

Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R082AY365TX
Granite Gravel 25-32 PZ
Last updated: 9/19/2023
Accessed: 02/07/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 082A–Texas Central Basin
The 82A MLRA is underlain primarily by igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Igneous and metamorphic outcrops include the Valley Spring Gneiss, Packsaddle Schist, and Town Mountain Granite of Precambrian age. Sedimentary rocks include the Hickory Sandstone and Lion Mountain Sandstone of Cambrian Age and the Hensel Sand of Cretaceous age. Holocene alluvium is on flood plains.
The Texas Central Basin (MLRA 82A) is a unique geological region within Texas. It is composed largely of Pre-Cambrian granite, gneiss and schist (Bureau of Economic Geology 1981). Depending upon the parent material and topography, a great variety of soils have developed that vary from shallow, fissured, rocky outcrops with minimal soil development to relatively deep, well-developed soils with textures that vary from fine sandy loams to sands to gravelly clay loams to cobbly clay loams and stony clay loams (Goerdel 2000).
Classification relationships
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) and Land Resource Unit (LRU) (USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, 2006)
Ecological site concept
Granite Gravel soils consist of deep and moderately deep, somewhat excessively drained, rapidly permeable soils formed in materials weathered from granite. Granite gravel makes up 35 to 80 percent of soils by volume.
The soil is highly permeable but has a limited water-holding capacity. Infiltration is rapid so that water is highly available when present but generally of short duration following rainfall events. Low available water capacity and moderate fertility limit the density and productivity of plants. The site generally does not receive additional water from outside the site. Runoff is negligible on slopes less than 3 percent, very low on 3 to 5 percent slopes, and low on 5 to 8 percent slopes.
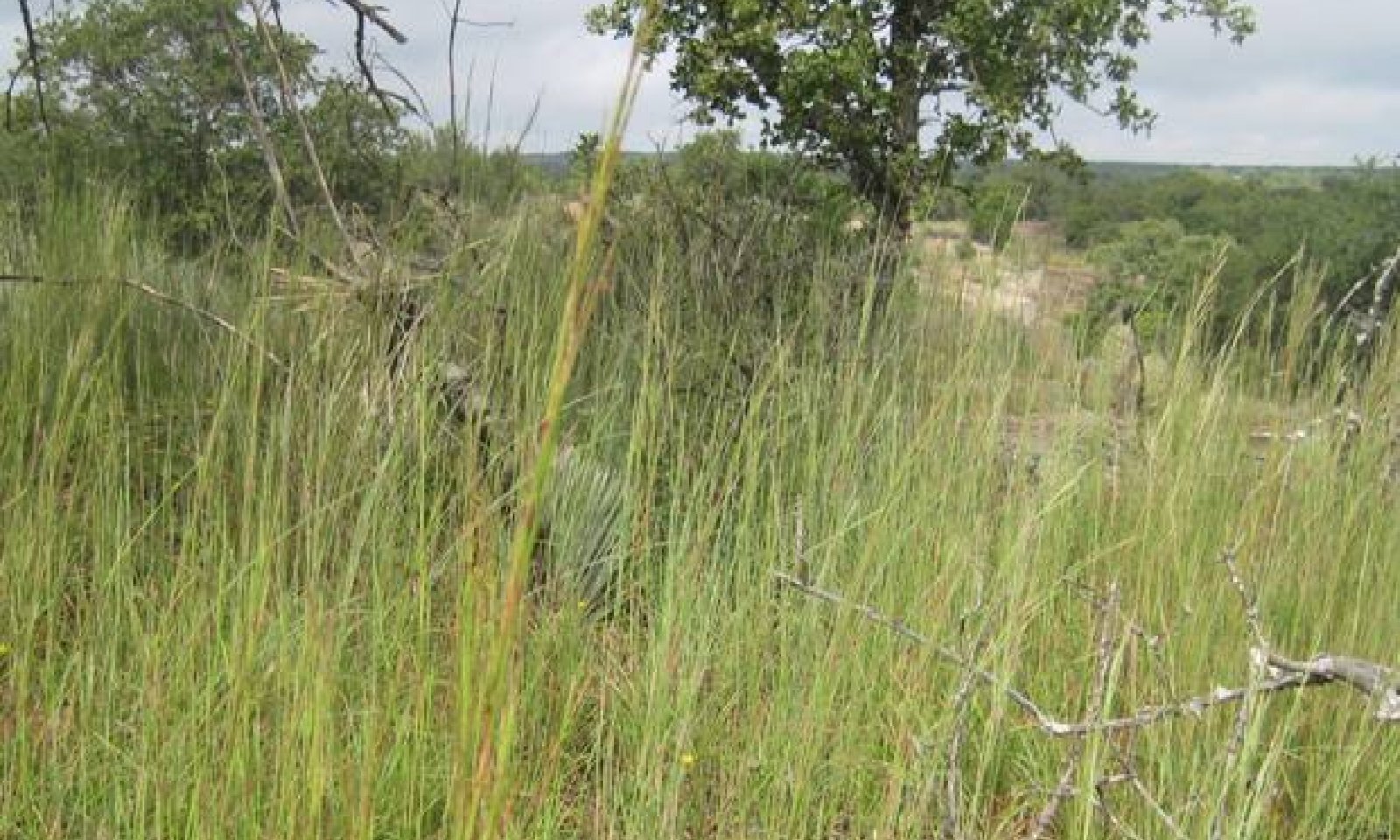
In reference condition, the site is an open savannah characterized by expanses of grassland (dominated by little bluestem and sideoats grama) interspersed with scattered mottes dominated by mature oak trees. This community requires relatively frequent fire and/or brush control (every 5 to 10 years) to maintain the savannah appearance. Without fire, shrubs will begin to dominate the open areas eventually resulting in a nearly closed canopy of shrubs and trees.
