
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R075XY063NE
Loess Breaks
Last updated: 4/17/2025
Accessed: 04/18/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
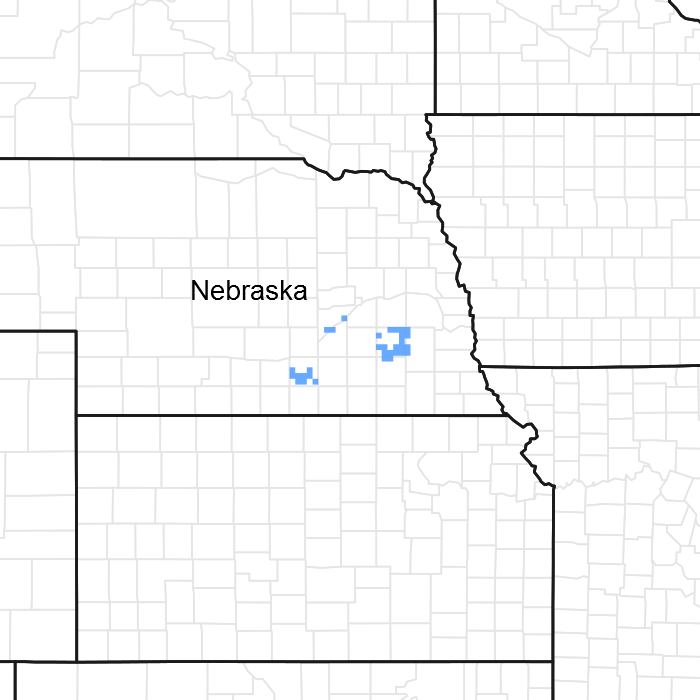
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 075X–Central Loess Plains
Named “The Central Loess Plains,” MLRA 75 is located primarily in south-central Nebraska, with about 10 percent lying in north-central Kansas. This approximately 5.3-million-acre landscape covers all or parts of 21 counties: Gosper, Phelps, Kearney, Adams, Clay, Fillmore, York, Hall, Hamilton, Seward, Butler, Polk, Saline, Gage, Harlan, Franklin, Thayer, Nuckolls, and Webster in Nebraska, with a significant presence in Republic and Washington counties in Kansas. This MLRA is home to the unique ecological system called “The Rainwater Basin,” which is comprised of a 24,000-acre network of wetlands and uplands that occupy portions of 13 of the northern counties and is internationally known for its significance to millions of migratory birds.
The landscape primarily consists of gently rolling plains, with a number of narrow, shallow stream valleys. The river valleys are broader, and most feature a number of terraces. The northern border is defined by the Platte River. The elevation in MLRA 75 ranges from nearly 2,600 feet to less than 1,100 feet above sea level. The local relief averages from 10 to 25 feet but may stretch to a maximum of 165 feet in some areas. The average annual precipitation ranges from 23 to 36 inches, and the number of freeze-free days range from 150 to 200.
Loess overlays the surface of almost all of the uplands in this MLRA. Alluvial clay, silt, sand, and gravel are deposited in the stream and river valleys and can be extensive in the major drainages. Terraces are common in the valleys along the river systems. The predominant soil orders in this geographic area are mesic, ustic Mollisols, commonly represented by the Geary, Hastings, Holder, Holdrege, Kenesaw, and Uly soil series. The matrix vegetation type is mixed-grass prairie, with big and little bluestem, switchgrass, Indiangrass, and sideoats and blue grama to make up the bulk of the warm-season species, while western wheatgrass is the dominant cool-season grass.
Seventy two percent of the land in this MLRA has been broken out of native prairie and farmed; the land is primarily planted to corn, wheat, and grain sorghum, while only eighteen percent of the grasslands remain intact. Livestock grazing, primarily by cattle, is the main industry on these remnants. Irrigation of croplands uses over 90 percent of the total annual water withdrawal in this area.
Wildlife flourishes in this combination of crop and grassland environment, with both mule and white-tailed deer being the most abundant wild ungulates. A variety of smaller species, including coyote, raccoon, opossum, porcupines, muskrat, beaver, squirrel, and mink thrive in the region, as well as several upland bird species. Grassland bird populations are somewhat limited by the lack of contiguous native prairie and fragmented habitat created by the farmland. The rivers, streams, and lakes harbor excellent fisheries, and an estimated tens of millions of migrating and local waterfowl use the wetland complexes. These complexes provide ideal habitat for a number of wading and shore bird species as well.
This landscape serves as a backdrop for a disturbance-driven ecosystem, evolving under the influences of herbivory, fire, and variable climate. Historically, these processes created a heterogeneous mosaic of plant communities and structure heights across the region. Any given site in this landscape experienced fire every 6 to 8 years. The fires were caused by lightning strikes and also were set by native Americans, who used fire for warfare, signaling, and to refresh the native grasses. These people understood the value of fire as a tool, and that the highly palatable growth following a fire provided both excellent forage for their horses and attracted grazing game animals such as bison and elk.
Fragmentation of the native grasslands by conversion to cropland, transportation corridors, and other developments have effectively disrupted the natural fire regime of this ecosystem. This has allowed encroachment by native and introduced shrubs and trees into the remnants of the native prairie throughout the MLRA. Aggressive fire suppression policies have exacerbated this process to the point that shrub and tree encroachment is a major ecological issue in the majority of both native and reseeded grasslands.
Even as post-European settlement's alteration of the fire regime allows the expansion of the woody component of the native prairie, introduction of eastern redcedar (ERC) as a windbreak species further facilitates invasion by this species. While eastern red cedar is native to Nebraska, the historic population in MLRA 75 was limited to isolated pockets in rugged river drainages which were subsequently insulated from fire. Widespread plantings of windbreaks with eastern redcedar as a primary component have provided a seed source for the aggressive woody plant. The ensuing encroachment into the native grasslands degrades the native wildlife habit and causes significant forage loss for domestic livestock.
Since it is not a root sprouter, eastern red cedar is very susceptible to fire when under six feet tall. Management with prescribed fire is exceedingly effective if applied before this stage. Larger redcedars can also be controlled with fire, but successful application requires the use of specifically designed ignition and holding techniques.
Classification relationships
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): Major Land Resource Area (MLRA)75 (USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006)
Level IV Ecoregions of the Conterminous United States
Ecological site concept
This ecological site is an upland site located in a run-off position with slopes greater than 30 percent. Slip slopes and cat-steps are evident.
