Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F111XC015IN
Dry Floodplain
Accessed: 12/06/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 111X–Indiana and Ohio Till Plain
A PROVISIONAL ECOLOGICAL SITE is a conceptual grouping of soil map unit components within a Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) based on the similarities in response to management. Although there may be wide variability in the productivity of the soils grouped into a Provisional Site, the soil vegetation interactions as expressed in the State and Transition Model are similar and the management actions required to achieve objectives, whether maintaining the existing ecological state or managing for an alternative state, are similar. Provisional Sites are likely to be refined into more precise group during the process of meeting the APPROVED ECOLOGICAL SITE DESCRIPTION criteria.
This PROVISIONAL ECOLOGICAL SITE has been developed to meet the standards established in the National Ecological Site Handbook. The information associated with this ecological site does not meet the Approved Ecological Site Description Standard, but it has been through a Quality Control and Quality Assurance processes to assure consistency and completeness. Further investigations, reviews and correlations are necessary before it becomes an Approved Ecological Site Description.
111C – Indiana and Ohio Till Plain, Northwestern Part. This MLRA is in the glaciated part of north-central Indiana and is dominated by glacial till plains broken in places by lake plains, outwash plains, and flood plains. Areas that parallel most of the major rivers and streams have deposits of sand.
Although it is an important agricultural region, MLRA 111C hosts a large proportion of Indiana’s biodiversity.
Classification relationships
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA)(USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006)
USFS Ecological Regions (USDA, 2007):
Sections - Central Till Plains, Beech Maple (222H), South Central Great Lakes (222J), Central Till Plains and Grand Prairies (251D)
Subsections - Kalamazoo-Elkhart Moraines and Plains (222Jh), Steuben Interlobate Moraines (222Ji), Bluffton Till Plains (222Ha), Entrenched Valleys (222Hf), Miami-Scioto Plain-Tipton Till Plain (222Hb), Kankakee Sands (251Dg) and Eastern Grand Prairie (251Dd).
NatureServe Systems anticipated (NatureServe, 2011): Agriculture-Pasture/Hay, Agriculture-Cultivated Crops and Irrigated Agriculture, Harvested Forest-Grass Regeneration, Harvested Forest-Herbaceous Regeneration, Introduced Upland Vegetation – Treed, North-Central Interior Dry-Mesic Oak Forest & Woodland, North-Central Interior Floodplain, North-Central Interior Wet Flatwoods, Ruderal Forest, Ruderal Upland-Old Field, South-Central Interior Large Floodplain.
LANDFIRE Biophysical Settings anticipated (USGS, 2010): Central Interior and Appalachian Swamp Systems, North-Central Interior Dry-Mesic Oak Forest and Woodland, North-Central Interior Beech-Maple Forest, Central Interior and Appalachian Floodplain Systems, North Central Wet Flatwoods, North-Central Interior Maple-Basswood Forest, Laurentian-Acadian Floodplain Systems.
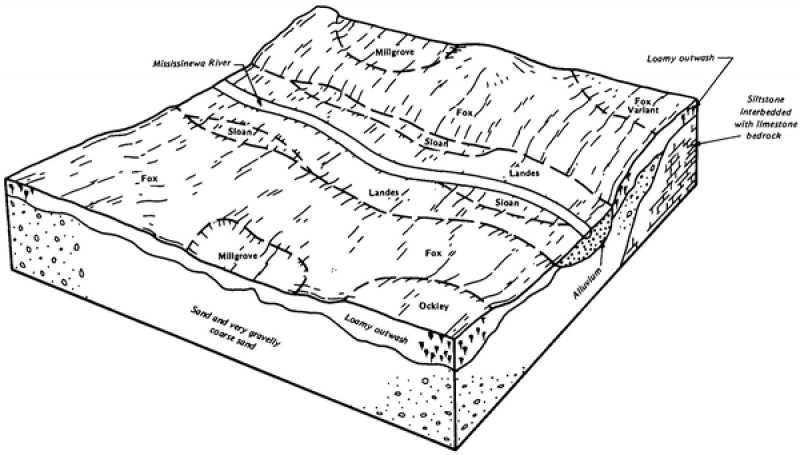
Ecological site concept
This site is a riparian site formed on alluvial parent materials that are somewhat moderately well drained or drying. It is located along the floodplain of lotic systems in loamy alluvial deposits often overlaying coarser materials. Active hydrologic and geomorphic processes, along with windthrow of established trees, drive the long interval disturbance regime of this site. There are 3 distinct states; 1. dry floodplain forest, 2. invaded state, and 3. agriculture state. Currently, just under 30% this site is in agriculture production with the remaining being naturally regenerated vegetation.
Associated sites
| F111XC007IN |
Glacial Ridge Located outside of the floodplain on adjacent, generally steep uplands. White oak and shagbark hickory are the dominate tree species. |
|---|---|
| F111XC014IN |
Wet Floodplain Located in floodplain, but not on terrace or levee. Dominated by sycamore and cottonwood trees. |
Similar sites
| F111XC014IN |
Wet Floodplain Located in floodplain, but not on terrace or levee. Dominated by sycamore and cottonwood trees. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Acer saccharum |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.