

Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R150BY650TX
Low Coastal Sand
Last updated: 9/22/2023
Accessed: 03/12/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
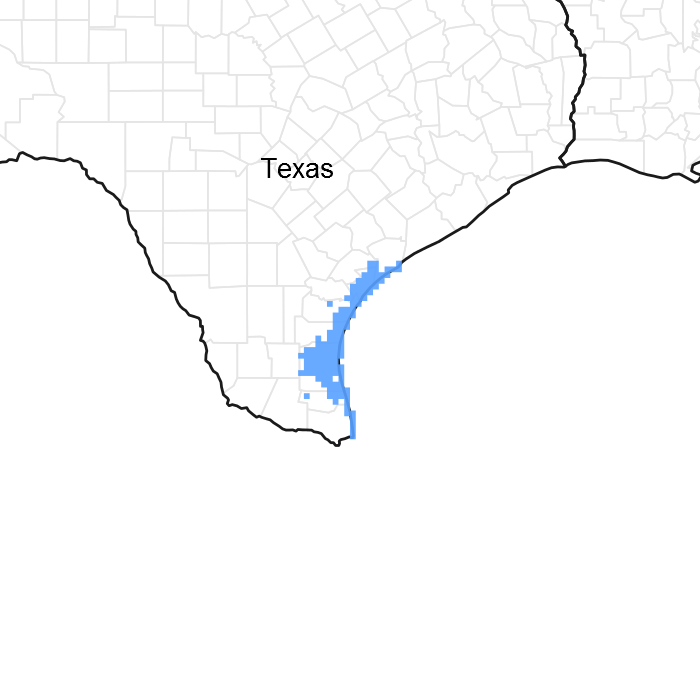
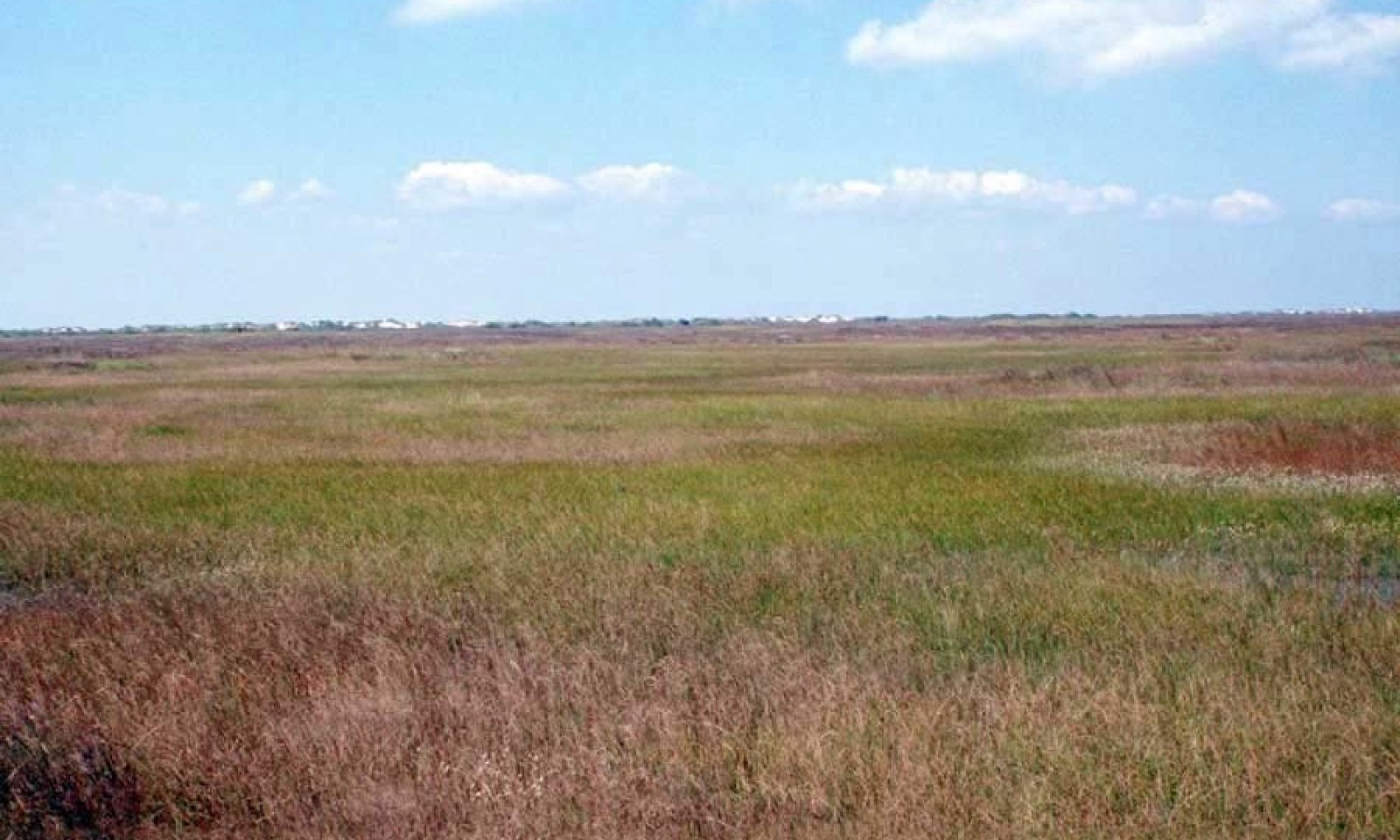
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 150B–Gulf Coast Saline Prairies
MLRA 150B is in the West Gulf Coastal Plain Section of the Coastal Plain Province of the Atlantic Plain and entirely in Texas. It makes up about 3,420 square miles. It is characterized by nearly level to gently sloping coastal lowland plains dissected by rivers and streams that flow toward the Gulf of Mexico. Barrier islands and coastal beaches are included. The lowest parts of the area are covered by high tides, and the rest are periodically covered by storm tides. Parts of the area have been worked by wind, and the sandy areas have gently undulating to irregular topography because of low mounds or dunes. Broad, shallow flood plains are along streams flowing into the bays. Elevation generally ranges from sea level to about 10 feet, but it is as much as 25 feet on some of the dunes. Local relief is mainly less than 3 feet. The towns of Groves, Texas City, Galveston, Lake Jackson, and Freeport are in the northern half of this area. The towns of South Padre Island, Loyola Beach, Corpus Christi, and Port Lavaca are in the southern half. Interstate 37 terminates in Corpus Christi, and Interstate 45 terminates in Galveston.
Classification relationships
USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006.
-Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 150B
Ecological site concept
Low Coastal Sands are sandy-textured soils located behind the Coastal Dunes and have a high water table.
Associated sites
| R150BY651TX |
Salt Flat This site is found on a lower landform and is characterized by having bare and sparse vegetation. |
|---|---|
| R150BY714TX |
Coastal Dune This site is on convex areas adjacent to the bay and are loamy or clayey throughout. |
| R150BY648TX |
Southern Coastal Sand This site is found on the barrier flat, but is slightly above the landscape. |
| R150BY713TX |
