Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R030XC237CA
Shallow Limestone Slopes
Last updated: 2/25/2025
Accessed: 03/12/2026
General information
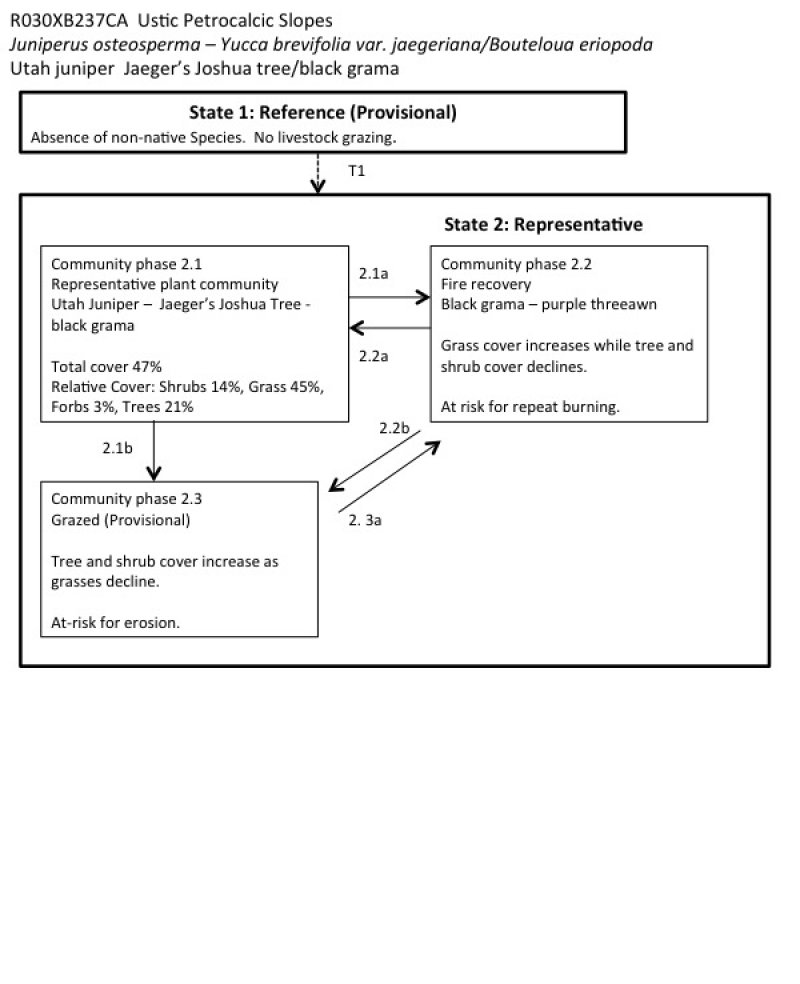
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 030X–Mojave Basin and Range
MLRA Description:
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 30, Mojave Desert, is found in southern California, southern Nevada, the extreme southwest corner of Utah and northwestern Arizona within the Basin and Range Province of the Intermontane Plateaus. The climate of the area is hot and dry with mostly hyperthermic and thermic soil temperature regimes. However, at higher elevations of this MLRA, generally above 5,000 feet, soil temperature regimes can be mesic, cryic and frigid. The most arid regimes of this MLRA can receive less than 4 inches (100 mm) Elevations range from below sea level to over 12,000 feet (3650 meters) in the higher mountain areas found within the MLRA. Due to the extreme elevational range found within this MLRA, land resource units (LRUs) were designated to group the MLRA into similar land units.
LRU Description:
The Bi-Modal Semi-Arid (XC) Land Resource Unit (LRU), represents a semi-arid zone as defined by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization and is a semi-arid region distinguished by other semi-arid regions of the Mojave by the amounts of summer precipitation it receives. Semi-arid regions in the western Mojave can experience hot and very dry summers whereas regions within the XC LRU can receive more than 2.5 inches (63.5 mm) of rain during the months of July, August and September. The Bi-Modal Semi-Arid LRU is found primarily in eastern Mojave such as in Nevada at the higher elevations, in California in the New York, Providence, Castle and Clark Mountain Ranges as well as the Cerbat and Virgin Mountains of Arizona. Elevations range from approximately 4000 to 12,000 feet (1500 to 3650 meters) and precipitation ranges 8 to 18 inches (200 – 450 mm) per year in the form of rain. Snow is not uncommon in this LRU with the chance of receiving 3 to 48 inches of snow per year.
