ranges from 2 to 12 inches thick. The soil moisture regime is ustic aridic. The soil temperature regime is mesic. Parent material kind includes old alluvium, old alluvium over residuum and slope alluvium over residuum.
Major soil series correlated to this ecological site include Manzanola, Razor, and Nunn.
Revisions to soil surveys are on-going. For the most recent updates, visit the Web Soil Survey, the official site for latest soils information: http://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/app/WebSoilSurvey.aspx.
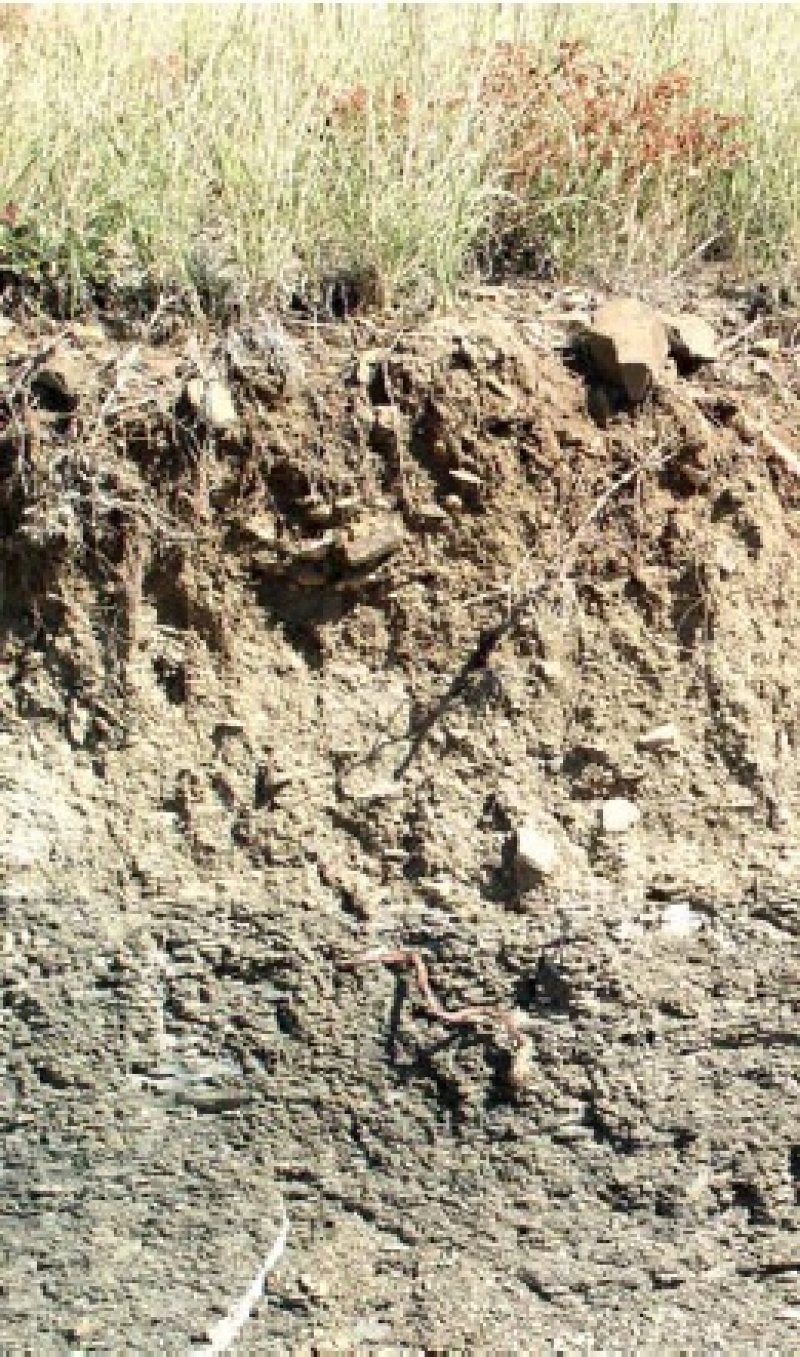

Figure 8. Razor silty clay
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Alluvium
(2) Slope alluvium |
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Clay loam (2) Silty clay (3) Silty clay loam |
| Drainage class | Well drained |
| Permeability class | Slow to moderately slow |
| Soil depth | 20 – 80 in |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 8% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | Not specified |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
4 – 9 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
14% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
15 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
14 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
6.6 – 9 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
15% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
Not specified |
Ecological dynamics
The information in this ESD, including the state-and-transition model (STM), was developed using archeological and historical data, professional experience, and scientific studies. The information is representative of a complex set of plant communities. The plant composition has been determined by study of rangeland relic areas, areas protected from excessive disturbance, seasonal-use pastures, short-duration or time-controlled grazing strategies, and historical accounts.
Not all scenarios or plants are included. Key indicator plants, animals, and ecological processes are described to inform land management decisions.
This region was historically occupied by large grazing animals, such as bison, along with pronghorn and mule deer. Deer and pronghorn are widely distributed throughout the MLRA. This is an important site for livestock grazing, especially cattle.
Drought has historically impacted the vegetation of this region. Changes in species composition vary depending upon the duration and severity of the drought cycle and prior grazing management. Recent drought events have increased mortality of blue grama significantly in some locales, along with other bunchgrasses, such as sand bluestem, little bluestem, needle and thread, Fendler threeawn, and squirreltail. Historic fire frequency (pre-industrial) is estimated at 15 to 20 years (Guyette, 2012), randomly distributed, and started by lightning at various times throughout the growing season. Early human inhabitants were also likely to start fires (deliberate or accidental).
