Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R048BY235CO
Dry Exposure
Last updated: 4/09/2025
Accessed: 03/14/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 048B–Southern Rocky Mountain Parks and Valleys
This area is in Colorado (96 percent) and Wyoming (4 percent). It makes up about 2,325 square miles (6,020 square kilometers). The town of Walden, in the northern part of this MLRA, is in a wide valley locally known as North Park. The town of Kremmling is in a valley locally known as Middle Park. The town of Hartsel, in the center of the southern part of the MLRA, is in a broad intermontane basin locally known as South Park. The northern part is bordered by the Medicine Bow, Routt, and Arapaho National Forests, and the southern part is bordered by the San Isabel and Pike National Forests. The Arapaho National Wildlife Refuge is directly south of the town of Walden.
This area is within the Southern Rocky Mountains Province of the Rocky Mountain System. It consists of nearly level to rolling mountain parks and valleys and a few narrow mountain ridges. It occurs as two separate parts in the center of the Southern Rockies. The southern half of the northern part is on the west side of the Continental Divide, and the rest of the MLRA is on the east side of the divide. Elevation ranges from 7,850 to 10,850 feet (2,395 to 3,310 meters). The head waters of North Platte River leaves Colorado and enters Wyoming in the northern half of the northern part of the MLRA (North Park). The headwaters of Colorado River is in the southern half of the northern part of the MLRA (Middle Park). The headwaters of South Platte River is in the southern part of the MLRA (South Park).
The mountain valleys and parks that are characteristic of this MLRA are surrounded by high mountain peaks of the adjacent Southern Rocky Mountains MLRA (48A). Steep slopes give rise to steep-gradient streams that can move cobbles and gravel from the mountain slopes down into the valleys. The coarse textured sediments on the surface of this area were deposited by either glacial meltwater or present-day rivers. Buried deep beneath the sediments is a complex of sedimentary and igneous rocks. Residuum from sedimentary rocks is on the steeper slopes that were not covered by alluvium and glacial outwash.
The average annual precipitation is mainly 10 to 16 inches (255 to 405 millimeters), but it is as high as 28 inches (710 millimeters) at the higher elevations that border the Southern Rocky Mountains MLRA. Precipitation generally increases with elevation. Rainfall occurs as high-intensity, convective thunderstorms during the growing season. About half of the annual precipitation falls as snow. Soil moisture is unevenly distributed within short distances because of snowdrifts. The amount of precipitation is highly influenced by rain shadows. The surrounding peaks receive most of the precipitation as storm systems traverse the area. The average annual temperature is 35 to 42 degrees F (1 to 6 degrees C). The freeze-free period averages 95 days and ranges from 70 to 120 days, decreasing in length with elevation.
The dominant soil order in this MLRA is Mollisols. Alfisols are of lesser extent. The soils are very shallow to deep, generally well drained, and loamy or clayey and have mixed or smectitic mineralogy. The soil temperature regime is dominantly cryic, but it is frigid in some small areas, primarily on south- or west-facing slopes. The soil moisture regime is mainly ustic, but a marginal aridic regime has been identified in areas where the average annual precipitation is less than about 12 inches (305 millimeters). The most extensive great group is Argicryolls (Hodden, Lucky, Parlin, Tiagos, and Cabin series), which commonly formed in outwash and slope alluvium on outwash terraces, fan remnants, hills, and mountain slopes. Haplocryolls (Redcloud and Tealson series) formed in outwash and slope alluvium on outwash terraces, valley side slopes, hills, and ridges. Haplocryalfs (Gebson and Harsha series) formed in slope alluvium and outwash on outwash terraces, fan remnants, hills, ridges, and mountain slopes. Cryaquolls (Dobrow and Randman series) formed in alluvium on stream terraces and flood plains.
Classification relationships
NRCS:
Major Land Resource Area 48B, Southern Rocky Mountain Parks (United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006).
