Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R024XY045NV
ERODED SLOPE 6-10 P.Z.
Last updated: 3/06/2025
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
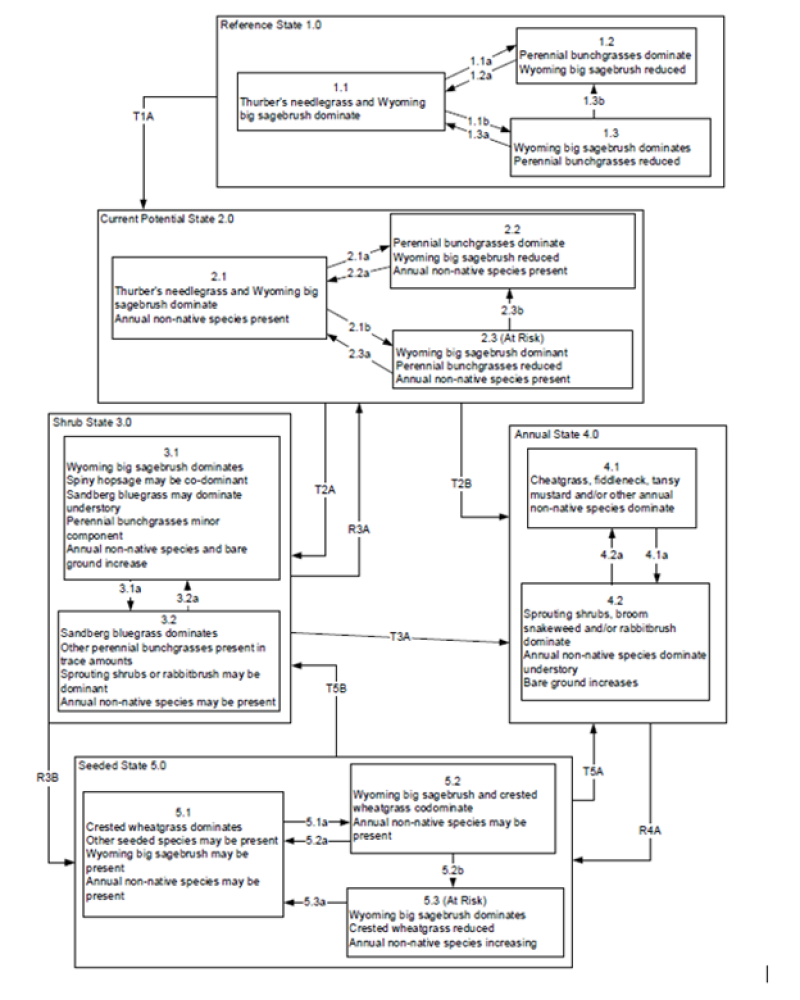
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 024X–Humboldt Basin and Range Area
Major land resource area (MLRA) 24, the Humboldt Area, covers an area of approximately 8,115,200 acres (12,680 sq. mi.). It is found in the Great Basin Section of the Basin and Range Province of the Intermontane Plateaus. Elevations range from 3,950 to 5,900 feet (1,205 to 1,800 meters) in most of the area, some mountain peaks are more than 8,850 feet (2,700 meters).
A series of widely spaced north-south trending mountain ranges are separated by broad valleys filled with alluvium washed in from adjacent mountain ranges. Most valleys are drained by tributaries to the Humboldt River. However, playas occur in lower elevation valleys with closed drainage systems. Isolated ranges are dissected, uplifted fault-block mountains. Geology is comprised of Mesozoic and Paleozoic volcanic rock and marine and continental sediments. Occasional young andesite and basalt flows (6 to 17 million years old) occur at the margins of the mountains. Dominant soil orders include Aridisols, Entisols, Inceptisols and Mollisols. Soils of the area are generally characterized by a mesic soil temperature regime, an aridic soil moisture regime and mixed geology. They are generally well drained, loamy and very deep.
Approximately 75 percent of MLRA 24 is federally owned, the remainder is primarily used for farming, ranching and mining. Irrigated land makes up about 3 percent of the area; the majority of irrigation water is from surface water sources, such as the Humboldt River and Rye Patch Reservoir. Annual precipitation ranges from 6 to 12 inches (15 to 30 cm) for most of the area, but can be as much as 40 inches (101 cm) in the mountain ranges. The majority of annual precipitation occurs as snow in the winter. Rainfall occurs as high-intensity, convective thunderstorms in the spring and fall.
Ecological site concept
This ecological site is on hills and rock pediments. Soils are shallow to a restrictive layer, well drained and formed in residuum/colluvium derived from mixed parent material. The soil profile is characterized by an ochric epipedon and strong effervescence, increasing with depth.
Important abiotic factors contributing to the presence of this ecological site include slopes typically greater than 30 percent and shallow soils resulting in droughty soil-site conditions.
Associated sites
| R024XY005NV |
LOAMY 8-10 P.Z. Important abiotic factors contributing to the presence of this ecological site include limited precipitation and the presence of the argillic horizon that helps retain soil moisture. The fine-textured/clay rich horizons, lying beneath the coarser-textured horizons become impermeable as the swelling matrix closes following wetting. |
|---|
Similar sites
| R024XY026NV |
STONY SLOPE 8-10 P.Z. Wyoming big sagebrush (ARTRW)-Shadscale sagebrush (ATCO) codominant; Thurber's needlegrass (ACTH7) minor species. |
|---|---|
| R024XY020NV |
DROUGHTY LOAM 8-10 P.Z. Thurber's needlegrass (ACTH7)- Indian ricegrass (ACHY) codominant grasses. |
| R024XY005NV |
LOAMY 8-10 P.Z. Thurber's needlegrass (ACTH7) dominant grass; more productive site. |
| R024XY047NV |
SHALLOW LOAM 8-10 P.Z. Wyoming big sagebrush (ARTRW); Less productive site. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Artemisia tridentata subsp. wyomingensis |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Achnatherum hymenoides |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.