Western wheatgrass (cool-season rhizomatous mid-grass) and blue grama (warm-season short bunchgrass) are the primary species while galleta (warm-season mid-rhizomatous) is secondary in abundance. Fourwing saltbush and winterfat are primary shrubs. American vetch, purple prairieclover, and scarlet globemallow are the primary forbs.
Deterioration of this site due to heavy, continuous grazing causes blue grama and galleta to increase. Blue grama will eventually form a sod-bound condition. Cool-season grasses such as western wheatgrass and green needlegrass decrease in frequency and production as do key shrubs such as fourwing saltbush and winterfat. American vetch, purple prairie clover, and other highly palatable forbs also decrease. Fendler's threeawn, annuals, and bare ground increase under heavy, continuous grazing or excessive defoliation. Years of non-use or lack of fire will cause litter to accumulate and reduce plant density. Much of this ecological site has been tilled and used for crop production.
Southeastern Colorado was strongly affected by extended drought conditions in the “Dust Bowl” period of the 1930s, with recurrent drought cycles in the 1950s and 1970s. Extreme to exceptional drought conditions have re-visited the area from 2002 to 2012, with brief interludes of near normal to normal precipitation years. “During periods of drought, high winds give rise to the dust storms which are especially characteristic of the southeastern plains (WRCC, 2022).” Recent drought events have increased mortality of blue grama upwards of 80 percent in some locales. The long-term effects of these latest drought years have yet to be determined.
Growth of native cool-season plants begins about April 15 and continues to mid-June. Native warm-season plants begin growth about May 1 and continue to about August 15. Regrowth of cool-season plants occurs in September and October in most years, depending on moisture. For detailed information, visit the Western Regional Climate Center website at https://wrcc.dri.edu/.
Drier and warmer climatic conditions exist in the central portion of MLRA 69. This area includes the eastern half of Pueblo county, northern Otero, extreme northwestern Bent, western edge of Kiowa, southern edge of Lincoln and all of Crowley County. These conditions are primarily caused by a rain shadow effect from the southern Rocky Mountains. Evapotranspiration rates (atmospheric demand) are higher in this area of MLRA 69. Total annual production is typically lower.
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Continuous, heavy grazing. Lack of fire. |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Heavy, continuous grazing. Lack of fire. |
| T1C | - | Mechanical tillage. |
| R2A | - | Prescribed grazing. Prescribed fire. |
| T2A | - | Heavy, continuous grazing. Lack of fire. |
| R3A | - | Prescribed grazing. Prescribed fire. |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Heavy, season-long grazing. Lack of fire. |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1B | - | Non-use. Lack of fire. |
| 1.2A | - | Prescribed grazing. Prescribed fire. |
| 1.3A | - | Prescribed grazing. Prescribed fire. |
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 4 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Reference
The Reference state is characterized by three community phases that exist within the natural range of variability for the site. These phases are maintained by a historic fire frequency estimated to be on 15 to 20 year intervals, grazing by large ungulates, and adequate recovery periods. High production of perennial grasses and extensive soil cover allow for increased soil moisture retention, vegetative production, and overall soil quality.
Dominant plant species
-
fourwing saltbush (Atriplex canescens), shrub
-
winterfat (Krascheninnikovia lanata), shrub
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
Community 1.1
Western Wheatgrass and Blue Grama
This is the interpretive plant community and is considered to be the reference plant community. This plant community evolved with grazing by large herbivores and is well suited for grazing by domestic livestock. The plant community consists of 70 to 90 percent grasses and grass-likes, 5 to 15 percent forbs and 5 to 15 percent shrubs. Dominant grasses include western wheatgrass, blue grama, and galleta. Other grasses and grass-like plants that occur in minor amounts are green needlegrass, alkali sacaton, buffalograss, sideoats grama, and sun sedge. Significant forbs are American vetch, purple prairieclover, and scarlet globemallow. Dominant shrubs that occupy this community are fourwing saltbush and winterfat. This plant community is diverse, stable, and productive. It is well suited to carbon sequestration, water yield, wildlife, and livestock use and is aesthetically pleasing. Community dynamics, nutrient cycle, water cycle, and energy flow are functioning properly. Plant litter is properly distributed with very little movement off-site, and natural plant mortality is very low. This community is resistant to disturbances with the exception of heavy, continuous grazing, tillage, and development into urban or other uses. Total annual production, during an average year, ranges from 300 to 1100 pounds per acre air-dry weight and averages 750 pounds.
