Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F111XA013IN
Loess Upland
Last updated: 9/11/2024
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
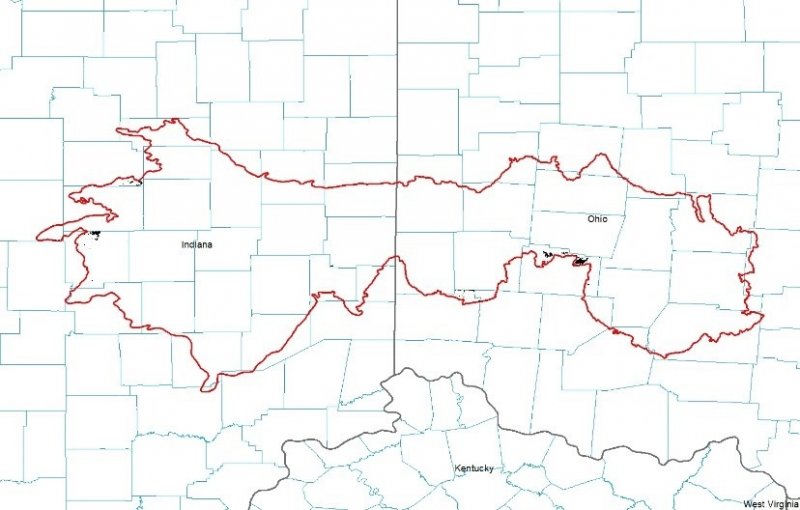
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 111X–Indiana and Ohio Till Plain
A PROVISIONAL ECOLOGICAL SITE is a conceptual grouping of soil map unit components within a Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) based on the similarities in response to management. Although there may be wide variability in the productivity of the soils grouped into a Provisional Site, the soil vegetation interactions as expressed in the State and Transition Model are similar and the management actions required to achieve objectives, whether maintaining the existing ecological state or managing for an alternative state, are similar. Provisional Sites are likely to be refined into more precise group during the process of meeting the APPROVED ECOLOGICAL SITE DESCRIPTION criteria.
This PROVISIONAL ECOLOGICAL SITE has been developed to meet the standards established in the National Ecological Site Handbook. The information associated with this ecological site does not meet the Approved Ecological Site Description Standard, but it has been through a Quality Control and Quality Assurance processes to assure consistency and completeness. Further investigations, reviews and correlations are necessary before it becomes an Approved Ecological Site Description.
111A – Indiana and Ohio Till Plain, Central Part. This area is in the Till Plains Section of the Central Lowland Province of the Interior Plains. It is dominated by broad, nearly level ground moraines that are broken in some areas by kames, outwash plains, and stream valleys along the leading edge of the moraines. Narrow, shallow valleys commonly are along the few large streams in the area. Elevation ranges from 680 to 1,250 feet (205 to 380 meters), increasing gradually from west to east. Relief is mainly a few meters, but in some areas hills rise as much as 100 feet (30 meters) above the adjoining plains.
The extent of the major Hydrologic Unit Areas (identified by four-digit numbers) that make up this MLRA is as follows: Wabash (0512), 46 percent; Great Miami (0508), 30 percent; Scioto (0506), 22 percent; and the Middle Ohio (0509), 2 percent. The major rivers in the area include the East and West Forks of the White River and the Whitewater River in Indiana and the Great Miami, Stillwater, Big Darby, Scioto, and Big Walnut Rivers in Ohio.
Surface deposits in this area include glacial deposits of till, lacustrine sediments, and outwash from Wisconsin and older glacial periods. A moderately thick mantle of loess covers much of the area. Most of this MLRA is underlain by Silurian and Devonian limestone and dolostone. Also, some areas of Late Ordovician shale and limestone are in the western part of the MLRA (USDA, 2006).
Classification relationships
Major Land Resource Area (USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006)
USFS Ecological Regions (USDA, 2007):
Sections – Southern Unglaciated Allegheny Plateau (221E), Central Till Plains, Beech Maple (222H), Interior Low Plateau-Transition Hills (223B), Interior Low Plateau-Bluegrass (223F)
Subsections - Lower Scioto River Plateau (221Eg), Bluffton Till Plains (222Ha), Miami-Scioto Plain-Tipton Till Plain (222Hb), Little Miami Old Drift Plain (222Hc), Mad River Interlobate Plains (222Hd), Darby Plains (222He), Brown County Hills (223Ba), Northern Bluegrass (223Fd), Muscatatuck Flats and Valleys (223Fe), Scottsburg Lowlands (223Ff)
