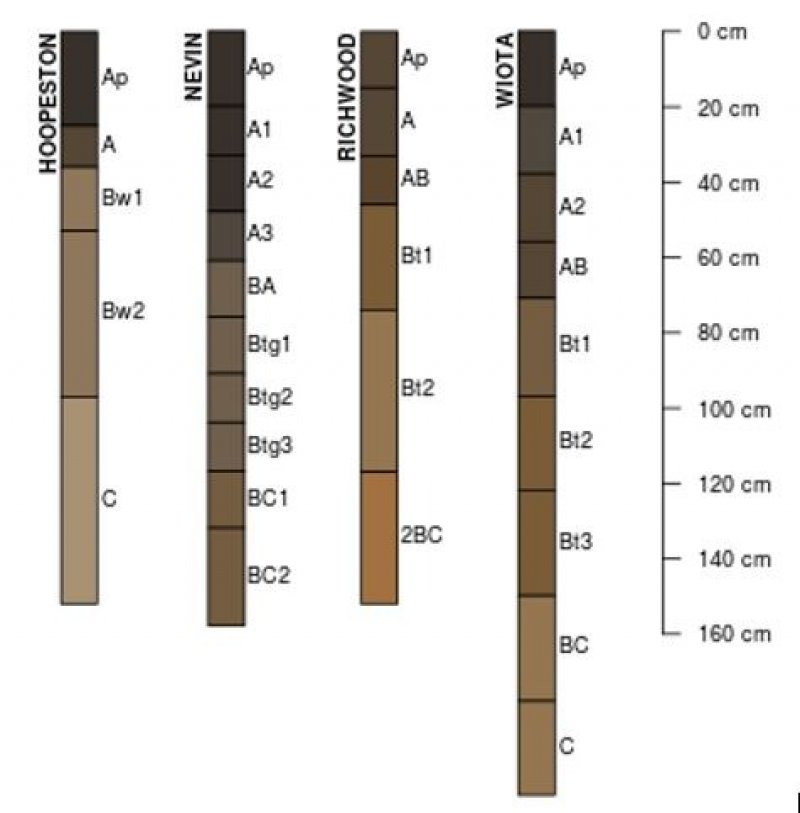
Ecological dynamics
The information in this Ecological Site Description, including the state-and-transition model (STM), was developed based on historical data, current field data, professional experience, and a review of the scientific literature. As a result, all possible scenarios or plant species may not be included. Key indicator plant species, disturbances, and ecological processes are described to inform land management decisions.
Ecological Dynamics
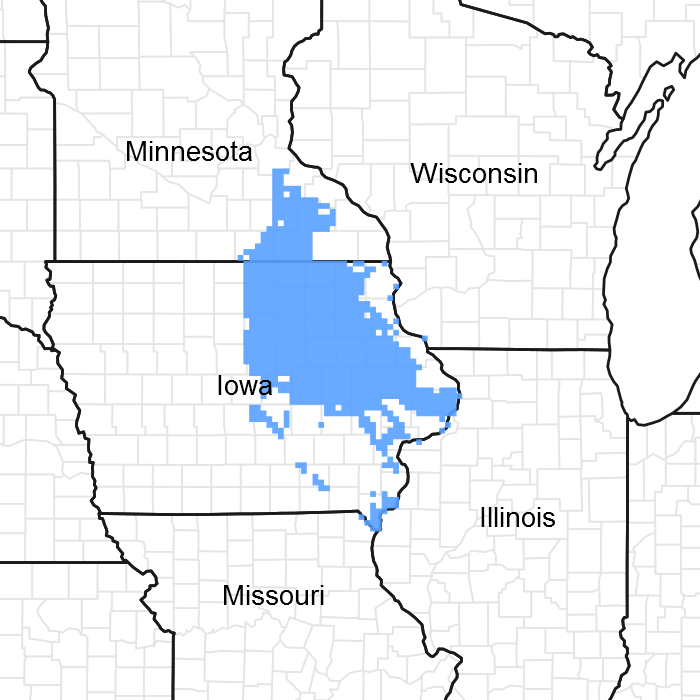
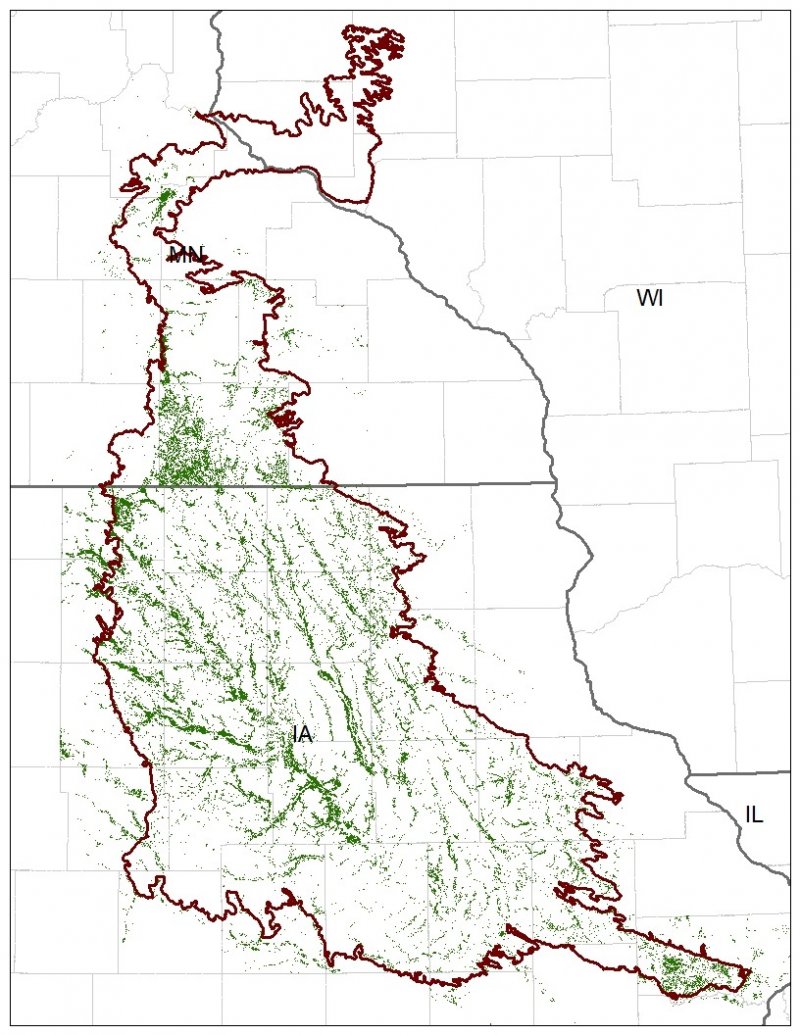
