Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R023XY066NV
ASHY LOAM 14-16 P.Z.
Last updated: 4/10/2025
Accessed: 03/05/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
Ecological site concept
Currently there is only a draft of the initial concept for this ecological site. The initial concept for this site places it within the Ashy or Loamy Skeletal Mod Deep 10-20 PZ High-Resilience Mountain Big Sagebrush and Idaho Fescue Ecological Site Group. To view the General STM and other information available for this ESG please go to https://edit.jornada.nmsu.edu/catalogs/esg/023X/R023XY906NV
The Ashy Loam 14-16” modal site occurs on mountain sideslopes and mountain valley fans on all aspects. Slope gradients of 2 to 15 percent are typical for this site. Elevations in this site range from 6,000 to 8,000 feet. Soils on this site are derived from colluvium and residuum of volcanic rocks. The soils in this site are moderately deep to deep and well drained and have high amounts of vitric volcanic ash throughout the soil profile, resulting in high water holding capacity. These soils are moderately coarse to medium textured and more than ten inches thick to the subsoil or underlying material. Soils are neutral to slightly acid. The plant community is dominated by Idaho fescue, needlegrasses, mountain big sagebrush and antelope bitterbrush. Bluebunch wheatgrass is also common throughout this site. Mountain big sagebrush is usually prevalent enough to dominate the visual aspect. Normal year production is 1,300 lb/ac.
Associated sites
| R023XY007NV |
LOAMY 14-16 P.Z. |
|---|---|
| R023XY017NV |
CLAYPAN 14-16 P.Z. |
| R023XY026NV |
MAHOGANY SAVANNA |
Similar sites
| R023XY072NV |
ASHY SLOPE 10-12 P.Z. ARTRW8 dominant shrub |
|---|---|
| R023XY084NV |
DEEP LOAMY 14-16 P.Z. PSSPS-ACTH7-FEID codominant grasses |
| R023XY007NV |
LOAMY 14-16 P.Z. FEID-PSSPS codominant grasses |
| R023XY094NV |
ASHY SLOPE 12-14 P.Z. PUTR2 rare to minor shrub |
| R023XY071NV |
ASHY LOAM 10-12 P.Z. ARTRT dominant shrub |
| R023XY064NV |
SOUTH SLOPE 16+ P.Z. PSSPS-BRMA4-LECI4 codominant grasses |
| R023XY015NV |
STONY LOAM 12-14 P.Z. PSSPS dominant grass |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Artemisia tridentata ssp. vaseyana |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Festuca idahoensis |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on plateaus and mountain sideslopes on all aspects. Slopes range from 4 to 50 percent, but slope gradients of 4 to 15 percent are most typical. Elevations are 4900 to 7200 feet.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Mountain
(2) Plateau |
|---|---|
| Elevation | 4,900 – 7,200 ft |
| Slope | 4 – 50% |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
The climate associated with this site is semiarid and characterized by cool, moist winters and warm, dry summers. Average annual precipitation is 12 to over 16 inches. Mean annual air temperature is 39 to 44 degrees F. The average growing season is about 70 to 90 days.
Nevada’s climate is predominantly arid, with large daily ranges of temperature, infrequent severe storms, heavy snowfall in the higher mountains, and great location variations with elevation. Three basic geographical factors largely influence Nevada’s climate: continentality, latitude, and elevation. Continentality is the most important factor. The strong continental effect is expressed in the form of both dryness and large temperature variations. Nevada lies on the eastern, lee side of the Sierra Nevada Range, a massive mountain barrier that markedly influences the climate of the State. The prevailing winds are from the west, and as the warm moist air from the Pacific Ocean ascend the western slopes of the Sierra Range, the air cools, condensation occurs and most of the moisture falls as precipitation. As the air descends the eastern slope, it is warmed by compression, and very little precipitation occurs. The effects of this mountain barrier are felt not only in the West but throughout the state, with the result that the lowlands of Nevada are largely desert or steppes. The temperature regime is also affected by the blocking of the inland-moving maritime air. Nevada sheltered from maritime winds, has a continental climate with well-developed seasons and the terrain responds quickly to changes in solar heating.