Associated sites
| R075XY058NE |
Loamy Plains This site is often located adjacent to Loess Breaks. |
|---|---|
| R075XY050NE |
Loamy Terrace This site is located below and sometimes adjacent to the Loess Breaks site. |
Similar sites
| R075XY059NE |
Limy Loess Slopes These sites are calcareous sites which display effervescence and are located adjacent to the Loess Breaks site but the slopes are less than 30%. Slip slopes and cat-steps are evident on Loess Breaks sites but absent on Limy Loess Slopes sites. |
|---|---|
| R075XY058NE |
Loamy Plains This site is often located adjacent to the Loess Breaks site but slopes are less than 30%. No catsteps are present. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Andropogon gerardii |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on hillslopes and valley sides that have been dissected by geologic erosion. The very steep slopes of this site are characteristically broken with a series of short slope slips, commonly referred to as “catsteps”. The depth and height of these catsteps intensifies with increasing slope. Vertical faces of loess, areas of broken sod, and deep gullies are common on this site. Vehicular traffic is very limited to impossible on this site. This site produces runoff to areas lower on the landscape.
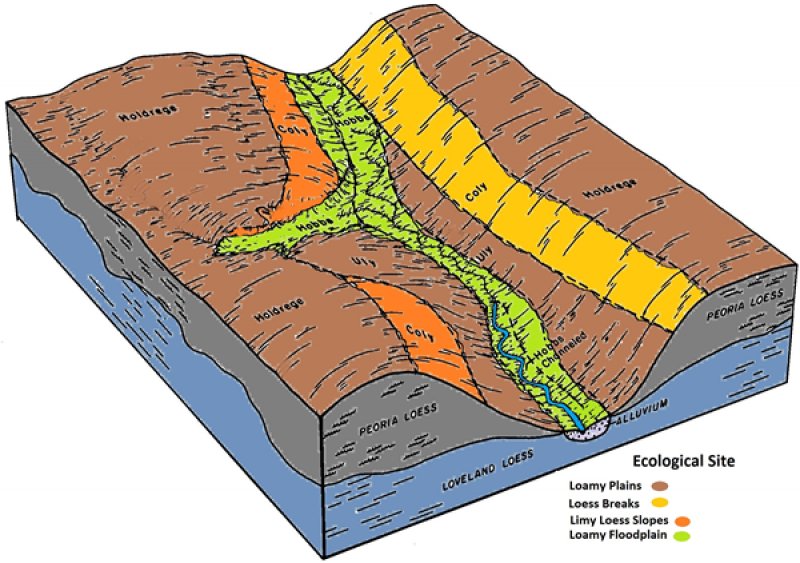
Figure 2. Block Diagram
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Hillslope
|
|---|---|
| Runoff class | High |
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 366 – 1,067 m |
| Slope | 30 – 100% |
| Water table depth | 203 cm |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
Like most Great Plains landscapes, the climate in this MLRA is under the sway of the continental effect. This creates a regime of extremes, with summer highs often in the triple digits, and winter lows plunging well below zero. Blizzards can occur anytime between early fall and late spring, often dropping the temperature more than 50 degrees in just a few hours. These events can pile up several feet of snow, often driven by winds in excess of 50 miles an hour. The resulting huge snow drifts can cause serious hardship for livestock, wildlife, and humans. Winters can be open, with bare ground for most of the season, or closed, with up to several feet of snow persisting until March. Most winters have a number of warm days, interspersed with dropping temperatures, usually associated with approaching cold fronts. Spring brings violent thunderstorms, hail, high winds, and frequent tornadoes. Daily winds range from an average of 14 miles per hour during the spring to 11 miles per hour during the late summer. Occasional strong storms may bring brief periods of high winds with gusts to more than 80 miles per hour.
Growth of native cool season plants begin in early April and continues to about mid-June. Native warm season plants begin growth in early June and continue to early August. Green up of cool season plants may occur in September and October.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 134-144 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | 162-172 days |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 711-787 mm |
| Frost-free period (actual range) | 128-148 days |
| Freeze-free period (actual range) | 155-179 days |
| Precipitation total (actual range) | 660-813 mm |
| Frost-free period (average) | 139 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | 168 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 737 mm |
Figure 3. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 4. Monthly minimum temperature range
Figure 5. Monthly maximum temperature range
Figure 6. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 7. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 8. Annual average temperature pattern
Climate stations used
-
(1) FAIRBURY 5S [USC00252820], Fairbury, NE
-
(2) GENEVA [USC00253175], Geneva, NE
-
(3) MINDEN [USC00255565], Minden, NE
-
(4) RED CLOUD [USC00257070], Red Cloud, NE
-
(5) YORK [USC00259510], York, NE
-
(6) BELLEVILLE [USC00140682], Belleville, KS
-
(7) WASHINGTON [USC00148578], Washington, KS
-
(8) AURORA [USC00250445], Aurora, NE
-
(9) FRIEND 3E [USC00253065], Friend, NE
-
(10) SEWARD [USC00257715], Seward, NE
-
(11) CLAY CTR [USC00251684], Saronville, NE
-
(12) DAVID CITY [USC00252205], David City, NE
-
(13) FAIRMONT [USC00252840], Fairmont, NE
-
(14) HASTINGS 4N [USC00253660], Hastings, NE
-
(15) HEBRON [USC00253735], Hebron, NE
-
(16) HOLDREGE [USC00253910], Holdrege, NE
-
(17) OSCEOLA [USC00256375], Osceola, NE
-
(18) RAGAN [USC00257002], Alma, NE
-
(19) SUPERIOR 4E [USC00258320], Hardy, NE
-
(20) SURPRISE [USC00258328], Surprise, NE
Influencing water features
This site is an upland site and functions independently from ground and surface water features.
Soil features
These very deep soils are characterized by thin (less than 7 inches) surface layers. Soil texture for both surface and subsoil layers of these soils range from silty to loamy. Calcium carbonates are found throughout but may be leached to 10 inches in some instances. Organic matter content is generally low to moderately low in the surface layer.
Coly is the only major soil series associated with this ecological site. More information can be found in the various soil survey reports. Contact the local USDA Service Center for internet links to soil survey data that includes more details specific to your location.

Figure 9. Coly Soil Profile
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Calcareous loess
|
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Silt loam |
| Drainage class | Well drained to excessively drained |
| Permeability class | Moderate |
| Soil depth | 203 cm |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 0% |
| Available water capacity (0-101.6cm) |
17.27 – 22.35 cm |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-101.6cm) |
1 – 8% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-101.6cm) |
0 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-101.6cm) |
0 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-101.6cm) |
7.4 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
0% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
0% |
Ecological dynamics
The Loess Breaks site developed under Northern Great Plains climatic conditions, light to severe grazing by bison and other large herbivores, sporadic natural or man-caused wildfires, and other biotic and abiotic factors which typically influence soil/site development. This continues to be a disturbance-driven site, by herbivory, fire, and variable climate. Changes occur in the plant communities due to weather variations, impacts of native and/or exotic plant and animal species, and management actions.