NatureServe Systems anticipated (NatureServe, 2011): Agriculture - Cultivated Crops and Irrigated Agriculture, Agriculture - Pasture/Hay, Allegheny-Cumberland Dry Oak Forest and Woodland, Appalachian (Hemlock)-Northern Hardwood Forest, Central Appalachian Pine-Oak Rocky Woodland, Central Interior Acidic Cliff and Talus, Central Interior Highlands Calcareous Glade and Barrens, Central Tallgrass Prairie, Clearcut - Grassland/Herbaceous, Introduced Upland Vegetation – Treed, Managed Tree Plantation, Mississippi River Riparian Forest, North-Central Interior and Appalachian Acidic Peatland, North-Central Interior Beech-Maple Forest, North-Central Interior Dry-Mesic Oak Forest and Woodland, North-Central Interior Floodplain, North-Central Interior Freshwater Marsh, North-Central Interior Oak Savanna, North-Central Interior Wet Flatwoods, North-Central Interior Wet Meadow-Shrub Swamp, North-Central Oak Barrens, Northeastern Interior Dry-Mesic Oak Forest, Ruderal Forest, Ruderal Upland - Old Field, South-Central Interior / Upper Coastal Plain Wet Flatwoods, South-Central Interior Large Floodplain, South-Central Interior Mesophytic Forest, South-Central Interior Small Stream and Riparian, Southern Appalachian Oak Forest, Southern Interior Low Plateau Dry-Mesic Oak Forest, Southern Ridge and Valley / Cumberland Dry Calcareous Forest, Successional Shrub/Scrub
LANDFIRE Biophysical Settings anticipated (USGS, 2010): Allegheny-Cumberland Dry Oak Forest and Woodland, Appalachian (Hemlock-) Northern Hardwood Forest, Central Interior and Appalachian Floodplain Systems, Central Interior and Appalachian Riparian Systems, Central Interior and Appalachian Shrub-Herbaceous Wetland Systems, Central Interior and Appalachian Swamp Systems, Central Interior Highlands Calcareous Glade and Barrens, Central Interior Highlands Dry Acidic Glade and Barrens, Central Tallgrass Prairie, Great Lakes Coastal Marsh Systems, North-Central Interior Beech-Maple Forest, North-Central Interior Dry-Mesic Oak Forest and Woodland, North-Central Interior Dry Oak Forest and Woodland, North-Central Interior Oak Savanna, North-Central Interior Wet Flatwoods, South-Central Interior Mesophytic Forest, South-Central Interior/Upper Coastal Plain Flatwoods, Southern Appalachian Oak Forest, Southern Interior Low Plateau Dry-Mesic Oak Forest
Ecological site concept
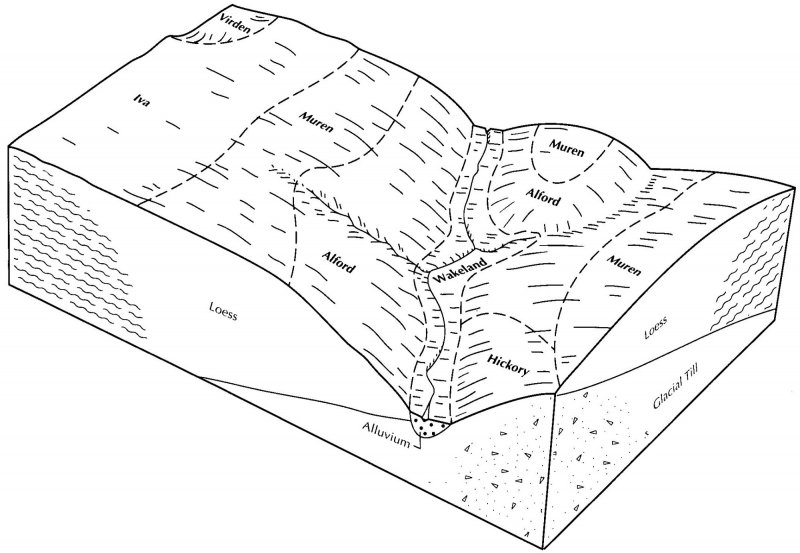
This site is formed on loess parent materials that are on mostly poorly to somewhat poorly drained soils. Ponding is frequent and the duration can greater than 30 days, but the depth is generally less than 7 inches. These sites are found on uplands and terraces with low to moderate slope (>6%). The depth of the loess is generally more than 5 feet and can be as deep as 12 feet and contributes to the gently rolling topography.
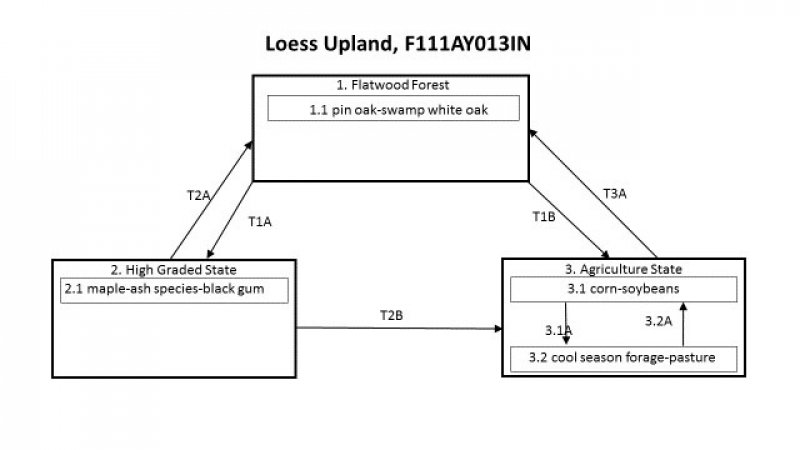
The characteristic vegetation of the site is that of a flatwoods dominated by pin oak and swamp white oak. Canopy associates include silver maple, white oak, and green ash. The large, seasonal fluctuation of water on the site allows for the co-existence of upland and lowland trees. Inundation of the site generally occurs in the spring which leads to a sparse and patchy understory. Fire did occur on the site, but high intensity fires were rare. Low intensity surface fires were more common on sites that are adjacent to more fire prone sites such as prairies and savannas. Ponding in the spring followed by summer drought along with windthrow were the most dominant disturbance factors. A large portion of this site is currently in agricultural production after the installation of drainage.
Associated sites
| F111XA014IN |
Outwash Upland Soil parent material is outwash; soils are somewhat poorly to moderately well drained; site is higher on the landscape. |
|---|---|
| F111XA009IN |
Till Ridge Soil parent material is glacial till; soils are moderately well to well drained; site is higher on the landscape |
Similar sites
| F111XA011IN |
Wet Lacustrine Forest Soil parent material is glacial till; soil surface is 3/2 Munsell or darker; soils are mollisols. |
|---|---|
| F111XA007IN |
Till Depression Flatwood Soil parent material is lacustrine; soils are very poorly to poorly drained. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus palustris |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.