
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R058BY130WY
Overflow (Ov) 10-14” PZ
Last updated: 9/15/2024
Accessed: 03/10/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
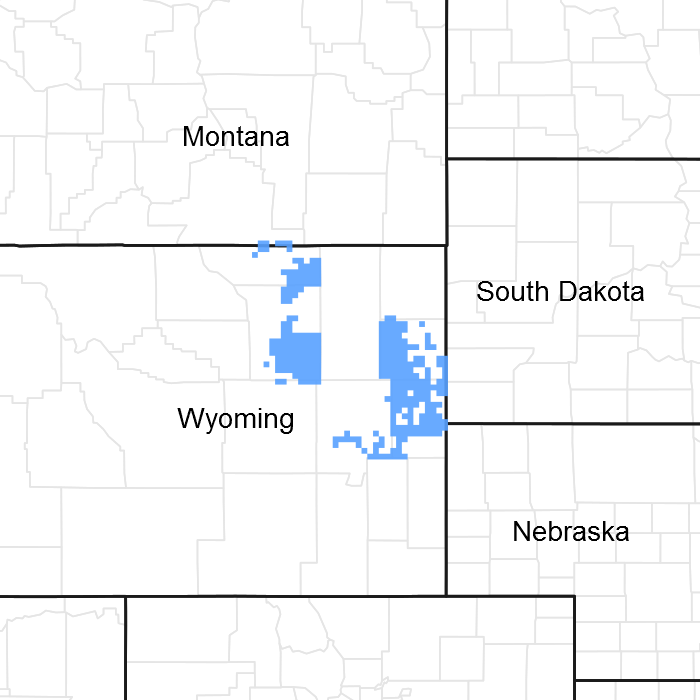
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 058B–Northern Rolling High Plains, Southern Part
MLRA 58B is located in northeastern Wyoming (95 percent) and extreme southeastern Montana (5 percent). It is comprised of sedimentary plains, scoria hills, and river valleys. The major rivers include the Powder, Tongue, Belle Fourche, Cheyenne, and North Platte. Tributaries include the Little Powder River, Little Missouri River, Clear Creek, Crazy Woman Creek, and others. This MLRA is traversed by Interstates 25 and 90, and U.S. Highways 14 and 16. The extent of MLRA 58B covers approximately 12.3 million acres. Major land uses include rangeland (approximately 93 percent), cropland, pasture, and hayland (approximately 2 percent), and forest, urban, and miscellaneous uses (approximately 5 percent). Cities include Buffalo, Casper, Sheridan, and Gillette, WY. Land ownership is mostly private. Federal lands include the Thunder Basin National Grassland (U.S. Forest Service) and lands administered by the Bureau of Land Management. Areas of interest in MLRA 58B in Wyoming include Fort Phil Kearny State Historic Site, Glendo State Park, and Lake DeSmet. The elevations in MLRA 58B increase gradually from north to south and range from approximately 2,900 to 5,900 feet. A few buttes are higher than 6,800 feet. The average annual precipitation in this area ranges from 10 to 17 inches per year. Precipitation occurs mostly during the growing season, often during rapidly developing thunderstorms. Mean annual air temperature is 46 degrees Fahrenheit. Summer temperatures may exceed 100 degrees Fahrenheit. Winter temperatures may drop to below zero. Snowfall averages 45 inches per year, but varies from 25 to over 70 inches in some locales.
Classification relationships
USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS):
Land Resource Region – G Western Great Plains Range and Irrigation; Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) – 58B Northern Rolling High Plains, Southern Part (USDA, 2006)
Relationship to Other Classifications:
USDA Forest Service (FS) Classification Hierarchy:
Province – 331 Great Plains-Palouse Dry Steppe; Section – 331G-Powder River Basin; Subsections – 331Gb Montana Shale Plains, 331Ge Powder River Basin, 331Gf South Powder River Basin-Scoria Hills (Cleland et al, 1997)
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Classification Hierarchy:
Level III Ecoregion – 43 Northwestern Great Plains; Level IV Ecoregion – 43p Scoria Hills, 43q Mesic-Dissected Plains, 43w Powder River Basin (EPA, 2013)
https://www.epa.gov/eco-research/ecoregions
Ecological site concept
This ecological site occurs along floodplains, drainageways, stream terraces, and alluvial fans where it receives additional moisture from overflow of intermittent streams or runoff from adjacent slopes. This site occurs at elevations ranging from 2,900 to 5,900 feet and on slopes ranging from 0 to 6 percent. This site occurs on all aspects, although aspect is not a significant factor. The soils of this ecological site are typically very deep and are well drained. The soil surface textures on this site typically loam, sandy loam, fine sandy loam, or very fine sandy loam but can have a wide variation since these soils typically result from water deposition.
Associated sites
| R058BY104WY |
Clayey (Cy) 10-14” PZ The Clayey 10-14 ecological site occurs on slopes of 0 to 15 percent, has soils with greater than 35 percent clay content, and has lower total annual production. The Clayey 10-14 ecological site is positioned above the Overflow 10-14 ecological site. The Clayey 10-14 ecological site does not receive additional moisture from flooding or run-in from adjacent areas. |
|---|---|
| R058BY106WY |
Clayey Overflow (CyO) 10-17” PZ The Clayey Overflow 10-14 ecological site occurs on slopes of 0 to 6 percent, has soils with greater than 35 percent clay content, and has very similar total annual production. The Clayey Overflow 10-14 ecological site is located on similar landform positions as the Overflow 10-14 ecological site. The Clayey Overflow 10-14 ecological site receives additional moisture from flooding or run-in from adjacent areas similar to the Overflow 10-14 ecological site. |
| R058BY122WY |
Loamy (Ly) 10-14” PZ The Loamy 10-14 ecological site occurs on slopes of 0 to 15 percent and has lower total annual production. The Loamy 10-14 ecological site is positioned above the Overflow 10-14 ecological site. The Loamy 10-14 ecological site does not receive additional moisture from flooding or run-in from adjacent areas. |
Similar sites
| R058BY138WY |
Saline Lowland (SL) 10-14” PZ The Saline Lowland 10-14 ecological site occurs on similar slopes and landform positions and has similar total annual production as the Overflow 10-14 ecological site, but the Saline Lowland 10-14 ecological site is dominated by salt tolerant species. The Saline Lowland 10-14 ecological site does not receive additional moisture from flooding or run-in from adjacent areas. |
|---|---|
| R058BY142WY |
Saline Subirrigated (SS) 10-14” PZ The Saline Sub-Irrigated 10-14 ecological site occurs on similar slopes and landform positions but has higher total annual production than the Overflow 10-14 ecological site. The Saline Sub-Irrigated 10-14 ecological site is dominated by salt tolerant species. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Artemisia cana |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Leymus cinereus |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Introduction of non-native, invasive, sod-forming grasses such as smooth brome and Kentucky bluegrass |
|---|---|---|
| T2A | - | Introduction of non-native grasses, noxious weeds, and other invasive plant species |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Drought, heavier stocking rates |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Grazing management that allows for adequate plant recovery, lighter stocking rates, normal or above average precipitation |