Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R018XE102CA
Steep Clayey Shallow
Last updated: 4/24/2024
Accessed: 04/28/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 018X–Sierra Nevada Foothills
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 018X–Sierra Nevada Foothills
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 18, Sierra Nevada Foothills is located entirely in California and runs north to south adjacent to and down-slope of the west side of the Sierra Nevada Mountains (MLRA 22A). MLRA 18 includes rolling to steep dissected hills and low mountains, with several very steep river valleys. Climate is distinctively Mediterranean (xeric soil moisture regime) with hot, dry summers, and relatively cool, wet winters. Most of the precipitation comes as rain; average annual precipitation ranges from 15 to 55 inches in most of the area (precipitation generally increases with elevation and from south to north). Soil temperature regime is thermic; mean annual air temperature generally ranges between 52 and 64 degrees F. Geology is rather complex in this region; there were several volcanic flow and ashfall events, as well as tectonic uplift, during the past 25 million years that contributed to the current landscape.
LRU notes
LRU 18XE is located on moderate to steep mountains and hills in the Tehachapi Foothills east of Bakersfield. This LRU covers the lower slopes around the southern end of the Greenhorn Mountains, the western sides of Breckenridge Mountain and the Tehachapi Mountains. The elevation ranges from 500 to 6500 feet above sea level and the geology of the region is predominately granitoid (both unaltered and metamorphosed). Similar to LRU 18XC to the north, vegetation series include blue oak, needlegrass and annual grasslands, as well as chamise, ceanothus, mixed oaks, and foothill pine, although this LRU tends to be more arid than with an annual precipitation range of only 8 to 31 inches per year. The lower precipitation and higher evaporative losses mean that these soils may not be able to completely leach excess salts, leading to a build-up of calcium and/or sodium in the subsoil. The soil temperature regime in this LRU is thermic and the soil moisture regimes are both xeric and aridic.
Classification relationships
CLASSIFICATION RELATIONSHIPS
This site is located within M261F, the Sierra Nevada Foothills Section, (McNab et al., 2007) of the National Hierarchical Framework of Ecological Units (Cleland et al., 1997), M261Fb, the Lower Foothills Metamorphic Belt Subsection.
Level III and Level IV ecoregions systems (Omernik, 1987, and EPA, 2011) are: Level III, Central California Foothills and Coastal Mountains and Level IV, Ecoregion 6ae, Tehachapi Foothills.
Ecological site concept
This site is characterized by moderately deep, fine-textured soils occurring on steep to very steep foothills typically formed on residuum weathered from gabbro. Slopes typically range from 15 to 50%. Precipitation typically ranges from 10 to 17 inches per year, and elevation ranges from 1940 to 4300 feet.
The overriding abiotic factors controlling vegetation expression on this site are high clay content (often 40% or more) and the smectitic mineralogy which leads to shrink-swell properties.These factors, coupled with steep, water shedding positions prevent the establishment of woody vegetation and severely impact the plant productivity. Infiltration of water is limited; roots often can not exploit the entire profile depth due to seasonal cracking during drying cycles. These are also highly erodible landscapes. The main soil component is Cibo (Fine, smectitic, thermic Aridic Haploxerert). Cibo soils are moderately deep, well drained soils.
This vegetation community consists of annual and perennial grasses and forbs. Dominant plants include soft brome (Bromus hordeaceus), desert needle grass (Achnatherum speciosum), fillaree (Erodium spp.), bur clover, (Medicago hispida), squirreltail (Elymus elymoides), fescue (Festuca spp.), rabbit brush (Chrysothamnus spp.) Annual production ranges from 700 to 1200 lbs per acre.
Associated sites
| F018XE201CA |
Granitic Hills and Mountains This site commonly occurs nearby. |
|---|
Similar sites
| R018XE103CA |
Loamy Low Hills Site relationships being developed. |
|---|---|
| R018XE104CA |
Thermic Granitic Hills Site relationships being developed. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Chrysothamnus |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Bromus hordeaceus |
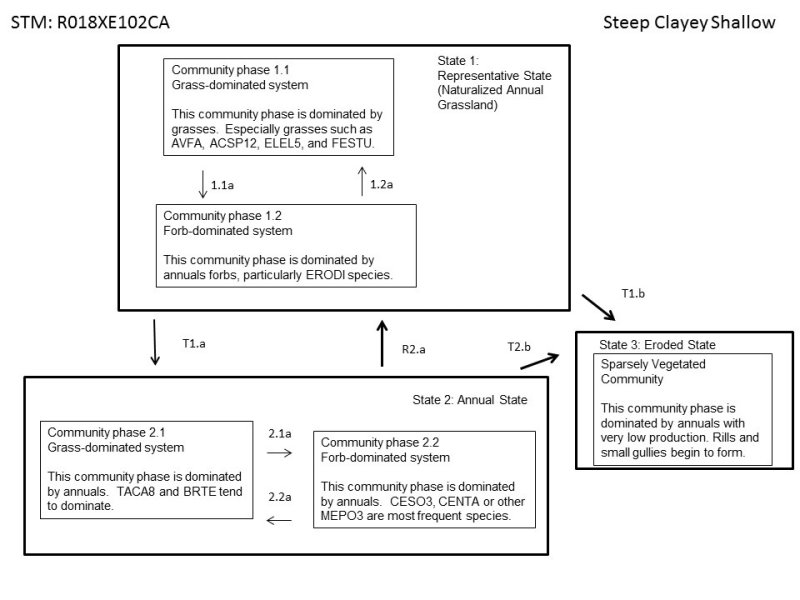
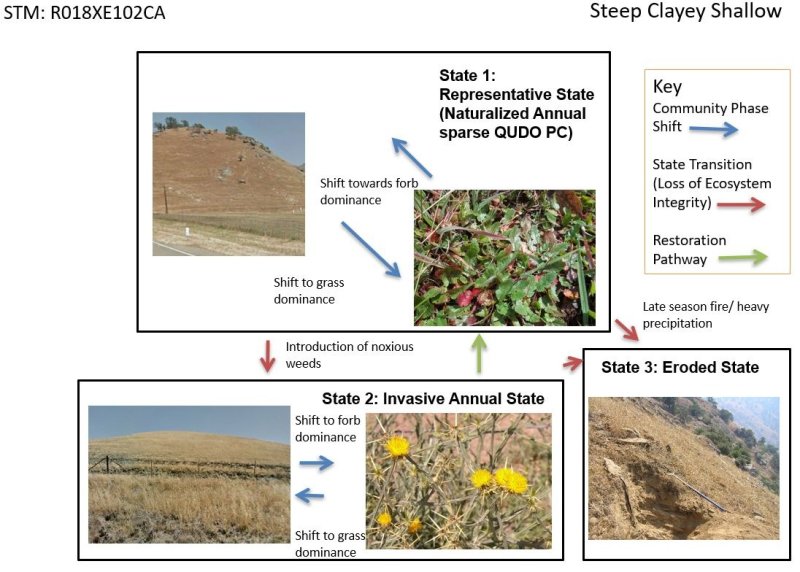
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.