One of the primary impacts to this landscape introduced by European-man is season-long continuous grazing by domestic livestock. This management practice causes the repeated removal of the growing point and excessive defoliation of the leaf area of individual warm-season tallgrasses. The resulting reduction of the ability of the plants to harvest sunlight depletes the root reserves, subsequently decreasing the root mass. This negatively impacts the ability of the plants to compete for life-sustaining nutrients, resulting in declining vigor and eventual mortality. The space created in the vegetative community is then occupied by a species that evades the negative grazing impacts by a growing season adaptation (such as a cool-season), a shorter structure, or a reduced palatability mechanism. Because of the steepness of slope, the Loess Breaks site normally receives less grazing pressure than the less steep adjacent sites, but the degree of erosion is greatly accelerated if the stabilizing vegetative community is significantly degraded.
The State-and-Transition Model (STM) is depicted below, and is made up of a Reference State, a Native/Invaded Grass State, and an Invaded Woody State. Each state represents the crossing of a major ecological threshold due to alteration of the functional dynamic properties of the ecosystem. The main properties observed to determine this change are the soil and vegetative communities and the hydrological cycle.
Each state may have one or more vegetative communities which fluctuate in species composition and abundance within the normal parameters of the state. Within each state, communities may degrade or recover in response to natural and man-caused disturbances such as variation in the degree and timing of herbivory, presence or absence of fire, and climatic and local fluctuations in the precipitation regime.
Interpretations are primarily based on the Reference State and have been determined by study of rangeland relic areas, areas protected from excessive disturbance, and areas under long-term rotational grazing regimes. Trends in plant community dynamics have been interpreted from heavily grazed to lightly grazed areas, seasonal use pastures, and historical accounts. Plant communities, states, transitional pathways, and thresholds have been determined through similar studies and experience.
Growth of native cool-season plants begins about April 1 and continues to about June 15. Native warm-season plants begin growth about May 15 and continue to about August 15. Green-up of cool-season plants may occur in September and October if adequate moisture is available.
The species distribution and abundance on this site are also influenced by the degree of inclination and aspect of the local topography. Northern and eastern slopes typically are cooler and wetter, generally producing more biomass than the drier and warmer exposures. Severe inclines receive less grazing pressure than the more moderate slopes.
The following is a diagram illustrating the common plant communities that can occur on the site and the transition pathways between communities.
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
State 1 submodel, plant communities
Communities 1, 5 and 2 (additional pathways)
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Reference State
This state describes the range of vegetative community phases that occur on the Loess Breaks site where the natural processes are mostly intact. The Reference Community is a representation of the native plant community phase that occupies a site that has been minimally altered by management. The Degraded Native Grass, the At-Risk Native Grass, and the Excessive Litter Communities are the phases that result from management decisions that are unfavorable for a healthy Reference Community. The Ephemeral Forb Community is the result of a high intensity disturbance event. High perennial grass cover and production allows for increased soil moisture retention, vegetative production, and overall soil quality.
Dominant plant species
-
big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii), grass
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
-
sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
composite dropseed (Sporobolus compositus), grass
Community 1.1
Reference Community
The Reference Community serves as a description of the native mixed-grass plant community that naturally occurs on the site when the natural disturbance regimes are intact, or closely mimicked by management practices. This phase is dynamic, with fluid relative abundance and spatial boundaries between the dominant structural vegetative groups. These fluctuations are primarily driven by different responses of the species to changes in precipitation timing and abundance, and fire and grazing events. The potential vegetation consists of approximately 75 to 85 percent grasses and grass-like plants, 5 to 0 percent forbs, and 2 to 5 percent shrubs. Little bluestem, big bluestem, and sideoats grama are the primary tall and mid-grass species in this community. Shortgrass species include blue grama and hairy grama. Western wheatgrass occurs as a secondary species in the western portion of the MLRA. The site has a very diverse forb population. This plant community is highly productive, diverse, and resistant to short term stresses such as drought and short periods of heavy stocking. The well-developed root systems support resiliency when allowed adequate recovery periods between grazing events. When exposed to long-term or frequent over-grazing events without adequate rest, this plant community will degrade. Total annual production ranges from 1,800 to 2,800 pounds of air dry vegetation per acre.
Dominant plant species
-
big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii), grass
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
-
sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), grass
Figure 10. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 1855 | 2118 | 2774 |
| Forb | 118 | 179 | 241 |
| Shrub/Vine | 45 | 84 | 123 |
| Total | 2018 | 2381 | 3138 |
Figure 11. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). NE7501, Central Loess Plains, warm season dominant. Native warm-season dominant, MLRA 75.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 21 | 33 | 18 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
Community 1.2
Degraded Native Grass Community
Little bluestem and sideoats grama are the dominant grasses. Big bluestem is declining, and this community phase signals a significant loss of production. This is due to continuous season-long grazing with inadequate recovery periods. Grazing-evasive warm-season grasses and cool-season grasses increase. The composition of the forb component remains diverse, but the potential for encroachment by invasive woody species becomes more likely, due to fewer deep rooted species and a reduced fuel load to carry fire. While this plant community is less productive and less diverse than the representative plant community, it remains sustainable in regard to site/soil stability, watershed function, and biologic integrity. Total annual production ranges from 1,250 to 2,250 pounds of air dry vegetation per acre.
Dominant plant species
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
-
sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), grass
Figure 12. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). NE7501, Central Loess Plains, warm season dominant. Native warm-season dominant, MLRA 75.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 21 | 33 | 18 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
Community 1.3
At-Risk Native Grass Community
In this plant community, the more palatable warm-season tallgrasses have been reduced to remnant populations by continued defoliation during their critical growth periods. Grazing-evasive warm-season grasses and cool-season grasses increase significantly. Blue grama, sideoats grama, and composite dropseed are the dominant warm season grasses. Kentucky bluegrass encroachment also occurs on flatter slopes. Soil health is affected by reduced efficiency in the nutrient, mineral, and hydrologic cycles as a result of decreases in plant litter and rooting depths. Total annual vegetative production declines to an average of 1,300 lbs./acre. Without a management change, this community is at-risk to degrade to the Native/Invaded Grass State.
Dominant plant species
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), grass
-
composite dropseed (Sporobolus compositus), grass
Figure 13. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). NE7502, Central Loess Plains, warm season at risk. Native warm-season at risk, reduced tall, warm-season grasses with increased cool-season grasses, MLRA 75.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 21 | 26 | 18 | 10 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
Community 1.4
Excessive Litter Community
The Excessive Litter Community describes the response of the community to the removal of the natural disturbances of herbivory and fire. As the undisturbed duff layer deepens, infiltration of the precipitation is interrupted and evaporation increases significantly, simulating drought-like conditions.