Associated sites
| R082AY600TX |
Gravelly Sandy Loam 25-32 PZ The Gravelly Sandy Loam site has more clay in the argillic horizon. |
|---|---|
| R082AY568TX |
Red Savannah 25-32 PZ The Red Savannah site has more clay in the argillic horizon and has less gravels. |
| R082AY366TX |
Granite Hill 25-32 PZ The Granite Hill site has less gravelly soils over granite and shallower to bedrock. |
Similar sites
| R082AY600TX |
Gravelly Sandy Loam 25-32 PZ The Gravelly Sandy Loam site soils have more clay in the argillic horizon. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus stellata |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Schizachyrium scoparium |
Physiographic features
These soils are on gently sloping to moderately sloping uplands. Slopes range from 1 to 8 percent. Elevation ranges from 730 to 2,000 feet. The site generally does not receive additional water from outside the site. Runoff is very low to low.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Plateau
> Ridge
(2) Hills > Hillslope |
|---|---|
| Runoff class | Very low to low |
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 730 – 2,000 ft |
| Slope | 1 – 8% |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
The climate for MLRA 82A is humid subtropical and is characterized by hot summers and relatively mild winters. The average first frost should occur around November 11 and the last freeze of the season should occur around March 21.
The average relative humidity in mid-afternoon is about 50 percent. Humidity is higher at night, and the average at dawn is about 80 percent. The sun shines 70 percent of the time possible during the summer and 50 percent in winter. The prevailing wind direction is from the south.
Approximately two-thirds of the annual rainfall occurs during the April to September period. Rainfall during this period generally falls as thunderstorms, and fairly large amounts of rain may fall in localized areas for a short period of time.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 210-240 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | 240-280 days |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 25-32 in |
| Frost-free period (actual range) | 210-240 days |
| Freeze-free period (actual range) | 240-280 days |
| Precipitation total (actual range) | 25-32 in |
| Frost-free period (average) | 225 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | 260 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 28 in |
Figure 2. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 3. Monthly minimum temperature range
Figure 4. Monthly maximum temperature range
Figure 5. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 6. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 7. Annual average temperature pattern
Climate stations used
-
(1) LLANO [USC00415272], Llano, TX
-
(2) MASON [USC00415650], Mason, TX
Influencing water features
This site does not have wetland or riparian influences. The site may shed water via runoff to lower positions on the landscape. The presence of ground cover and deep-rooted grasses and forbs can help facilitate infiltration of rainfall into the soil profile.
Wetland description
N/A
Figure 8.
Soil features
Granite Gravel soils consist of deep and moderately deep, well to somewhat excessively drained, moderately to rapidly permeable soils formed in materials weathered from granite. Granite gravel makes up 20 to 60 percent of soils by volume. Open patches of gravel make up a notable feature of this ecological site. Plant interspaces can be large with the majority of ground cover coming from litter and rock fragments at the soil surface.
The soil is highly permeable but has a limited water-holding capacity. Infiltration is rapid so that water is highly available when present but generally of short duration following rainfall events. Low available water capacity and moderate fertility limit the density and productivity of plants.