Dominant plant species
-
fourwing saltbush (Atriplex canescens), shrub
-
winterfat (Krascheninnikovia lanata), shrub
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
Figure 9. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 230 | 600 | 870 |
| Forb | 35 | 75 | 115 |
| Shrub/Vine | 35 | 75 | 115 |
| Total | 300 | 750 | 1100 |
Figure 10. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). CO6901, Warm-season/cool-season co-dominant; MLRA-69; upland fine textured soils..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
Community 1.2
Blue Grama and Galleta Grass
This plant community evolved with heavy, season-long herbivory without adequate recovery periods and reduced fire frequency. Key species such as western wheatgrass, green needlegrass, American vetch, fourwing saltbush, and winterfat have been reduced and blue grama and galleta have increased in abundance in the community. Sand dropseed, purple threeawn, sixweeks fescue, bottlebrush squirreltail, and hairy goldaster have also increased. This plant community is at risk of reducing or losing western wheatgrass, green needlegrass, American vetch, fourwing saltbush, and winterfat. Continuous, heavy spring grazing with summer deferment will reduce the cool-season component (western wheatgrass, green needlegrass, and sun sedge) of this plant community and increase the warm-season component. Continuous summer grazing with spring deferment will reduce the warm-season component (sideoats grama and alkali sacaton) of this plant community and increase the cool-season component. Blue grama is increasing at the expense of the cool-season grasses and deep-rooted shrubs. Water cycle, nutrient cycle and energy flow are becoming impaired due to a shift in root structure and species composition. Less litter is being produced. Total aboveground carbon has been reduced due to decreases in forage and litter production. Reduction of rhizomatous wheatgrass, nitrogen fixing forbs, shrub component, and increased warm-season short-grasses has begun to alter the biotic integrity of this community. Water and nutrient cycles are impaired. Total annual production, during an average year, ranges from 100 to 700 pounds per acre air-dry weight and averages 400 pounds.
Dominant plant species
-
plains pricklypear (Opuntia polyacantha), shrub
-
rubber rabbitbrush (Ericameria nauseosa ssp. nauseosa var. glabrata), shrub
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
James' galleta (Pleuraphis jamesii), grass
Community 1.3
Blue Grama and Western Wheatgrass, Excessive Litter
This plant community occurs when grazing is removed for long periods of time in the absence of fire. Plant composition is similar to the reference plant community, however individual species production and frequency will be lower. Much of the nutrients are tied up in excess litter. The semiarid environment and the absence of animal impact and herd effect to break down litter, slows nutrient recycling. Aboveground litter also limits sunlight from reaching plant crowns. Many plants, especially bunchgrasses die off. Thick litter and absence of grazing or fire reduce seed germination and establishment. In advanced stages, plant mortality can increase and erosion may eventually occur if bare ground increases. This plant community is at risk of losing many key species and if ungrazed or ungrazed without fire can go to a vegetative state resembling the Increased Bare Ground State. This plant community will change rapidly with the return of natural disturbances (grazing or fire). This plant community is uncommon in the natural range of variability. Total annual production can vary from 200 to 1000 pounds of air-dry vegetation per acre and averages 600 pounds during an average year.
Dominant plant species
-
fourwing saltbush (Atriplex canescens), shrub
-
winterfat (Krascheninnikovia lanata), shrub
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2
Heavy, season-long grazing without adequate recovery opportunity between grazing events and reduced fire frequency shifts the reference plant community to the 1.2 community.
Pathway 1.1B
Community 1.1 to 1.3
Non-use or lack of fire will shift the reference plant community toward the 1.3 community. Due to the accumulation of standing plant litter the cycling of nutrients is impaired. Plant decadence and mortality increase as a result of this community pathway.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1
Prescribed grazing that allows for adequate recovery periods, and prescribed fire shift this plant community back to the reference plant community.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Burning | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Grazing |
Pathway 1.3A
Community 1.3 to 1.1
The return of normal fire frequency and appropriate grazing management shift this community to the reference community. Shifts in community phases are reversible through succession, disturbances, and short-term climatic variations that are within the natural range of variability for the site.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Burning | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Grazing |
State 2
Shortgrass
The Shortgrass state contains one community phase. This state evolved under long-term, heavy grazing pressure without adequate recovery and proper stocking rates, and a lack of fire. This is a very stable state and is resistant to change due to the high tolerance of blue grama to grazing. The loss of dominant and sub-dominant functional/structural groups such as cool-season grasses, nitrogen fixing legumes, and shrubs reduces the biodiversity and productivity of this site.
Dominant plant species
-
plains pricklypear (Opuntia polyacantha), shrub
-
rubber rabbitbrush (Ericameria nauseosa ssp. nauseosa var. glabrata), shrub
-
broom snakeweed (Gutierrezia sarothrae), shrub
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
Community 2.1
Blue Grama
This plant community evolved with heavy, continuous grazing and occurs frequently throughout most of the eastern plains of Colorado. Most of the key grasses, forbs, and palatable shrub species are absent. Western wheatgrass and galleta may persist in trace amounts, though greatly reduced in vigor and not readily seen. Blue grama dominates the community with a tight “sod-bound” appearance. Purple threeawn, sand dropseed, sixweeks fescue, and hairy goldaster have increased. This plant community is resistant to change due to the grazing tolerance of blue grama. A significant amount of production and diversity has been lost from this community when compared to the reference community. Loss of cool-season grasses, palatable shrubs, and nitrogen fixing forbs have negatively impacted energy flow and nutrient cycling. Water infiltration is reduced significantly due to the massive shallow root system “root pan”, characteristic of "sod-bound" blue grama. Soil loss may be obvious where flow paths are connected. Total annual production, during an average year, ranges from 50 to 400 pounds per acre air-dry weight and averages 200 pounds.