Due to the relatively high volume of summer rainfall, soil moisture regimes may have been designated as ustic-aridic, however emerging soil moisture data suggests the xeric-aridic soil moisture regime may be more appropriate and is likely to dominate this LRU. Soils within this LRU also have a cool thermic or cooler soil temperature regime. The combination of cooler temperatures [mean annual air temperatures lower than 62 degrees F (17 degrees C)] with summer monsoonal rains help to create a unique climate within the Mojave Desert which may be more similar to the Southern Nevada Basin and Range (MLRA). Vegetation at the lower elevations of this LRU includes blackbrush, Joshua tree, juniper, pinyon pine, and mountain big sagebrush. At the higher elevations, vegetation includes oaks, Mojave sagebrush, Ponderosa pine, white fir, limber pine and the Great Basin bristlecone pine.
This site is part of group concept R030XC043NV.
Classification relationships
Juniperus osteosperma Woodland Alliance (Sawyer et al. 2009)
Ecological site concept
**This site will need to be updated with NASIS component data from 13LJ3, and possibly more mapunits. At the time of drafting, only MU4300 was in NASIS.
This ecological site occurs on ballenas (step, eroded alluvial fan remnants) and hillslopes at elevations between approximately 4500 to 5500 feet and slopes ranging from 8 to 30 percent. Mean annual precipitation ranges from 7 to 9 inches and the soil moisture regime is aridic bordering on ustic. Soils are shallow to bedrock or a petrocalcic horizon and formed in alluvium from limestone parent material or residuum and colluvium from mixed limestone and volcanic sources. Reference plants include Utah juniper (Juniper osteosperma), Jaeger’s Joshua Tree (Yucca brevifolia var. jaegariana), and black grama (Bouteoloua eriopoda). Production reference value (RV) is 670 pounds per acre. This site occurs in the narrow elevation band in the eastern Mojave Desert where Utah juniper dominates over pinyon pine (Sawyer et al. 2009). Shallow droughty soils support relatively sparse, small-statured juniper. These droughty soils also support relatively abundant purple needlegrass (Aristida purpurea), which can increase in cover with disturbance on this site. High summer precipitation supports black grama. Dry, rocky calcic soils support calciphiles such as roughseed cryptantha (Cryptantha flavoculata) and slim tridens (Tridens muticus). Relatively steep slopes and a high cover of surface rock fragments increases run-on, and creates microsites for plant establishment, which supports a high diversity of shrubs and forbs. This site is in a transitional area between thermic to mesic soil temperature regimes, which also supports higher diversity, with a mixture of warm and cool desert species.
This site is part of group concept R030XC043NV.
Associated sites
| R030XY219CA |
Ustic Ephemeral Drainageway Order 3 This site is found in 3rd order drainageways and associated landforms. A complex of vegetation communities is present that are associated with flooding frequency. Reference plants include desert willow (Chilopsis linearis), Mojave rabbitbrush (Ericameria paniculata) , woolly fruit bur ragweed (Ambrosia eriocentra), desert almond (Prunus fasciculata), black grama (Bouteloua eriopoda), and big galleta (Pleuraphis rigida). |
|---|---|
| R030XY220CA |
Ustic Ephemeral Drainageways Order 2 This site is found on adjacent 2nd ephemeral drainageways. A complex of vegetation communities is present that are associated with different flooding frequencies. Reference plants include purple sage (Salvia dorrii), woolly fruit bur ragweed (Ambrosia eriocentra), desert almond (Prunus fasciculata), black grama (Bouteloua eriopoda), and big galleta (Pleuraphis rigida). |
Similar sites
| R030XB015NV |
SHALLOW GRAVELLY SLOPE 7-9 P.Z. This site occurs on hills and mountain slopes. inset fans at elevations of 3000 to 6000 ft. Slopes of 15 to 30% are typical. This site receives rare surface flooding. Soils range from very shallow to moderately deep. Reference plants include blackbrush, black grama, and big galleta, and disturbance plants include red brome, Cooper’s goldenbush, and big galleta. Production range is 150-250-400. |
|---|---|
| R030XB014NV |
SHALLOW GRAVELLY LOAM 7-9 P.Z. This site occurs on less steep fan remnants and fan piedmonts with deep soils. This site is dominated by blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima), and big galleta (Pleuraphis rigida) and black grama (Bouteloua eriopoda) are important species. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Juniperus osteosperma |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Bouteloua eriopoda |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.