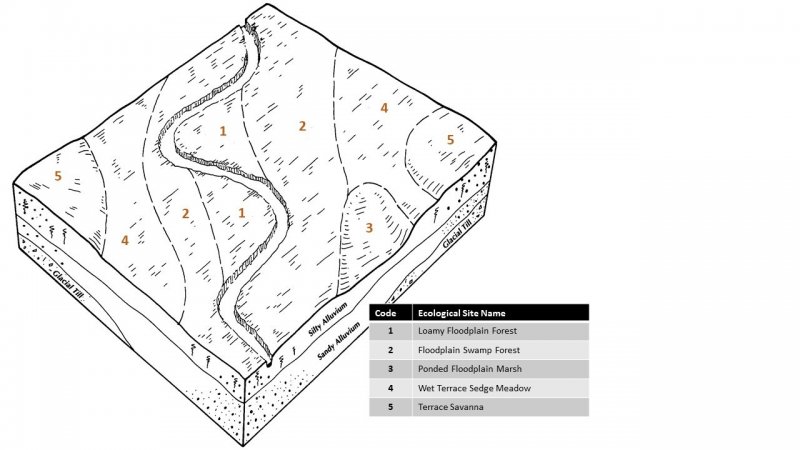
The MLRA lies within the transition zone between the eastern deciduous forests and the tallgrass prairies. The heterogeneous topography of the area results in variable microclimates and fuel matrices that in turn support prairies, savannas, woodlands, and forests. Terrace Savannas form an aspect of this vegetative continuum. This ecological site occurs on low stream terraces on somewhat poorly to excessively-drained soils. Species characteristic of this ecological site consist of a mix of herbaceous vegetation and scattered trees.
