Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site NX118AY010
Calcareous Bottomland
Last updated: 1/03/2019
Accessed: 02/12/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
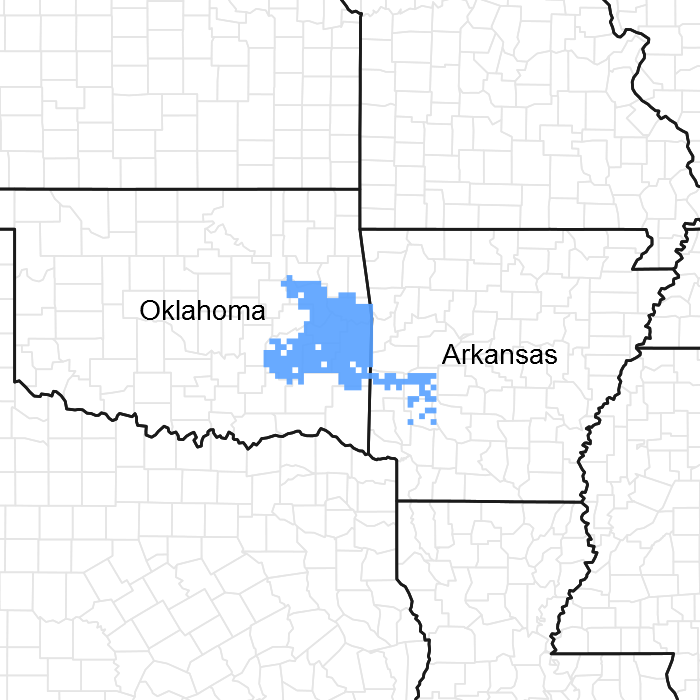
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 118A–Arkansas Valley and Ridges, Eastern Part
118A—Arkansas Valley and Ridges, Eastern Part Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) is in Arkansas (75 percent) and Oklahoma (25 percent) encompassing an area of approximately 6,755 square miles (17,510 square kilometers). The towns of Poteau and Sallisaw, OK, and Booneville, Clarksville, Fort Smith, Greenwood, and Ozark, AR, are in the western part. The Arkansas towns of Conway, Morrilton, Russellville, and Searcy are in the eastern section along with a part of Little Rock in the southeast corner. Interstate 40 passes through from east to west and parallels the northern side of the Arkansas River. The Ozark National Forest and the northern fringe of the Ouachita National Forest occur in this area as does Ft. Chaffee, Camp Joseph T. Robinson, and Little Rock Air Force Base (USDA 2006).
Most of 118A is in the Arkansas Valley Section of the Ouachita Province of the Interior Highlands. Long, narrow ridges and high flat-topped mountains capped with sandstone trend northeastward. Crests are narrow and rolling on ridges and broad and flat on mountaintops. The intervening valleys are broad and smooth. Elevation ranges from 300 ft. (90 m) on the lowest valley floors to 2,750 ft. (840 m) on the mountaintops. The Arkansas River is a major inland navigational river. It flows from the northwestern part of the MLRA, at Robert S. Kerr Lake, in Oklahoma to Little Rock in the southeast.
The ridges and valleys of 118A are underlain by slightly folded to level beds of sandstone and shale, respectively. The area principally consists of the following geologic groups: Savanna, McAlester, Hartshorne sandstone, and the upper and lower Atoka. These are of Pennsylvanian age (formed approximately 300 million years ago). The terrace deposits along the Arkansas River include a complex sequence of unconsolidated gravel, sandy gravel, sands, silty sands, silts, clayey silts, and clays. At least three terrace levels are recognized. The lowest is the youngest.
Classification relationships
This ecological site is found in Major Land Resource Area 118A - the Arkansas Valley and Ridges, Eastern Part. MLRA 118A is located within Land Resource Region N - the East and Central Farming and Forest Region (USDA 2006). In addition, MLRA118A falls within area #37 of EPA Ecoregion Level III - the Arkansas Valley (USEPA 2013). The Calcareous Bottomland ecological site occurs in United States Forest Service Ecoregions -255A – the Prairie Parkland (Subtropical) Province, M222A – the Ozark Broadleaf Forest-Meadow Province, and -251E – the Prairie Parkland (Temperate) Province (Bailey 1995). This ecological site is found primarily in 37b - Arkansas River Floodplain of EPA Ecoregion IV (Woods et. al. 1996).
South-Central Interior Large Floodplain - CES202.705 and
(NatureServe 2017).
Ecological site concept
The Calcareous Bottomlands ecological site occurs on floodplains, natural levees, and stream terraces formed from alluvium of mixed sedimentary geologies within EPA Ecoregion 37b - the Arkansas River Floodplains section of the Arkansas Valley and Ridges major land resource area. Potential natural vegetation is southern floodplain forest. Bottomland hardwood species including Quercus macrocarpa (bur oak), Platanus occidentalis (American sycamore), Liquidamber styraciflua (sweetgum), Salix spp. (willows), Populus deltoides (eastern cottonwood), Fraxinus pennsylvanica (green ash), Carya illinoinensis (pecan), Celtis occidentalis (hackberry), and Ulmus spp. (elm) were once extensive (Woods, Foti et. Al. 2004). The driest areas may have been dominated by oak-hickory forests. The Calcareous Bottomlands are fertile and have been widely cleared for agriculture – nearly 60 percent of the ecological site has been converted to row crops and 20 percent to pasture and hayland. Forest remains in the most frequently flooded areas. Their fertility and extensive use for agriculture distinguishes these sites from the Loamy Bottomlands. They are drier than the Poorly to Somewhat Poorly Drained Bottomland and Terraces and the Somewhat Poorly Drained Calcareous Bottomlands.
