Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R043CY805OR
Mountain Rockland (JUOC/CELE3/FEID)
Last updated: 3/31/2025
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 043C–Blue and Seven Devils Mountains
This MLRA covers the Blue and Seven Devils Mountains of Oregon, Washington and Idaho. The area is characterized by thrust and block-faulted mountains and deep canyons composed of sedimentary, metasedimentary, and volcanic rocks. Elevations range from 1,300 to 9,800 feet (395 to 2,990 meters). The climate is characterized by cold, wet winters and cool, dry summers. Annual precipitation, mostly in the form of snow, averages 12 to 43 inches (305 to 1,090 millimeters) yet ranges as high as 82 inches (2,085 millimeters) at upper elevations. Soil temperature regimes are predominately Frigid to Cryic and soil moisture regimes are predominately Xeric to Udic. Mollisols and Andisols are the dominant soil orders. Ecologically, forests dominate but shrub and grass communities may occur on south aspects and lower elevations as well as in alpine meadow environments. Forest composition follows moisture, temperature and elevational gradients and typically ranges from ponderosa pine and Douglas-fir plant associations at lower elevations, grand fir at middle elevations and subalpine fir and Engelman spruce at upper elevations. Historical fire regimes associated with these forest types range from frequent surface fires in ponderosa pine - Douglas Fir forest types to mixed and stand replacing fire regimes in grand fir and subalpine fir types. A large percentage of the MLRA is federally owned and managed by the U.S. Forest Service for multiple uses.
Classification relationships
Plant Assoc. of Blue and Ochoco Mountains (R6 E TP-036-92)
western juniper/mountain mahogany - CJS4
western juniper/mountain mahogany/elk sedge - CJS42
mountain mahogany/elk sedge - SD40
mountain mahogany/Idaho fescue-bluebunch wheatgrass - SD4111
Ecological site concept
This is a shrub site dominated by curl-leaf mountain mahogany (Cercocarpus ledifolius), antelope bitterbrush (Purshia tridentate) and Idaho fescue (Festuca idahoensis) in its reference phase. Ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa), Western juniper (Juniperus occidentalis), mountain big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentate ssp. vaseyana), wax currant (Ribes cereum) and bluebunch wheatgrass (Pseudoroegneria spicata) are prominent. Historically, the ecological dynamics of this site were driven by infrequent fire and cycles of drought. Presently, reference conditions are less common and current dynamics are also influenced by the spread of invasive species, the expansion of western juniper, livestock grazing pressures and fire suppression.
On ridges, shoulders or upper mountainslopes, western juniper and ponderosa pine may form an open forest savannah with understory of curl-leaf mountain mahogany, antelope bitterbrush, and perennial bunchgrasses (FEID/PSSPS/POSE/CAGE). This community typically forms on moderate to steep slopes at mid-elevations. Soils are typically skeletal (>35% coarse fragments), shallow to deep, and are developed from colluvium and/or residuum derived from rhyolitic tuff, andesite, basalt or sedimentary sources. In areas of the southern Blue Mountains, it may be associated with ultramafic geologies (serpentine, peridotite, etc)
This is a provisional ecological site that groups characteristics at a broad scale with little to no field verification and is subject to extensive review and revision before final approval. All data herein was developed using existing information and literature and should be considered provisional and contingent upon field validation prior to use in conservation planning.
Associated sites
| R043CY807OR |
Scabland (PSSPS-POSE-DAUN) Adjacent scabland areas with very shallow to shallow soils |
|---|
Similar sites
| R043CY804OR |
Cool Mountain Bunchgrass (ARTRV/FEID) Lower large coarse fragment content, deeper soils with less cobbles and stones on the surface |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Juniperus occidentalis |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Cercocarpus ledifolius |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Festuca idahoensis |
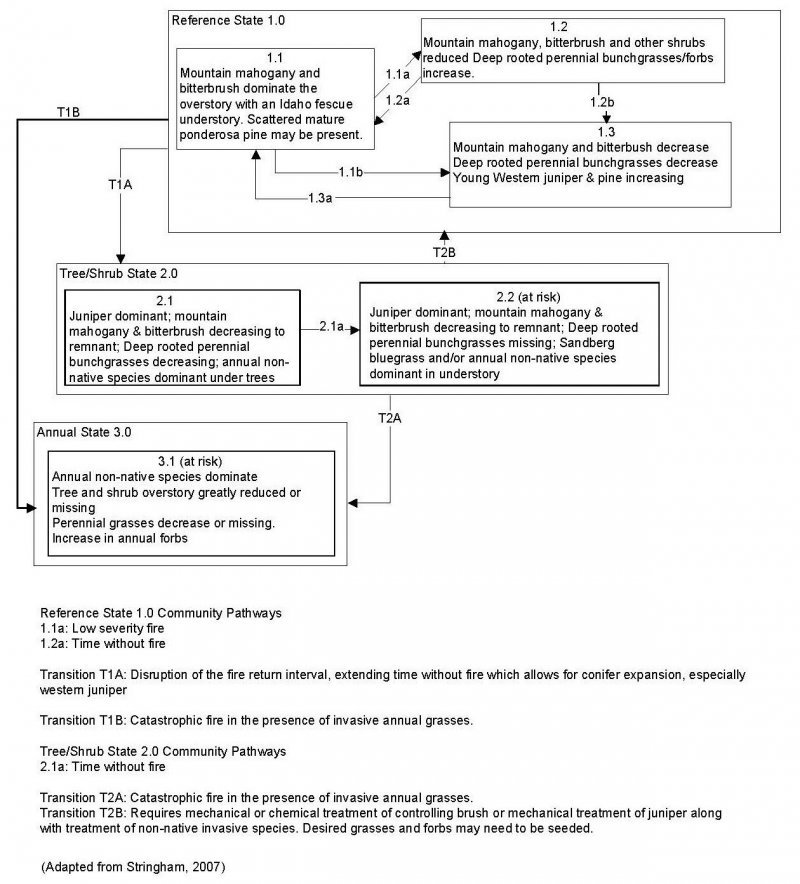
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Disruption of the fire return interval |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Catastrophic fire in the presences of invasive annual grasses |
| R2B | - | Mechanical or chemical treatment of dominant shrubs or juniper along with treatment of non-native invasive species. |
| T2A | - | Catastrophic fire in the presences of invasive annual grasses |