Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F018XI204CA
North-facing Steep Draws and Hillslopes
Last updated: 4/24/2024
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 018X–Sierra Nevada Foothills
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 18, Sierra Nevada Foothills is located entirely in California and runs north to south adjacent to and down-slope of the west side of the Sierra Nevada Mountains (MLRA 22A). MLRA 18 includes rolling to steep dissected hills and low mountains, with several very steep river valleys. Climate is distinctively Mediterranean (xeric soil moisture regime) with hot, dry summers, and relatively cool, wet winters. Most of the precipitation comes as rain; average annual precipitation ranges from 15 to 55 inches in most of the area (precipitation generally increases with elevation and from south to north). Soil temperature regime is thermic; mean annual air temperature generally ranges between 52 and 64 degrees F. Geology is rather complex in this region; there were several volcanic flow and ashfall events, as well as tectonic uplift, during the past 25 million years that contributed to the current landscape.
LRU notes
This LRU (designated XI) is located on moderate to steep hills in the Sierra Nevada Foothills east of Sacramento, Stockton and Modesto, CA. Various geologies occur in this region: metavolcanics, granodiorite, slate, marble, argillite, schist and quartzite, as well as ultramafic bands to a limited and localized extent. It includes mesa formations from volcanic flows, where vernal pool habitats occur. Soil temperature regime is thermic and soil moisture regime is xeric. Elevation ranges between 300 and 3400 feet above sea level. Precipitation ranges from 14 to 42 inches annually. Most precipitation falls between the months of November and March in the form of rain. Dominant vegetation includes annual grasslands, blue oak (Quercus douglasii), interior live oak (Quercus wislizeni), chamise (Adenostoma fasciculatum), buckbrush (Ceanothus cuneatus), and foothill pine (Pinus sabiniana).
Classification relationships
CLASSIFICATION RELATIONSHIPS
This site is located within M261F, the Sierra Nevada Foothills Section, (McNab et al., 2007) of the National Hierarchical Framework of Ecological Units (Cleland et al., 1997), M261Fb, the Lower Foothills Metamorphic Belt Subsection.
Level III and Level IV ecoregions systems (Omernik, 1987, and EPA, 2011) are: Level III, Central California Foothills and Coastal Mountains and Level IV, Ecoregion 6b, Northern Sierran Foothills, Ecoregion 6c, Comanche Terraces.
