Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R048AY008NM
Mountain Brush
Last updated: 3/05/2024
Accessed: 04/02/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
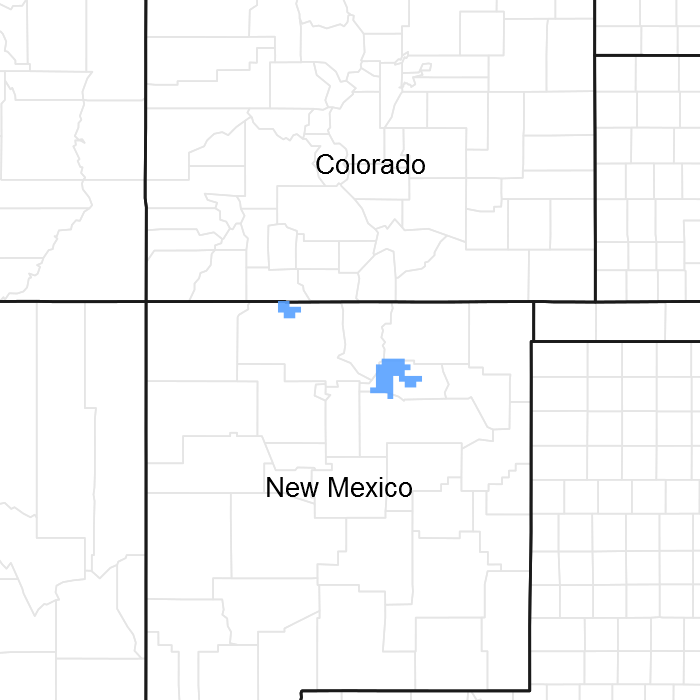
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 048A–Southern Rocky Mountains
This area is in Colorado (76 percent), New Mexico (11 percent), Utah (8 percent), and Wyoming (5 percent). It makes up about 45,920 square miles (119,000 square kilometers). The towns Jemez Springs, Los Alamos, Red River and Eagle Nest, New Mexico, are in this MLRA. This MLRA has numerous national forests, the Carson National Forest and part of the Santa Fe National Forest in New Mexico. The Jemez, Picuris, Santa Clara, and Taos Indian Reservations are in this MLRA. Most of this area is in the Southern Rocky Mountains Province of the Rocky Mountain System. Small parts of the southwest corner and some isolated areas farther west are in the Canyon Lands Section of the same province and division. The Southern Rocky Mountains consist primarily of two belts of strongly sloping to precipitous mountain ranges trending north to south. Several basins, or parks, are between the belts. The ranges include the Sangre de Cristo Mountains, Jemez Mountains, and Tusas Mountains. Elevation typically ranges from 6,500 to 13,167 feet (1,980 to 1,039 meters) in this area. The Rio Grande is a National Wild and Scenic River in northern New Mexico, which is in the southern part of this MLRA.
The mountains in this area were formed mainly by crustal uplifts during the late Cretaceous and early Tertiary periods. The rocks exposed in the mountains are mostly Precambrian igneous and metamorphic rocks, which in many places are flanked by steeply dipping Mesozoic sedimentary rocks. Younger igneous rocks, primarily basalt and andesitic lava flows, tuffs, breccias, and conglomerates, are throughout this area. Representative formations in this area are the Silver Plume and Pikes Peak granites, San Juan Volcanics, and Mancos Shale. Many of the highest mountain ranges were reshaped by glaciation during the Pleistocene. Alluvial fans at the base of the mountains are recharge zones for local basin and valley fill aquifers. They also are important sources of sand and gravel.
The dominant soil orders in this MLRA are Mollisols, Alfisols, Inceptisols, and Entisols. The soils in the area dominantly have a frigid or cryic soil temperature regime and an ustic or udic soil moisture regime. Mineralogy is typically mixed, smectitic, or paramicaceous. In areas with granite, gneiss, and schist bedrock, Glossocryalfs (Seitz, Granile, and Leadville series) and Haplocryolls (Rogert series) formed in colluvium on mountain slopes. Dystrocryepts (Leighcan and Mummy series) formed on mountain slopes and summits at the higher elevations. In areas of andesite and rhyolite bedrock, Dystrocryepts (Endlich and Whitecross series) formed in colluvium on mountain slopes. In areas of sedimentary bedrock, Haplustolls (Towave series) formed on mountain slopes at low elevations and with low precipitation. Haplocryolls (Lamphier and Razorba series), Argicryolls (Cochetopa series), and Haplocryalfs (Needleton series) formed in colluvium on mountain slopes at high elevations.