Coastal Swale This site is also found on the barrier flat and is much lower on the landscape often ponding water for periods of time. It is lower than Low Coastal Sand. |
| R150BY715TX |
Firm Brackish Marsh This site is found on the barrier flat but is slightly lower on the landscape. |
Similar sites
| R150BY708TX |
Sandy Flat This site is on located closer to bays and the Gulf of Mexico. These are higher dunes and are drier sites. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Borrichia frutescens |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Spartina patens |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on nearly level soils on planar to concave barrier island flats. These soils are subject to occasional flooding by high surges from strong tropical storms and are ponded after periods of heavy rainfall. Slopes range from 0 to 1 percent.
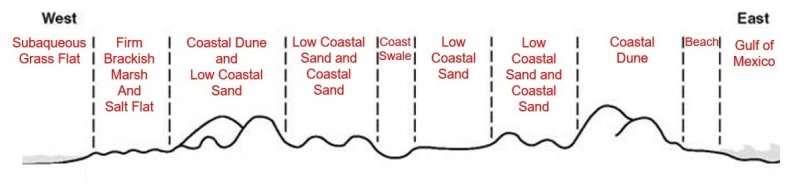
Figure 2.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Barrier island
> Barrier flat
(2) Barrier island > Depression |
|---|---|
| Runoff class | Negligible to very low |
| Flooding duration | Very brief (4 to 48 hours) to long (7 to 30 days) |
| Flooding frequency | Rare to frequent |
| Ponding duration | Long (7 to 30 days) |
| Ponding frequency | None to frequent |
| Elevation | 0 – 5 m |
| Slope | 0 – 3% |
| Ponding depth | 0 – 15 cm |
| Water table depth | 25 – 76 cm |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
The climate is predominately maritime, controlled by the warm and very moist air masses from the Gulf of Mexico. The climate along the upper coast of the barrier islands is subtropical subhumid and the climate on the lower coast of Padre Island is subtropical semiarid (due to high evaporation rates that exceed precipitation). Almost constant sea breezes moderate the summer heat along the coast. Winters are generally warm and are occasionally interrupted by incursions of cool air from the north. Spring is mild and damaging wind and rain may occur during spring and summer months. Tropical cyclones or hurricanes can occur with wind speeds of greater than 74 mph and have the potential to cause flooding from torrential rainstorms. Despite the threat of tropical storms, the storms are rare. Throughout the year, the prevailing winds are from the southeast to south-southeast.