Ecological site concept
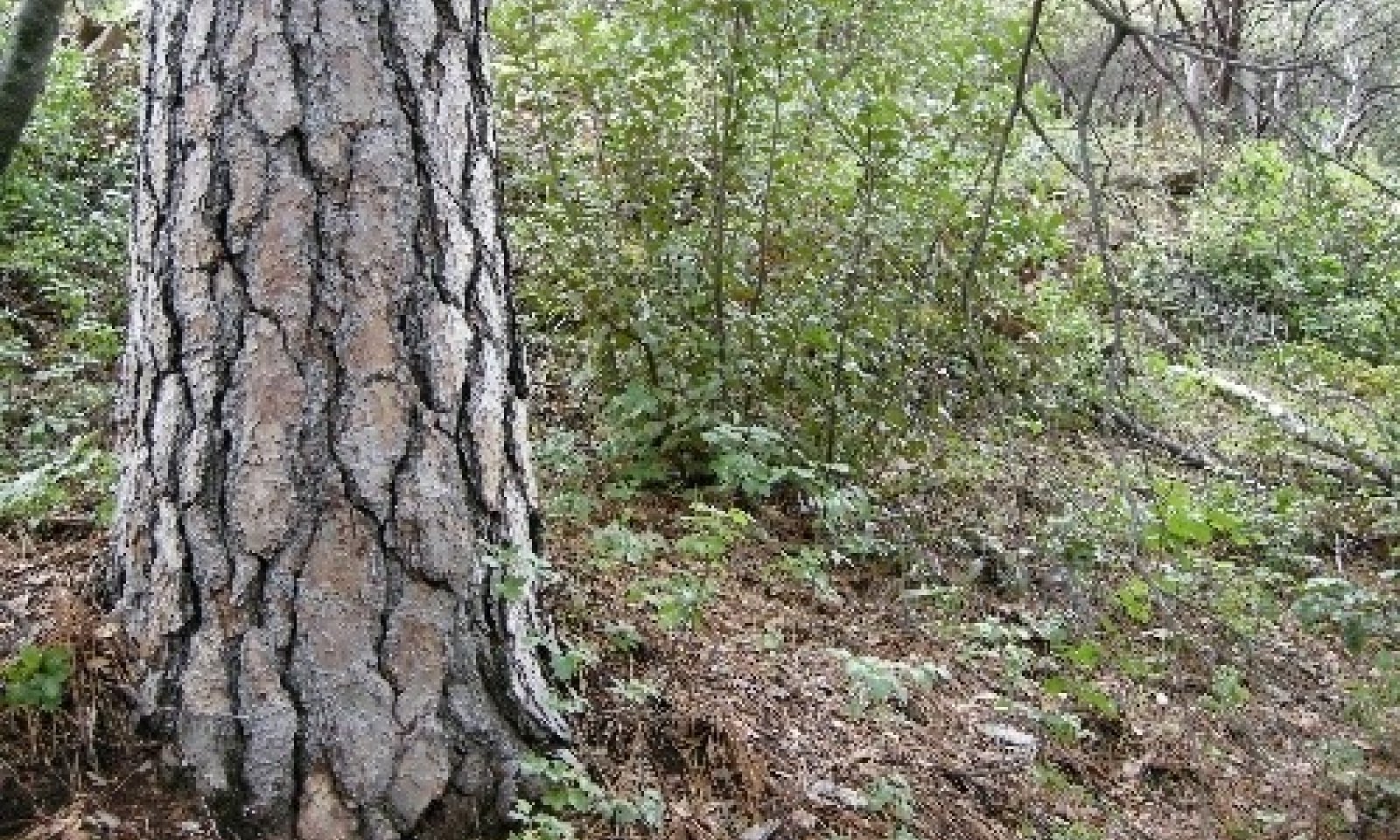
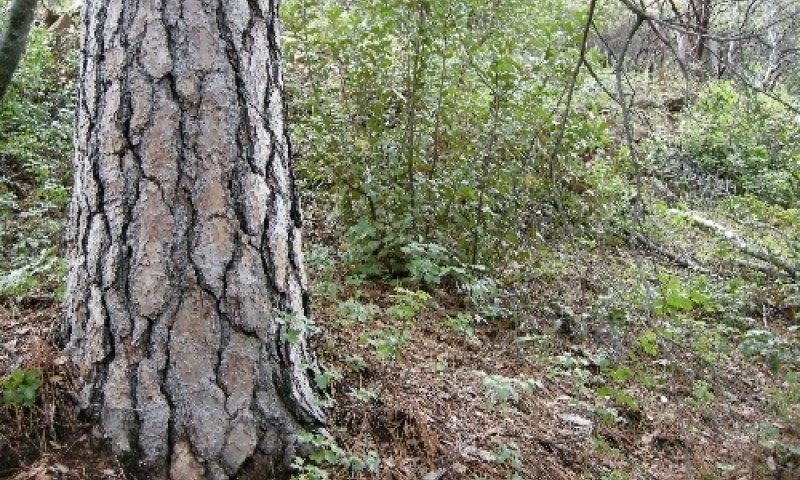
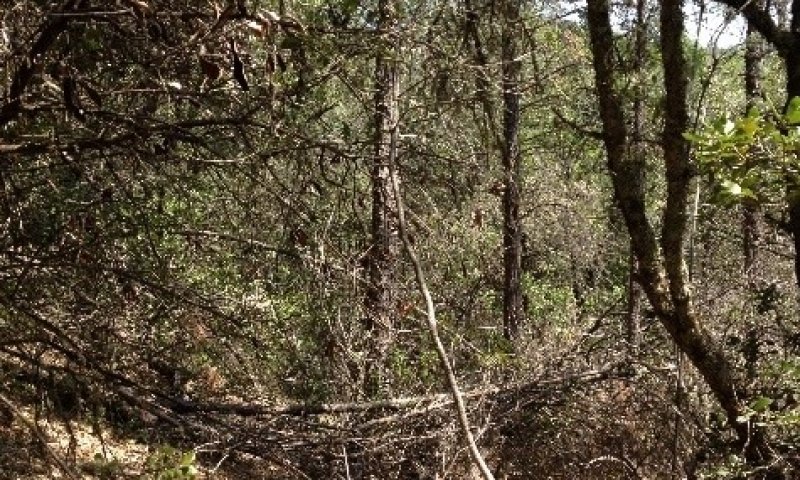
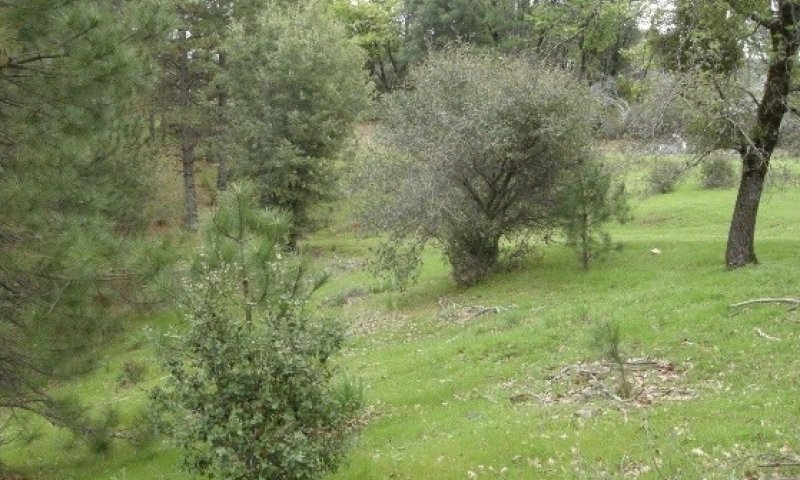
This site is found on steep hills on north-facing aspects on backslopes and footslopes, often in cooler drainages where soil temperatures border mesic. Parent material is generally of metasedimentary or granitic origin. Slopes typically range from 25 to 60%. Mean annual precipitation typically ranges from 32 to 38 inches, and elevation ranges from 1250 to 2000 feet.
Slope aspect is the overriding abiotic factor defining this ecological site, and tends to result in vegetation patterns that mimic those found in higher elevation mesic soil temperature regimes, even in the adjoining MLRA 22A (Sierra Nevada Mountains). The most common soil map unit component by acreage is the Sierra component. This component is a very deep, fine-loamy mixed, active, thermic Ultic Haploxeralf derived from intrusive igneous parent material. This ecological site is not restricted to a specific geology, it also occurs on phyllite, schist, and other metasedimentary soils, especially Deerflat components, which are also very deep.