LRU notes
This site is part of the RM-1 sub-resource area. This site is found on the east side of Sangre de Cristo mountains.
Classification relationships
This ecological site is correlated to soil components at the Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) level which is further described in USDA AgHandbook 296.
Ecological site concept
This site is located on the sides of basalt-capped mesas and escarpments of sandstone, basalt, shale and limestone. This site is formed on the upland leading away from vertical basalt escarpments and basalt-capped mesas. They are formed from a variety of materials derived from sandstone, basalt, shale and limestone. Rock outcrop is common and may occupy from 15 percent to 50 percent of the area. Slopes range from 5 to 25 percent. The exposure is mainly to the east, south and west. However, this site may occur on the drier north-facing slopes. North and east-facing slopes are generally more productive and tend to grow more woody vegetation. Elevation ranges from 7,500 to 9,000 feet above sea level.
The soils on this site are shallow, well drained over sandstone, shale, basalt and limestone. Rock outcrops are common and occupy the nearly vertical basalt escarpments, ridges and benches of exposed sandstone, limestone and shale. Rubbleland occurs at the base of the basalt escarpments. The surface textures is usually clay loam and the subsoils are clay loam and clayey shale. The surface runoff is medium too rapid and the erosion hazard is severe. Effective rooting depth is from 12 to 20 inches.
Soils correlated to this site include:
Krakon
Associated sites
| R048AY005NM |
Mountain Malpais This site is characterized by flat to moderately steep topography. It is frequently found as mesa, mountains slopes and ridges where the basalt caps are present. The site’s terrain may be interrupted by extrusions of the basalt, leaving a rough or choppy appearance to the topography. The basaltic stone cover typically exists over a portion of the site where igneous extrusions occur. Boulders on the surface are common. The dominant slope range is from 3 to 30 percent, but it some site range up to 55 percent. The exposure varies but has little significance on plant production. Elevation ranges from 6,800 to 9,000 feet above sea level. These soils are well drained, very shallow to shallow, and formed in debris from basalt and other volcanic rock or metamorphic rock. The surface texture is cobbly, very cobbly silt loam; stony, very stony, very cobbly loam; stony, very stony silt loam; and cobbly sandy loam. The texture of the subsoil layers ranges from very stony silt loam, very cobbly loam to extremely stony clay. The effective rooting depth is 6 to 20 inches. |
|---|---|
| R048AY006NM |
Mountain Meadow The site occurs as lower lying drainageways, flood plains, swales or other depressional areas where extra moisture accumulates as a result of runoff from surrounding higher sites. A high water table is characteristic of this site particularly in the spring and a portion of the area may have open water during this season. Springs or seeps bring the water table to the subsoil or even to the surface, in which instance the site may colloquially be called a “cienaga”. Slopes vary from flat to gently sloping, not to exceed 5 percent. The exposure varies and is not significant. Elevation ranges from 7,000 to 9,500 feet above sea level. These soils consist of deep to very deep soils and poorly to very poorly drained. The surface texture ranges from a very fine sandy loam to a mucky silty clay and clay surface layers. They have an active water table, which varies from the surface to 3 feet below the surface. They are normally non-saline and have high organic content. These soils have moderate to moderately slow permeability. Available water-holding capacity is moderate. The effective rooting depth is 20 inches to more than 60 inches. |
