Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site EX043B23A154
Shale (Sh) Absaroka Lower Foothills
Last updated: 10/04/2019
Accessed: 02/12/2026
General information
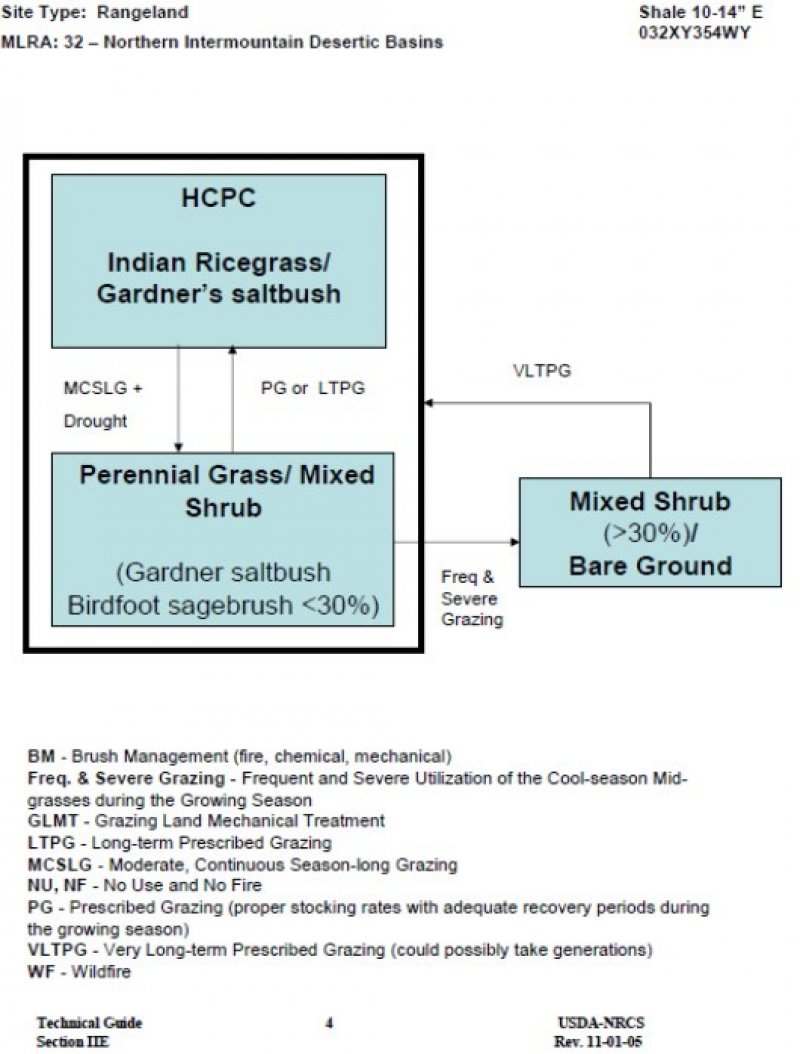
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 043B–Central Rocky Mountains
Major Land Resource Unit (MLRA) 43B: Central Rocky Mountains
43B – Central Rocky Mountains – The Central Rocky Mountains extends from northern Montana to southern extent of Wyoming and from Idaho to central Wyoming. The southern extent of 43B is comprised of a combination of metamorphic, igneous, and sedimentary mountains and foothills. Climatic changes across this extent are broad and create several unique breaks in the landscape.
Further information regarding MLRAs, refer to: United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2006. Land Resource Regions and Major Land Resource Areas of the United States, the Caribbean, and the Pacific Basin. U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook 296.
Available electronically at: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/ref/?cid=nrcs142p2_053624#handbook.
LRU notes
Land Resource Unit (LRU) 43B23A: Absaroka Lower Foothills
Based on the shifts in geology, precipitation patterns and other climatic factors, as well as elevations and vegetation, the Absaroka Range was divided into LRU 23. Further division of this LRU is necessary due to the gradient moving from the foothills to the summit, as well as aspect shifts (north/east face versus south/west face). Subset A is set for the lower elevations within the foothills with 10 to 14 inches of precipitation. To verify or identify the LRU A (the referenced LRU for this ecological site), refer to the Wyoming LRU matrix key contained within the Ecological Site Key. This particular LRU occurs along the eastern lower foothills of the Absaroka Range. This LRU starts north of Clark, WY and runs to the Thermopolis, WY area. Once the foothills cross into the Northern Beartooth Range, the climatic patterns and elevational changes shifts the plant community and allows for a break in LRU's near the Montana state line. As the LRU follows to the south and tracks east with the intersection of the Absaroka and Owl Creek Ranges, the face changes aspect and geology creating a shift in plant dynamics and a break in the LRU. The extent of soils currently correlated to this ecological site does not fit within the digitized boundary. Many of the noted soils are provisional and will be reviewed and corrected in mapping update projects. Other map units are correlated as small inclusions within other MLRA’s/LRU’s based on elevation, landform, and biological references.