Nevada lies within the mid-latitude belt of prevailing westerly winds which occur most of the year. These winds bring frequent changes in weather during the late fall, winter and spring months, when most of the precipitation occurs. To the south of the mid-latitude westerlies, lies a zone of high pressure in subtropical latitudes, with a center over the Pacific Ocean. In the summer, this high-pressure belt shifts northward over the latitudes of Nevada, blocking storms from the ocean. The resulting weather is mostly clear and dry during the summer and early fall, with scattered thundershowers. The eastern portion of the state receives significant summer thunderstorms generated from monsoonal moisture pushed up from the Gulf of California, known as the North American monsoon. The monsoon system peaks in August and by October the monsoon high over the Western U.S. begins to weaken and the precipitation retreats southward towards the tropics (NOAA 2004).
Average annual precipitation is 16 to over 20 inches. Mean annual air temperature is 41 to 44 degrees F. The average growing season is about 50 to 70 days.
Mean annual precipitaion at the Bear Creek, Nevada SNOTEL station (170501020301) is 37.69 inches.
monthly mean precipitation is:
January 3.84; February 3.75; March 4.38; April 4.9;
May 3.99; June 2.82; July .95; August 1.66;
September 1.22; October 2.12;
November 3.67; December 4.38.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (average) | 80 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (average) | |
| Precipitation total (average) | 14 in |
Figure 1. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 2. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 3. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 4. Annual average temperature pattern
Influencing water features
There are no influencing water features associated with this site.
Soil features
The soils associated with this site have formed in residuum or colluvium derived from volcanic parent materials. The soils are generally moderately deep to deep and well drained. Surface soils are moderately coarse to medium textured and more than ten inches thick to the subsoil or underlying material. The surface soils are slightly acid to neutral. Permeability is moderate and the soils are well drained. Available water capacity is low to high. There are high amounts of vitric volcanic ash and glass throughout the soil profile which enhances the water holding capacity of these soils. The soil series associated with this site include: Bearbutte, Boltz, Nutzan, and Reluctan.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Surface texture |
(1) Fine sandy loam (2) Loam (3) Very gravelly sandy loam |
|---|---|
| Family particle size |
(1) Loamy |
| Drainage class | Well drained |
| Permeability class | Moderately slow to moderately rapid |
| Soil depth | 20 – 60 in |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 8 – 71% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 5% |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
3.8 – 6.1 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
1% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
Not specified |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
Not specified |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
5.6 – 7.3 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
8 – 71% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
55% |
Ecological dynamics
Where management results in abusive grazing use by livestock and/or feral horses, palatable perennial grass and forb species will decrease while shrub species increase. Excessive cattle use in late summer and fall will adversely affect bitterbrush production and seedling survival. Species likely to invade this site are cheatgrass and exotic annual forbs. Fire on this site in fair to poor condition can result in cheatgrass-Douglas' rabbitbrush dominant communities. Juniper commonly invades this site in absence of fire.
Fire Ecology:
Presettlement fire return intervals in mountain big sagebrush communities varied from 15 to 25 years. Mountain big sagebrush is highly susceptible to injury from fire. It is often top-killed by fire and will not resprout. Antelope bitterbrush is considered a weak sprouter and is often killed by summer or fall fire. Antelope bitterbrush in some areas may sprout after light-severity spring fire. High fuel consumptions increase antelope bitterbrush mortality and therefore favors seedling establishment. Idaho fescue grows in a dense, fine-leaved tuft. Fires tend to burn within the accumulated fine leaves at the base of the plant and may produce temperatures sufficient to kill some of the root crown. Mature Idaho fescue plants are commonly reported to be severely damaged by fire in all seasons. Western needlegrass is moderately damaged by fire. The recovery time is between 3 and 5 years. Thurber’s needlegrass is classified as moderately resistant, but depending on season of burn, phenology, and fire severity, this perennial bunchgrass is moderately to severely damaged by fire. Early season burning is more damaging to this needlegrass than late season burning. Burning bluebunch wheatgrass may remove most of the aboveground biomass but does not usually result in plant mortality. Bluebunch wheatgrass is generally favored by burning. Burning stimulates flowering and seed production. However, season of burning affects mortality.