The average annual precipitation is 45 to 57 inches in the northeastern half of this area, 26 inches at the extreme southern tip of the area, and 30 to 45 inches in the rest of the area. Precipitation is abundant in spring and fall in the southwestern part of the area and is evenly distributed throughout the year in the northeastern part. Rainfall typically occurs as moderate-intensity, tropical storms that produce large amounts of rain during the winter. The average annual temperature is 68 to 74 degrees F. The freeze-free period averages 340 days and ranges from 315 to 365 days.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 365 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | 365 days |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 660-813 mm |
| Frost-free period (actual range) | 365 days |
| Freeze-free period (actual range) | 365 days |
| Precipitation total (actual range) | 660-864 mm |
| Frost-free period (average) | 365 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | 365 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 737 mm |
Figure 3. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 4. Monthly minimum temperature range
Figure 5. Monthly maximum temperature range
Figure 6. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 7. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 8. Annual average temperature pattern
Climate stations used
-
(1) CORPUS CHRISTI NAS [USW00012926], Corpus Christi, TX
-
(2) PADRE IS NS [USC00416739], Padre Island Ntl Seashor, TX
-
(3) PORT MANSFIELD [USC00417184], Port Mansfield, TX
-
(4) PORT ISABEL CAMERON AP [USW00012957], Los Fresnos, TX
-
(5) PORT ISABEL [USC00417179], Port Isabel, TX
Influencing water features
This is a wet site receiving water from runoff and seepage from adjacent sites. It has a permanent water table at a depth of 10 to 30 inches throughout the most years. Some areas are ponded for extended periods of time. Flooding occurs in most areas due to high tides or storms.
Wetland description
Somewhat to very poorly drained sites have hydric soils. Onsite investigation needed to determine local conditions.
Soil features
The soils are very deep, poorly drained, very slowly permeable, neutral to strongly alkaline, fine sands. The depth of the surface horizon ranges from 6 to 19 inches, and the depth of the soils are greater than 80 inches. Surface runoff is negligible because of seepage from adjoining sites and the relative landscape position; a water table is present in this soil at a depth of 10 to 30 inches. Soils correlated to this site include: Drumbay, Lopeno, Mustang, and Potrero.
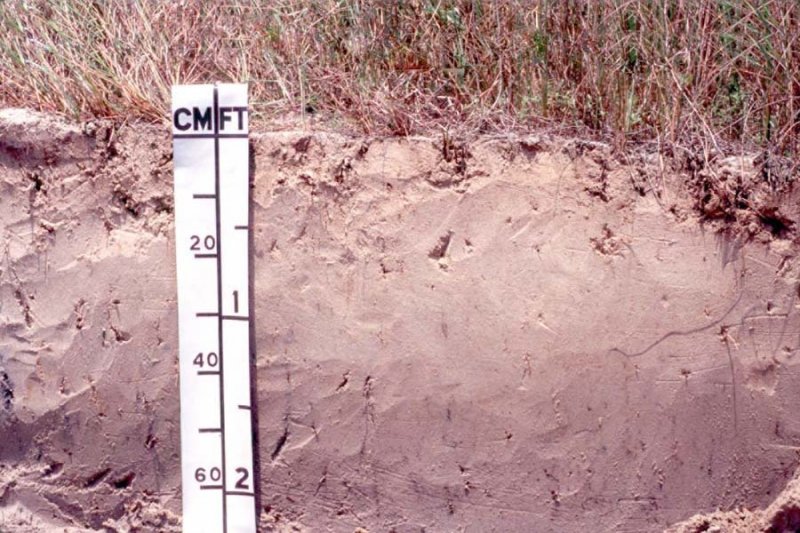

Figure 9. Profile of the Mustang series.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Eolian sands
–
igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rock
|
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Fine sand (2) Sand |
| Family particle size |
(1) Sandy |
| Drainage class | Somewhat poorly drained to poorly drained |
| Permeability class | Very slow |
| Soil depth | 203 cm |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 0% |
| Available water capacity (0-152.4cm) |
5.08 – 7.62 cm |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-152.4cm) |
0 – 15% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-152.4cm) |
2 – 6 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-152.4cm) |
0 – 13 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-152.4cm) |
6.6 – 9 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (116.8-152.4cm) |
0 – 11% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (116.8-152.4cm) |
0 – 1% |
Ecological dynamics
The Texas coastline is composed of barrier islands, peninsulas, bays, estuaries, and natural or man-made passes. These mobile environments are constantly reshaped by the process of erosion and accretion. Hurricane activity can significantly change the island's environment. The barrier island region is subdivided into habitats based on landform and vegetation. The Low Coastal Sand ecological site lies on the bayward side of the foredunes. This nearly level site is in a planar to concave position in the landscape commonly intermingled with other associated ecological sites. The variety of vegetation is greater than other inland sites.
