Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F111XE404OH
Dry Outwash Upland
Last updated: 9/11/2024
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
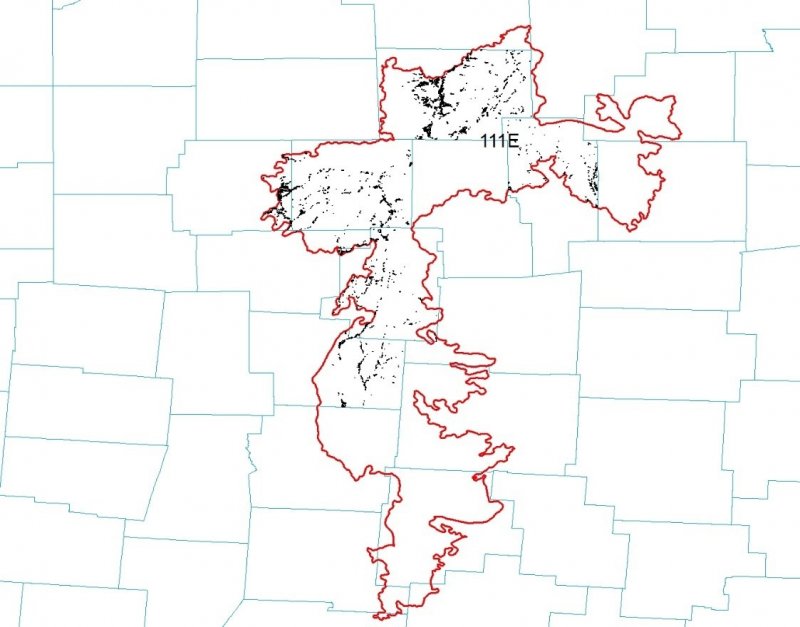
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 111X–Indiana and Ohio Till Plain
111E – Indiana and Ohio Till Plain, Eastern Part. Most of this area is in the Till Plains Section of the Central Lowlands Province of the Interior Plains. The northeast tip of the area is in the Southern New York Section of the Appalachian Highlands. The entire area has been glaciated. It is dominated by ground moraines that are broken in places by kames, lake plains, outwash plains, terraces, and stream valleys. Narrow, shallow valleys commonly are along the few large streams in the area. Elevation ranges from 580 to 1,400 feet (175 to 425 meters), increasing gradually from west to east. Relief is mainly a few meters, but in some areas hills rise as much as 100 feet (30 meters) above the adjoining plain.
The extent of the major Hydrologic Unit Areas (identified by four-digit numbers) that make up this MLRA is as follows: Scioto (0506), 33 percent; Muskingum (0504), 31 percent; and Western Lake Erie (0410), 28 percent; Upper Ohio (0503), 5 percent; and Southern Lake Erie (0411), 3 percent. The headwaters of many rivers in central Ohio, including the Vermillion, Black Fork, Sandusky, Little Scioto, and Olentangy Rivers, are in this MLRA.
This MLRA is underlain by late Devonian shale and sandstone. Surficial materials include glacial deposits of till, glaciolacustrine sediments, and outwash from Wisconsin and older glacial periods.
Classification relationships
Major Land Resource Area (USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006)
USFS Ecological Regions (USDA, 2007):
Sections –Central Till Plains, Beech Maple (222H), Western Glaciated Allegheny Plateau (221F)
Subsections – Allegheny Plateau (221Fa), Bluffton Till Plains (222Ha), Miami-Scioto Plain – Tipton Till Plain (222Hb)
NatureServe Systems anticipated (NatureServe, 2011): Agriculture - Cultivated Crops and Irrigated Agriculture, Agriculture – Pasture/Hay, North-Central Interior Dry-Mesic Oak Forest and Woodland, North-Central Interior Beech-Maple Forest, Ruderal Forest
LANDFIRE Biophysical Settings anticipated (USGS, 2010): North-Central Interior Dry-Mesic Oak Forest and Woodland, North-Central Interior Beech-Maple Forest
Ecological site concept
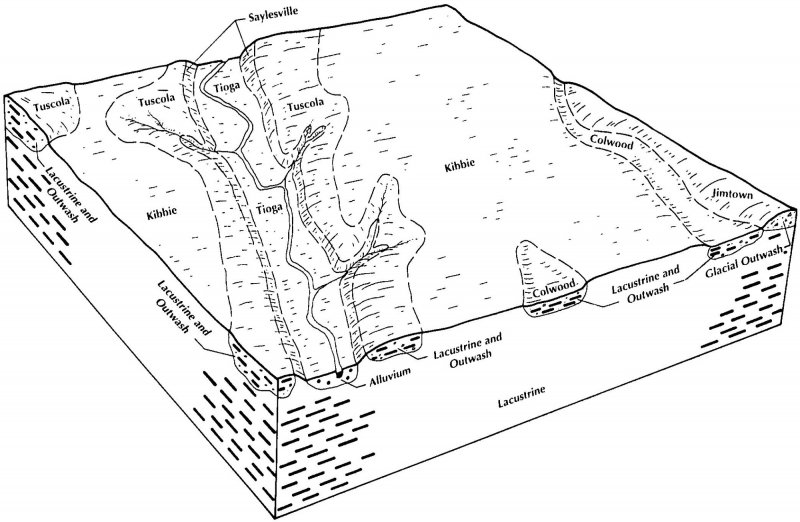
This site is an upland site formed on glacial outwash and colluvium parent materials in soils that are moderately well drained or drier. The soils have a relatively light soil surface color (lighter than 3/2 Munsell). This site is found on, generally, steeper topography than the Outwash Upland site which leads to it being better drained and drier. Slopes for this site can range from flat (summits) to quite steep with an average maximum of 18 percent.