Associated soil series for Granite Gravel include Click and Lou. It should be noted that there is a small percentage of inclusions of other soils as well but for cartographic reasons too small to delineate.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Residuum
–
granite
|
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Very gravelly coarse sandy loam (2) Sandy loam |
| Family particle size |
(1) Loamy-skeletal (2) Fine-loamy |
| Drainage class | Well drained to somewhat excessively drained |
| Permeability class | Moderate to rapid |
| Depth to restrictive layer | 40 – 80 in |
| Soil depth | 40 – 80 in |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 40% |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
1.5 – 5.5 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
Not specified |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
2 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
2 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
5.6 – 7.3 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (4-40in) |
20 – 60% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (4-40in) |
2% |
Ecological dynamics
Ecological Dynamics of the Site:
The Granite Gravel 25-32” PZ reference site is a fire-influenced Midgrass Savannah interspersed with perennial forbs and mixed shrubs. The site consists of three stable states: Savannah State (1.0), Shrubland State (2.0), and Eroded State (3.0).
The Texas Central Basin (MLRA 82A) is a unique geological region within Texas. It is composed largely of Pre-Cambrian granite, gneiss and schist (Bureau of Economic Geology 1981). Depending upon the parent material and topography, a great variety of soils have developed that vary from shallow, fissured, rocky outcrops with minimal soil development to relatively deep, well-developed soils with textures that vary from fine sandy loams to sands to gravelly clay loams to cobbly clay loams and stony clay loams (Goerdel 2000).
Precipitation patterns are highly variable. Long-term droughts, occurring three to four times per century, cause shifts in species composition by causing a die-off of seedlings, less drought-tolerant species, and some woody species. Droughts also reduce biomass production and create open space that is colonized by opportunistic species when precipitation increases. Wet periods allow little bluestem, sideoats grama, and hardwoods to increase in dominance. The site also tends to have many opportunistic plants such as three-awns (Aristida spp.) and annuals that take advantage of the short flush of available water.
Climatic variation and topographic variability interact to influence vegetation responses to disturbances such as fire and grazing. The vegetation of the region developed under a humid, subtropical climate. Weather variation is great; precipitation is highly variable with seasonal, annual, and multi-year droughts (3-6 years) common as well as seasons and years with well above average precipitation; average conditions rarely exist. Typically the spring and fall are periods of highest precipitation while mid to late summer is usually a hot, droughty period. Winters are moderate with scattered precipitation sometimes in the form of short-lived snow and ice storms (Carr 1969, Bomar 1983).
The herbaceous savannah species adapted to fire and grazing disturbances by maintaining below-ground perennating tissues. Prior to European settlement, fires would likely have been frequent (approximately every 7-12 years) (Scifres and Hamilton 1993, Frost 1998) and burned any time of year as long as there were ample fuels, dry conditions, and an ignition source.
Fire was a major influence on vegetation structure and composition prior to settlement. Lightning and Native Americans were primary ignition sources, and the latter is considered to have increased the frequency and extent of fire as their populations increased. Fires occurred at all seasons but those that occurred during the hot, dry, late-summer season following fine fuel (grass) accumulation in the spring and early summer were perhaps the most intense and had the greatest influence on the character of the vegetation. Fires were frequent, and any area may have burned once within each 7-12 year interval (Scifres and Hamilton 1993, Frost 1998). Fire generally favors the herbaceous component of the community and hinders the establishment and growth of woody species under intense hot, dry conditions. Some individuals of trees (e.g. oak species) and resprouting shrubs (e.g. mesquite) were able to escape fires, and as they matured, they became fire-resistant components of the vegetation except for infrequent stand-replacing crown fires. These woody species became effectively uncoupled from the herbaceous and shrub layer even if the herbaceous species composition was substantially altered by grazing or other factors. If, however, the oaks were killed or removed it is very difficult for them to reestablish into mature single-stemmed trees due to the resprouting nature of the tree, particularly under current land use conditions. While fire had influenced these communities for millennia, as the land was settled with homesteads and crops were established, fires were purposely prevented or stopped. Most of the remaining rangeland was overgrazed, which reduced fuel loads and hence effectively fire-proofed the plant communities from the effect of fires. This was a primary factor in the increase of woody species within the Central Basin.
