Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F113XY916IL
Sandy Outwash Woodland
Last updated: 5/17/2024
Accessed: 02/26/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 113X–Central Claypan Areas
The eastern Illinois portion of the Central Claypan Areas MLRA is in the Till Plains Section of the Central Lowland Province of the Interior Plains (USDA-NRCS, 2006) and includes the Southern Till Plain Natural Division of the natural divisions of Illinois (Schwegman, 1973; 1997; IDNR, 2018) in south-central Illinois. South-central Illinois is a dissected Illinoisan till plain south of the terminal Wisconsin moraine. This region consists of nearly level to gently sloping, old till plains. Stream valleys are shallow and generally are narrow. Elevation is about 660 feet (200 meters), increasing gradually from south to north. Local relief is generally low on the broad, flat till plains and flood plains and high on the dissected hills bordering rivers or drainage systems. The Kaskaskia, Little Muddy, Little Wabash, Embarras, and Skillet Fork rivers are part of this area. This region is covered with loess, which overlies old glacial drift (Illinoisan till) that has a high content of clay. Fragipans are also present. Pennsylvanian limestone and shale bedrock underlay the glacial till. The dominant soil orders in this region are Alfisol and Mollisol. The soils in the area predominantly have a mesic soil temperature regime, an aquic or udic soil moisture regime, and mixed or smectitic mineralogy. They generally are very deep, well drained to poorly drained, and loamy or clayey. (USDA-NRCS, 2006). Northern crayfish frog (Lithobates areolatus), ornate box turtle (Terrapene ornata ornate) and remnant populations of greater prairie-chickens (Tympanuchus cupido) are characteristic animals of this region (IDNR, 2018).
Classification relationships
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) (USDA-NRCS, 2006):
113 – Central Claypan Areas, Eastern Part
U.S. Forest Service Ecoregions (Cleland et al. 2007):
Domain: Humid Temperate Domain
Division: Hot Continental Division
Province: Eastern Broadleaf Forest (Continental)
Province Code: 222
Section: Central Till Plains, Oak-Hickory Section
Section Code: 222G
Ecological site concept
The historic pre-European settlement vegetation on this site was dominated by broadleaf deciduous trees. Sandy Outwash Woodland occur on outwash terraces and upland ridges adjacent to stream valleys. Soils are well drained and very deep. (Nelson 2010; SSS NRCS OSD 2018; NatureServe 2018).
This black oak woodland community is moderately closed with typically 70 to 80 percent canopy cover. The more open stands tend to have well-developed shrub layers while more closed-canopy stands have fewer shrubs. Black oak, (Quercus velutina L. *) is the dominant tree species and makes up the great majority of the canopy (up to 70 percent) in most stands. Other common tree species include white oak (Quercus alba L.), pignut hickory (Carya glabra (Mill.) Sweet), shagbark hickory (Carya ovata (Mill.) K. Koch), red maple (Acer rubrum L.) and black cherry (Prunus serotina Ehrh.). Shrubs such as gray dogwood (Cornus racemosa Lam.), American hazelnut (Corylus americana Walter), and blueberry (Vaccinium spp.) are typical. The ground layer contains species such as American hogpeanut (Amphicarpaea bracteata (L.) Fernald), aster (Asteraceae spp.), Pennsylvania sedge (Carex pensylvanica Lam.), spotted geranium (Geranium maculatum L.), feathery false lily of the valley (Maianthemum racemosum (L.) Link), and western brackenfern (Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn). Where Pennsylvania sedge forms dense sods, it may exclude shrub or sapling cover. The herbaceous layer can also include tall hairy agrimony (Agrimonia gryposepala Wallr.), beaked agrimony (Agrimonia rostellata Wallr.), American hogpeanut (Amphicarpaea bracteata (L.) Fernald), rattlesnake fern (Botrychium virginianum (L.) Sw.), eastern woodland sedge (Carex blanda Dewey), pointedleaf ticktrefoil (Desmodium glutinosum (Muhl. ex Willd.) Alph. Wood), nakedflower ticktrefoil (Desmodium nudiflorum (L.) DC.), fourleaf yam (Dioscorea quaternata J.F. Gmel.), licorice bedstraw (Galium circaezans Michx.), Christmas fern (Polystichum acrostichoides (Michx.) Schott), and poverty oatgrass (Danthonia spicata (L.) P. Beauv. ex Roem. & Schult.), among others. Fire is the primary disturbance factor that maintains this ecological site, while drought, windthrow, and grazing are secondary factors (LANDFIRE 2009; Nelson 2010; NatureServe 2018; Voigt and Mohlenbrock 1964; White 1978).