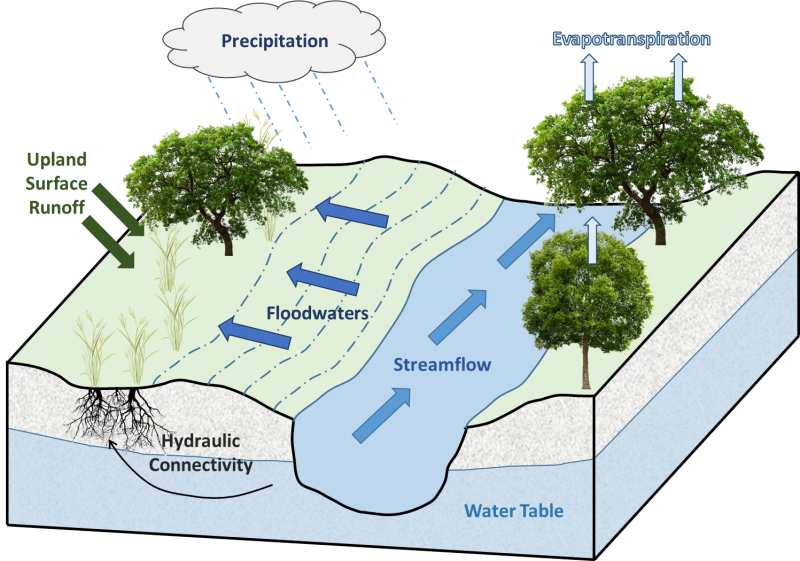
Fire and rare flooding are critical disturbance factors that maintain Terrace Savannas. Fire intensity typically consisted of periodic fires occurring every 1 to 5 years (LANDFIRE 2009). Ignition sources included summertime lightning strikes from convective storms and bimodal, human ignitions during the spring and fall seasons. Native Americans regularly set fires to improve sight lines for hunting, driving large game, improving grazing and browsing habitat, agricultural clearing, and enhancing vital ethnobotanical plants (Barrett 1980; White 1994). Infrequent flooding influenced plant community composition as evidenced by the co-dominance of oak species with floodplain associated species.
Drought and herbivory by native ungulates have also played a role in shaping this ecological site. The periodic episodes of reduced soil moisture in conjunction with the somewhat poorly to excessively-drained soils have favored the proliferation of plant species tolerant of such conditions. Drought can also slow the growth of plants and result in dieback of certain species. Bison (Bos bison) grazing, while present, served a more limited role in community composition and structure than lands further west. Prairie elk (Cervus elaphus) and white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) likely contributed to woody species reduction but are also considered to be of a lesser impact compared to the west (LANDFIRE 2009). When coupled with fire, periods of drought and herbivory can further delay the establishment of woody vegetation (Pyne et al. 1996).
Today, Terrace Savannas may be extirpated from the MLRA due to type-conversions to agricultural production lands. A return to the historic plant community may not be possible following extensive land modification, but long-term conservation agriculture or savanna reconstruction can help to restore some biotic diversity and ecological function. The state-and-transition model that follows provides a detailed description of each state, community phase, pathway, and transition. This model is based on available experimental research, field observations, literature reviews, professional consensus, and interpretations.