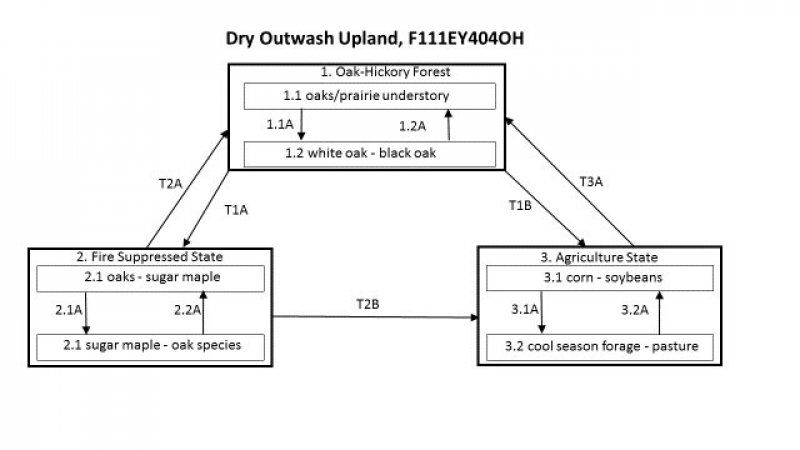
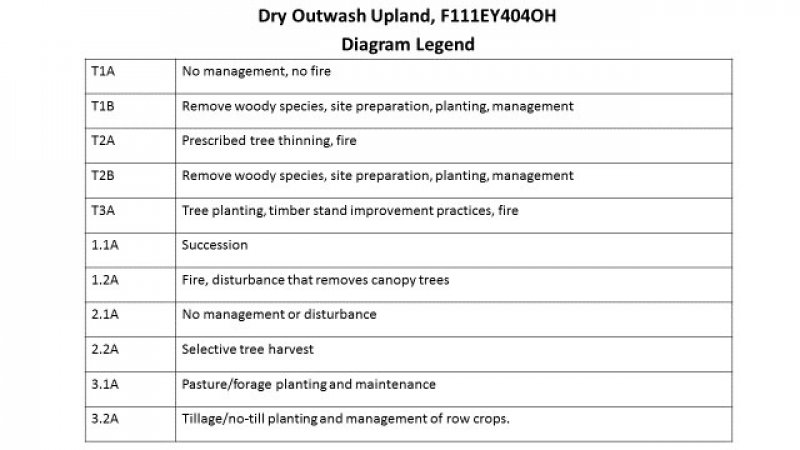
The characteristic vegetation of the site is that of a somewhat dry forest dominated largely by oak species, such as white oak and black oak that can tolerate the increased drainage of the site. Hickory species are also common throughout the site along with sugar maple in somewhat fire protected areas, black cherry, and sassafras. Moderate fire return interval (40-60yrs) for low intensity fires and stand replacing fires every 100-200yrs contributed to the dominance of oak species on the site. Changes in the fire regime have led to many of the extant representation of the site to have a greater amount of fire sensitive, shade tolerate species occupying both the understory and canopy than what was present at the time of European settlement. In this state, the site progress through a phase that in characterized by a co-dominance in the canopy of oaks and sugar maples. Continued absence of fire or lack of timber stand management allows the site to more resemble a mesic forest as dominated by sugar maple and American beech. Currently, the majority of the site is in agricultural production, with the majority being used for growing corn and soybeans, though some areas are used for growing cool season forage and pasture.
Associated sites
| F111XE403OH |
Outwash Upland Soils are very poorly to somewhat poorly drained |
|---|---|
| R111XE401OH |
Wet Outwash Mollisol Soils are very poorly or poorly drained; soil surface is darker in color |
| R111XE402OH |
Dry Outwash Mollisol Soils are somewhat poorly drained or dried; soil surface is darker in color |
Similar sites
| R111XE402OH |
Dry Outwash Mollisol Soils are somewhat poorly drained or dried; soil surface is darker in color |
|---|---|
| F111XE302OH |
Dry Restricted Located on residuum parent material; restrictive layer within 36 inches of soil surface. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus alba |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.