Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F124XY007OH
Upper Floodplain
Last updated: 9/26/2024
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 124X–Western Allegheny Plateau
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 124—Western Allegheny Plateau (USDA-NRCS, 2006)
MLRA 124, Western Allegheny Plateau extends from and includes western PA just north of Pittsburgh through southeastern OH to and includes northeastern KY. This area is primarily in the Kanawha Section of the Appalachian Province of the Appalachian Highlands. This MLRA is on an unglaciated dissected plateau with narrow level valley floors, rolling ridgetops, and hilly to steep slopes with dendritic stream drainages. A notable exception is the broad, Teays Valley, and other glacio-fluvial and glacio-lacustrine features attributed to nearby Pleistocene glaciation. Elevation ranges from 660 to 1310 feet (200 to 400 meters). The geology is predominantly cyclic beds of sandstone, siltstone, clay, shale and coal of Pennsylvanian age. Soils are dominated by Udalfs, Udults, and Ochcrepts with a mesic temperature regime in combination with five parent materials, residuum, colluvium, alluvium, eolian, and extra-glacial material of glacio-fluvial and glaciolacustrine mesic materials. The climate is predominately a humid continental to temperate, with 940 to 1145 millimeters (37 to 45 inches) of precipitation. Average annual temperature is 8 to 13 degree C (46 to 56 degrees F) with a freeze-free period averaging 185 days. Much of the areas is either forest or in farms, principally for hay and pasture, with fruits and vegetables grown locally. Coal and gas extraction are important industries in the northern part of the MLRA.
Classification relationships
USDA-NRCS (USDA 2006):
Land Resource Region (LRR): N—East and Central Farming and Forest Region
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 124—Western Allegheny Plateau
USDA-FS (Cleland et al. 2007):
Province: 221 - Eastern Broadleaf Province
Section: 221E - Southern Unglaciated Allegheny Plateau
Subsection: 221Ea - Pittsburgh Low Plateau
221Eb - Teays Plateau
221Ee - Unglaciated Muskingam Plains
221Ef - Western Hocking Plateau
221Eg - Lower Scotio River Plateau
221En - Kinniconick and Licking Knobs
Section: 221H - North Cumberland Plateau (in Part)
Subsection: 221Hb - Kinniconick and Licking Knobs
221He - Miami - Scioto Plain - Tipton Till Plain
Ecological site concept
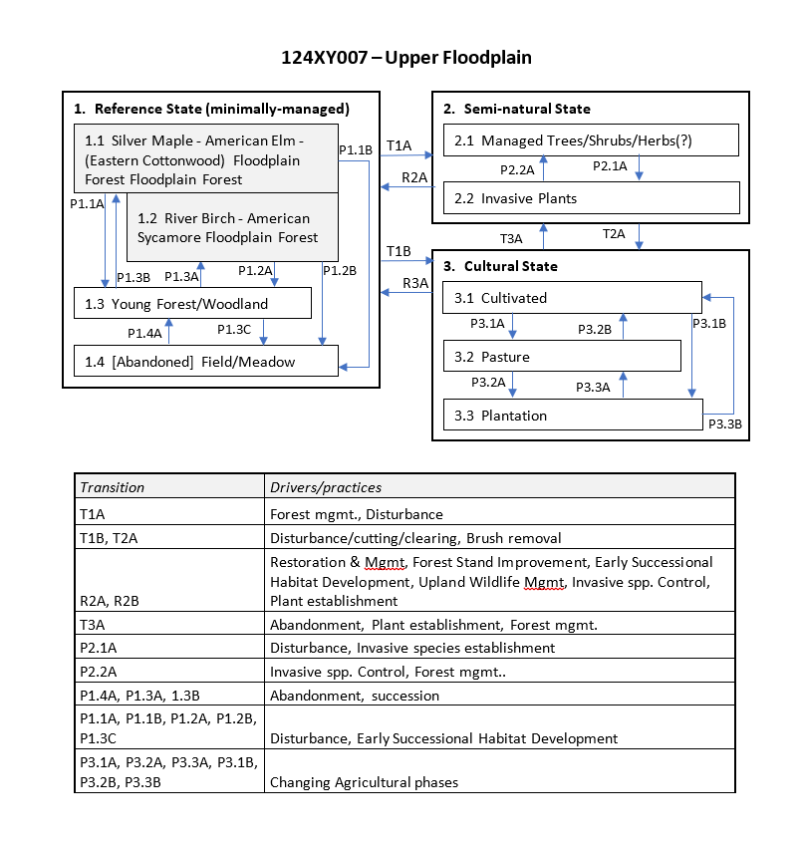
Within the dissected plateau of the unglaciated Western Allegheny Plateau, landscapes of narrow valleys are common and fewer major valleys are broad with underfit rivers. The Upper Floodplain ecological site is situated along low gradient, river systems ranging in size from small to large rivers. Potentially, the Upper Floodplain ecological site may be split between small and medium to large size rivers, and split again, into levees and high floodplains. The parent material is recent alluvium weathered from sandstones siltstones, shales, and limestones, ranging from sandy-skeletal to fine-silty. River flood frequency is variable, ranging from rare to frequent. Frequent flooding is defined as more than a 50 percent chance of flooding in any year. Rare flooding is defined as 1 to 5 percent chance of flooding in any year or nearly 1 to 5 times in 100 years. The soils range from well-drained to somewhat poorly drained. Representative soils include: Chagrin, Clifty, Cuba, Genesee, Grigsby, Haymond, Holton, Huntington, Kinnick, Landes, Lindside, Lobdell, Newark, Nolin, Orrville, Philo, Pope, Rossburg, Shoals variant, Skidmore, Stendal, Stokly, Stonelick, Tioga, Wappinger, and Wilber. Reference plant communities include: Central Green Ash - Elm - Hackberry Floodplain Forest, Midwestern Silver Maple - Elm Floodplain Forest, and Beech - Mixed Hardwood Floodplain Forest
Associated sites
| F124XY008OH |
Wet Floodplain and Drainageway Wet Floodplain and Drainageway ecological sites are lower in the flood frequency profile or in depressions such as sloughs. |
|---|

Figure 1.

Figure 2.
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Acer saccharinum |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Vitis riparia |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Boehmeria cylindrica |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.