Dominant plant species
-
big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii), grass
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
Community 1.5
Ephemeral Forb Community
This community describes the flush of forbs that occurs in response to a major disturbance, or combination of disturbances. Growing season wildfire followed by hail, extreme prolonged drought, or extreme defoliation by herbivores are all examples of these disturbances. The native warm-season grasses reestablish dominance within a few years of the event.
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2
A shift from the Reference Community to the Degraded Native Grass Community occurs with continuous season-long grazing and inadequate recovery periods during the growing season
Pathway 1.1B
Community 1.1 to 1.4
Prolonged interruption of the natural disturbances of herbivory and fire will result in conversion from this community to the Excessive Litter Community.
Pathway 1.1C
Community 1.1 to 1.5
A high-impact disturbance event or combination of events causing excessive defoliation of the vegetation, i.e., a growing season wildfire followed by a significant hailstorm, or a prolonged intensive grazing event, or long-term drought.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1
Reversing the downward trend to the previous community can be achieved with prescribed grazing early and late in the growing season to reduce undesirable cool season grasses. Targeting the peak growth period of cool season grasses with high intensity grazing events followed by rest will allow the tall native warm season grasses to rejuvenate. Appropriately timed prescribed fire will accelerate this process.
Pathway 1.2B
Community 1.2 to 1.3
Maintaining continuous season-long grazing with inadequate recovery periods during the growing season further degrades the site to the At-Risk Native Grass Community.
Pathway 1.2C
Community 1.2 to 1.4
Prolonged interruption of the natural disturbances of herbivory and fire will result in conversion from this community to the Excessive Litter Community.
Pathway 1.2D
Community 1.2 to 1.5
A high-impact disturbance event or combination of events causing excessive defoliation of the vegetation, i.e., a growing season wildfire followed by a significant hailstorm, or a prolonged intensive grazing event, or long-term drought.
Pathway 1.3A
Community 1.3 to 1.2
Reversing the downward trend to the previous community can be achieved with prescribed grazing early and late in the growing season to reduce undesirable cool-season grasses. Targeting the peak growth period of cool season grasses with high intensity grazing events followed by rest will allow the native warm-season tallgrasses to rejuvenate. Appropriately timed prescribed fire will accelerate this process.
Conservation practices
| Access Control | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Grazing |
Pathway 1.3B
Community 1.3 to 1.4
Prolonged interruption of the natural disturbances of herbivory and fire will result in conversion from this community to the Excessive Litter Community.
Pathway 1.3C
Community 1.3 to 1.5
A high-impact disturbance event, or combination of events causing excessive defoliation of the vegetation, i.e., a growing season wildfire followed by a significant hailstorm, or a prolonged intensive grazing event, or long-term drought, etc.
Pathway 1.4A
Community 1.4 to 1.1
Reintroduction of the natural processes of herbivory and fire will allow the vegetation to return to the previous community.
Pathway 1.4B
Community 1.4 to 1.2
Reintroduction of the natural processes of herbivory and fire will allow the vegetation to return to the previous community.
Pathway 1.4C
Community 1.4 to 1.3
Reintroduction of the natural processes of herbivory and fire will allow the vegetation to return to the previous community.
Pathway 1.4D
Community 1.4 to 1.5
Re-introduction of the natural processes of herbivory and fire will allow the vegetation to return to the previous community.
Pathway 1.5A
Community 1.5 to 1.1
Restoration occurs naturally once the disturbance event has subsided. Allowing growing season rest will accelerate the recovery.
Pathway 1.5B
Community 1.5 to 1.2
Restoration occurs naturally once the disturbance event has subsided. Allowing growing season rest will accelerate the recovery.
Pathway 1.5C
Community 1.5 to 1.3
Restoration occurs naturally once the disturbance event has subsided. Allowing growing season rest will accelerate the recovery.
Pathway 1.5D
Community 1.5 to 1.4
Restoration occurs naturally once the disturbance event has subsided. Allowing growing season rest will accelerate the recovery.
State 2
Native/Invaded Grass State
This state has been degraded from the Reference State and much of the native warm-season tall- and midgrass community has been replaced by less desirable plants. The loss of warm-season grasses has negatively impacted energy flow and nutrient cycling. Water infiltration is reduced due to the shallow root system and rapid runoff characteristics of the grazing-evasive plant communities. The Native Evaders/Invaded Grass and the Smooth Brome Communities are the components of the Native/Invaded Grass State.
Dominant plant species
-
Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
composite dropseed (Sporobolus compositus), grass
-
smooth brome (Bromus inermis), grass
Community 2.1
Native Evaders/Invaded Grass Community
This plant community represents a shift from the Reference State across a plant community threshold. With continued grazing pressure, blue grama, Kentucky bluegrass, and composite dropseed will become the dominant plant species, with only trace remnants of the more palatable warm-season midgrasses such as sideoats grama and little bluestem. Composite dropseed is a grazing-evasive warm-season midgrass with low palatability. Continuous and heavy grazing pressure will maintain this plant community in a sod-bound condition. Forb richness and diversity has decreased. With the decline and loss of deeper penetrating root systems, a compacted layer may form in the soil profile below the more shallow replacement root systems. Grazing management practices that allow for adequate periods of recovery between grazing events will favor mid and tall warm-season grasses. Appropriately timed prescribed fire will accelerate the restoration process.
Dominant plant species
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
composite dropseed (Sporobolus compositus), grass
-
Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis), grass
Figure 14. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). NE7503, Central Loess Plains, warm season/cool season co-dominant. Native warm-season plant community encroached with cool-season grasses, MLRA 75.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 27 | 25 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
Community 2.2
Smooth Brome Community
This plant community contains predominately smooth brome but also contains some native warm-season grass remnants. Production of plant communities dominated by smooth brome is highly variable, depending upon the percentages of composition present and outside inputs such as fertilizer and weed control. Clipping or ocular estimates of production should be conducted to verify current annual production.
Dominant plant species
-
smooth brome (Bromus inermis), grass
Figure 15. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). NE7504, Central Loess Plains, cool season dominant, warm season remnants. Cool season, smooth brome with native warm season remnants, MLRA 75.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 2 | 13 | 29 | 19 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
Pathway 2.1A
Community 2.1 to 2.2
This community will be converted to a Smooth Brome Community through excessive warm season grazing with inadequate rest.
Pathway 2.2A
Community 2.2 to 2.1
Restoration can be achieved by herbicide treatment and reseeding. If adequate native remnants are present, appropriately timed prescribed fire and a follow-up prescribed grazing program may achieve the desired results.