Dominant plant species
-
plains pricklypear (Opuntia polyacantha), shrub
-
rubber rabbitbrush (Ericameria nauseosa ssp. consimilis var. nitida), shrub
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
Figure 11. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). CO6904, Warm-season dominant; MLRA-69; upland fine textured soils..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 45 | 25 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
State 3
Eroded
This state lacks stability, diversity, and productivity. Litter levels are extremely low. Most of the more palatable species have been replaced by increasers and annuals. Due to the increased bare ground erosion is evident and flow paths are continuous. Rills may occur on steeper slopes. The nutrient cycle, water cycle, and overall energy flow are greatly impaired. Organic matter and carbon reserves are greatly reduced.
Dominant plant species
-
plains pricklypear (Opuntia polyacantha), shrub
-
rubber rabbitbrush (Ericameria nauseosa ssp. nauseosa var. glabrata), shrub
-
broom snakeweed (Gutierrezia sarothrae), shrub
-
Fendler threeawn (Aristida purpurea var. longiseta), grass
-
cheatgrass (Bromus tectorum), grass
Community 3.1
Purple Threeawn and Downy Brome
Purple threeawn, curlycup gumweed, and annual plants such as sixweeks fescue, cheatgrass, and Russian thistle have increased. Blue grama may persist in localized areas. Introduced species such as field bindweed can also be present, especially on prairie dog towns. Total annual production varies from 50 to 150 pounds of air-dry vegetation per acre.
Dominant plant species
-
plains pricklypear (Opuntia polyacantha), shrub
-
rubber rabbitbrush (Ericameria nauseosa ssp. consimilis var. nitida), shrub
-
Fendler threeawn (Aristida purpurea var. longiseta), grass
-
cheatgrass (Bromus tectorum), grass
-
Russian thistle (Salsola), other herbaceous
Figure 12. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). CO6904, Warm-season dominant; MLRA-69; upland fine textured soils..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 45 | 25 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
State 4
Tilled
This state is defined by two separate vegetation communities that are highly variable. They are derived through two distinct management scenarios, and are not related successionally. Infiltration, runoff, and soil erosion vary depending on the vegetation present. The Reference state ecosystem has been driven beyond the limits of ecological resilience and has crossed a threshold into the Tillage state. The designation of the Tillage State denotes changes in plant community composition and soil structure. These changes affect the following ecological processes: hydrologic function, biotic integrity, and soil site stability.
Dominant plant species
-
Fendler threeawn (Aristida purpurea var. longiseta), grass
-
sand dropseed (Sporobolus cryptandrus), grass
-
Russian thistle (Salsola), other herbaceous
-
burningbush (Bassia scoparia), other herbaceous
Community 4.1
Purple Threeawn and Sand Dropseed, Go-Back Land
Go-back land is created when the soil is tilled or farmed (sodbusted) and abandoned. All of the native plants are eliminated, soil organic matter is reduced, soil structure is degraded, and a compacted layer (plow pan) is formed. Residual synthetic chemicals may remain from past farming operations and erosion processes are active. Erosion is a major concern. Go-back land succeeds through several plant communities beginning with an early annual plant community, which initiates the revegetation process. Plants such as Russian thistle, burningbush, and other annuals begin to establish. These plants give some protection from erosion and start to build minor levels of soil organic matter. This early annual plant community lasts for two to several years. Red threeawn, sand dropseed, and several other early perennials can dominate the plant community for five to eight years or more. Eventually western wheatgrass, blue grama, and other natives can become reestablished. Prescribed grazing can accelerate the successional process.
Dominant plant species
-
Fendler threeawn (Aristida purpurea var. longiseta), grass
-
sand dropseed (Sporobolus cryptandrus), grass
-
Russian thistle (Salsola), other herbaceous
-
burningbush (Bassia scoparia), other herbaceous
Community 4.2
Seeded
This plant community can vary considerably depending on various factors. The Seeded Plant community is a product of the conservation practice of rangeland seeding on go-back land or recently cropped land for the purpose of converting it to permanent vegetation. Plant species native to the site are used throughout the MLRA due to their suitability to the semi-arid climate. Native species are the most adapted to site conditions and therefore can be sustained in the MLRA. Improved cultivars (named varieties) of plant materials are used to enhance seeding establishment and meet specific reclamation resource objectives. There are several factors that make seeded rangeland a different grazing resource than native rangeland. Factors such as species selected, stand density, varieties, and harvest efficiency all impact the production level and palatability. This results in uneven utilization when both seeded and native rangelands are in the same grazing unit. Therefore, the seeded rangeland should be managed as a separate grazing unit if possible. Species diversity on seeded rangeland is often lower than that of the reference plant community and native forb species will generally take longer to re-establish.
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
Continuous, heavy grazing without adequate recovery periods between grazing events and lack of fire result in shifts between states. This transition involves a major loss of plant diversity resulting in the degradation of biotic integrity.
Transition T1B
State 1 to 3
Heavy, continuous grazing without adequate recovery periods between grazing events and lack of fire moves this plant community across an ecological threshold to the Increased Eroded state. Resilience and resistance to disturbance are lost. Soil site stability, hydrologic function, and biotic integrity are significantly degraded.
Transition T1C
State 1 to 4
Tillage (plowed & abandoned) will cause this state to transition across an ecological threshold to the Tilled state. The resulting change in plant species and soil structure will adversely affect hydrologic function, biotic integrity, and soil site stability. This transition is considered to be non-restorable due to the adverse affects on the ecological functioning of the plant communities in the Tilled state.
