Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R022AE217CA
Frigid Volcanic Slopes
Accessed: 03/03/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
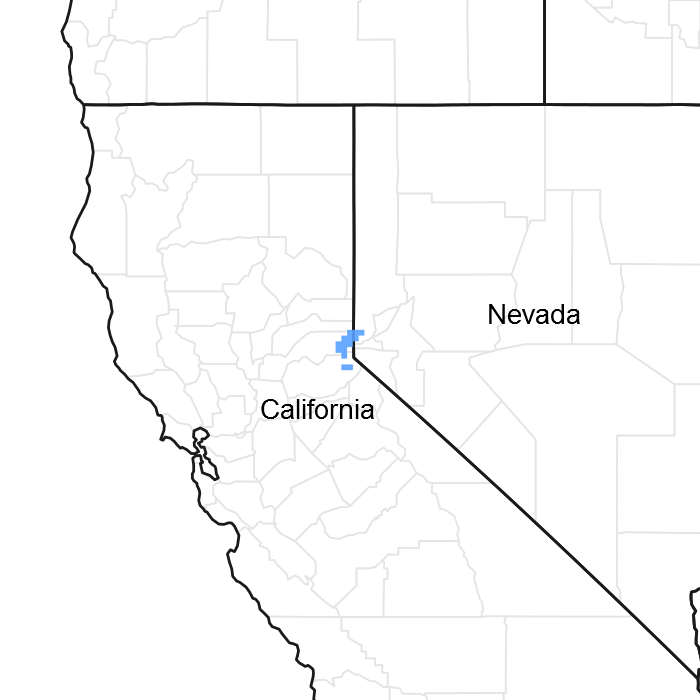
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 022A–Sierra Nevada and Tehachapi Mountains
Major Land Resource Area 22A, Sierra Nevada Mountains, is located predominantly in California and a small section of western Nevada. The area lies completely within the Sierra Nevada Section of the Cascade-Sierra Mountains Province. The Sierra Nevada range has a gentle western slope, and a very abrupt eastern slope. The Sierra Nevada consists of hilly to steep mountains and occasional flatter mountain valleys. Elevation ranges between 1,500 and 9,000 ft throughout most of the range, but peaks often exceed 12,000 ft. The highest point in the continental US occurs in this MLRA (Mount Whitney, 14,494 ft). Most of the Sierra Nevada is dominated by granitic rock of the Mesozoic age, known as the Sierra Nevada Batholith. The northern half is flanked on the west by a metamorphic belt, which consists of highly metamorphosed sedimentary and volcanic rocks. Additionally, glacial activity of the Pleistocene has played a major role in shaping Sierra Nevada features, including cirques, arêtes, and glacial deposits and moraines. Average annual precipitation ranges from 20 to 80 inches in most of the area, with increases along elevational and south-north gradients. Soil temperature regime ranges from mesic, frigid, and cryic. Due to the extreme elevational range found within this MLRA, Land Resource Units (LRUs) were designated to group the MLRA into similar land units.
LRU "E" Northern Sierran Upper Montane: This LRU occurs at the mid elevations of the Sierra Nevada, from the Sonora Pass area to the higher mountains in the vicinity of Quincy. Elevations are typically between 5,500 feet to 8,500 feet, with the lower elevations typically on southern aspects, and the higher elevations on northern aspects. The frost-free season is 60 to 125 days, MAAT ranges from 40 to 50 F, and MAP ranges from 35 to 85 inches. The soil temperature regime is mostly frigid, with some cryic soil temperatures at the upper elevations and northern aspects. Soil moisture regimes are mostly xeric, but may be udic where snow persists through spring.