State 3
Invaded Woody State
Once the tree canopy cover reaches 15 percent with an average tree height exceeding 5 feet, the threshold is crossed to the Invaded Woody State. The primary coniferous interloper is eastern redcedar. Honeylocust and green ash number among the deciduous native trees, along with several exotic introduced species including Siberian elm. These woody species are encroaching due to lack of prescribed fire and other brush management practices. Typical ecological impacts are a loss of native warm-season grasses, degraded forage productivity and reduced soil quality. This state consists of the Eastern Red Cedar/Honeylocust Community.
Dominant plant species
-
eastern redcedar (Juniperus virginiana), tree
-
honeylocust (Gleditsia triacanthos), tree
Community 3.1
Eastern Red Cedar/Honeylocust Community
This community has at least a 15 percent canopy of Eastern redcedar. Honeylocust encroachment may occur in the eastern portion of the MLRA, when brush management and prescribed burning is absent over an extended period of time. Generally, this site is very conducive to eastern redcedar seedling invasion especially when adjacent to a seed source. Eastern redcedars will eventually dominate the site, resulting in a closed canopy, reduced forage production and limited livestock grazing and wildlife habitat value. Eastern redcedar control can usually be accomplished with prescribed burning while the trees are six foot tall or less and fine fuel production is over 1,500 pounds per acre. Trees of all heights can be controlled with the use of specifically adapted preparation, and ignition and holding techniques. Mechanical removal followed by a chemical treatment on stumps is effective on locust. Total annual production during an average year varies significantly, depending on the production level prior to encroachment and the percentage of canopy cover.
Figure 16. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). NE7505, Central Loess Plains, woody encroachment. Woody plant encroachment with warm- and cool-season grasses MLRA 75.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 3 | 8 | 12 | 20 | 25 | 14 | 5 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
Heavy grazing without adequate recovery periods will cause this state to lose a significant proportion of warm-season tall- and midgrass species and cross a threshold to the Native/Invaded Grass State. Water infiltration and other hydrologic functions will be reduced due to the root matting presence of sod-forming grasses. With the decline and loss of deeper penetrating root systems, soil structure and biological integrity are catastrophically degraded to the point that recovery is unlikely. Once this occurs, it is highly unlikely that grazing management alone will return the community to the Reference State.
Transition T1B
State 1 to 3
Disruption of the natural fire regime and the planting of invasive exotic and native woody species can cause this state to shift to the Invaded Woody State.
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
Disruption of the natural fire regime and the planting of invasive exotic and native woody species can cause this state to shift to the Invaded Woody State.
Restoration pathway R3A
State 3 to 1
Prescribed burning, wildfire, harvest, and brush management will move this plant community toward one of the herbaceous dominated plant communities. The forb component of a site with heavy tree density or canopy cover will initially increase following tree removal through mechanical brush management treatments and prescribed fire. If resprouting brush or trees such as honeylocust or Siberian elm are present, stumps must be chemically treated immediately after mechanical removal. Ongoing brush management such as hand cutting, chemical spot treatments or periodic prescribed burning is required to prevent a return to this state.
Conservation practices
| Brush Management | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Burning |
Restoration pathway R3B
State 3 to 2
Prescribed burning, wildfire, harvest, and brush management will move this plant community toward one of the herbaceous dominated plant communities. The forb component of a site with heavy tree density or canopy cover will initially increase following tree removal through mechanical brush management treatments and prescribed fire. If resprouting brush or trees such as honeylocust or Siberian elm are present, stumps must be chemically treated immediately after mechanical removal. Ongoing brush management such as hand cutting, chemical spot treatments or periodic prescribed burning is required to prevent a return to this state.
Conservation practices
| Brush Management | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Burning |
Additional community tables
Table 6. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 2 | Warm-Season Midgrass | 595–1191 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 476–834 | 20–35 | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 239–476 | 10–20 | ||
| composite dropseed | SPCOC2 | Sporobolus compositus var. compositus | 0–119 | 0–5 | ||
| 1 | Warm-Season Tallgrass | 358–595 | ||||
| big bluestem | ANGE | Andropogon gerardii | 358–476 | 15–20 | ||
| switchgrass | PAVI2 | Panicum virgatum | 0–119 | 0–5 | ||
| Indiangrass | SONU2 | Sorghastrum nutans | 0–72 | 0–3 | ||
| prairie sandreed | CALO | Calamovilfa longifolia | 0–72 | 0–3 | ||
| 3 | Native Cool-Season Grasses | 0–119 | ||||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| Canada wildrye | ELCA4 | Elymus canadensis | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| porcupinegrass | HESP11 | Hesperostipa spartea | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| 4 | Warm-Season Shortgrass | 0–119 | ||||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 0–119 | 0–5 | ||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| plains muhly | MUCU3 | Muhlenbergia cuspidata | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| 5 | Grasslike | 0–72 | ||||
| threadleaf sedge | CAFI | Carex filifolia | 0–72 | 0–3 | ||
| sedge | CAREX | Carex | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 6 | Forbs | 119–239 | ||||
| Forb, perennial | 2FP | Forb, perennial | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| Cuman ragweed | AMPS | Ambrosia psilostachya | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| white heath aster | SYER | Symphyotrichum ericoides | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| longbract spiderwort | TRBR | Tradescantia bracteata | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| purple prairie clover | DAPUA | Dalea purpurea var. arenicola | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| scarlet beeblossom | GACO5 | Gaura coccinea | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| hairy false goldenaster | HEVI4 | Heterotheca villosa | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| dotted blazing star | LIPU | Liatris punctata | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| Nuttall's sensitive-briar | MINU6 | Mimosa nuttallii | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| yellow sundrops | CASE12 | Calylophus serrulatus | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| silverleaf Indian breadroot | PEAR6 | Pediomelum argophyllum | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| white penstemon | PEAL2 | Penstemon albidus | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| slimflower scurfpea | PSTE5 | Psoralidium tenuiflorum | 0–48 | 0–2 | ||
| upright prairie coneflower | RACO3 | Ratibida columnifera | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| prairie groundsel | PAPL12 | Packera plattensis | 0–24 | 0–1 | ||
| Missouri goldenrod | SOMI2 | Solidago missouriensis | 0–24 | 0–1 | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 0–24 | 0–1 | ||
| groundplum milkvetch | ASCR2 | Astragalus crassicarpus | 0–24 | 0–1 | ||
| lotus milkvetch | ASLO4 | Astragalus lotiflorus | 0–24 | 0–1 | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 7 | Shrubs | 48–119 | ||||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 24–72 | 1–3 | ||
| leadplant | AMCA6 | Amorpha canescens | 24–72 | 1–3 | ||
| prairie rose | ROAR3 | Rosa arkansana | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| western snowberry | SYOC | Symphoricarpos occidentalis | 24–48 | 1–2 | ||
| devil's-tongue | OPHU | Opuntia humifusa | 0–24 | 0–1 | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
LIVESTOCK – GRAZING INTERPRETATIONS:
Grazing by domestic livestock is one of the major income-producing industries in the area. This site is well adapted to managed grazing by domestic livestock. Rangeland in this area may provide year-long forage for cattle, sheep, or horses. The predominance of herbaceous plants across all plant community phases best lends these sites to grazing but browsing livestock such as goats will utilize native and invasive forbs and brush. During the dormant period, the protein levels of the forage maybe lower than the minimum needed to meet livestock (primarily cattle and sheep) requirements and supplementation based on a reliable forage analysis may be necessary.