Restoration pathway R2A
State 2 to 1
Long-term prescribed grazing with proper stocking and prescribed fire are the management actions required to recover to the Reference state. The species to target for management are those that were dominant or sub-dominant within the reference plant community according to documented functional/structural groups. This restoration may take greater than 40 years to accomplish.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Burning | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Grazing |
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
Long-term, heavy continuous grazing without adequate recovery periods between grazing events and lack of fire move this state across an ecological threshold to the Eroded state. This transition may take greater than 25 years to accomplish. Resilience and resistance to disturbance will be lost. Soil site stability, hydrologic function, and biotic integrity will be significantly degraded.
Restoration pathway R3A
State 3 to 1
Long-term prescribed grazing with adequate recovery periods, proper stocking rate, and prescribed fire are the management actions required to recover to the Reference state. The species to target for management are those that were dominant or sub-dominant within the reference plant community according to the documented functional and structural groups. It is theorized that this restoration may take greater than 80 years to accomplish.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Burning | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Grazing |
Additional community tables
Table 6. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | 525–675 | |||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 225–265 | – | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 150–225 | – | ||
| James' galleta | PLJA | Pleuraphis jamesii | 75–115 | – | ||
| green needlegrass | NAVI4 | Nassella viridula | 40–75 | – | ||
| buffalograss | BODA2 | Bouteloua dactyloides | 15–40 | – | ||
| alkali sacaton | SPAI | Sporobolus airoides | 0–40 | – | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 0–25 | – | ||
| Grass, perennial | 2GP | Grass, perennial | 0–25 | – | ||
| squirreltail | ELELE | Elymus elymoides ssp. elymoides | 0–25 | – | ||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 10–25 | – | ||
| saltgrass | DISP | Distichlis spicata | 0–15 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 0–10 | – | ||
| Indian ricegrass | ACHY | Achnatherum hymenoides | 0–10 | – | ||
| Fendler threeawn | ARPUL | Aristida purpurea var. longiseta | 0–10 | – | ||
| composite dropseed | SPCOC2 | Sporobolus compositus var. compositus | 0–10 | – | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 0–10 | – | ||
| tumblegrass | SCPA | Schedonnardus paniculatus | 0–10 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 2 | 40–115 | |||||
| Forb, perennial | 2FP | Forb, perennial | 10–40 | – | ||
| American vetch | VIAM | Vicia americana | 15–40 | – | ||
| scarlet globemallow | SPCO | Sphaeralcea coccinea | 10–25 | – | ||
| purple prairie clover | DAPUP | Dalea purpurea var. purpurea | 10–25 | – | ||
| dotted blazing star | LIPU | Liatris punctata | 10–15 | – | ||
| leafy false goldenweed | OOFOF | Oonopsis foliosa var. foliosa | 0–15 | – | ||
| white locoweed | OXSE | Oxytropis sericea | 0–10 | – | ||
| oppositeleaf bahia | PIOP | Picradeniopsis oppositifolia | 0–10 | – | ||
| woolly plantain | PLPA2 | Plantago patagonica | 0–10 | – | ||
| slimflower scurfpea | PSTE5 | Psoralidium tenuiflorum | 0–10 | – | ||
| upright prairie coneflower | RACO3 | Ratibida columnifera | 0–10 | – | ||
| silky sophora | SONU | Sophora nuttalliana | 0–10 | – | ||
| scarlet beeblossom | GACO5 | Gaura coccinea | 0–10 | – | ||
| red dome blanketflower | GAPI | Gaillardia pinnatifida | 0–10 | – | ||
| prairie sunflower | HEPE | Helianthus petiolaris | 0–10 | – | ||
| hairy false goldenaster | HEVI4 | Heterotheca villosa | 0–10 | – | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 0–10 | – | ||
| twogrooved milkvetch | ASBI2 | Astragalus bisulcatus | 0–10 | – | ||
| woolly locoweed | ASMO7 | Astragalus mollissimus | 0–10 | – | ||
| rush skeletonplant | LYJU | Lygodesmia juncea | 0–10 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 3 | 40–115 | |||||
| fourwing saltbush | ATCA2 | Atriplex canescens | 40–75 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 10–40 | – | ||
| winterfat | KRLA2 | Krascheninnikovia lanata | 15–40 | – | ||
| plains pricklypear | OPPO | Opuntia polyacantha | 0–10 | – | ||
| shadscale saltbush | ATCO | Atriplex confertifolia | 0–10 | – | ||
| tree cholla | CYIMI | Cylindropuntia imbricata var. imbricata | 0–10 | – | ||
| rubber rabbitbrush | ERNAG | Ericameria nauseosa ssp. nauseosa var. glabrata | 0–10 | – | ||
| James' seaheath | FRJA | Frankenia jamesii | 0–10 | – | ||
| broom snakeweed | GUSA2 | Gutierrezia sarothrae | 0–10 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
WILDLIFE INTERPRETATIONS:
The combination of clayey soils and grasses, forbs, and shrubs found on this ecological site provide habitat for numerous wildlife species. Historic large grazers that influenced these communities were bison and pronghorn. Bison are currently found only as domestic livestock. Pronghorn and mule and white-tailed deer use this ecological site. Domestic grazers share these habitats with wildlife. The grassland communities of eastern Colorado are home to many bird species. Changes in the composition of the plant community when moving from the reference community to other communities on this ecological site may result in species shifts in bird species. The occasional wetland or spring found on this site provides essential seasonal water needed for reproductive habitat by some reptiles and amphibians. Because of a lack of permanent water, fish are not common.