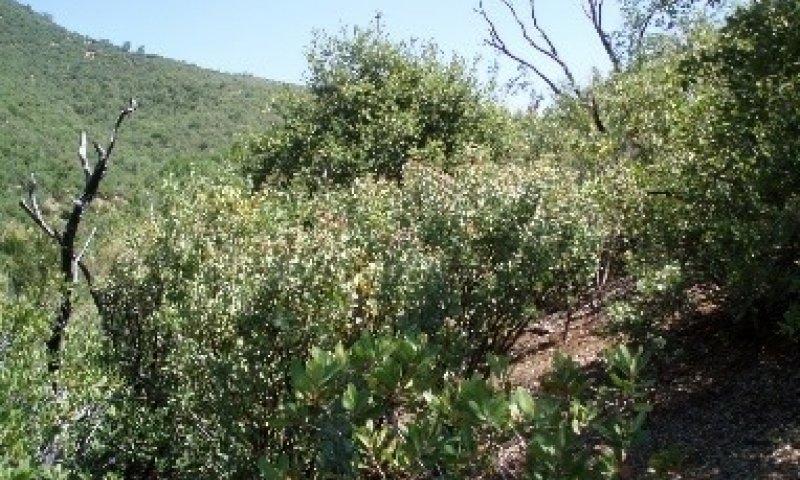
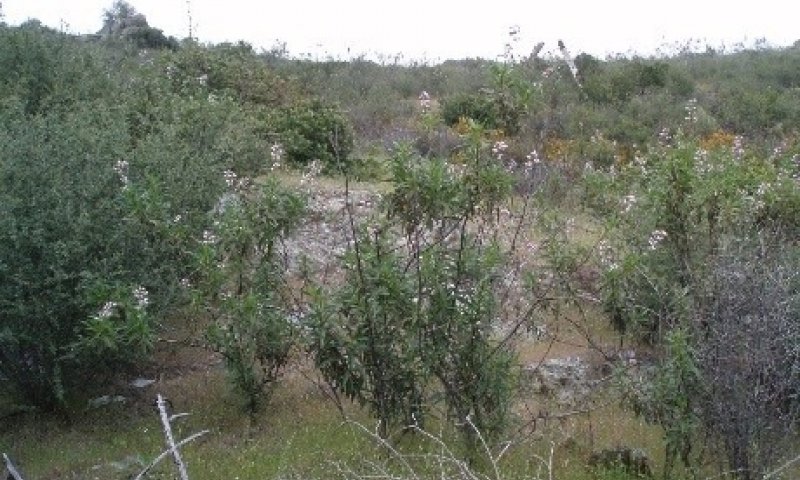
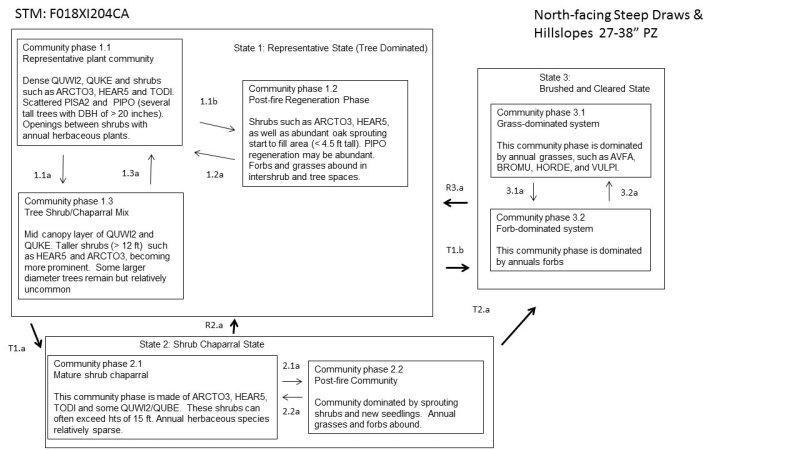
The dominant vegetation in this ecological site consists of dense forests (mean canopy cover ~ 51%) with species such as California black oak (Quercus kelloggii), interior live oak (Quercus wislizeni) and scattered ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa). Toyon (Heteromeles arbutifolia), manzanita (Arctostaphylos spp.), dense poison oak (Toxicodendron diversilobum), and sparse to moderately dense herbaceous annual forbs and grasses also occupy this site. This ecological site often hosts native perennial bunch grasses at 0 to 2 % cover. Herbaceous annual production generally makes up less than 2% of total production, and trees/and or shrubs exceed 90% of total annual production.
Similar sites
| F018XI205CA |
Thermic Granitic Foothills Site relationships being developed. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus kelloggii |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Toxicodendron diversilobum |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Avena fatua |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.