A grazing management strategy that protects the resource, maintains or improves rangeland health, and is consistent with management objectives will include appropriate stocking rates based on the carrying capacity of the land. In addition to useable forage, stocking rates should consider ecological condition of the land, trend of the site, grazing history, season of use, stock density, kind and class of livestock, forage quality, and harvest efficiency based on plant preference. It should also consider site accessibility and distance to drinking water. Average annual production must be measured or estimated to properly assess useable forage production and carrying capacity.
Carrying capacities and production estimates listed below are conservative estimates that should be used as guidelines in the initial stages of grazing lands planning. Often, the plant community does not entirely match any particular plant community (as described in the ecological site description). Because of this a resource inventory conducted as part of a field visit is recommended to document plant composition and production. More precise carrying capacity estimates can be calculated based on field verified production and species composition along with animal preference data for the type and class of animals and level of grazing management. With consultation of the land manager, more intensive grazing management may result in improved harvest efficiencies and increased carrying capacity.
Suggested stocking rates (carrying capacity) for cattle under continuous season-long grazing under normal growing conditions are listed below:
-Reference Community: 2125 lbs/acre production and 0.58 AUM/acre carrying capacity*
-Degraded Native Grass Community: 1750 lbs/acre production and 0.48 AUM/acre carrying capacity*
*Continuous season-long grazing by cattle under average growing conditions with 25 percent harvest efficiency. Air dry forage requirements are based on 3 percent of animal body weight or 912 lbs/acre (air-dry weight) per Animal Unit Month (AUM).
If excessive defoliation or grazing distribution problems occur, reduced stocking rates are needed to maintain plant health and vigor. Year-to-year and season-to-season fluctuations in forage production are expected due to weather conditions. To avoid overuse of forage plants when conditions are unfavorable to forage production, timely adjustments to livestock number or in the length of grazing periods are needed.
WILDLIFE INTERPRETATIONS:
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 75 lies primarily within the loess mixed-grass prairie ecosystem mixed with tallgrass prairie in lower areas. Prior to European settlement, this area consisted of diverse grassland habitats interspersed with varying densities of depressional wetlands and limited woody riparian corridors. These habitats provided critical life cycle components for the grassland birds, prairie dogs and herds of roaming bison, elk, and pronghorn that historically occupied this landscape. Diverse populations of small mammals and insects provided a bountiful prey base for raptors and omnivores such as coyotes, foxes, raccoons and opossums. Bobcats, wolves, and mountain lions occupied the apex predator niche. In addition, a wide variety of reptiles and amphibians thrived in this landscape.
The loess mixed-grass prairie was a disturbance-driven ecosystem with fire, herbivory and climate functioning as the primary disturbances. Following European settlement, elimination of fire, widespread conversion to cropland, and other sources of habitat fragmentation significantly altered the appearance and functionality of the entire ecosystem. The reduced stability of the system is reflected by major changes in the composition and abundance of the native flora and fauna. Introduced and invading species further degrade the ecological integrity of the plant and animal communities.
Bison and prairie dogs were historically keystone species but free-roaming bison herds and nearly all prairie dogs have been extirpated. The loss of bison and fire as ecological drivers greatly influenced the character of the remaining native grasslands and the habitats that they provide. In addition to free-ranging bison, extirpated species include pronghorn, wolves and swift fox.
Historically, an ecological mosaic of Loamy Plains, Clayey Plains, Limy Loess Slopes, Loess Breaks, Closed Upland Depression, Loamy Terrace, and Loamy Floodplain sites, provided habitat for species requiring unfragmented grasslands. Important habitat features and components found commonly or exclusively on modern day remnants include upland nesting habitat for grassland birds and game birds; nesting and escape cover for waterfowl; forbs and insects for brood rearing habitat; and a forage source for small and large herbivores.
Fragmentation has reduced habitat quality for numerous area-sensitive species, as highlighted by the decline of the greater prairie chicken. Many grassland nesting bird populations such as dickcissel and Henslow's sparrow are also declining. In this fragmented landscape, native grassland bird populations face increasing competition from the opportunistic European starlings and house sparrows and are subject to nest parasitism from brown-headed cowbirds. Tree encroachment creates habitat that favors generalist species such as American robin and mourning dove and provides perches for raptors, increasing the predation mortality. Introduced and invasive plant species such as smooth brome, Kentucky bluegrass, nodding plumeless thistle (musk thistle), and Canada thistle further degrade the biological integrity of many of these remnant prairies.
1. REFERENCE STATE: The predominance of tall- and midgrasses plus a high diversity of forbs and shrubs in this community makes it ideal for grazers and mixed-feeders. Pollinating insects play a large role in maintaining the forb community and provide a food source for grassland birds and other grassland dependent species. The vegetative structural diversity provides habitat for reptiles, amphibians, and a wide array of native and introduced bird species including Henslow's sparrow, western meadowlark, northern bobwhite, and ringneck pheasants. The abundant prey base supports populations of Swainson’s hawk, burrowing, short-eared and great horned owls and other grassland raptors. Western meadowlark and American crow overwinter in this habitat.
The diversity of grasses, forbs and shrubs provide high nutrition levels for small and large herbivores including moles, mice, ground squirrels, white-tailed jackrabbit, and white-tailed deer. The structure of this plant community provides suitable thermal, protective and escape cover for small herbivores and grassland birds. Many wide-ranging predators utilize this plant community including coyote, badger, red fox and least and long-tailed weasels.
As the plant community degrades to more midgrasses and fewer tallgrasses, less winter and escape cover are provided. It also provides less cover for predators. As the plant community shifts from warm-season tallgrasses to midgrasses, it favors grassland birds that prefer shorter vegetation. This structural community provides better habitat for greater prairie chicken, lark bunting, and lark sparrow populations. Habitat in plant community 1.3 is much the same as 1.2 but provides less winter protection because of the reduced plant height and cover.