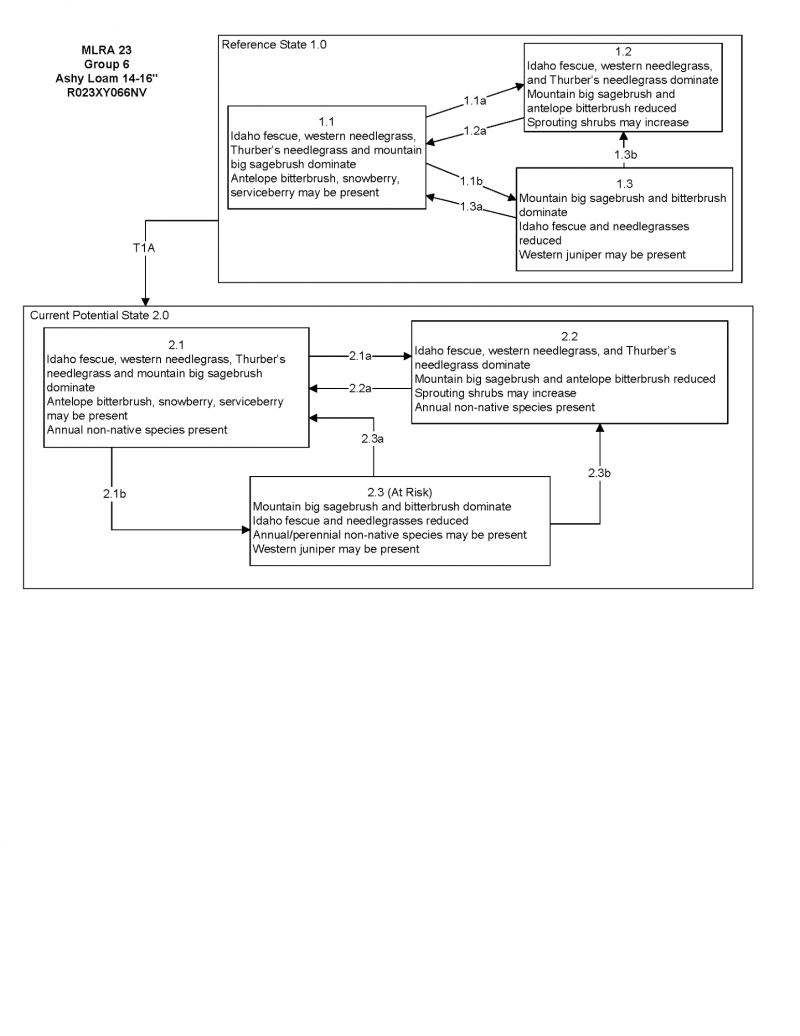
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
Ecosystem states
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Reference Plant Community
Community 1.1
Reference Plant Community
The reference plant community is dominated by mountain big sagebrush, antelope bitterbrush, Idaho fescue and western and/or Thurber's needlegrass. Potential vegetative composition is about 60% grasses, 10% forbs and 30% shrubs. Approximate ground cover (basal and crown) is about 30 to 35 percent.
Figure 5. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 600 | 780 | 1020 |
| Shrub/Vine | 293 | 373 | 484 |
| Forb | 100 | 130 | 170 |
| Tree | 7 | 17 | 26 |
| Total | 1000 | 1300 | 1700 |
Additional community tables
Table 6. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Primary Perennial Grasses | 816–1300 | ||||
| Idaho fescue | FEID | Festuca idahoensis | 520–650 | – | ||
| western needlegrass | ACOCO | Achnatherum occidentale ssp. occidentale | 130–260 | – | ||
| Thurber's needlegrass | ACTH7 | Achnatherum thurberianum | 130–260 | – | ||
| bluebunch wheatgrass | PSSPS | Pseudoroegneria spicata ssp. spicata | 36–130 | – | ||
| 2 | Secondary Perennial Grasses/Grasslikes | 36–104 | ||||
| Columbia needlegrass | ACNEN2 | Achnatherum nelsonii ssp. nelsonii | 7–26 | – | ||
| sedge | CAREX | Carex | 7–26 | – | ||
| big squirreltail | ELMU3 | Elymus multisetus | 7–26 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECO26 | Hesperostipa comata | 7–26 | – | ||
| basin wildrye | LECI4 | Leymus cinereus | 7–26 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 3 | Perennial | 65–195 | ||||
| milkvetch | ASTRA | Astragalus | 7–39 | – | ||
| tapertip hawksbeard | CRAC2 | Crepis acuminata | 7–39 | – | ||
| buckwheat | ERIOG | Eriogonum | 7–39 | – | ||
| lupine | LUPIN | Lupinus | 7–39 | – | ||
| phlox | PHLOX | Phlox | 7–39 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 4 | Primary Shrubs | 260–520 | ||||
| mountain big sagebrush | ARTRV | Artemisia tridentata ssp. vaseyana | 130–260 | – | ||
| antelope bitterbrush | PUTR2 | Purshia tridentata | 130–260 | – | ||
| 5 | Secondary Shrubs | 36–104 | ||||
| Utah serviceberry | AMUT | Amelanchier utahensis | 13–39 | – | ||
| curl-leaf mountain mahogany | CELE3 | Cercocarpus ledifolius | 13–39 | – | ||
| yellow rabbitbrush | CHVI8 | Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus | 13–39 | – | ||
| currant | RIBES | Ribes | 13–39 | – | ||
| mountain snowberry | SYOR2 | Symphoricarpos oreophilus | 13–39 | – | ||
|
Tree
|
||||||
| 6 | Evergreen | 7–26 | ||||
| Utah juniper | JUOS | Juniperus osteosperma | 7–26 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Livestock Interpretations:
This site is suitable for livestock grazing. Grazing management should be keyed to perennial grass production. Idaho fescue provides important forage for many types of domestic livestock. The foliage cures well and is preferred by livestock in late fall and winter. Western needlegrass has a spreading and deeply penetrating root system, which makes it resistant to trampling. Thurber’s needlegrass species begin growth early in the year and remain green throughout a relatively long growing season. This pattern of development enables animals to use Thurber’s needlegrass when many other grasses are unavailable. Cattle prefer Thurber’s needlegrass in early spring before fruits have developed as it becomes less palatable when mature. Thurber’s needlegrasses are grazed in the fall only if the fruits are softened by rain. Bluebunch wheatgrass is considered one of the most important forage grass species on western rangelands for livestock. Although bluebunch wheatgrass can be a crucial source of forage, it is not necessarily the most highly preferred species. Mountain big sagebrush is eaten by domestic livestock but has long been considered to be of low palatability, and a competitor to more desirable species. Antelope bitterbrush is important browse for livestock. Domestic livestock and mule deer may compete for antelope bitterbrush in late summer, fall, and/or winter. Cattle prefer antelope bitterbrush from mid-May through June and again in September and October.
Stocking rates vary over time depending upon season of use, climate variations, site, and previous and current management goals. A safe starting stocking rate is an estimated stocking rate that is fine tuned by the client by adaptive management through the year and from year to year.
Wildlife Interpretations:
Mountain big sagebrush is highly preferred and nutritious winter forage for mule deer and elk. Sagebrush-grassland communities provide critical sage-grouse breeding and nesting habitats. Meadows surrounded by sagebrush may be used as feeding and strutting grounds. Sagebrush is a crucial component of their diet year-round, and sage-grouse select sagebrush almost exclusively for cover. Sage-grouse prefer mountain big sagebrush and Wyoming big sagebrush communities to basin big sagebrush communities. Pronghorn antelope, mule deer, elk, and bighorn sheep utilize antelope bitterbrush extensively. Mule deer use of antelope bitterbrush peaks in September, when antelope bitterbrush may compose 91 percent of the diet. Winter use is greatest during periods of deep snow. Antelope bitterbrush seed is a large part of the diets of rodents, especially deer mice and kangaroo rats. Idaho fescue provides important forage for several wildlife species. It is reported to be good forage for pronghorn, and deer in ranges of northern Nevada. Western needlegrass provides valuable forage for many species of wildlife. Thurber needlegrass is valuable forage for wildlife. Bluebunch wheatgrass is considered one of the most important forage grass species on western rangelands for wildlife. Bluebunch wheatgrass does not generally provide sufficient cover for ungulates, however, mule deer are frequently found in bluebunch-dominated grasslands.