USFS:
M331I – North Parks and Ranges Section Southern Rocky Mountain Steppe - Open Woodland - Coniferous Forest - Alpine Meadow
EPA:
21i – Sagebrush Parks and 21j – Grassland Parks < 21 Southern Rockies < 6.2 Western Cordillera < 6 Northwestern Forested Mountains North American Deserts (Griffith, 2006).
USGS: Southern Rocky Mountain Province
Ecological site concept
R048BY235CO Dry Exposure occurs on ridges, mountainsides, breaks, fans and terraces. Slopes is between 10 to 50 percent. Soils are shallow (5 to 20 inches). Soils are derived from alluvium from sedimentary rock. Soil surface texture is usually cobbly loam or gravelly coarse sandy loam with loamy textured subsurface. It is a needle and thread – prairie Junegrass community. It has a typic ustic moisture regime. The effective precipitation ranges from 16 to 20 inches.
Associated sites
| R048AY303CO |
Loamy Slopes R048AY303CO Loamy Slopes occurs on alluvial fans, terraces, hills mountains and mountainsides. Slopes is between 25 to 65%. Soils are moderately deep to deep (20 to 60+ inches). Soils are derived from alluvium from sandstone and siltstone or sandstone; residuum or colluvium from sandstone or outwash from basalt. Soil surface texture is cobbly sandy loam or cobbly, very flaggy or channery loam with loamy-skeletal textured subsurface. It is a mountain mahogany – Indian ricegrass community. It has an aridic ustic moisture regime and frigid temperature. The effective precipitation ranges from 12 to 18 inches. |
|---|---|
| R048AY238CO |
Brushy Loam R048AY238CO Brushy Loam occurs on hills, mountains, complex landslides, and benches. Slopes is between 3 to 35%. Soils are moderately deep to deep (20 to 60+ inches), soils derived from colluvium, residuum, slope alluvium and alluvium from sandstone and shale. Soil surface texture is loam or clay loam with fine-textured subsurface. It is a Gambel oak – slender wheatgrass community. |
Similar sites
| R048AY240CO |
Shallow Pine R048AY240CO Shallow Pine occurs on mountains and mountainsides. Slopes are 5 to 50%. Soils are shallow (10 to 20 inches). Soils are derived from slope alluvium from volcanic breccia, gneiss, granite, or sandstone and/or residuum from granite, granodiorite and/or gneiss. Soil surface texture is a gravelly to very gravelly sandy loam or very gravelly loam with loamy-skeletal subsurface. It is a Ponderosa Pine - Arizona fescue – mountain muhly community. |
|---|---|
| R048AY229CO |
Rocky Loam R048AY229CO – Rocky Loam occurs on ridges, mountainside, mountain slopes and mountains. Soils are very shallow to shallow (less than 20 inches) loamy-skeletal soils derived from residuum from granite, gneiss, phyllite, schist, sandstone and/or limestone. Soil surface texture are generally coarse sandy loams to light clay loams. It is a mountain big sagebrush – western wheatgrass community. |
