Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F140XY002NY
Frigid Steep Shallow Till Uplands
Last updated: 10/01/2024
Accessed: 03/12/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 140X–Glaciated Allegheny Plateau and Catskill Mountains
This area is primarily in the Southern New York Section of the Appalachian Plateaus Province of the Appalachian Highlands. The top of the dissected plateau in this MLRA is broad and is nearly level to moderately sloping. The narrow valleys have steep walls and smooth floors. The Catskills in the east have steep slopes. Elevation is typically 650 to 1,000 feet on valley floors; 1,650 to 2,000 feet on the plateau surface; and 3,600 feet or more in parts of the Catskills.
The average annual precipitation in most of this area is 30 to 45 inches. Rainfall occurs as high-intensity, convective thunderstorms during the summer, but most of the precipitation in this area occurs as snow. The average annual temperature is 40 to 50 degrees F.
The dominant soil order in this MLRA is Inceptisols. The soils in the area dominantly have a mesic soil temperature regime, an aquic or udic soil moisture regime, and mixed mineralogy. Frigid soils are found within the higher elevations.
This area supports forest vegetation, particularly hardwood species. Beech-birch-maple and elm-ash-red maple are the potential forest types. The extent of oak species increases from east to west, particularly in areas of shallow and dry soils. In some areas conifers, such as white pine, are important. Aspen, hemlock, northern white-cedar, and black ash grow on the wetter soils. In some parts of the area, sugar maple has potential economic significance. Some of the major wildlife species in this area are white-tailed deer, cottontail, turkey, pheasant, and grouse.
Classification relationships
USDA NRCS:
LRR: R - Northeastern Forage and Forest Region
MLRA 140 - Glaciated Allegheny Plateau and Catskills Mountains
EPA Ecoregions:
Level III: 60 - Northern Allegheny Plateau and 58 - Northeastern Highlands
Level IV: 60a - Glaciated Low Allegheny Plateau, 60b - Delaware-Neversink Highlands, 60c - Catskills Transition, and 58y - Catskill High Peaks
USDA USFS:
200 Humid Temperate Domain
212 Laurentian Mixed Forest Province
M212 Adirondack - New England Mixed Forest - Coniferous Forest - Alpine Meadow Province
NY Natural Heritage Program Plant Community Classifications:
Beech-Maple Mesic Forest
Appalachian Oak-Hickory Forest
International Vegetation Classification Associations:
Sugar Maple - Yellow Birch - American Beech / Hobblebush Forest (CEGL006631)
Sugar Maple - American Beech - White Ash / Jack-in-the-Pulpit Forest _CEGL006632)
American Beech - Sugar Maple Glaciated Midwest Forest (CEGL005013 )
Northern Red Oak - Sugar Maple - American Beech / Mapleleaf Viburnum Forest (CEGL006633 )
Northern Red Oak - Sugar Maple / Mapleleaf Viburnum - Northern Spicebush Forest (CEGL006635 )
NatureServe Ecological Systems:
Laurentian-Acadian Northern Hardwood Forest (CES201.564 )
North-Central Interior Beech-Maple Forest (CES202.693 )
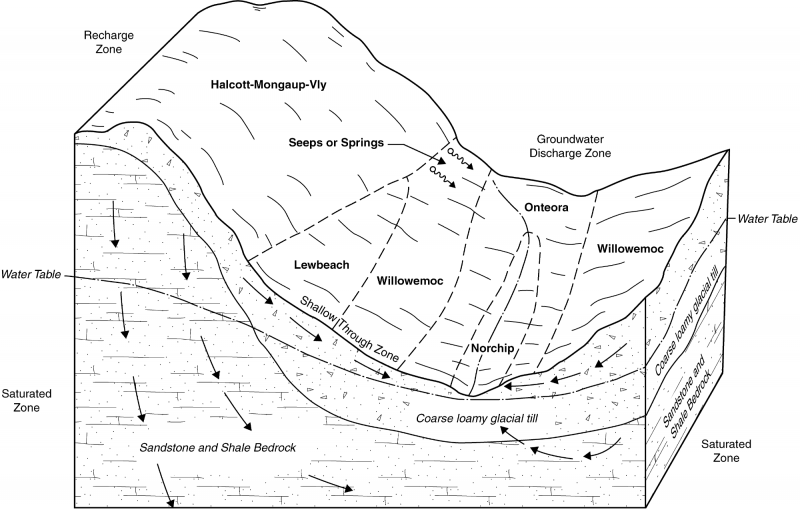
Ecological site concept
Landform/Landscape Position:
The site occurs on moderately steep to very steep mountain slopes and ridges. Slopes are typically greater than 30% but range from 16-70%.
Soils:
The soils consists of shallow (to bedrock), somewhat excessively drained and well drained soils formed in loamy till derived from sandstone, siltstone, and shale. Soil temperature regime is frigid. Reaction is very strongly acid or strongly acid throughout the mineral soil. Soil components Halcott, Hawksnest, and Wasnot with slopes of greater than 15% are correlated to this site.
Vegetation:
Reference community is a Northern Hardwood Forest. Characteristic vegetation includes:
Trees: American beech (Fagus grandifolia), sugar maple (Acer saccharum), red oak (Quercus rubra), yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis), red maple (Acer rubrum). Conifers such as eastern white pine (Pinus strobus) and hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) are minor components.
Shrubs: witch-hazel (Hamamelis virginiana), hobblebush (Viburnum lantanoides), maple-leaved viburnum (Viburnum acerifolium)
Herbaceous: hay-scented fern (Dennstaedtia punctilobula), painted trillium (Trillium undulatum), and sessile-leaved bellwort (Uvularia sessilifolia)
Associated sites
| F140XY003NY |
Cold Shallow Till Uplands |
|---|
Similar sites
| F140XY030NY |
Well Drained Dense Till |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Acer saccharum |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Hamamelis virginiana |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Dennstaedtia punctilobula |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.