| R048AY007NM |
Mountain Shale This site is located in mountainous terrain on mountain slopes and hillslopes. Slopes are dominantly moderately steep to steep with gradients varying from 15 to 75 percent. Topography varies from relatively uniform slopes of considerable length to short, steep, choppy terrain. Elevation ranges from 7,000 to 9,000 feet above sea level. This site consists of soils that are shallow to moderately deep and are well drained. The surface texture is very stony clay, very stony clay loam, cobbly loam, and stony silty clay loam soils. The soils are derived from shale parent material. The effective rooting depth is 5 to 40 inches. Shale and sandstone outcrops are common. The subsoil is typically compacted clay, which restricts root penetration. |
Similar sites
| R048AY009NM |
Mountain Breaks This site occurs on mesa and canyon side-slopes and other mountain breaks. The site consists of productive areas interspersed with areas of low production, rock outcrop and badland. Slopes and exposure vary. Slopes range from 9 to 45 percent. Elevation ranges from 9,100 to 10,500 feet above sea level. Soil depths is deep. Surface texture is generally a gravelly loam. Subsoils range from gravelly clay loam, gravelly sandy clay loam to very gravelly sandy clay loam. The soil profile is generally high in rock fragments. Boulders are scattered about the site. There usually are pockets on the site where run-in of precipitation results in good soil-moisture relationships. This ecological site used to have the ID number of R048BY001NM in RM-2 subresource area in 1982. |
|---|---|
| R048AY013NM |
Mountain Slopes This site occurs on valley sides and hills ranging from relatively uniform, long slopes to short and choppy. Exposure is usually southern and/or western, which creates a relatively droughty site. Slopes range from 15 to 45 percent. Elevation ranges from 7,200 to 8,600 feet above sea level. The soils are generally moderately deep to deep over interbedded shale and sandstone parent materials. Surface textures is usually a loam. Subsoils range from sandy clay loam, clay loam to clay. This ecological site used to have the ID number of R048BY006NM in RM-2 subresource area in 1982. |
| R048AY238CO |
Brushy Loam This site occurs on hills, mountains, complex landslides, and benches. Slopes is between 3 to 35%. Soils are moderately deep to deep (20 to 60+ inches), soils derived from colluvium, residuum, slope alluvium and alluvium from sandstone and shale. Soil surface texture is loam or clay loam with fine-textured subsurface. It is a Gambel’s oak – slender wheatgrass community. It has a typic ustic moisture regime. The effective precipitation ranges from 16 to 20 inches. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Quercus gambelii |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Muhlenbergia montana |
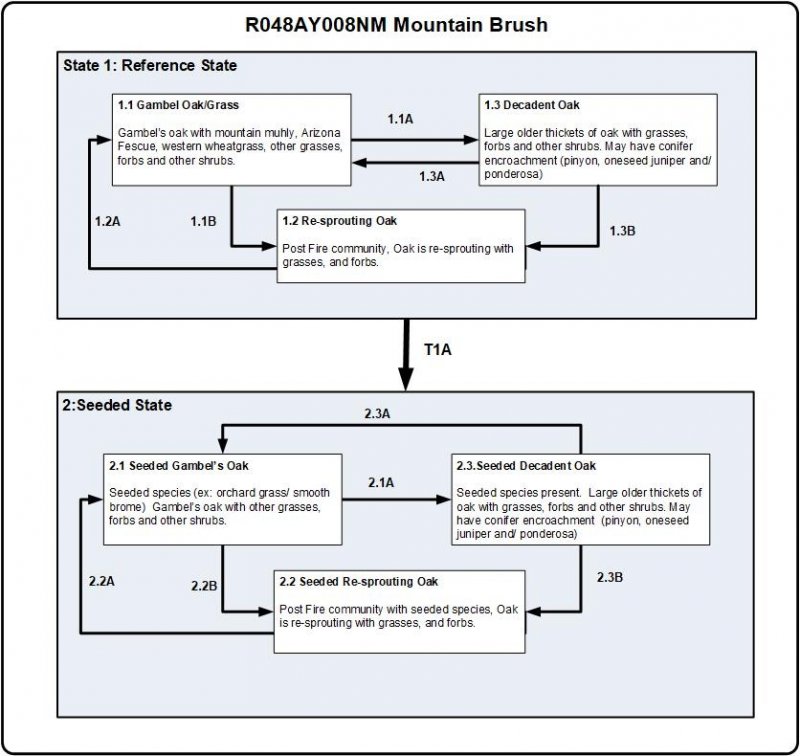
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.