*All plant common and scientific names in this document were obtained from the U.S. Department of Agriculture – Natural Resources Conservation Service National PLANTS Database (USDA NRCS 2018).
Associated sites
| F113XY920IL |
Silty Floodplain Forest This ecological site is located in the floodplains below Sandy Outwash Woodlands. |
|---|---|
| F113XY919IL |
Wet Silty Floodplain Forest This ecological site is located in the floodplains below Sandy Outwash Woodlands. |
| F113XY905IL |
Wet Upland Woodland This ecological site is typically located adjacent to Sandy Outwash Woodlands. |
Similar sites
| F113XY915IL |
Lacustrine Terrace Forest This ecological site is in similar landscape positions but on finer textured soils. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus velutina |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Corylus americana |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Carex pensylvanica |
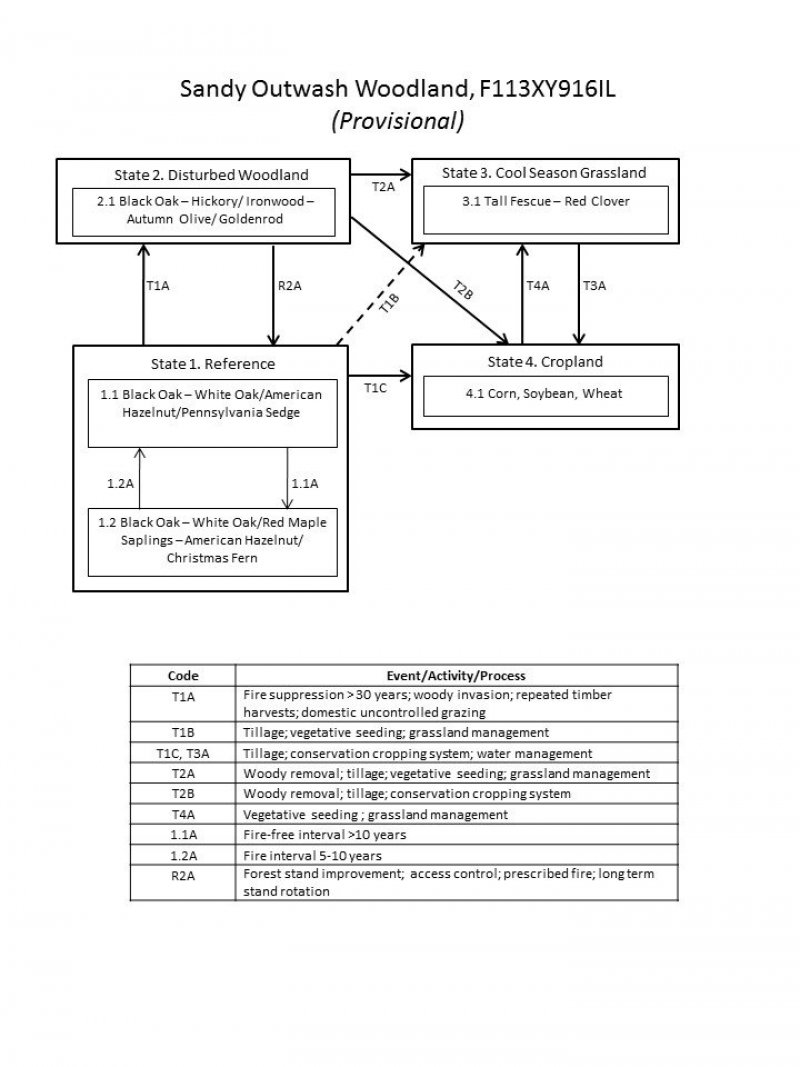
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
| T1A | - | Long-term fire suppression; disturbances |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Clearing; vegetative seeding; grassland management |
| T1C | - | Tillage; conservation cropping system; water management |
| R2A | - | Forest stand improvement; access control; prescribed fire; long term stand rotation |
| T2A | - | Woody removal; tillage; vegetative seeding; grassland management |
| T2B | - | Woody removal; tillage; conservation cropping system |
| T3A | - | Tillage; conservation cropping system; water management |
| T4A | - | Vegetative seeding ; grassland management |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Fire interval >10 years. |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Fire interval >10 years. |