Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F006XA008WA
Cryic Xeric Mountain Slopes (Subalpine fir Cold Moderately Dry Shrub/Herb)
Last updated: 2/14/2025
Accessed: 03/04/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 006X–Cascade Mountains, Eastern Slope
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 006X–Cascade Mountains, Eastern Slope.
Stretching from northern Washington to southern Oregon, MLRA 6 encompasses the mountain slopes, foothills, elevated plateaus and valleys on the eastern slopes of the Cascade mountains. This MLRA is a transitional area between the Cascade Mountains to the west and the lower lying Columbia Basalt Plateau to the east. Situated in the rain shadow of the Cascade Crest, this MLRA receives less precipitation than portions of the cascades further west and greater precipitation than the basalt plateaus to the east. Geologically, the majority of the MLRA is dominated by Miocene volcanic rocks, while the northern portion is dominated by Pre-Cretaceous metamorphic rocks and the southern portion is blanketed with a thick mantle of ash and pumice from Mount Mazama. The soils in the MLRA dominantly have a mesic, frigid, or cryic soil temperature regime, a xeric soil moisture regime, and mixed or glassy mineralogy. They generally are moderately deep to very deep, well drained, and loamy or ashy. Biologically, the MLRA is dominated by coniferous forest, large expanses of which are dominated by ponderosa pine, Douglas-fir or lodgepole pine. Areas experiencing cooler and moister conditions include grand fir, white fir, and western larch while the highest elevations include pacific silver fir, subalpine fir and whitebark pine. Economically, timber harvest and recreation are important land uses in these forests. Historically, many of these forests would have experienced relatively frequent, low and mixed severity fire favoring the development of mature forests dominated by ponderosa pine or Douglas-fir. In the southern pumice plateau forests, less frequent, higher severity fire was common and promoted the growth of large expanses of lodgepole pine forests.
LRU notes
This ecological site typically resides on northerly-facing mountain slopes, at elevations of 4400 to 7200 feet with slope gradients of 25 to 60 percent. The climate is cold and moderately dry with 55 to 90 frost-free days, mean annual precipitation of 30 to 50 inches, and mean annual air temperatures of 36 to 40 degrees Fahrenheit. This covers the subalpine fir zone of cold, high elevation areas with persistent slow-melting snow that causes a short growing season.
Classification relationships
The ecological site relates to the Wenatchee National Forest plant associations:
CES211 - Subalpine fir/Cascade azalea (ABLA2/RHAL)
CES213 - Subalpine fir/Cascade azalea/smooth woodrush (ABLA2/RHAL-LUHI)
Ecological site concept
The soils are dominantly Inceptisols, specifically Andic Dystrocryepts, with a loamy-skeletal particle-size class, surface textures of ashy silt loam or ashy fine sandy loam, and andic soil properties. The parent material is volcanic ash over glacial till, colluvium, and residuum. The soils are well drained, have no flooding, ponding or water table and are typically 20 to 40 inches deep to a root-restricting feature. These soils are typically in the cryic soil temperature and udic soil moisture regimes, with less extensive areas in a xeric moisture regime.
The reference community is dominated by an overstory of ABLA and PIEN with a diverse assemblage of cold adapted shrub and herbaceous species. Seral tree species include PICO (until 100 yrs.), warmer sites will have PSME, PIMO3, LAOC and higher elevations will have PIAL, LALY. The understory includes: ARLA8, CACO11, CARU, GOOB2, LULA4, ORSE, OSMOR, PAMY, RHAL2, VAME, VAMY2, VASC, LUHI4.
Associated sites
| F006XA004WA |
Cold Cryic Xeric Mountain Slopes (Subalpine fir Cold Dry Shrub) |
|---|
Similar sites
| F006XA003WA |
Cryic Xeric Mountain Slopes (Subalpine fir Cool Moderately Dry Shrub/Herb) Warmer, lower elevation. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Abies lasiocarpa |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Vaccinium scoparium |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Luzula glabrata |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
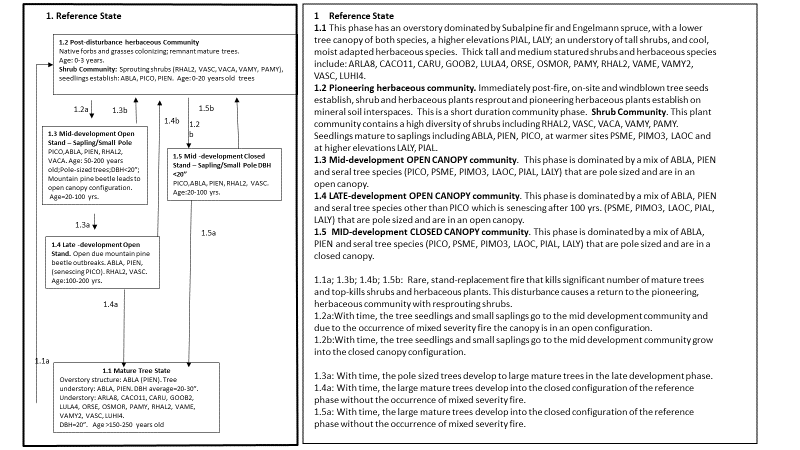
Ecosystem states
State 1 submodel, plant communities
Communities 1, 5 and 2 (additional pathways)
| 1.1A | - | Rare, stand-replacement fire |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Time and mixed severity fire |
| 1.2B | - | Time |
| 1.3B | - | Rare, stand-replacement fire |
| 1.3A | - | Time |
| 1.4A | - | Time and absence of fire |
| 1.4B | - | Rare, stand-replacement fire |
| 1.5A | - | Time and absence of fire |
| 1.5B | - | Rare, stand-replacement fire |