2. NATIVE/INVADED GRASS STATE: Although the amount of Kentucky bluegrass in this plant community varies, the generally lower structure height favors the suite of grassland birds that prefer more visual space. Increased dominance by Kentucky bluegrass with lower plant diversity provides less habitat for ringneck pheasant, northern bobwhite and mixed-feeders, such as white-tailed deer and small mammals. Insect populations are somewhat reduced but still play a large role in maintaining the forb community and provide a moderate forage supply for grassland birds and other species. The reduced stature of this plant community still provides suitable thermal, protective and escape cover for small herbivores and grassland birds.
3. INVADED WOODY STATE: The Eastern Redcedar/ Honeylocust Community provides habitat niches for white-tailed deer, wild turkey, raccoon, and Cooper’s, and sharp-shinned hawk among other species. Birds that are habitat generalists, such as the Bell’s Vireo, common yellowthroat, Eastern kingbird, mourning dove, American goldfinch, northern bobwhite, field sparrow, solitary vireo, and pigmy nuthatch use woody cover for nesting, food, and breeding habitats. While a woody component of the grassland provides specific short-term habitats for some species, an expansive forest component is very detrimental to grassland wildlife species diversity and abundance overall.
Hydrological functions
Water is the principal factor limiting forage production on this site, which is dominated by soils in hydrologic group B. Permeability is moderate, and runoff potential is medium to high. In general, the infiltration rate is directly proportional to vegetative cover, while the runoff potential is inversely proportional. An exception is sod-bound shortgrasses. The T erosion factor is 5. (Refer to NRCS Section 4, National Engineering Handbook (NEH-4) for runoff quantities and hydrologic curves).
Recreational uses
This site provides hunting opportunities for upland game species, and white-tailed deer. The wide varieties of plants which bloom from spring until fall have an aesthetic value that appeals to visitors.
Wood products
No appreciable wood products are present on the site. Eastern redcedar can be utilized for veneer or furniture.
Other products
No appreciable other products.
Other information
Site Development and Testing Plan:
Future work is needed to validate the information in this Provisional Ecological Site Description. Additional data collection and evaluation may also be needed to develop this ESD to the Approved, then Correlated level. This could include field activities to collect low, medium and high intensity sampling, soil correlations, and analysis of that data. Field reviews of the project plan should be done by soil scientists and vegetation specialists. A final field review, peer review, quality control, and quality assurance reviews of the ESD will be needed to produce the final document.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented here has been derived from field observations from range-trained personnel and literature and soil surveys.
Other references
High Plains Regional Climate Center, University of Nebraska. (http://hpcc.unl.edu, accessed 12/05/16)
Johnsgaard, P.A. 2001. “The Nature of Nebraska.” University of Nebraska Press.
LaGrange, T.G. 2015. Final Report submitted to EPA for the project entitled: Nebraska’s Wetland Condition Assessment: An Intensification Study in Support of the 2011 National Survey (CD# 97714601), and the related project entitled: Nebraska's Supplemental Clean Water Act §106 Funds, as Related to Participation in National Wetland Condition Assessment (I – 97726201). Nebraska Game and Parks Commission, Lincoln.
Muhs, Daniel R., E. Bettis III, J. Aleinikoff, J. McGeehin, J. Beann, G. Skipp, B. Marshall, H. Roberts, W. Johnson, and R. Benton.
"Origin and paleoclimatic significance of late Quaternary loess in Nebraska: Evidence from stratigraphy, chronology, sedimentology, and geochemistry" (2008). USGS Staff -- Published Research. Paper 162. http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usgsstaffpub/162 Accessed 12/05/16.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. NRCS National Ecological Site Handbook. January, 2014.
U.S. Dept. of Agriculture. NRCS National Engineering Handbook, Section 4. August, 2011.
Personal communications with professional ecologists and wildlife experts.
Rolfsmeier, S.B. and G. Steinauer. 2010. "Terrestrial Ecological Systems and Natural Communities of Nebraska", (version IV)
Nebraska Natural Heritage Program.
USDA, NRCS. National Water and Climate Center, Portland, OR. http://wcc.nrcs.usda.gov Accessed 12/05/16.
USDA, NRCS.1997. National Range and Pasture Handbook.
USDA, NRCS. National Soil Information System, Information Technology Center, Fort Collins, CO. http://nasis.nrcs.usda.gov Accessed 12/05/16.
USDA, NRCS. 2002. The PLANTS Database, Version 3.5 http://plants.usda.gov Accessed 12/05/16. National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA.
USDA, NRCS Soil Surveys from Gosper, Phelps, Kearney, Adams, Hamilton, Polk, York, Butler, Seward, Saline, Fillmore, Clay, Franklin, Webster, Nuckolls, Thayer and Jefferson counties in Nebraska, and Republic and Washington counties in Kansas.
Contributors
Doug Whisenhunt
Nadine Bishop
Approval
Suzanne Mayne-Kinney, 4/17/2025
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | Jeff Nichols, Nadine Bishop |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | Kristin Dickinson, Acting State Range Management Specialist, kristin.dickinson@usda.gov |
| Date | 11/30/2024 |
| Approved by | Suzanne Mayne-Kinney |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
Rills may occur on the site. When they do occur, they are shallow or less than 2 inches (5 cm) deep and narrow or less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) wide. On extremely steep slopes (greater than 45 percent) rills may be more frequent, deeper, and wider. -
Presence of water flow patterns:
Water flow patterns may occur on the site. Where they do occur, they are rare, narrow (3 to 6 inches or 7.5 to 15cm), moderately long (12 to 18 inches or 30 to 45 cm), and disconnected, disrupted by perennial vegetation. On extremely steep slopes (greater than 45 percent) water flow patterns may be more frequent, deeper, and wider. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
Occasionally, bunch grasses may be pedestalled, with no exposed roots. On extremely steep slopes (greater than 45 percent) erosional pedestals will be more frequent. Drought, wildfire, and prescribed burns should not increase the incidence of pedestals except on the steepest slopes. -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
Bare ground ranges from 5 to 10 percent. Bare ground patches should be no larger than 6 to 8 inches (15 to 20 cm) in diameter and scattered across the site. Multi-year drought can cause the amount of bare ground to increase to 15 to 20 percent with patches of 8 to 12 inches (20 to 30 cm). Cross-sectional viewing of this site appears to have more bare ground than vertical viewing due to exposed loess-steps. Nearly vertical slopes should not be included in the evaluation as those areas are not part of the loess hills site but are considered a non-site. Bare ground is exposed mineral soil that is not covered by vegetation (basal and/or foliar canopy), litter, standing dead vegetation, gravel/rock, and visible biological crust (e.g., lichen, mosses, algae). -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
A few gullies may be present in areas where the headlands are annually cropped. These areas should have no active headcutting and sides of the gully are covered with vegetation. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
Slight wind scouring is possible on areas of exposed loess. -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Fine litter movement of 1 to 3 feet (0.3 to 1 meter) is possible during intense rains. Coarse litter may move but will move shorter distances than fine litter. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Soil stability ratings will be 3 to 5 in the interspaces and 5 to 6 under canopy. -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
A-horizon ranges is typically 4 inches deep (10 cm). Soil color is dark grayish brown (10YR 4/2) when dry and very dark grayish brown (10YR 3/2) when moist. Soil structure is moderate fine granular, slightly hard, and slightly alkaline. AC-horizon ranges from 4 to 7 inches (10 to 18 cm). Soil color is light brownish gray (10YR 6/2) when dry and dark grayish brown (10YR 4/2) when moist. Structure is weak fine granular, very friable, slightly hard. Soil is moderately alkaline. The depth to secondary carbonates is 0 to 10 inches resulting in strong effervescence. See Official Soils Description for additional details. The soil series correlated to this site is Coly. -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
Plant community composition of 75 to 85 percent grasses and grass-likes, 5 to 10 percent forbs, and 2 to 5 percent shrubs will optimize infiltration on the site. The grass and grass-like portion is composed of native, perennial, warm-season, tall grasses (15 to 25%), perennial, native, warm-season, mid-grasses (25 to 50%), perennial, native, cool-season grasses (0 to 5%), perennial, native, warm-season, short grasses (0 to 5%), and grass-likes (0 to 3%). Infiltration can be adversely impacted by the invasion of Kentucky bluegrass, smooth brome, tall fescue, and trees when present above 10 percent (subdominant designation). -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
None. No compaction layers are expected to occur on this site. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Phase 1.1:
1. Perennial, native, warm-season, midgrass – 531- 1063 #/ac (25-50%), (2 species minimum): little bluestem, sideoats grama, composite dropseed, plains muhly.