Ecological site concept
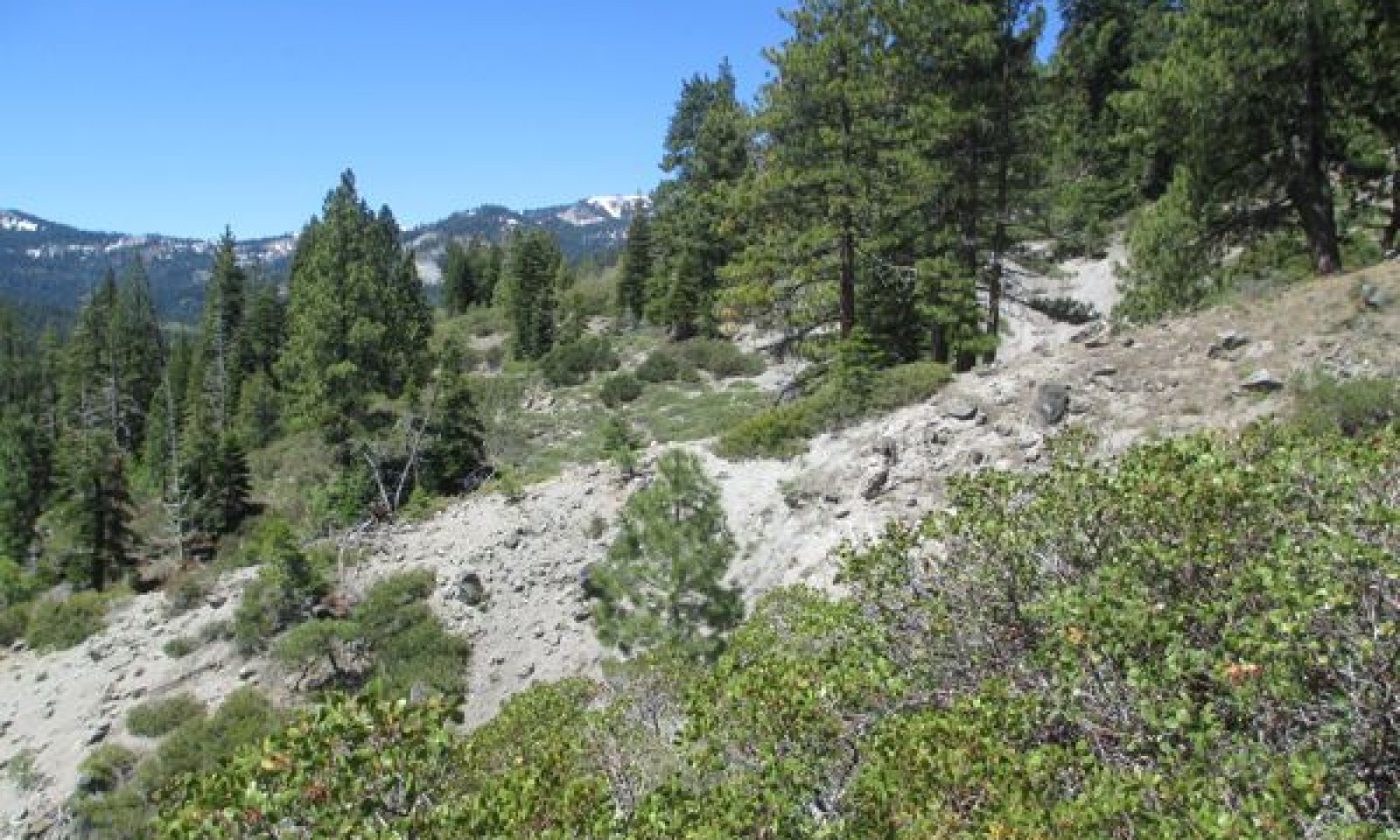
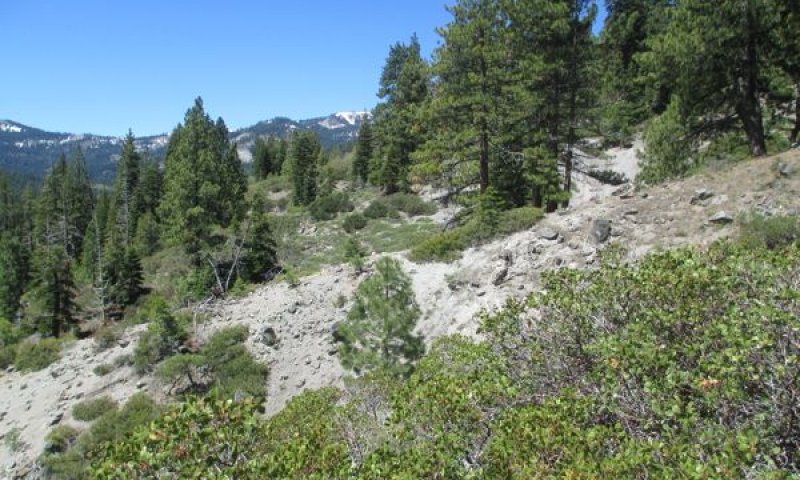
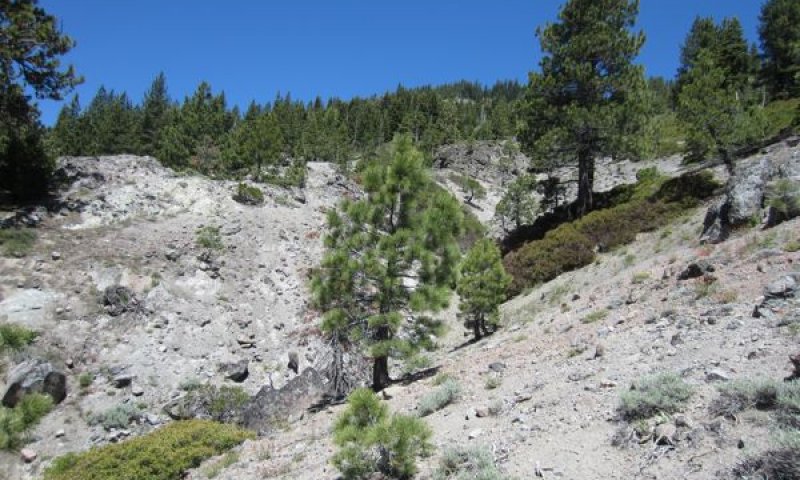
This ecological site is associated with shallow loamy soils that have developed over strongly cemented andesitic bedrock. Elevations range from 6,200 to 7,700 feet and slopes are typically between 30 and 70 percent. This site is typically found on undulating south facing slopes in patchy areas of shallow soil, with exposed bedrock within a forest matrix. Shallow, erosion prone soils and warm aspects support only sparse tree cover, and the dominant vegetation is open and diverse montane chaparral. Huckleberry oak (Quercus vaccinifolia) is the most frequent shrub, and greenleaf manzanita (Arctostaphylos patula) is also common. The loamy volcanic soils and undulating, dissected landscape support a higher diversity of shrubs and forbs than is found in montane chaparral communities associated with granitic substrates and more uniform slopes. Forbs are especially diverse on this site, with up to 27 different species occurring at a single location. Forbs tend to be distributed in more open patches of soil and around exposed bedrock.
Associated sites
| F022AE008CA |
Frigid Loamy Moraine Slopes Occurs on adjacent moraine slopes with very deep soils volcanic soils. The vegetation is red fir (Abies magnifica) - white fir (Abies concolor) forest. |
|---|---|
| F022AE013CA |
Frigid, Loamy, Volcanic Mountain Slopes Occurs on adjacent mountain slopes with loamy, moderately deep to deep andesitic soils. The vegetation is a white fir (Abies concolor) mixed conifer forest. White fir, jeffrey pine (Pinus jeffreyi), sugar pine (Pinus lambertiana) and incense cedar (Calocedrus decurrens) are all important species. |
| R022AX104CA |
Sphagnum Fen Occurs on sphagnum fens. |
| R022AX107CA |
Frigid C Channel System Occurs along C type channels with gravelly to cobbly channel substrates. The vegetation is dominated by Lemmons willow (Salix lemmonii) with mixed forbs. |
Similar sites
| R022AE213CA |
Steep Rubbly Slope This site is associated with very steep, rubbly slopes. It has a denser shrub cover and lower diversity of herbaceous species. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Quercus vacciniifolia |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Erigeron peregrinus |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.