The plant communities are dynamic, and composition may vary dramatically with variations in annual rainfall, grazing, and fire. This landscape is typically a vegetated barrier flat unless impacted by recent hurricane activity. Because of southern proximity and nearness to the Gulf of Mexico, extreme climatic variations ranging from extended drought to hurricanes are possible. Bare ground may predominate during droughts or following hurricanes while a midgrass prairie may predominate under proper management and non-droughty periods.
Historically, the site been an open prairie comprised of a midgrass plant community. The co-dominant grasses are marshhay cordgrass (Spartina patens) and gulfdune paspalum (Paspalum monostachyum). Other important associated grasses include bushy bluestem (Andropogon glomeratus), seacoast bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), and slimleaf rosette grass (Dichanthelium linearifolium). American bulrush (Scirpus pungens) and additional minor amounts of perennial forbs, can also be found.
Changes in the reference community occur with continued overuse by livestock. This resulting community is because of the decline of gulfdune paspalum, seacoast bluestem, and slimleaf rosette grass. Marshhay cordgrass, seashore dropseed (Sporobolus virginicus), seashore saltgrass (Distichlis spicata), and red lovegrass (Eragrostis secundiflora), will be dominants with perennial and annual forbs including sea-ox-eye daisy (Borrichia frutescens), round pennywort (Hydrocotle umbellata), frogfruit (Phyla lanceolata) and narrowleaf marshelder (Iva angustifolia), tend to increase.
Further degradation will result in a community dominated by annuals. Severe overgrazing of this plant community causes gulfdune paspalum to be virtually absent. Sandbur (Cenchrus spp.), red lovegrass, seashore saltgrass, fringed signalgrass (Urochloa ciliatissima), annual panicums (Panicum spp.), camphor daisy (Haplopappus phyllocephala), round pennywort, frogfruit, and other forbs dominate this plant community. Severe overuse results in a large amount of bare ground, which results in blowing sand. Blowing sand further accelerates community degradation.
The intensity of a hurricane plays a large role in the plant community. Due to the extensive creeping rhizomes and ability to tolerate high salinity levels, gulfdune paspalum can survive a moderately-intensive hurricane while other species cannot. Following a hurricane, the plant community will consist of gulfdune paspalum and various annual pioneer plants. Following a severe hurricane, vegetation will be virtually devoid. Length of recovery to reference conditions will depend on the severity and the ability to defer from grazing or other major natural disturbance.
Active sand dunes occur on this site. Overuse by livestock exacerbates dune formation. Continuous dunes sometimes cover several square miles. The dunes add to landscape diversity but can pose management problems because they migrate across the landscape and may cover fences, roads, equipment, and buildings. Cutting native hay near a sand dune and mulching the dune with the hay while lightly incorporating the hay into the soil is an effective method of stabilizing dunes.