GRAZING INTERPRETATIONS:
The following table lists suggested initial stocking rates for an animal unit (1000 pound beef cow) under continuous grazing (yearlong grazing or growing-season-long grazing) based on normal growing conditions. However, continuous grazing is not recommended. These estimates should only be used as preliminary guidelines in the initial stages of the conservation planning process. Often, the existing plant composition does not entirely match any particular plant community described in this ecological site description. Therefore, field inventories are always recommended to document plant composition, total production, and palatable forage production. Carrying capacity estimates that reflect on-site conditions should be calculated using field inventories.
If the following production estimates are used, they should be adjusted based on animal kind or class and on the specific palatability of the forage plants in the various plant community descriptions. Under a properly stocked, properly applied, prescribed grazing management system that provides adequate recovery periods following each grazing event, improved harvest efficiencies eventually result in increased carrying capacity. See USDA-NRCS Colorado Prescribed Grazing Standard and Specification Guide (528).
The stocking rate calculations are based on the total annual forage production in a normal year multiplied by 25 percent harvest efficiency divided by 912.5 pounds of ingested air-dry vegetation for an animal unit per month (AUM).
Plant Community Production (lbs. /acre) and Stocking Rate (AUM/acre)
Reference Community - (750) (0.21)
1.2 Community - (400) (0.11)
1.3 Community - (600) (0.16)
2.1 Community - (200) (0.05)
These are guidelines and an on-site visit is required prior to developing a grazing plan and stocking rate.
Grazing by domestic livestock is one of the major income-producing industries in the area. Rangelands in this area provide yearlong forage under prescribed grazing for cattle, sheep, horses and other herbivores.
Hydrological functions
Water is the principal factor limiting forage production on this site. This site is dominated by soils in hydrologic group D. Infiltration and runoff potential for this site is moderate depending on ground cover. In many cases areas with greater than 75 percent ground cover have the greatest potential for high infiltration and lower runoff. An example of an exception would be where shortgrasses form a strong sod and dominate the site. Areas where ground cover is less than 50 percent have the greatest potential to have reduced infiltration and higher runoff (refer to NRCS Section 4, National Engineering Handbook (USDA–NRCS, 1972–2012) for runoff quantities and hydrologic curves).
Recreational uses
This site provides hunting, hiking, photography, bird watching, and other opportunities. The wide varieties of plants that bloom from spring until fall have an aesthetic value that appeals to visitors.
Wood products
No appreciable wood products are present on the site.
Other products
General Data (MLRA and Revision Notes, Hierarchical Classification, Ecological Site Concept, Physiographic, Climate, and Water Features, and Soils Data):Updated. All “Required” items are complete to Provisional level.
Community Phase Data (Ecological Dynamics, STM, Transition & Recovery Pathways, Reference Plant Community, Species Composition List, Annual Production Table):
Updated. All “Required” items are complete to Provisional level.
NOTE: Annual Production Table and Species Composition List are from the “Previously Approved” ESD (2004). These need review for future updates at the next Approved level. Minor edit was made to Species Composition List.
Each Alternative State/Community:Complete to Provisional level. Narrative for each state and community has been updated.
Supporting Information (Site Interpretations, Assoc. & Similar Sites, Inventory Data References, Agency/State Correlation, References):
Updated. All “Required” items are complete to Provisional level.
Animal CommunityWildlife Interpretations:First “overview” paragraph retained.
Individual Plant Community phase interpretations are removed and need to be updated at next “Approved” level.
Livestock Interpretations:
Updated to reflect the plant community name revisions. The Stocking rate calculations remain the same because they are based on the “Legacy” Total Annual Production table.
The stocking rate calculations need to be updated when Total Annual Production and Plant Community annual production is revised at the next “Approved” level.
Hydrology:
From “Previously Approved” ESD (2004). This needs to be updated at next “approved” level.
Other Site Interpretation:
Recreational Uses, Wood Products, Other Products, and Plant Preferences table, and Rangeland Health Reference Sheet carried over from “Previously Approved” ESD (2004).
Other information
Relationship to Other Classifications:
NRCS Classification Hierarchy:
Physiographic Divisions of the United States (Fenneman, 1946): Physiographic DivisionPhysiographic ProvincePhysiographic SectionLand Resource RegionMajor Land Resource Area (MLRA)Land Resource Unit (LRU).
USFS Classification Hierarchy:
National Hierarchical Framework of Ecological Units (Cleland et al, 181-200):
DomainDivisionProvinceSectionSubsectionLandtype Association LandtypeLandtype Phase.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
NRI: references to Natural Resource Inventory data
Information presented here has been derived from data collection on private and federal lands using:
• Double Sampling (clipped 2 of 5 plots)*
• Rangeland Health (Pellant et al., 2005)
• Soil Stability (Pellant et al., 2005)
• Line Point Intercept : Foliar canopy, basal cover (Forb, Graminoid, Shrub, subshrub, Lichen, Moss, Rock fragments, bare ground, % Litter) (Herrick et al., 2005)
• Soil pedon descriptions collected on site (Schoeneberger et al., 2012)
*NRCS double-sampling method, CO NRCS Similarity Index Worksheet 528(1).
Additional reconnaissance data collection using numerous ocular estimates and other inventory data; NRCS clipping data for USDA program support; Field observations from experienced range trained personnel. Specific data information is contained in individual landowner/user case files and other files located in county NRCS field offices.