While shrublands within MRLA 82 have traditionally been viewed as “degraded” relative to livestock production, it is important to recognize that they are not necessarily degraded from the ecological perspective of primary productivity, biomass accumulation, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity. The productivity of shrublands may be equal to or greater than that of the grassland they replaced. In addition, shrubs help modify soils and microclimate to increase levels of organic matter and nutrients in the upper soils horizons (Boutton et al. 2009, Boutton & Liao 2010). This nutrient enhancement by shrubs can offset grazing-induced losses of soil nutrients and contribute to enhancing grass production when shrub cover is reduced. While shrub communities may have adverse impacts on grasses and grassland fauna, other plants and animals may benefit (Archer & Smeins 1991, Bestelmeyer et al. 2003). Thus, while ecosystem biodiversity certainly changes, it does not necessarily decrease with a shift from grass to woody dominance on these sites.
Soil and topographic variation interact with weather variation and land use to produce diverse plant communities across the Central Basin and on the Granite Gravel Site. Accounts of earlier explorers and settlers suggest the Central Basin was likely a mosaic of grassland, savannah, and woodlands (Foster 1917). In the reference plant community, midgrasses dominated the shortgrasses due to their ability to capture the sunlight and shade as well as being favored by the frequent fires. Plant communities vary from open grassland to savannah/parkland to shrubland/woodland to nearly closed canopy forest. The reference community for the Granite Gravel Ecological Site is defined as a fire-influenced grassland savannah that was widespread at the time of settlement but which did occur in a mosaic of shrublands, woodlands, and forests across much of the Central Basin (Smeins 1980, Weniger 1984). Almost all sites have a two or three-layered structure of over-story trees, mid-story shrubs and a ground layer of grasses and forbs.
Historical photographs suggest the nature of the vegetation structure depending on topography, soil properties, and time since the last major disturbances (such as drought or fire). However, the occurrence of extensive grasslands and grassland fauna (pronghorn, for example) is mentioned in numerous historical accounts.
Grasses that historically dominate Central Basin sites include little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), meadow dropseed (Sporobolus compositus), plains lovegrass (Eragrostis intermedia), plains bristlegrass (Setaria vulpiseta), Arizona cottontop (Digitaria californica), and sand dropseed (Sporobolus cryptandrus). Locally abundant tallgrasses include Indiangrass (Sorghastrum nutans) and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum). Shortgrasses that occur in the understory of mid- and tallgrasses or on shallow soils or disturbed areas include buffalograss (Bouteloua dactyloides), common curly-mesquite (Hilaria belangeri), hairy grama (Bouteloua hirsuta), and red grama (B. trifida) (Whitehouse 1933, Riskind and Diamond 1988). The composition and productivity of grassland communities would have varied with annual rainfall, soil depth, and the extent of argillic horizon development.
Historically, overstory species composition consisted of post oak (Quercus stellata), blackjack oak (Q. marilandica), live oak (Q. virginiana), honey mesquite (Prosopis glandulosa var. glandulosa), Texas hickory (Carya texana), elm species (Ulmus spp.) and others. The shrub layer was potentially diverse with saplings of the tree layer along with whitebrush (Aloysia gratissima), lotebush (Ziziphus obtusifolia), algerita (Mahonia trifoliata), Texas persimmon (Diospyros texana), prickly pear cactus (Opuntia spp.) and others.
With the exception of Ashe juniper, all native woody species found in the Central Basin readily resprout following fire. This trait has frustrated managers and played an important role in driving sites towards the Shrubland State. High numbers of fire sprouting shrubs make shrubland communities very resilient.
An important aspect of this site is the relationship of mature hardwood trees to each of the communities. Mature hardwoods are very resilient and remain constant whether surrounded by reference community grasslands, degraded grasslands, native-dominated shrublands, or invasive-dominated shrublands. Their presence or absence is not driven by grazing management and generally only slightly by prescribed fire. They remain relatively stable over a short management period (5-10 years) unless removed by mechanical or chemical means. Throughout this ecological site, mature oaks can occur in any of the communities if they were not historically removed. They are most likely to occur in mottes and remain relatively constant regardless of what is occurring in the rest of the community, particularly in the understory. Communities will have an absence of hardwoods if the hardwoods were harvested, burned, chained, or sprayed at some point. Once the hardwoods are removed, it is not easy to return to the Savannah State due to the difficulty, expense, and time involved.
Hardwoods were frequently removed from this site during the European settlement period due to their high value for construction and firewood. Additionally, many examples exist where hardwoods were removed as part of a broad scale brush removal program. This was done with chaining, herbicides, root plowing, and other general means.
Oak mottes on this site formed under different conditions than currently found. This may be due to climate shift or increased competition from aggressive shrub species. However, while reestablishment is slow, there are many examples of second-growth hardwood woodlands on this site. Hardwoods eventually reestablish when there is a lack of fire or tree clearing.