| R048AY230CO |
Shallow Loam R048AY230CO – Shallow Loam occurs on mountain, hills, ridges, mountain sides and mountain slopes. Soils are very shallow to shallow (less than 20 inches) loamy-skeletal soils derived from slope alluvium from trachyte, volcanic breccia, gneiss, granite and/or sandstone; residuum from weathered volcanic breccia, tuff, igneous rock, sandstone or sandstone and shale. Soils surface textures are gravelly to very gravelly loam, gravelly to very gravelly sandy loam, cobbly loam, or very cobbly sandy loam. It is an Arizona fescue - mountain muhly community with scattered mountain mahogany, snowberry and current. |
| R048AY235CO |
Dry Exposure R048AY235CO Dry Exposure occurs on steep slopes, ridges, hill tops and other exposed, tree-less areas seen from high mountain valleys and parks on very shallow to shallow soils. Soil textures are gravelly sandy loams to gravelly loams; light colored. Soils have a droughty desert pavement. It is a winterfat - fringed sagewort - bunchgrass community. It has an ustic aridic moisture regime and frigid temperature regime. The effective precipitation ranges from 12 to 16 inches. |
| R048BY232CO |
Dry Shallow Loam R048BY232CO Dry Shallow Loam occurs on hills, pediments, ridges and knobs. Slopes is between 1 to 30%. Soils are shallow to moderately deep (10 to 40 inches). Soils are derived from slope alluvium from volcanic breccia, limestone, sandstone, shale, gneiss, granodiorite, and/or schist; colluvium from limestone; or residuum from limestone and sandstone. Soil surface texture is usually loam, channery loam, very gravelly loam, sandy loam or gravelly sandy loam with loamy or loamy-skeletal textured subsurface. It is a Arizona fescue – Indian ricegrass community. It has an aridic ustic moisture regime. The effective precipitation ranges from 10 to 16 inches. |
| R048AY307CO |
Shallow Slopes R048AY307CO – Shallow Slopes occurs on hillsides, ridges, mountainside and canyon walls. Soils are shallow (less than 20 inches) loamy textured soils derived from residuum from sandstone and limestone. Soil surface textures are generally sandy loam or gravelly sandy loam. It is a black sagebrush – western wheatgrass community. It has an aridic ustic moisture regime and frigid temperature regime. The effective precipitation ranges from 12 to 16 inches. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Hesperostipa comata |
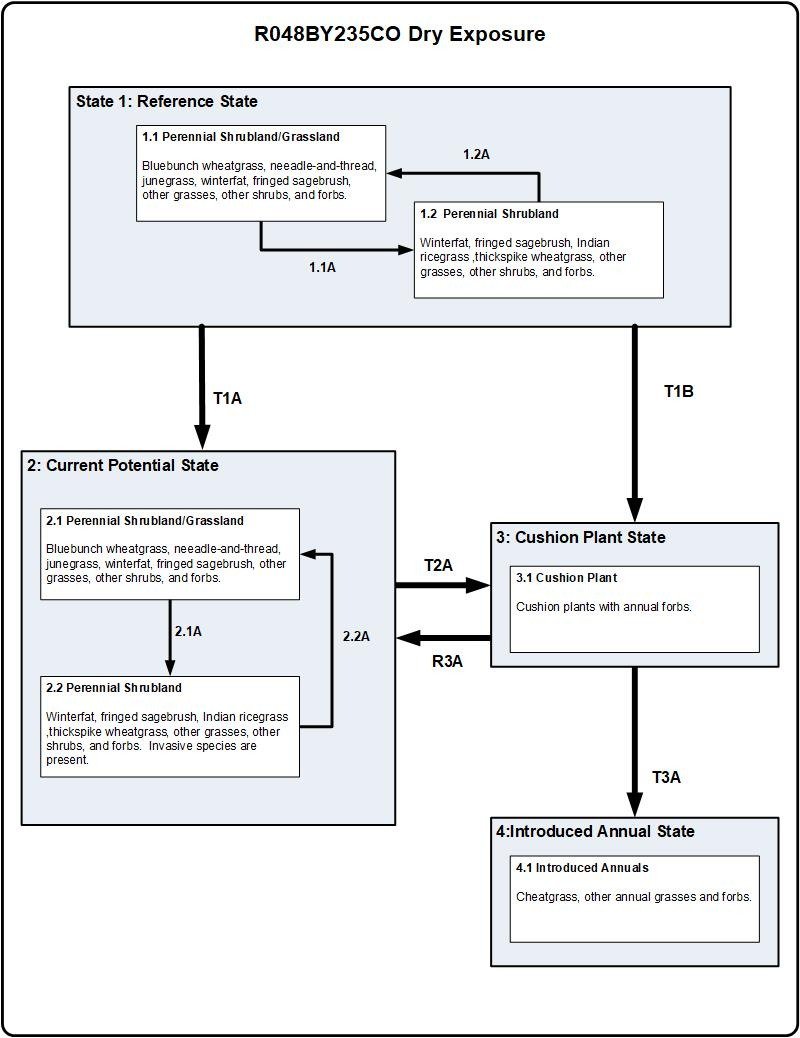
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.