Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R030XB140CA
Shallow Hill 4-6" P.Z.
Last updated: 10/21/2024
Accessed: 04/27/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
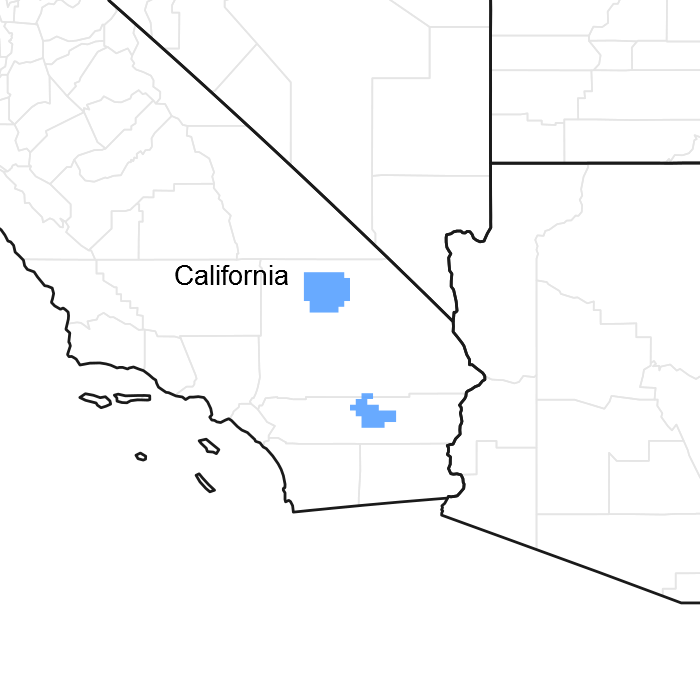
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 030X–Mojave Basin and Range
MLRA Description:
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 30, Mojave Desert, is found in southern California, southern Nevada, the extreme southwest corner of Utah and northwestern Arizona within the Basin and Range Province of the Intermontane Plateaus. The climate of the area is hot (primarily hyperthermic and thermic; however at higher elevations, generally above 5000 feet, mesic, cryic and frigid) and dry (aridic). Elevations range from below sea level to over 12,000 feet in the higher mountain areas found within the MLRA. Due to the extreme elevational range found within this MLRA, Land Resource Units (LRUs) were designated to group the MLRA into similar land units.
LRU Description:
This LRU (designated by ’XB’) is found across the eastern half of California, much of the mid-elevations of Nevada, the southernmost portions of western Utah, and the mid-elevations of northwestern Arizona. Elevations range from 1800 to 5000 feet and precipitation ranges from 4 to 9 inches per year, but is generally between 5-6 inches. This LRU is characterized primarily by the summer precipitation it receives, ranging from 18 – 35% but averages 25%. Summer precipitation falls between July and September in the form of rain, and winter precipitation falls starting in November and ends between February and March, also mostly in the form of rain; however it does receive between 0 and 3 inches of snow, with an average of 1 inch. The soil temperature regime is thermic and the soil moisture regime is typic-aridic. Vegetation includes creosote bush, burrobush, Nevada jointfir, ratany, Mojave yucca, Joshua tree, chollas, cactus, big galleta grass and several other warm season grasses. At the upper portions of the LRU, plant production and diversity are greater and blackbrush is a common dominant shrub.
Classification relationships
This ecological site is found within the Larrea tridentata Shrubland Alliance (Sawyer et al. 2009).
Ecological site concept
This site occurs on steep sideslopes of fan remnants, hillslopes and mountains on all exposures between 3525 ft (1075 m) and 3800 ft (1150 m) and on northerly exposures between 2800 ft (850m) and 3525 ft (1075 m). Slope gradients of 15 to 50 percent are typical. Soils range from very shallow to shallow or if deeper, they are shallow to a diagnostic horizon like an argillic or calcic horizon.
Production representative value (RV) is 315 pounds per acre, and depending on annual precipitation and annual forb production, ranges from 165 to 543 pounds per acre. Shrubs dominate this site, with burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) dominant, and creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) co-dominant. A high diversity of secondary shrubs and subshrubs are present, and perennial grasses contribute a minor component. This site has similar properties to R030XB139CA, but it has additional moisture (lower solar radiation index, higher precipitation zone, or landscape position), which allows for greater total production and an increase in the importance of burrobrush.
The data in the following sections is from major (15% of map unit or greater) components only.
This is a group concept and provisional STM that also covers R030XB123CA, R030XB213CA, R030XD040CA.
Associated sites
| R030XB005NV |
Arid Active Alluvial Fans This ecological site occurs on adjacent fan aprons. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) and burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) are co-dominant. |
|---|---|
| R030XB077NV |
STEEP SOUTH SLOPE This ecological site occurs on adjacent south-facing slopes. Brittlebush (Encelia farinosa) and creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) are dominant. |
| R030XB136CA |
Dry Wash This ecological site occurs on adjacent ephemeral drainageways. Burrobrush (Hymenoclea salsola) and creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) are dominant. |
| R030XB139CA |
Shallow Dry Hill 4-6 P.Z. This ecological site occurs on adjacent slopes with less available moisture. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) is dominant. |
| R030XB148CA |
Sandy Plain This ecological site is found on adjacent fan aprons on fan remnants. Big galleta (Pleuraphis rigida) and Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) are dominant species. |
| R030XB189CA |
Shallow Cool Hills This ecological site occurs on adjacent slopes with a cool thermic soil temperature regime. Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima) dominates and California juniper (Juniperus californica) is typically an important secondary species. |
| R030XB225CA |
Warm Sloping Pediments This ecological site occurs on adjacent dissected pediments. Hall's shrubby spurge (Tetracoccus hallii) and burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) are dominant. |
| R030XD003CA |
Hyperthermic Steep South Slopes This ecological site occurs on adjacent, hyperthermic, typically south-facing slopes. Brittlebush (Encelia farinosa) is dominant. |
| R030XD040CA |
Hyperthermic Steep North Slopes This ecological site occurs on adjacent, hyperthermic, typically north-facing slopes. Burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) and Parish's goldeneye (Vigueira parishii) are important species. |
| R030XY128CA |
Broad, Gravelly, Hyperthermic Ephemeral Stream This ecological site occurs in medium-sized drainageways adjacent to this site. Desert lavender (Hyptis emoryi), creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) and burrobrush (Hymenoclea salsola) are dominant species. |
Similar sites
| R030XB001NV |
LIMY HILL 5-7 P.Z. This ecological site is similar, but receives a greater proportion of summer precipitation. Big galleta (Pleuraphis rigida) and low woollygrass (Dasyochloa pulchella) are the dominant grasses. |
|---|---|
| R030XB193CA |
Very Shallow To Moderately Deep Gravelly Slopes This ecological site occurs on soils with an argillic horizon. Shrub diversity is higher, with burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa), Nevada ephedra (Ephedra nevadensis), Parish's goldeneye (Viguiera parishii), jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) and waterjacket (Lycium andersonii) all important species. |
| R030XB139CA |
Shallow Dry Hill 4-6 P.Z. This ecological site has less available moisture. Production is lower, and burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) is a minor species. |
| R030XD001CA |
Hyperthermic Dry Hills This ecological site occurs on slopes with a hyperthermic soil temperature regime. Shrub pecies composition is similar, but production is lower, and there is a negligible grass component. |
| R030XB146CA |
Volcanic Hill 5-7" P.Z. This ecological site occurs on slopes with volcanic parent material. Eastern Mojave buckwheat (Eriogonum fasciculatum) and burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) are co-dominant. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Ambrosia dumosa |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Achnatherum speciosum |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.