Moisture Regime: Aridic Ustic or Ustic Aridic – Progressive Initial mapping has shown that soil correlations completed prior to 2014 were identified as ustic aridic, after further evaluation of climatic and soil taxonomy information the proper moisture regime is aridic ustic. Both are recorded here until an update project is completed to correct the previous correlations.
Temperature Regime: Frigid
Dominant Cover: Rangeland – Sagebrush Steppe (major species is Wyoming Big Sagebrush)
Representative Value (RV) Effective Precipitation: 10-14 inches (254 – 355 mm)
RV Frost-Free Days: 80-110 days
Classification relationships
Relationship to Other Established Classification Systems:
National Vegetation Classification System (NVC):
3 Xeromorphic Woodland, Scrub & Herb Vegetation Class
3.B Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland Subclass
3.B.1 Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland formation
3.B.1.NE Western North American Cool Semi-Desert Scrub & Grassland Division
M169 Great Basin & Intermountain Tall Sagebrush Shrubland & Steppe Macrogroup
Ecoregions (EPA):
Level I: 10 North American Deserts Level II: 10.1 Cold Deserts
Level III: 10.1.18 Wyoming Basin
Level IV: 10.1.18.b Big Horn Basin and
10.1.18.d Foothills and Low Mountains
Ecological site concept
• Site receives no additional water.
• Slope is < 60%
• Soils are:
- saline, sodic, saline-sodic, and/or gypsic
- Very Shallow (depth to restrictive layer is < 10” (25 cm).
- With < 30% cover of surface fragments (gravels, cobbles, stones)
- Textures usually range from silt loam to clay
- Clay content is ≥ 35% in mineral soil profile (0-10”).
- With an average particle size class ≥ 35% but < 60% clay
The Shale site concept is based on soils that are very shallow (depth to a paralithic or lithic (bedrock) contact is 10” (25 cm)). The underlying parent material or residuum is of shale or other salt-laden sedimentary bedrock.
The Shale ecological site is very similar and is generally associated with the Saline Upland Clayey ecological site. Cody shale and bentonite escarpments are common geology associated with this site. Shale ecological site is less than 10 inches to shale parent material (bedrock) and Saline Upland Clayey is greater than 10 inches. Saline Upland Clayey is typically found over shale bedrock or inter-bedded sedimentary bedrock, typically on lower gentler slopes, and in many cases will have a very similar plant community. The production potential and erosion hazard are the two interpretive characteristics that differ between these two sites.
Associated sites
| R032XY358WY |
Shallow Clayey (SwCy) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone Shallow Clayey will be found on the same landform as shale where the soils are deeper and where the salts are not as prevalent or are not present in the system. |
|---|---|
| R032XY344WY |
Saline Upland (SU) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone Saline Upland site has similar plants but higher production and will occur down-slope or on deeper soils on the same landform as the Shale site. |
| R032XY376WY |
Very Shallow (VS) 10-14" East Precipitation Zone Very Shallow soils are simlar to shale, however they lack the chemistry (salts) and are associated with sandstone or inter-bedded sedimentary bedrock where shales are found only on shale parent material. Very Shallow is found in association with Shale sites on exposed inter-bedded sedimentary uplifts. |
Similar sites
| R032XY254WY |
Shale (Sh) 5-9” Wind River Basin Precipitation Zone Shale 5-9" Wind River Basin Precipitation zone is lower in production that this site. |
|---|---|
| R032XY154WY |
Shale (Sh) 5-9” Big Horn Basin Precipitation Zone Shale 5-9" Big Horn Basin Precipitation zone is lower in production that this site. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Atriplex gardneri |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Achnatherum hymenoides |
Legacy ID
R043BX554WY
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.