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Loss of vegetative cover |
|---|---|---|
| R2A | - | Natural regeneration over time |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Prairie
Dominant plant species
-
saltmeadow cordgrass (Spartina patens), grass
-
gulfdune paspalum (Paspalum monostachyum), grass
Community 1.1
Midgrass Prairie
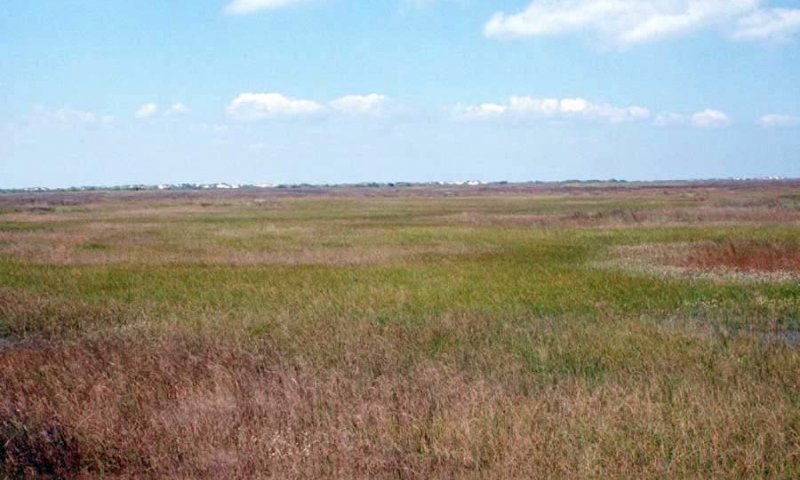

Figure 10. 1.1 Midgrass Prairie Community
The reference plant community for the site is an open grassland plain composed of midgrasses. Widely varying amounts of gulfdune paspalum and marshhay cordgrass dominate the site. The prairie consists of midgrasses dominated by gulfdune paspalum, marshhay cordgrass, or any combination thereof. Seacoast bluestem occurs on moderately drained flats and swales while bushy bluestem occurs in poorly drained areas. American bulrush is also associated with these grass communities in poorly drained areas. Other important associated perennial and annual forbs include mistflower (Conoclinium coelestinum), sea lavender (Limonium carolinianum), bushy sea-ox-eye, and narrowleaf marshelder. Heavy grazing results in a change in the plant community composition by strongly reducing the occurrence of gulfdune paspalum and increasing the abundance of forbs.
Figure 11. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 2018 | 2993 | 3945 |
| Forb | 224 | 370 | 538 |
| Total | 2242 | 3363 | 4483 |
Figure 12. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX7755, Open Warm-Season Grassland. Shortgrass community with forbs.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 15 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 5 |
Community 1.2
Shortgrass/Annual Prairie
This community may have remnants of marshhay cordgrass and bushy bluestem but has a greater abundance of forbs such as American snoutbean (Rhynchosia americana), round pennywort, frogfruit, and narrow-leaf marshelder than reference conditions. This site occurred due to overgrazing but can be restored with prescribed grazing and periodic prescribed burning. Further heavy abusive grazing will cause a further decline until only shortgrasses are present. Species include seashore saltgrass, seashore dropseed, and three awns, as well as annual and perennial forb species such as partridge pea (Chamaecrista fasciculata), annual crotons (Croton spp.), western ragweed (Ambrosia psilostachya), narrowleaf marshelder, round pennywort, and frogfruit. Grass species such as knotroot bristlegrass (Setaria geniculata) and whorled dropseed (Sporobolus coromandelianus) will be common in this condition. There is also an increase in bare ground in this plant community.
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2
The transition to Community 1.2 occurs because of overgrazing, lack of fire, or naturally occurring drought conditions.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1
The restoration back to Community 1.1 requires prescribed grazing, the return of prescribed fire, and/or more average rainfall conditions returning.
State 2
Hurricane Impacted
Vegetation severely reduced or absent.
Community 2.1
Hurricane Impacted
This plant community is caused by the destructive forces of hurricanes. The vegetation has been burned due to high winds laden with coastal water. Vegetation has also been buried under thick sediment deposits of sand. Some areas are scoured and devoid of vegetation and may temporarily suffer complete vegetative loss. This community can be restored back to the Midgrass Prairie State (1) given enough time for the vegetation to recover. Usually, deferment and time are the best options for recovery.
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
Transition to State 2 is caused by the associated effects of Hurricanes. This includes storm surges, wind scouring of plants, and burial of vegetation by sediment deposition.
Restoration pathway R2A
State 2 to 1
Restoration back to the Midgrass Prairie State (1) typically requires time and deferment of grazing. Time for recovery depends on the severity of the hurricane.