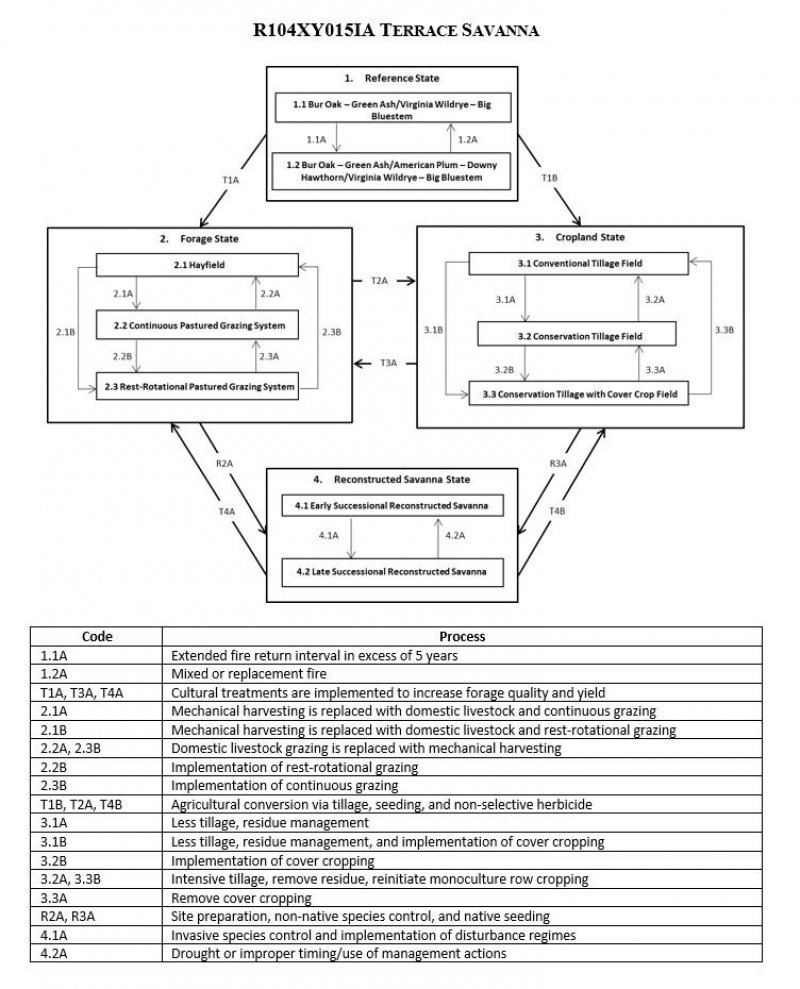
State 1
Reference State
The reference plant community is categorized as a lowland savanna community, dominated by herbaceous vegetation and scattered trees. The two community phases within the reference state are dependent on fire and infrequent flooding. The frequency, intensity, and duration of these disturbances alter species composition, cover, and extent. Surface fires are the dominant fire regime, comprising approximately 96 percent of all fires and occurring every five years. Mixed and replacement fires comprise the remaining 4 percent, occurring approximately every 3 and 1 years, respectively (LANDFIRE 2009). Flooding was infrequent, occurring once every 20 to 100 years, and influenced tree canopy composition. Drought and herbivory have more localized impacts in the reference phases, but do contribute to overall species composition, diversity, cover, and productivity.
Community 1.1
Bur Oak – Green Ash/Virginia Wildrye – Big Bluestem
Sites in this reference community phase are dominated by a mix of grasses, sedges, and forbs with scattered trees. Bur oak is the dominant upland tree species present. Lowland species are also a significant component of the canopy, such as green ash. Other likely canopy associates include American basswood and common hackberry. The tree layer comprises no more than 20 percent cover and tree size class is medium (9 to 21-inch DBH). Vegetative cover is continuous (up to 100 percent) with species such as Virginia wildrye, big bluestem, … Surface fires every 5 years will maintain this class, but an extended fire return interval will shift the community to phase 1.2 (LANDFIRE 2009).
Community 1.2
Bur Oak – Green Ash/American Plum – Downy Hawthorn/Virginia Wildrye – Big Bluestem
This reference community phase represents a successional shift due to an extended fire return interval. This fire-free period allows woody shrubs to establish, such as American plum (Prunus americana Marshall) and downy hawthorn (Crataegus mollis Scheele) (Delong and Hooper 1996). Tree cover can increase to as much as 60 percent, and tree size class moves from medium to large (21 to 33-inch DBH). Surface fires every 5 years will maintain this community, but mixed or replacement fires will shift the community back to phase 1.1 (LANDFIRE 2009).