Phase 1.2:
1. Perennial, native, warm season, midgrass: little bluestem, sideoats grama, composite dropseed, plains muhly.
Phase 1.3:
1. Perennial, native, warm season, midgrass: little bluestem, sideoats grama, composite dropseed, plains muhly; 2. Perennial, native, warm-season, shortgrass: blue grama, hairy grama.Sub-dominant:
Phase 1.1:
1. Perennial, native, warm-season, tallgrass – 319-531 #/ac (15-25%), (1 species minimum): big bluestem, Indiangrass, prairie sandreed, switchgrass.
Phase 1.2:
1. Perennial, native, cool-season grass: western wheatgrass, Canada wildrye, needle and thread, porcupinegrass, prairie, Junegrass, Scribner’s rosettegrass; 2. Perennial, native, warm-season, tallgrass: big bluestem, Indiangrass, prairie sandreed, switchgrass.
Phase 1.3:
1. Perennial, native, cool season grass: western wheatgrass, Canada wildrye, needle and thread, porcupinegrass, prairie Junegrass, Scribner’s rosettegrass;Other:
Minor - .Phase 1.1:
1. Native forbs (perennial and annual) – 106-213 (5-10%): species will vary from location to location; 2. Shrubs and cacti - 43-106 #ac (2-5%): leadplant, prairie rose, twist spine pricklypear, western snowberry, other shrubs; 3. Perennial, native, cool-season grass – 0- 106 #/ac (0-5%): western wheatgrass, Canada wildrye, needle and thread, porcupinegrass, prairie Junegrass, Scribner’s rosettegrass; 4. Perennial, native, warm-season, shortgrass – 0-106#/ac (0-5%): blue grama, hairy grama; 5. Grass-likes – 0-64 #/ac (0-3%): Sedges.
Minor - .Phase 1.2: 1. Perennial, native, warm season, shortgrass: blue grama, hairy grama; 2. Native forbs (annual and perennial): species will vary from location to location; 3. Shrubs and cacti: leadplant, prairie rose, twist spine
pricklypear, western snowberry, other shrubs; 4. Grass-likes: sedges and other grass-likes.
Minor - .Phase 1.3:
1. Perennial, native, warm season, tallgrass: big bluestem, Indiangrass, prairie sandreed, switchgrass; 2. Shrubs and cacti: leadplant, prairie rose, twist spine pricklypear, western snowberry, other shrubs; 3. Native forbs; 4. Grasslikes.
Trace: Phase 1.3
1. Introduced, cool-season grasses.Additional:
The Reference Community (1.1) consists of seven F/S groups. These groups in order of abundance are perennial, native, warm-season, midgrass; perennial, native, warm-season, tallgrass; native forbs (perennial and annual); shrubs
and cacti; perennial, native, cool-season grass; perennial, native, warm-season, shortgrass; and grass-likes. The Degraded Native Grass Community (1.2) consists of seven F/S groups. These groups in order of abundance are perennial, native, warm-season, midgrass; perennial, native, cool-season grass, perennial, native, warm-season tallgrass; perennial, native, warm-season short-grass; native forbs, shrubs, and grass-likes. The At-Risk Community (1.3) consists of eight F/S groups. These groups in order of abundance are perennial, native, warm-season, midgrass; perennial, native, warm-season shortgrass; perennial, native, cool-season grass; perennial, native, warm-season tallgrass, shrubs, forbs, grass-likes, and introduced, cool-season grass. -
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
A few (less than 3 percent) dead centers may occur in bunchgrasses. Shrubs may show some dead branches (less than 5 percent) as plants age. Plant mortality may increase to 10 to 15 percent following a multi-year drought, wildfire, or a combination of the two events. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Plant litter cover is evenly distributed throughout the site and is expected to be 35 to 45 percent and 0.25 inch (0.65 cm) depth. Litter cover during and following extended drought ranges from 15 to 30 percent. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
Production is shown in air-dry values. The Representative Value (RV) = 2,125 pounds per acre. Low production years = 1,800 pounds per acre. High production years = 2,800 pounds per acre. -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
No non-native invasive species are present. Eastern redcedar, honey locust, and Siberian elm known invasives that have the potential to become dominant or co-dominant on the site. Consult the state noxious weed and state watch lists for potential invasive species on each ecological site. NOTE: Invasive plants (for the purposes of the IIRH protocol) are plant species that are typically not found on the ecological site or should only be in trace or minor categories under the natural disturbance regime and have the potential to become a dominant or codominant species on the site if their establishment and growth are not actively controlled by natural disturbances or management interventions. Species listed characterize degraded states AND have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
All perennial species exhibit high vigor relative to climatic conditions. Perennial grasses should have vigorous rhizomes or tillers; vegetative and reproductive structures are not stunted. All perennial species should be capable of reproducing annually.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.