Additional community tables
Table 6. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Midgrasses | 1211–2367 | ||||
| gulfdune paspalum | PAMO4 | Paspalum monostachyum | 1211–2367 | – | ||
| saltmeadow cordgrass | SPPA | Spartina patens | 1211–2367 | – | ||
| 2 | Midgrasses | 303–592 | ||||
| bushy bluestem | ANGL2 | Andropogon glomeratus | 303–592 | – | ||
| slimleaf panicgrass | DILI2 | Dichanthelium linearifolium | 303–592 | – | ||
| shore little bluestem | SCLI11 | Schizachyrium littorale | 303–592 | – | ||
| 3 | Midgrass | 202–395 | ||||
| common threesquare | SCPU10 | Schoenoplectus pungens | 202–395 | – | ||
| 4 | Midgrasses | 202–395 | ||||
| saltgrass | DISP | Distichlis spicata | 202–395 | – | ||
| seashore dropseed | SPVI3 | Sporobolus virginicus | 202–395 | – | ||
| 5 | Midgrasses | 101–197 | ||||
| Grass, perennial | 2GP | Grass, perennial | 101–197 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 6 | Forbs | 112–269 | ||||
| blue mistflower | COCO13 | Conoclinium coelestinum | 112–269 | – | ||
| floating marshpennywort | HYRA | Hydrocotyle ranunculoides | 112–269 | – | ||
| American snoutbean | RHAM | Rhynchosia americana | 112–269 | – | ||
| lavender thrift | LICA17 | Limonium carolinianum | 112–269 | – | ||
| lanceleaf fogfruit | PHLA3 | Phyla lanceolata | 112–269 | – | ||
| bushy seaside tansy | BOFR | Borrichia frutescens | 112–269 | – | ||
| 7 | Forb | 112–269 | ||||
| Jesuit's bark | IVFR | Iva frutescens | 112–269 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
The animal communities of the Coastal Prairie communities are influenced by fresh and salt water inundations. Cattle and many species of wildlife make extensive use of the site. White-tailed deer may be found scattered across the prairie and are found in heavier concentrations where woody cover exists. Feral hogs are present and at times become abundant. Coyotes are abundant and fill the mammalian predator niche. Rodent populations rise during drier periods and fall during periods of inundation. Alligators are locally abundant and make frequent use of the marshes depending on salt concentrations in the marshes.
The region is a major flyway for waterfowl and migrating birds. Hundreds of thousands of ducks, geese, and sandhill cranes abound during winter. Whooping cranes are an important endangered species that occur in the area, especially near Aransas National Wildlife Refuge. Northern harriers are common predatory birds seen patrolling marshes. Curlews, plovers, sandpipers, and willets are shorebirds that make use of the tidal areas. Seagulls and terns are plentiful throughout the year trolling the shores as well. Further inland, rails, gallinules, and moorhens make use of the brackish marshes.
Recreational uses
The Padre Island National Seashore is a popular tourist designation throughout the year. Because the National Seashore endeavors to preserve Padre Island in its natural state, visiting the island is very much like stepping back into the past. Birdwatching and saltwater fishing are other recreational uses.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented was derived from the Range Site Description, NRCS clipping data, literature, field observations, and personal contacts with range-trained personnel.
Other references
Archer, S. 1994. Woody plant encroachment into southwestern grasslands and savannas: rates, patterns and proximate causes. Ecological implications of livestock herbivory in the West, 13-68.
Archer, S. and F. E. Smeins. 1991. Ecosystem-level processes. Grazing Management: An Ecological Perspective. Edited by R.K. Heischmidt and J.W. Stuth. Timber Press, Portland, OR.
Bailey, V. 1905. North American Fauna No. 25: Biological Survey of Texas. United States Department of Agriculture Biological Survey. Government Printing Office, Washington D. C.
Beasom, S. L, G. Proudfoot, and J. Mays. 1994. Characteristics of a live oak-dominated area on the eastern South Texas Sand Plain. In the Caesar Kleberg Wildlife Research Institute Annual Report, 1-2.
Bestelmeyer, B. T., J. R. Brown, K. M. Havstad, R. Alexander, G. Chavez, and J. E. Herrick. 2003. Development and use of state-and-transition models for rangelands. Journal of Range Management, 56(2):114-126.
Briske, B. B, B. T. Bestelmeyer, T. K. Stringham, and P. L. Shaver. 2008. Recommendations for development of resilience-based State-and-Transition Models. Rangeland Ecology and Management, 61:359-367.
Brown, J. R. and S. Archer. 1999. Shrub invasion of grassland: recruitment is continuous and not regulated by herbaceous biomass or density. Ecology, 80(7):2385-2396.
Butzler, R. E. 2006. The Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Lycium carolinianum Walt. M. S. Thesis. Texas A&M, College Station, TX.
Chabreck, R. H. 1972. Vegetation, water and soil characteristics of the Louisiana coastal region. Louisiana State University Agriculture Experiment Station Bulletin, 664.
Davis, W. B. 1974. The Mammals of Texas. Texas Parks and Wildlife Department Bulletin, 41.
Drawe, D. L., A. D. Chamrad, and T. W. Box. 1978. Plant communities of the Welder Wildlife Refuge. The Welder Wildlife Refuge, Sinton, TX.
Drawe, D. L., K. R. Kattner, W. H. McFarland, and D. D. Neher. 1981. Vegetation and soil properties of five habitat types on north Padre Island. Texas Journal of Science, 33:145-157.
Everitt, J. H., D. L. Drawe, and R. I. Leonard. 2002. Trees, Shrubs, and Cacti of South Texas. Texas Tech University Press, Lubbock, TX.
