Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site EX043B23A150
Sandy (Sy) Absaroka Lower Foothills
Last updated: 10/04/2019
Accessed: 04/22/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
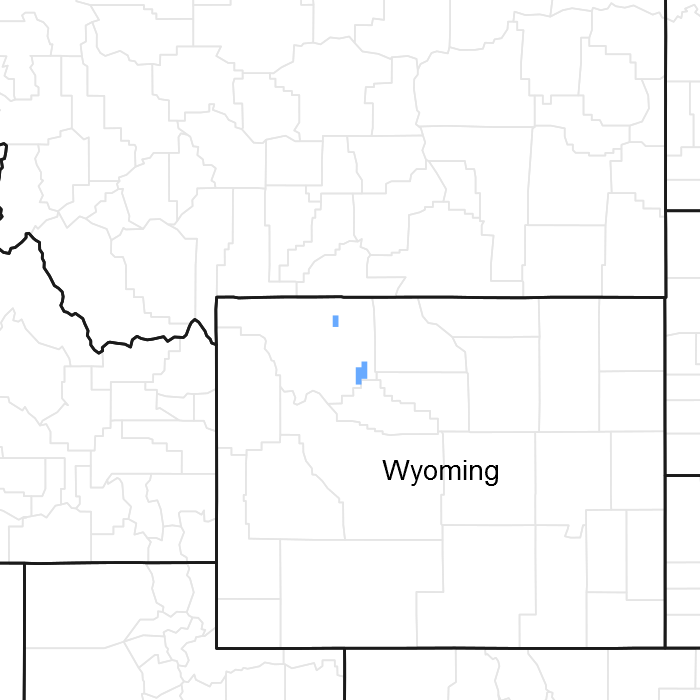
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 043B–Central Rocky Mountains
Major Land Resource Unit (MLRA) 43B: Central Rocky Mountains
43B – Central Rocky Mountains – The Central Rocky Mountains extends from northern Montana to southern extent of Wyoming and from Idaho to central Wyoming. The southern extent of 43B is comprised of a combination of metamorphic, igneous, and sedimentary mountains and foothills. Climatic changes across this extent are broad and create several unique breaks in the landscape.
Further information regarding MLRAs, refer to: United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2006. Land Resource Regions and Major Land Resource Areas of the United States, the Caribbean, and the Pacific Basin. U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook 296.
Available electronically at: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/ref/?cid=nrcs142p2_053624#handbook.
LRU notes
Land Resource Unit (LRU) 43B23A: Absaroka Lower Foothills
Based on the shifts in geology, precipitation patterns and other climatic factors, as well as elevations and vegetation, the Absaroka Range was divided into LRU 23. Further division of this LRU is necessary due to the gradient moving from the foothills to the summit, as well as aspect shifts (north/east face versus south/west face). Subset A is set for the lower elevations within the foothills with 10 to 14 inches of precipitation. To verify or identify the LRU A (the referenced LRU for this ecological site), refer to the Wyoming LRU matrix key contained within the Ecological Site Key. This particular LRU occurs along the eastern lower foothills of the Absaroka Range. This LRU starts north of Clark, WY and runs to the Thermopolis, WY area. Once the foothills cross into the Northern Beartooth Range, the climatic patterns and elevational changes shifts the plant community and allows for a break in LRU's near the Montana state line. As the LRU follows to the south and tracks east with the intersection of the Absaroka and Owl Creek Ranges, the face changes aspect and geology creating a shift in plant dynamics and a break in the LRU. The extent of soils currently correlated to this ecological site does not fit within the digitized boundary. Many of the noted soils are provisional and will be reviewed and corrected in mapping update projects. Other map units are correlated as small inclusions within other MLRA’s/LRU’s based on elevation, landform, and biological references.
Moisture Regime: Aridic Ustic or Ustic Aridic – Progressive Initial mapping has shown that soil correlations completed prior to 2014 were identified as ustic aridic, after further evaluation of climatic and soil taxonomy information the proper moisture regime is aridic ustic. Both are recorded here until an update project is completed to correct the previous correlations.
Temperature Regime: Frigid
Dominant Cover: Rangeland – Sagebrush Steppe (major species is Wyoming Big Sagebrush)
Representative Value (RV) Effective Precipitation: 10-14 inches (254 – 355 mm)
RV Frost-Free Days: 80-110 days
Classification relationships
Relationship to Other Established Classification Systems:
National Vegetation Classification System (NVC):
3 Xeromorphic Woodland, Scrub & Herb Vegetation Class
3.B Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland Subclass
3.B.1 Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland formation
3.B.1.NE Western North American Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland Division
M169 Great Basin & Intermountain Tall Sagebrush Shrubland & Steppe Macrogroup
G302 Artemisia Tridentata - Artemisia tripartita - Purshia tridentata Big Sagebrush Steppe Group
Ecoregions (EPA):
Level I: 10 North American Deserts Level II: 10.1 Cold Deserts
Level III: 10.1.18 Wyoming Basin
Level IV: 10.1.18.b Big Horn Basin and
10.1.18.d Foothills and Low Mountains
Ecological site concept
• Site receives no additional water.
• Slope is <35%
• Soils are:
o Textures range from loamy sand to very fine sandy loam in top 4” (10 cm) of mineral soil surface
o Clay content is ≤18% in top 4” (10 cm) of mineral soil surface
o All subsurface horizons in the particle size control section have a weighted average of <18% clay. (The particle size control section is the segment of the profile from either the start of an argillic horizon for 50 cm’s or from 25-100 cm’s).
o Moderately deep to very deep (20-80+ in. (50-200+ cm))
o <3% stone and boulder cover and 20% or less cobble and gravel cover
o Not skeletal (<35% rock fragments) within 20” (50 cm) of mineral soil surface
o None to Slightly effervescent throughout top 20” (50 cm) of mineral soil surface
o Non-saline, sodic, or saline-sodic
The Sandy ecological site concept is based on minimal (none to slight) influence from salts, carbonates, gypsum or other chemistry within the top 20 inches (50 cm) of the mineral soil surface. The main soil characteristic is a moderately deep to very deep soil that is coarse textured with less than 18% clay throughout the soil profile; the dominant soil textural classes are loamy sand to sandy loam in the subsurface. The plant community transitions from sandy to loamy as the control section increases above 18% clays with increased rhizomatous wheatgrasses, additional forb species, and increased ground cover.