References
-
Guyette, R.P., M.C. Stambaugh, D.C. Dey, and R. Muzika. 2012. Predicting Fire Frequency with Chemistry and Climate. Ecosystems 15:322–335.
Other references
Data collection for this ecological site was done in conjunction with the progressive soil surveys within the Upper Arkansas Valley (MLRA 69) of Colorado. The site has been mapped and correlated with soils in the following soil surveys: Baca County, Bent County, Crowley County, El Paso County Area, Fremont County Area, Huerfano County Area, Kiowa County, Las Animas County: Parts of Huerfano and Las Animas, Lincoln County, Otero County, Prowers County, and Pueblo Area: Parts of Pueblo and Custer Counties.
30 Year Climatic and Hydrologic Normals (1981-2010) Reports. National Water and climate Center: Portland, OR. August 2015
ACIS-USDA Field Office Climate Data (WETS), period of record 1971-2000 http://agacis.rcc-acis.org (powered by WRCC) Accessed March 2016
Andrews, R. and R. Righter. 1992. Colorado Birds. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, CO. 442
Armstrong, D.M. 1972. Distribution of mammals in Colorado. Univ. Kansas Museum Natural History Monograph #3. 415.
Butler, LD., J.B. Cropper, R.H. Johnson, A.J. Norman, G.L. Peacock, P.L. Shaver, and K.E. Spaeth. 1997, revised 2003. National Range and Pasture Handbook. National Cartography and Geospatial Center’s Technical Publishing Team: Fort Worth, TX. http://www.glti.nrcs.usda.gov/technical/publications/nrph.html Accessed August 2015
Clark, J., E. Grimm, J. Donovan, S. Fritz, D. Engrstom, and J. Almendinger. 2002. Drought cycles and landscape responses to past Aridity on prairies of the Northern Great Plains, USA. Ecology, 83(3), 595-601.
Cleland, D., P. Avers, W.H. McNab, M. Jensen, R. Bailey, T. King, and W. Russell. 1997. National Hierarchical Framework of Ecological Units, published in Ecosystem Management: Applications for Sustainable Forest and Wildlife Resources, Yale University Press
Cooperative climatological data summaries. NOAA. Western Regional Climate Center: Reno, NV. Web. http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/climatedata/climsum Accessed August 2015
Egan, Timothy. 2006. The Worst Hard Time. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company: New York, NY.
Fitzgerald, J.P., C.A. Meaney, and D.M. Armstrong. 1994. Mammals of Colorado. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, CO. 467. Hammerson, G.A. 1986. Amphibians and reptiles in Colorado. CO Div. Wild. Publication Code DOW-M-I-3-86. 131.
Herrick, Jeffrey E., J.W. Van Zee, K.M. Haystad, L.M. Burkett, and W.G. Witford. 2005. Monitoring Manual for Grassland, Shrubland, and Savanna Ecosystems, Volume II. U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Jornada Experimental Range, Las Cruces, N.M.
Kingery, H., Ed. (1998) Colorado Breeding Birds Atlas. Dist. CO Wildlife Heritage Foundation: Denver, CO. 636.
National Water & Climate Center. USDA-NRCS. USDA Pacific Northwest Climate Hub: Portland, OR. http://www.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/ Accessed March 2016
National Weather Service Co-op Program. 2010. Colorado Climate Center. Colorado State Univ. Web. http://climate.atmos.colostate.edu/dataaccess.php March 2016
Pellant, M., P. Shaver, D.A. Pyke, J.E. Herrick. (2005) Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health, Version 4. BLM National Business Center Printed Materials Distribution Service: Denver, CO.
PLANTS Database. 2015. USDA-NRCS. Web. http://plants.usda.gov/java/ Accessed August 2015. February 2016
PRISM Climate Data. 2015. Prism Climate Group. Oregon State Univ. Corvallis, OR. http://www.prism.oregonstate.edu/ Accessed August 2015.
Rennicke, J. 1990. Colorado Wildlife. Falcon Press, Helena and Billings, MT and CO Div. Wildlife, Denver CO. 138.
Schoeneberger, P.J., D.A. Wysockie, E.C. Benham, and Soil Survey Staff. 2012. Field book for describing and sampling soils, Version 3.0. Natural Resources Conservation Service, National Soil Survey Center: Lincoln, NE.
The Denver Posse of Westerners. 1999. The Cherokee Trail: Bent’s Old Fort to Fort Bridger. The Denver Posse of Westerners, Inc. Johnson Printing: Boulder, CO
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. September, 1991. Changes in Vegetation and Land Use I eastern Colorado, A Photographic study, 1904-1986.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2006. Land Resource Regions and Major Land Resource areas of the United States, the Caribbean, and the Pacific Basin. US Department of Agriculture Handbook 296.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. National Geospatial Center of Excellence. Colorado annual Precipitation Map from 1981-2010, Annual Average Precipitation by State
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2009. Part 630, Hydrology, National Engineering Handbook
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 1972-2012. National Engineering Handbook Hydrology Chapters. http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detailfull/national/water/?&cid=stelprdb1043063 Accessed August 2015.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. National Soil Survey Handbook title 430-VI. http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/ref/?cid=nrcs142p2_054242 Accessed July 2015
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Soil Survey Division Staff. 1993. Soil Survey Manual.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture.1973. Soil Survey of Baca County, Colorado.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. 1970. Soil Survey of Bent County, Colorado.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. 1968. Soil Survey of Crowley County, Colorado.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. 1981 Soil Survey of El Paso County Area, Colorado.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. 1995. Soil Survey of Fremont County Area, Colorado.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. 1983. Soil Survey of Huerfano County Area, Colorado.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture.1981. Soil Survey of Kiowa County, Colorado.