Hydrological functions
Runoff is medium to very high. Permeability is slow to moderately rapid. Hydrologic soil group is A, B, and C. There are no rills. Water flow patterns are typically non-existent but can rarely occur on steeper slopes (over 15% gradient) in areas recently subjected to intense summer convection storms or rapid snowmelt. Pedestals and gullies are non-existent. Frost heaving of shallow rooted plants should not be considered a "normal" condition. Perennial herbaceous plants (especially deep-rooted bunchgrasses [i.e., Idaho fescue] slow runoff and increase infiltration. Shrub canopy and associated litter break raindrop impact and provide opportunity for snow catch and accumulation on site.
Recreational uses
Aesthetic value is derived from the diverse floral and faunal composition and the colorful flowering of wild flowers and shrubs during the spring and early summer. This site offers rewarding opportunities to photographers and for nature study. This site is used for camping and hiking and has potential for upland and big game hunting.
Other products
Native Americans used big sagebrush leaves and branches for medicinal teas, and the leaves as a fumigant. Bark was woven into mats, bags and clothing.
Other information
Antelope bitterbrush has been used extensively in land reclamation. Antelope bitterbrush enhances succession by retaining soil and depositing organic material and in some habitats and with some ecotypes, by fixing nitrogen.
Supporting information
Type locality
| Location 1: Washoe County, NV | |
|---|---|
| Township/Range/Section | T43N R23E S14 |
| UTM zone | N |
| UTM northing | 304094 |
| UTM easting | 4612764 |
| Latitude | 41° 38′ 33″ |
| Longitude | 119° 21′ 8″ |
| General legal description | SE 1/4, Adjacent to Badger Mountain exclosure, Badger Mountain, USF&WS Sheldon Refuge, Washoe County, Nevada. This site also occurs in Humboldt County, Nevada. |
Other references
Fire Effects Information System (Online; http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/).
USDA-NRCS Plants Database (Online; http://www.plants.usda.gov).
Contributors
GKB
Approval
Kendra Moseley, 4/10/2025
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | GK BRACKLEY |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | State Rangeland Management Specialist |
| Date | 06/20/2006 |
| Approved by | Kendra Moseley |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
None -
Presence of water flow patterns:
Water flow patterns are typically non-existent but can rarely occur on steeper slopes (over 15% gradient) in areas recently subjected to intense summer convection storms or rapid snowmelt. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
Pedestals are non-existent. Frost heaving of shallow rooted plants should not be considered a "normal" condition. -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
Bare ground ± 35%; surface rock fragments less than 35%; shrub canopy 15 to 25%; foliar cover of perennial herbaceous plants ± 50%. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
Gullies are non-existent. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
None -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Fine litter (foliage from grasses and annual & perennial forbs) is expected to move the distance of slope length during intense summer convection storms or rapid snowmelt events. Persistent litter (large woody material) will remain in place except during catastrophic events. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Soil stability values should be 3 to 6 on most soil textures found on this site. (To be field tested.) -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
Surface structure is typically granular. Soil surface colors are dark and the soils are typified by a mollic epipedon. Organic matter of the surface 2 to 4 inches is typically more than 2.5 percent. Organic matter content can be more or less depending on micro-topography. -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
Perennial herbaceous plants (especially deep-rooted bunchgrasses [i.e., Idaho fescue] slow runoff and increase infiltration. Shrub canopy and associated litter break raindrop impact and provide opportunity for snow catch and accumulation on site. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
Compacted layers are not typical. Platy or massive sub-surface horizons and subsoil argillic horizons shallow to the surface are not to be interpreted as compacted soil layers. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Reference Plant Community: Deep-rooted, cool season, perennial bunchgrasses >> tall shrubs (mountain big sagebrush & antelope bitterbrush). (By above ground production)Sub-dominant:
Associated shrubs (mountain browse species) = deep-rooted, cool season, perennial forbs = fibrous, shallow-rooted, cool season, perennial and annual forbs > shallow-rooted, cool season, perennial grasses and grass-like plants. (By above ground production)Other:
Additional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Dead branches within individual shrubs are not uncommon and standing dead shrub canopy material may be as much as 15% of total woody canopy; some of the mature bunchgrasses (<10%) have dead centers. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Between plant interspaces (± 35%) and litter depth is ± ½ inch. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
For normal or average growing season (through June) ± 1300 lbs/ac; Spring moisture significantly affects total production. -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
Cheatgrass and thistles are invaders on this site. Rabbitbrush spp. and western juniper are increasers on this site. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
All functional groups should reproduce in average (or normal) and above average growing season years.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.