Associated sites
| NX118A01Y007 |
Seasonally Wet Terraces and Footslopes |
|---|
Similar sites
| NX118AY011 |
Somewhat Poorly Drained Calcareous Bottomland |
|---|---|
| F119XY013AR |
Loamy Floodplain |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Ulmus americana |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Legacy ID
F118AY010AR
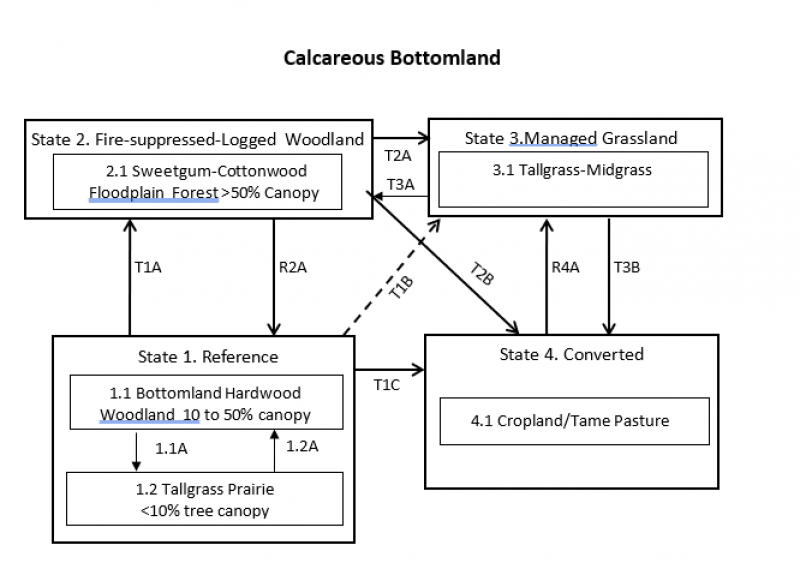
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
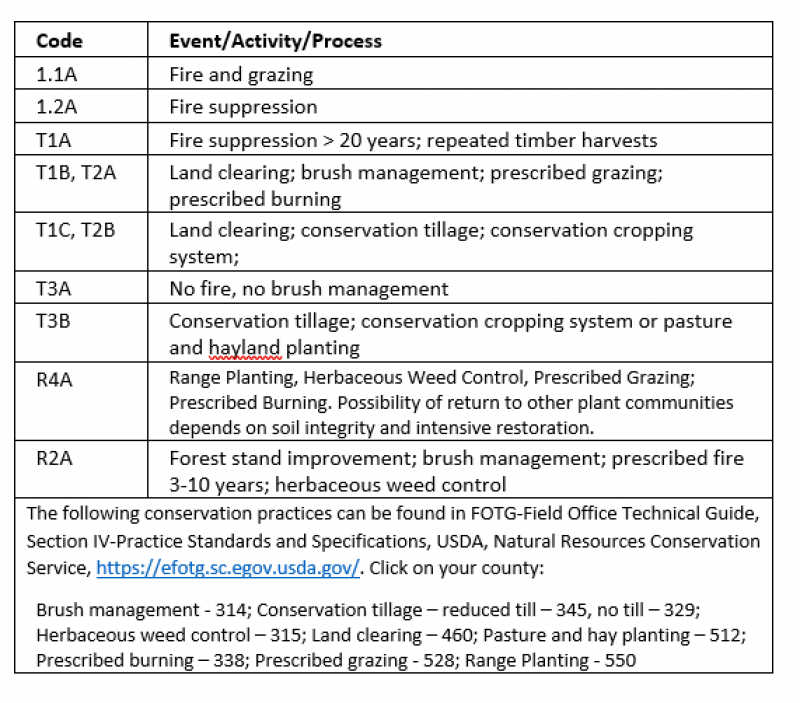
| T1A | - | Fire suppression > 20 years; repeated timber harvests |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Land clearing; brush management; prescribed grazing; prescribed burning |
| T1C | - | Land clearing; conservation tillage; conservation cropping system; drainage installation |
| R2A | - | Forest stand improvement; brush management; prescribed fire 3-10 years; herbaceous weed control |
| T2A | - | Land clearing; brush management; prescribed grazing; prescribed burning |
| T2B | - | Land clearing; conservation tillage; conservation cropping system; drainage installation |
| T3A | - | No fire, no brush management |
| T3B | - | Conservation tillage; conservation cropping system or pasture and hay land planting. |
| R4A | - | Range Planting, Herbaceous Weed Control, Prescribed Grazing; Prescribed Burning. Possibility of return to other plant communities depends on soil integrity and intensive restoration. |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Fire and grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Fire suppression |