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2
Extended fire return interval in excess of 5 years.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1
Mixed or replacement fire.
State 2
Forage State
The forage state occurs when the site is converted to a farming operation that emphasizes domestic livestock production known as grassland agriculture. Fire suppression, periodic cultural treatments (e.g., clipping, drainage, soil amendment applications, planting new species and/or cultivars, mechanical harvesting) and grazing by domesticated livestock transition and maintain this state (USDA-NRCS 2003). Early settlers seeded non-native species, such as smooth brome (Bromus inermis Leyss.) and Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.), to help extend the grazing season (Smith 1998). Over time, as lands were continuously harvested or grazed by herds of cattle, the non-native species were able to spread and expand across the landscape, reducing the native species diversity and ecological function.
Community 2.1
Hayfield
Sites in this community phase consist of forage plants that are planted and mechanically harvested. Mechanical harvesting removes much of the aboveground biomass and nutrients that feed the soil microorganisms (Franzluebbers et al. 2000; USDA-NRCS 2003). As a result, soil biology is reduced leading to decreases in nutrient uptake by plants, soil organic matter, and soil aggregation. Frequent biomass removal can also reduce the site’s carbon sequestration capacity (Skinner 2008).
Community 2.2
Continuous Pastured Grazing
This community phase is characterized by continuous grazing where domestic livestock graze a pasture for the entire season. Depending on stocking density, this can result in lower forage quality and productivity, weed invasions, and uneven pasture use. Continuous grazing can also increase the amount of bare ground and erosion and reduce soil organic matter, cation exchange capacity, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability and retention (Bharati et al. 2002; Leake et al. 2004; Teague et al. 2011). Smooth brome, Kentucky bluegrass, and white clover (Trifolium repens L.) are common pasture species used in this phase. Their tolerance to continuous grazing has allowed these species to dominate, sometimes completely excluding the native vegetation.
Community 2.3
Periodic-rest Pastured Grazing
This community phase is characterized by periodic-rest grazing where the pasture has been subdivided into several smaller paddocks. Subdividing the pasture in this way allows livestock to utilize one or a few paddocks, while the remaining area is rested allowing plants to restore vigor and energy reserves, deepen root systems, develop seeds, as well as allow seedling establishment (Undersander et al. 2002; USDA-NRCS 2003). Periodic-rest pastured grazing includes deferred periods, rest periods, and periods of high intensity – low frequency, and short duration methods. Vegetation is generally more diverse and can include orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.), timothy (Phleum pretense L.), red clover (Trifolium pratense L.), and alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). The addition of native prairie species can further bolster plant diversity and, in turn, soil function. This community phase promotes numerous ecosystem benefits including increasing biodiversity, preventing soil erosion, maintaining and enhancing soil quality, sequestering atmospheric carbon, and improving water yield and quality (USDA-NRCS 2003).
Pathway 2.1A
Community 2.1 to 2.2
Mechanical harvesting is replaced with domestic livestock utilizing continuous grazing.
Pathway 2.1B
Community 2.1 to 2.3
Mechanical harvesting is replaced with domestic livestock utilizing periodic-rest grazing.
Pathway 2.2A
Community 2.2 to 2.1
Domestic livestock are removed, and mechanical harvesting is implemented.
Pathway 2.2B
Community 2.2 to 2.3
Periodic-rest grazing replaces continuous grazing.
Pathway 2.3B
Community 2.3 to 2.1
Domestic livestock are removed, and mechanical harvesting is implemented.
Pathway 2.3A
Community 2.3 to 2.2
Continuous grazing replaces periodic-rest grazing.
State 3
Cropland State
The continuous use of tillage, row-crop planting, and chemicals (i.e., herbicides, fertilizers, etc.) has effectively eliminated the reference community and many of its natural ecological functions in favor of crop production. Corn and soybeans are the dominant crops for the site, and oats (Avena L.) and alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) may be rotated periodically. These areas are likely to remain in crop production for the foreseeable future.