Foster, J. H. 1917. Pre-settlement fire frequency regions of the United States: A first approximation. Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference Proceedings, 20.
Frost, C. C. 1995. Presettlement fire regimes in southeastern marshes, peatlands, and swamps. Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference Proceedings, 19:39-60.
Fulbright, T. E., D. D. Diamond, J. Rappole, and J. Norwine. 1990. The Coastal Sand Plain of Southern Texas. Rangelands, 12:337-340.
Fulbright, T. E., J. A. Ortega-Santos, A. Lozano-Cavazos, and L. E. Ramirez-Yanez. 2006. Establishing vegetation on migrating inland sand dunes in Texas. Rangeland Ecology and Management, 59:549-556.
Gosselink, J.D., C.L. Cordes, and J.W. Parsons. 1979. An. Ecological characterization study of the Chenier Plain Coastal Ecosystem of Louisiana and Texas. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Office of Biological Services, Washington, D.C.
Gould, F. W. 1975. The Grasses of Texas. Texas A&M University Press, College Station, TX.
Gould, F. W. and T. W. Box. 1965. Grasses of the Texas Coastal Bend. Texas A&M University Press, College Station, TX.
Grace, J. B., L. K. Allain, H. Q. Baldwin, A. G. Billock, W. R. Eddleman, A. M. Given, C. W. Jeske, and R. Moss. 2005. Effects of prescribed fire in the coastal prairies of Texas. USGS Open File Report, 2005-1287.
Hamilton, W. and D. Ueckert. 2005. Rangeland woody plant control: Past, present, and future. Brush management: Past, present, and future, 3-16.
Harcombe, P. A. and J. E. Neaville. 1997. Vegetation types of Chambers County, Texas. The Texas Journal of Science, 29:209-234.
Hatch, S. L., J. L. Schuster, and D. L. Drawe. 1999. Grasses of the Texas Gulf Prairies and Marshes. Texas A&M University Press, College Station, TX.
Johnson, M. C. 1963. Past and present grasslands of southern Texas and northeastern Mexico. Ecology 44(3):456-466.
Lehman, V. W. 1965. Fire in the range of Attwater’s prairie chicken. Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference Proceedings, 4:127-143.
Mann, C. 2004. 1491: New Revelations of the Americas before Columbus. Vintage Books, New York City, NY.
Mapston, M. E. 2007. Feral Hogs in Texas. Texas Agrilife Extension Bulletin, B-6149
McAtee, J. W., C. J. Scifres, D. L. and Drawe. 1979. Digestible energy and protein content of gulf cordgrass following burning or shredding. Journal of Range Management, 376-378.
McGowen, J. H., L. F. Brown, T. J. Evans, W. L. Fisher, and C. G. Groat. 1976. Environmental geologic atlas of the Texas Coastal Zone-Bay City-Freeport area. The University of Texas at Austin, Bureau of Economic Geology, Austin, TX.
Miller, D. L., F. E Smeins, and J. W. Webb. 1998. Response of a Texas Distichlis spicata coastal marsh following Lesser Snow Goose herbivory. Aquatic Botany, 61:301-307.
Miller, D. L., F. E. Smeins, and J. W. Webb. 1996. Mid-Texas coastal marsh change (1939-1991) as influenced by Lesser Snow Goose herbivory. Journal of Coastal Research, 12:462-476.
Miller, D. L., F. E. Smeins, J. W. Webb, and M. T. Longnecker. 1997. Regeneration of Scirpus americanus in a Texas coastal marsh following Lesser Snow Goose herbivory. Wetlands, 17:31-42.
Oefinger, R. D. and C. J. Scifres. 1977. Gulf cordgrass production, utilization, and nutritional value following burning. Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin, B-1176.
Palmer, G. R., T. E. Fulbright, and G. McBryde. 1995. Inland sand dune reclamation on the Coastal Sand Plain of Southern Texas. Caesar Kleberg Wildlife Research Institute Annual Report, 1994-1995.
Prichard, D. 1998. Riparian area management: A user guide to assessing proper functioning condition and the supporting science for lotic areas. Bureau of Land Management, Denver, CO.
Rappole, J. H. and G. W. Blacklock. 1985. Birds of the Texas Coastal Bend: Abundance and distribution. Texas A&M University Press, College Station, TX.
Scifres, C. J. and W. T. Hamilton. 1993. Prescribed burning for brushland management: The South Texas example. Texas A&M Press, College Station, TX.
Scifres, C. J., J. W. McAtee, and D. L. Drawe 1980. Botanical, edaphic, and water relationships of gulf cordgrass (Spartina spartinae [Trin.] Hitchc.) and associated communities. The Southwestern Naturalist, 25(3):397-409.
