Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F121XY005KY
Black Shale Upland
Last updated: 10/01/2024
Accessed: 02/26/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 121X–Kentucky Bluegrass
General: MLRA 121 is in Kentucky (83 percent), Ohio (11 percent), and Indiana (6 percent). It makes up about 10,680 square miles (27,670 square kilometers). The cities of Cincinnati, Ohio, and Louisville, Frankfort, and Lexington, Kentucky, are in this area.
Physiography: This area is primarily in the Lexington Plain Section of the Interior Low Plateaus Province of the Interior Plains.
Soils: The dominant soil orders in MLRA 121 are Alfisols, Inceptisols, and Mollisols. The soils in the area dominantly have a mesic soil temperature regime, an udic soil moisture regime, and mixed mineralogy. They are shallow to very deep, generally well-drained, and loamy or clayey. Hapludalfs formed in residuum on hills and ridges (Beasley, Cynthiana, Eden, Faywood, Lowell, and McAfee series) and in loess over residuum on hills and ridges (Carmel and Shelbyville series). Paleudalfs (Crider and Maury series) formed in loess or other silty sediments over residuum on hills and ridges. Fragiudalfs (Nicholson series) formed in loess over residuum on ridges. Hapludolls formed in residuum on hills and ridges (Fairmount series) and in alluvium on floodplains (Huntington series). Eutrudepts (Nolin series) formed in alluvium on flood plains.
Geology: Most of this area has an Ordovician-age limestone that has been brought to the surface in the Jessamine Dome, a high part of a much larger structure called the Cincinnati Arch. The strata of limestone have a propensity to form caves and karst topography. Younger units of thin-bedded shale, siltstone, and limestone occur at the eastern and western edges of the area.
The area has no coal-bearing units. Pleistocene-age loess deposits cover most of the bedrock units in this MLRA, and some glacial lake sediments are at the surface in the northwest corner of the area. Unconsolidated alluvium is deposited in the river valleys.
Classification relationships
Acidic sub-xeric forest: Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission
Acidic xeric forest/woodland: Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission
Xeric Virginia pine forest/woodland: Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission.
Ecological site concept
The Black Shale Upland ecological site encompasses dry hardwood and dry hardwood-pine forest communities on soils of various depths, aspects, and micro-topography which are underlain by acidic hard black shale. Representative soils include: Berea, Blago, Colyer, Covedale, Greenbriar, Jessietown, Muse, Rohan, Trappist.
The range of variation in plant composition on these sites vary mainly due to soil depth, available water, and aspect. The floristic expression of these sites likely varies considerably due to depth differences and future field work may result in one or more ecological site description developed within the current PES soil grouping.
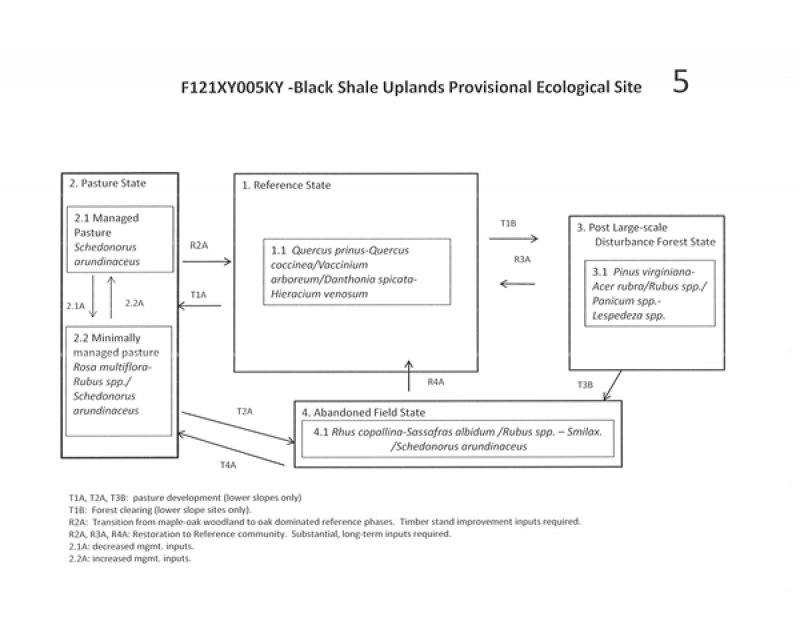
State 1. (Reference): Black Shale Uplands Provisional Ecological Site (PES)
State 1, Phase 1.1: Plant species dominants:
Quercus prinus-Quercus coccinea/Vaccinium arboreum/Danthonia spicata-Hieracium venosum
(chestnut oak – scarlet oak / farkleberry / poverty oat grass – rattlesnake weed.
State 2, Phase 1.2: Plant species dominants: Quercus prinus-Pinus virginiana/ Vaccinium/Antennaria plantaginifolia-Lespedeza spp.
(chestnut oak – Virginia pine/ blueberry / women’s tobacco – lespedeza)
State: 2. Pasture
State 2, Phase 2.1: Managed Pasture. Plant species dominants: Schedonorus arundinaceus (tall fescue)
State 2, Phase 2.2: Minimally Managed Pasture. Plant species dominants: Rosa multiflora- Rubus spp. /Schedonorus arundinaceus
State: 3 – Post Large-Scale Disturbance Forest
State 3, Phases 3.1: Post Large-Scale Disturbance Forest State. Plant species dominants:
Pinus virginiana-Acer rubra /Rubus spp. / Panicum spp.-Lespedeza spp.
(Virginia pine – red maple / blackberry / panic grass – lespedeza)
State: 4. Abandoned Field
State 4, Phase 4.1: Plant species dominants: Rhus copallina-Sassafras albidum /Rubus spp. – Smilax. /Schedonorus arundinaceus
Transitioning to a reference condition will require timber stand improvement practices to control non-native vegetation and manage for higher quality oak or hickory species.
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus prinus |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Vaccinium arboreum |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Danthonia spicata |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.