Western Regional Climate Center. 2022. Climate of Colorado, climate of the eastern plains. https://wrcc.dri.edu/Climate/narrative_co.php (accessed 9 August 2022).
Contributors
Doug Whisenhunt Ecological Site Specialist NRCS
Kimberly A. Diller Ecological Site Specialist NRCS
Ben P. Berlinger Rangeland Management Specialist NRCS Retired
Laura L. Craven MLRA Project Leader NRCS
Approval
Kirt Walstad, 4/15/2025
Acknowledgments
Project Staff:
Kimberly Diller, Ecological Site Specialist, NRCS MLRA, Pueblo SSO
Laura Craven, MLRA 69 Soil Survey Leader, NRCS MLRA Pueblo SSO
Amber Wyndham, Soil Scientist, NRCS MLRA Pueblo SSO
Ben Berlinger, Rangeland Management Specialist, Retired NRCS La Junta, CO
Program Support:
Rachel Murph, NRCS State Rangeland Management Specialist
David Kraft, NRCS MLRA Ecological Site Specialist-QA (acting), Emporia, KS
Chad Remley, Regional Director, N. Great Plains Soil Survey, Salina, KS
B.J. Shoup, State Soil Scientist, Denver
Eugene Backhaus, State Resource Conservationist, Denver
Chanda Garcia, NRCS State Biologist, NRCS, Denver CO
Patty Knupp, Area 3 Biologist, NRCS, Pueblo CO
Partners/Contributors:
James Kulbeth, Natural Resources Specialist, Department of the Army, Fort Carson, CO
John Lamman, Rangeland Management Specialist, BLM, Cañon City, CO
Steve Olson, Botanist, USFS, Pueblo, CO
Renee Rondeau, Ecologist, CO Natural Heritage Program, Hesperus, CO
Terri Schultz, The Nature Conservancy, Ft. Collins, CO
John Valentine, District Manager, CO State Land Board, Pueblo, CO
Those involved in developing earlier versions of this site description include: Ben Berlinger, rangeland management specialist (RMS); Scott Woodall, RMS; Lee Neve, soil scientist; Julie Elliott, RMS; Terri Skadeland, Colorado State biologist; and Herman Garcia, Colorado State RMS.
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | Ben Berlinger, Daniel Nosal, Kimberly Diller |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | Ben Berlinger, Area Rangeland Management Specialist, La Junta, CO, |
| Date | 01/12/2005 |
| Approved by | Kirt Walstad |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
None -
Presence of water flow patterns:
Typically none, if present (steeper slopes following intense storms) short and not connected. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
None -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
5-7% or less bare ground, with bare patches generally less than 2-3 inches in diameter. Extended drought can cause bare ground to increase upwards to 15-25% with bare patches reaching upwards to 12-18 inches in diameter. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
None -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
None -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Minimal and short. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Stability class rating anticipated to be 5-6 in interspace at soil surface. These values need verification at reference site. -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
Average SOM is 1-3%. Soils are typically deep to moderately deep, light brownish-gray to light olive-brown, weak very thin platy to weak fine granular structure, approximately 0-4 inches in depth. -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
Diverse grass, forb, shrub functional/structural groups and diverse root structure reduces raindrop impact slows overland flow providing increased time for infiltration to occur. Extended drought reduces short/mid bunchgrasses causing decreased infiltration and increased runoff following intense storms. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
None -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
cool season mid rhizomatous > warm season short bunchgrass >Sub-dominant:
shrubs = warm season mid rhizomatous > cool season mid bunchgrass >Other:
warm season forbs > leguminous forbs > cool season forbs = warm season mid bunchgrass > warm season short stoleniferous > grasslike > annual native grassesAdditional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Typically minimal. Expect short/mid bunchgrass mortality/decadence during and following drought. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Litter cover during and following extended drought ranges from 10-20%. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
300 lbs./ac. low precipitation years; 750 lbs./ac. average precipitation years; 1100 lbs./ac. above average precipitation years. After extended drought or the first growing season following wildfire, production may be significantly reduced by 100 – 250 lbs./ac. -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
Invasive plants should not occur in reference plant community. Cheatgrass, Russian thistle, kochia, other non-native annuals may invade following extended drought or fire if a seed source is available. Oneseed juniper may infrequently invade from adjacent sites with lack of fire. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
The only limitations are weather related, wildfire, and natural disease that may temporarily reduce reproductive capability.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Continuous, heavy grazing. Lack of fire. |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Heavy, continuous grazing. Lack of fire. |
| T1C | - | Mechanical tillage. |
| R2A | - | Prescribed grazing. Prescribed fire. |
| T2A | - | Heavy, continuous grazing. Lack of fire. |
| R3A | - | Prescribed grazing. Prescribed fire. |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Heavy, season-long grazing. Lack of fire. |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1B | - | Non-use. Lack of fire. |
| 1.2A | - | Prescribed grazing. Prescribed fire. |
| 1.3A | - | Prescribed grazing. Prescribed fire. |