Community 3.1
Conventional Tillage Field
Sites in this community phase typically consist of monoculture row-cropping maintained by conventional tillage practices. They are cropped in either continuous corn or alternating periods of corn and soybean crops. The frequent use of deep tillage, low crop diversity, and bare soil conditions during the non-growing season negatively impacts soil health. Under these practices, soil aggregation is reduced or destroyed, soil organic matter is reduced, erosion and runoff are increased, and infiltration is decreased, which can ultimately lead to undesirable changes in the hydrology of the watershed (Tomer et al. 2005).
Community 3.2
Conservation Tillage Field
This community phase is characterized by periodically alternating crops and utilizing various conservation tillage methods to promote soil health and reduce erosion. Conservation tillage methods include strip-till, ridge-till, vertical-till, or no-till planting operations. Strip-till keeps seedbed preparation to narrow bands less than one-third the width of the row where crop residue and soil consolidation are left undisturbed in-between seedbed areas. Strip-till planting may be completed in the fall and nutrient application either occurs simultaneously or at the time of planting. Ridge-till uses specialized equipment to create ridges in the seedbed and vegetative residue is left on the surface in between the ridges. Weeds are controlled with herbicides and/or cultivation, seedbed ridges are rebuilt during cultivation, and soils are left undisturbed from harvest to planting. Vertical-till operations employ machinery that lightly tills the soil and cuts up crop residue, mixing some of the residue into the top few inches of the soil while leaving a large portion on the surface. No-till management is the most conservative, disturbing soils only at the time of planting and fertilizer application. Compared to conventional tillage operations, conservation tillage methods can improve soil ecosystem function by reducing soil erosion, increasing organic matter and water availability, improving water quality, and reducing soil compaction.
Community 3.3
Conservation Tillage with Cover Crop Field
This community phase applies conservation tillage methods as described above as well as adds cover crop practices. Cover crops typically include nitrogen-fixing species (e.g., legumes), small grains (e.g., rye, wheat, oats), or forage covers (e.g., turnips, radishes, rapeseed). The addition of cover crops not only adds plant diversity but also promotes soil health by reducing soil erosion, limiting nitrogen leaching, suppressing weeds, increasing soil organic matter, and improving the overall soil ecosystem. In the case of small grain cover crops, surface cover and water infiltration are increased, while forage covers can be used to graze livestock or support local wildlife. Of the three community phases for this state, this phase promotes the greatest soil sustainability and improves ecological functioning within a row crop operation.
Pathway 3.1A
Community 3.1 to 3.2
.1A – Tillage operations are greatly reduced, alternating crops occurs on a regular interval, and crop residue remains on the soil surface.
Pathway 3.1B
Community 3.1 to 3.3
Tillage operations are greatly reduced or eliminated, alternating crops occurs on a regular interval, crop residue remains on the soil surface, and cover crops are planted following crop harvest.
Pathway 3.2A
Community 3.2 to 3.1
Intensive tillage is utilized, and monoculture row-cropping is established.
Pathway 3.2B
Community 3.2 to 3.3
Cover crops are implemented to minimize soil erosion.
Pathway 3.3B
Community 3.3 to 3.1
Intensive tillage is utilized, cover crops practices are abandoned, monoculture row-cropping is established on a more-or-less continuous basis.
Pathway 3.3A
Community 3.3 to 3.2
Cover crop practices are abandoned.