Shiflet, T. N. 1963. Major ecological factors controlling plant communities in Louisiana marshes. Journal of Range Management, 16:231-235.
Singleton, J. R. 1951. Production and utilization of waterfowl food plants on the east Texas gulf coast. Journal of Wildlife Management, 15:46-56.
Smeins, F. E., D. D. Diamond, and W. Hanselka. 1991. Coastal prairie, 269-290. Ecosystems of the World: Natural Grasslands. Edited by R. T. Coupland. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Smeins, F. E., S. Fuhlendorf, and C. Taylor, Jr. 1997. Environmental and land use changes: A long term perspective. Juniper Symposium, 1-21.
Snyder, R. A. and C. L. Boss. 2002. Recovery and stability in barrier island plant communities. Journal of Coastal Research, 18:530-536.
Stoddart, L. A., A. D. Smith, and T. W. Box. 1975. Range management. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York, NY.
Stringham, T. K., W. C. Krueger, and P. L. Shaver. 2001. State and transition modeling: An ecological process approach. Journal of Range Management, 56(2):106-113.
Thornthwaite, C. W. 1948. An approach towards a rational classification of climate. Geographical Review, 38: 55-94.
Thurow, T. L. 1991. Hydrology and erosion. Grazing Management: An Ecological Perspective. Edited by R.K. Heitschmidt and J.W. Stuth. Timber Press, Portland, OR.
Urbatsch, L. 2000. Chinese tallow tree Triadica sebifera (L.) Small. USDA-NRCS, National Plant Center, Baton Rouge, LA.
Van’t Hul, J. T., R. S. Lutz, and N. E. Mathews. 1997. Impact of prescribed burning on vegetation and bird abundance on Matagorda Island, Texas. Journal of Range Management, 50:346-360.
Vines, R. A. 1977. Trees of Eastern Texas. University of Texas Press, Austin, TX.
Vines, R. A. 1984. Trees of Central Texas. University of Texas Press, Austin, TX.
Wade, D. D., B. L. Brock, P. H. Brose, J. B. Grace, G. A. Hoch, and W. A. Patterson III. 2000. Fire in Eastern ecosystems. Wildland fire in ecosystems: effects of fire on flora. Edited by. J. K. Brown and J. Kaplers. United States Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Ogden, UT.
Warren, W. S. 1998. The La Salle Expedition to Texas: The journal of Henry Joutel, 1684-1687. Edited by W. C. Foster. Texas State Historical Association, Austin, TX.
Weaver, J. E. and F. E. Clements. 1938. Plant ecology. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY.
Williams, A. M., R. A. Feagin, W.K. Smith, and N. L. Jackson. 2009. Ecosystem impacts of Hurricane Ike on Galveston Island and Bolivar Peninsula: Perspectives of the coastal barrier island network (CBIN). Shore and Beach, 7(2):1-5.
Williams, L. R. and G. N Cameron. 1985. Effects of removal of pocket gophers on a Texas coastal prairie. The American Midland Naturalist Journal, 115:216-224.
Wright, H.A. and A.W. Bailey. 1982. Fire Ecology: United States and Southern Canada. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ.
Contributors
Jason Hohlt, RMS, NRCS, Kingsville, TX
Acknowledgments
Contributing Authors:
Justin Clary, RMS, NRCS, Temple, TX
Shanna Dunn, SS, NRCS, Corpus Christi, TX
Vivian Garcia, RMS, NRCS, Corpus Christi, TX
Stan Reinke, RMS, NRCS, Corpus Christi, TX
Tim Reinke, RMS, NRCS, Victoria, TX
Homer Sanchez, RMS, NRCS, Temple, TX
Site Development and Testing Plan:
Future work, as described in a Project Plan, to validate the information in this Provisional Ecological Site Description is needed. This will include field activities to collect low, medium and high-intensity sampling, soil correlations, and analysis of that data. Annual field reviews should be done by soil scientists and vegetation specialists. A final field review, peer review, quality control, and quality assurance reviews of the ESD will be needed to produce the final document. Annual reviews of the Project Plan are to be conducted by the Ecological Site Technical Team.
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | |
| Date | 03/12/2026 |
| Approved by | Bryan Christensen |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
-
Presence of water flow patterns:
-
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
-
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
-
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
-
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
-
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
-
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
-
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
-
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
-
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
-
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Sub-dominant:
Other:
Additional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
-
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
-
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
-
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
-
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Loss of vegetative cover |
|---|---|---|
| R2A | - | Natural regeneration over time |