Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F144AY019NH
Wet Lake Plain
Last updated: 10/04/2024
Accessed: 04/27/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 144A–New England and Eastern New York Upland, Southern Part
MLRA 144A: New England and Eastern New York Upland, Southern Part
The eastern half of the eastern part of this MLRA is in the Seaboard Lowland Section of the New England Province of the Appalachian Highlands. The western half of the eastern part and the southeastern half of the western part are in the New England Upland Section of the same province and division. The northwestern half of the western part is in the Hudson Valley Section of the Valley and Ridge Province of the Appalachian Highlands. This MLRA is a very scenic area of rolling to hilly uplands that are broken by many gently sloping to level valleys that terminate in coastal lowlands. Elevation ranges from sea level to 1,000 feet (0 to 305 meters) in much of the area, but it is 2,000 feet (610 meters) on some hills. Relief is mostly about 6 to 65 feet (2 to 20 meters) in the valleys and about 80 to 330 feet (25 to 100 meters) in the uplands.
This area has been glaciated and consists almost entirely of till hills, drumlins, and bedrock-controlled uplands with a mantle of till. It is dissected by narrow glacio-fluvial valleys. The southernmost boundary of the area marks the farthest southward extent of Wisconsinian glaciation on the eastern seaboard. The river valleys and coastal plains are filled with glacial lake sediments, marine sediments, and glacial outwash. The bedrock in the eastern half of the area consists primarily of igneous and metamorphic rocks of early Paleozoic age. Granite is the most common igneous rock, and gneiss, schist, and slate are the most common metamorphic rocks. In the parts of the MLRA in eastern and southeastern New York, Devonian- to Pennsylvanian-age sandstone, shale, and limestone are dominant. Carbonate rocks, primarily dolomite and limestone, are the dominant kinds of bedrock in the part of this MLRA in northwestern Connecticut.
Classification relationships
USDA-NRCS (USDA 2006):
Land Resource Region (LRR): N—East and Central Farming and Forest Region
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 144A— New England and Eastern New York Upland, Southern Part.
USDA-FS (Cleland et al. 2007)
Province: 221 - Eastern Broadleaf Province
Section: 221A - Lower New England
Subsection: 221Aa – Boston Basin
221Ac – Narragansett-Bristol Lowland and Islands
221Ad – Southern New England Coastal Lowland
221Ae – Hudson Highlands
221Ag - Southeast New England Coastal Hills and Plains
221Ah - Worcester-Monadnock Plateau
221Ai – Gulf of Maine Coastal Plain
221Ak - Gulf of Maine Coastal Lowland
Section: 221B – Hudson Valley
Subsection: 221Ba – Hudson Limestone Valley
221Bb - Miami – Taconic Foothills
221Bc – Hudson Glacial Lake Plains
Ecological site concept
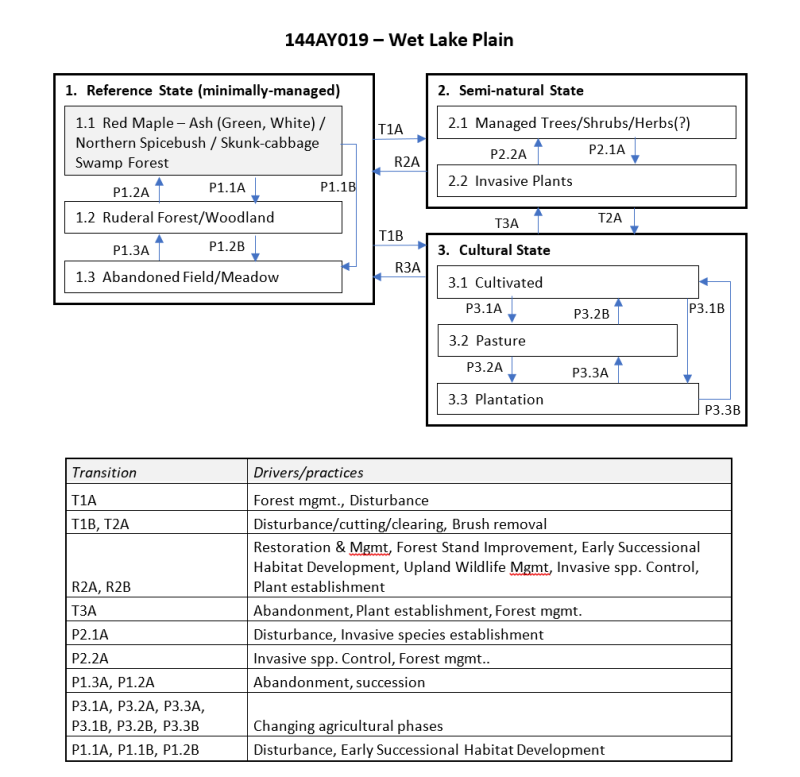
The Wet Lake Plain ecological site consists of very deep, poorly drained soils formed in clayey, silty and loamy over clayey sediments. They are nearly level to gently sloping soils in low-lying positions on glaciolacustrine and marine terraces. There may be two geographically distinct areas: inland sites along the Hudson Valley,NY with representative soils Madalin, Parsippany, and Passaic; and coastal sites in Northeast MA and Southeast NH with representative soils Scitico (coastal), Shaker, Raynham (coastal) and Squamscott. The reference community is typified by a red maple – hardwoods swamp forest. These communities may be perched or show seepage and maybe considered minerotrophic (slightly enriched). Canopy dominants include red maple (Acer rubrum) with green ash (Fraxinus pennsylvanica) or white ash (Fraxinus americana). Other trees include pin oak (Quercus palustris) and black gum (Nyssa sylvatica). Shrubs include northern spicebush (Lindera benzoin) and winterberry holly (Ilex verticillate), and northern arrowwood (Viburnum dentatum var lucidum). Groundcover is variable w/ skunk cabbage (Symplocarpus foetidus)and and/or ferns: cinnamon fern (Osmunda cinnamomea), royal fern (Osmunda regalis), marsh fern (Thelypteris palustrius); and sedges: Gray’s sedge (Carex grayi) , fringed sedge (Carex crinata), hop sedge (Carex lupulina). Depending on the water table fluctuations, the “perched” wetlands may contain a more diverse shrub layer.
Associated sites
| F144AY018NY |
Moist Lake Plain |
|---|
Similar sites
| F144AY008CT |
Moist Till Uplands |
|---|---|
| F144AY012CT |
Sandy Low Floodplain |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Acer rubrum |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Lindera benzoin |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Osmunda regalis |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.