The sandy site can be found in several different catenas throughout the basin. In an escarpment catena it occurs with shallow and very shallow soils. Hillslope catenas have sandy and loamy occurring in a complex mosaic pattern where the geology is controlled by inter-bedded sandstone and shale; or in areas where the parent material is alluvial. Locations controlled by primarily sandstone bedrock, sandy sites can be found in structural-controlled stable areas adjacent to sandstone rock outcrop.
Associated sites
| R032XY366WY |
Shallow Sandy (SwSy) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone Shallow Sandy sites are generally located on the break of slopes, on or surrounding rock outcrops before it transitions into more gently rolling landforms with deeper soils. Similar plant communities with more pincushion forbs and a higher percentage of bluebunch wheatgrass, but a marked reduction in production and increased bare ground. |
|---|---|
| R032XY328WY |
Lowland (LL) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone The Lowland site will have similar soils, outside of the presence of a water-table during parts of the year at a depth. This water-table influences the vegetation so have Basin big sagebrush, and other water demanding plants. |
| R032XY304WY |
Clayey (Cy) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone The Clayey ecological site has similar production potential; however, responses to disturbance, management and climatic changes will be different. Location on the landscapes are similar, but Clayey sites tend to fall along alluvial drainages or below shale outcrops/outwashes. Exist together on inter-bedded sedimentary beds. |
| R032XY312WY |
Gravelly (Gr) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone Gravelly sites have the potential for bluebunch wheatgrass, and lack production that Sandy sites hold, and are higher in “pincushion” forbs. They occur on hills slopes or ridges where the surface is wind swept exposing the gravels. Sandy occurs inward or down slope from the exposed alluvium. |
| R032XY322WY |
Loamy (Ly) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone Loamy sites will also be similar in production, but again response to management, disturbance and climatic shifts will vary. Loamy sites are generally found in the central or posterior edge of a landform such as alluvial fans, fan aprons, outwashes, and pediments. |
Similar sites
| R032XY250WY |
Sandy (Sy) 5-9” Wind River Basin Precipitation Zone Sandy 5-9" Wind River Basin Precipitation zone is lower in production than this site. |
|---|---|
| R032XY150WY |
Sandy (Sy) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone, Sandy 5-9" Big Horn Basin Precipitation zone is lower in production than this site. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Artemisia cana |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Achnatherum hymenoides |
Legacy ID
R043BX550WY
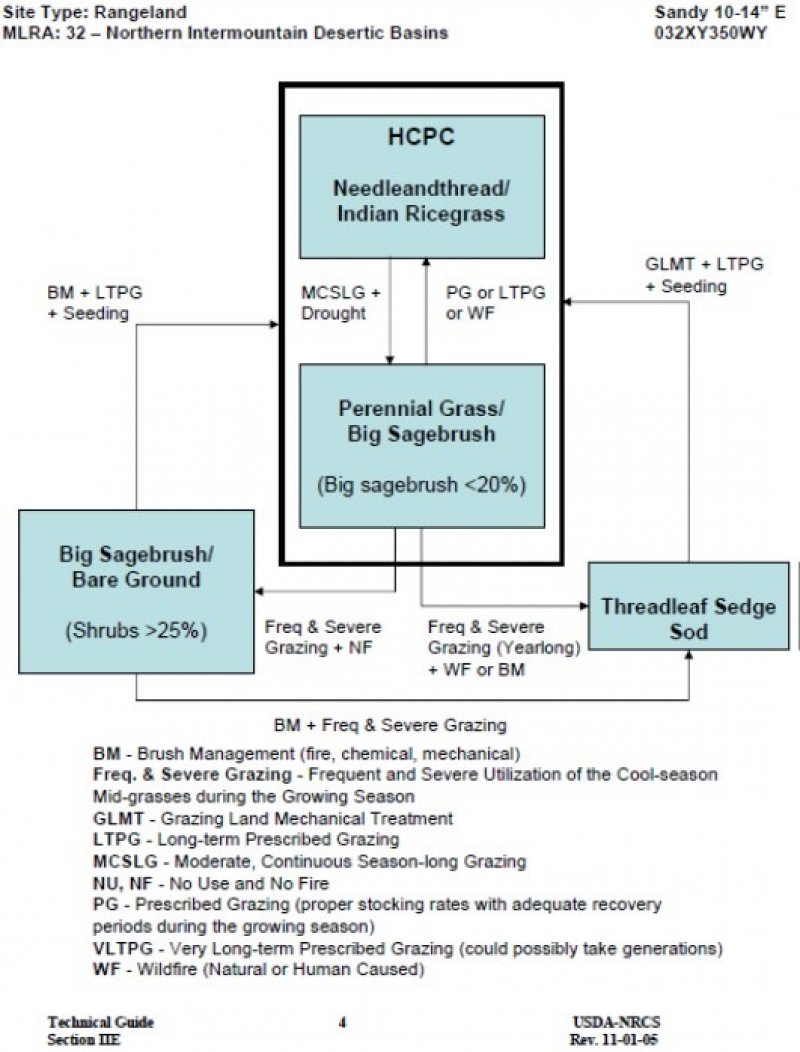
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.