State 4
Reconstructed Savanna State
Savanna reconstructions have become an important tool for repairing natural ecological functions and providing habitat protection for numerous grassland dependent species. Because the historic plant and soil biota communities of the tallgrass prairie were highly diverse with complex interrelationships, historic savanna replication cannot be guaranteed on landscapes that have been so extensively manipulated for extended timeframes (Kardol and Wardle 2010; Fierer et al. 2013). Therefore, ecological restoration should aim to aid the recovery of degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystems. A successful restoration will have the ability to structurally and functionally sustain itself, demonstrate resilience to the natural ranges of stress and disturbance, and create and maintain positive biotic and abiotic interactions (SER 2002). The reconstructed savanna state is the result of a long-term commitment involving a multi-step, adaptive management process. Tree plantings may be required to reproduce the overstory canopy (Asbjornsen et al. 2005). Diverse, species-rich seed mixes may be important to utilize as they allow the site to undergo successional stages that exhibit changing composition and dominance over time (Smith et al. 2010). On-going management via prescribed fire and/or light grazing can help the site progress from an early successional community dominated by annuals and some weeds to a later seral stage composed of native perennial grasses, forbs, shrubs, and eventually mature bur oaks. Establishing a prescribed fire regime that mimics natural disturbance patterns can increase native species cover and diversity while reducing cover of non-native forbs and grasses. Light grazing alone can help promote species richness, while grazing accompanied with fire can control the encroachment of undesirable woody vegetation (Brudvig et al. 2007).
Community 4.1
Early Successional Reconstructed Savanna
This community phase represents early community assembly and is highly dependent on the timing and priority of planting and/or tree thinning operations and the herbaceous seed mix utilized. If oak planting is needed, acorns should be planted shortly after harvest as acorns germinate shortly after seedfall and require no cold stratification. Browse protection may need to be installed to protect newly established seedlings from animal predation (Gucker 2011). If selective tree removal is needed, canopy reduction should encompass between 16 to 45 percent of the undesirable species in a single year (Asbjornsen et al. 2005). The seed mix should look to include a diverse mix of native cool-season and warm-season annual and perennial grasses and forbs typical of the reference state. Native, cool-season annuals can help to provide litter that promotes cool, moist soil conditions to the benefit of the other species in the seed mix. The first season following site preparation and seeding will typically result in annuals and other volunteer species forming a majority of the vegetative cover. Control of non-native species, particularly perennial species, is crucial at this point to ensure they do not establish before the native vegetation (Martin and Wilsey 2012). After the first season, native warm-season grasses should begin to become more prominent on the landscape and over time close the canopy.
Community 4.2
Late Successional Reconstructed Savanna
Appropriately timed disturbance regimes (e.g., prescribed fire) applied to the early successional community phase can help increase the beta diversity, pushing the site into a late successional community phase over time. While oak savanna communities are dominated by grasses, these species can suppress forb establishment and reduce overall diversity and ecological functioning (Martin and Wilsey 2006; Williams et al. 2007). Reducing accumulated plant litter from such tallgrasses as big bluestem and Indiangrass allows more light and nutrients to become available for forb recruitment, allowing for greater ecosystem complexity (Wilsey 2008). Prescribed fire should be used on a cycle no less than every five years to allow the oaks to establish and mature (Gucker 2011).
Pathway 4.1A
Community 4.1 to 4.2
Selective herbicides are used to control non-native species, and prescribed fire and/or light grazing help to increase the native species diversity and control non-oak woody vegetation.
Pathway 4.2B
Community 4.2 to 4.1
Reconstruction experiences a decrease in native species diversity from drought or improper timing of management actions (e.g., reduced fire frequency, use of non-selective herbicides).
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
Cultural treatments to enhance forage quality and yield transitions the site to the forage state (2).
Transition T1B
State 1 to 3
Tillage, seeding of agricultural crops, and non-selective herbicide transition the site to the cropland state (3).
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
Tillage, seeding of agricultural crops, and non-selective herbicide transition this site to the cropland state (3).
Restoration pathway R2A
State 2 to 4
Site preparation, tree planting, invasive species control, and seeding native species transition this site to the reconstructed savanna state (4).
Transition T3A
State 3 to 2
Cultural treatments to enhance forage quality and yield transitions the site to the forage state (2).
Restoration pathway R3A
State 3 to 4
Site preparation, tree planting, invasive species control, and seeding native species transition this site to the reconstructed savanna state (4).
Transition T4A
State 4 to 2
Cultural treatments to enhance forage quality and yield transition the site to the forage state (2).
Transition T4B
State 4 to 3
Tillage, seeding of agricultural crops, and non-selective herbicide transition this site to the cropland state (3).