Infection of live oak by oak wilt (Ceratocystis fagacearum) has lead to the death of many individuals and mottes. An increase in tree density and the grafting of roots amongst individuals has facilitated the spread of the pathogen, which is transmitted primarily through root connections (Appel 1995).
Ashe juniper (Juniperus ashei), which is very abundant on the surrounding limestone derived soils of the Edwards Plateau, is relatively uncommon in the Central Basin, but it is found scattered across the Central Basin as infrequent individuals or mottes. Observation indicates that it has been increasing in population and extent within the Central Basin during the past two decades (Walter and Wyatt 1982). Juniper has the ability to take over large tracts of land as near monocultures, known as “cedar breaks.”
Even reference sites show the influence of introduced species. King Ranch bluestem (Bothriochloa ischaemum) has become almost ubiquitous, occurring on sites where it has not been seeded. It tends to replace little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium) and can function similarly in the community as far as structure, size and soil-holding capacity. However, unlike little bluestem, King Ranch bluestem acts like an invader and moves to unoccupied areas.
The large ungulate fauna of the region prior to settlement consisted of bison (Bos bison), pronghorn antelope (Antilocarpa americana) and white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Bison and pronghorn occasionally occurred in large numbers and may have intensively grazed the rangelands for short periods. However, they were largely migratory and free-roaming, so that when the forage became limited they moved on, often not to return for long periods. Their long-term impacts on the plant communities were considered to be relatively minor and may have had positive influences on production and diversity (Knapp et al. 1999, Fuhlendorf and Engle 2001).
While archeological evidence indicates that bison occurred in the region, there is also evidence of centuries of absence (Dillehay 1974). In addition, their numbers may have varied seasonally as herds migrated. When present, bison may have grazed certain areas heavily and then moved on. The infrequent but intense, short-duration grazing by these species suppressed woody species and invigorated herbaceous species (Eidson and Smeins 1999). After a burn, they would intensely graze the burn until no forages remained. Then, they moved off, probably not returning until the next fire cycle, which could have been 5 to 10 years. This suggests heavy short-term grazing followed by long rest periods. Activities of other native herbivores (termites, cutter ants, soil nematodes, kangaroo rats) also influenced vegetation productivity and dynamics.
Currently, white-tailed deer are the primary native large herbivores. At settlement, large numbers of deer occurred, but as human populations increased (with unregulated harvest) their numbers declined substantially. Eventually, laws and restrictions on deer harvest were put in place which assisted in the recovery of the species. Females were not harvested for several decades following the implementation of hunting laws, which helped create population booms. In addition, suppression of fire favored woody plants which provided additional browse and cover for the deer. Due to their impacts on livestock production, large predators (red wolves (Canis rufus), mountain lions (Felis concolor), black bears (Ursus americanus) and eventually coyotes (Canis latrins)) were reduced in numbers or eliminated (Schmidly 2002).
The screwworm (Cochilomyia hominivorax) was essentially eradicated by the mid-1960s, and while this was immensely helpful to the livestock industry, this removed a significant control on deer populations (Teer, Thomas & Walker 1965, Bushland 1985).
Recently, increased management of the deer herd, because of their economic importance through lease hunting, has decreased deer populations with the objectives of improving individual deer quality and improving habitat. High fences, controlled harvest based on numbers, sex ratios, condition and monitoring of habitat quality have been effective in managing the deer herd on individual properties. However, across the Central Basin, excess numbers still exist which may lead to habitat degradation and significant die-offs during stress periods such as extended droughts.
The Central Basin is home to a variety of non-indigenous (exotic) ungulates, mostly introduced for hunting (Schmidly 2002). These animals are important sources of income to some landowners, but as with the white-tailed deer, their populations must be managed to prevent degradation of the habitat for themselves as well as for the diversity of native wildlife in the area. Many other species of medium and small sized mammals, birds, and insects can have significant influences on the plant communities in terms of pollination, herbivory, seed dispersal, and creation of local disturbance patches, all of which contribute to the plant species diversity.
Supplemental feeding of deer and exotics can also contribute to range degradation if it allows survival of excess numbers of animals.
Feral hogs have become well established within the Central Basin. Hogs use all of the ecological sites within MLRA 82. They cause considerable damage to soils and vegetation.
The faunal array of the Central Basin changed radically with the introduction of domestic species. Early on, wild mustangs released from early Spanish settlements roamed in large herds and had significant impacts on the vegetation. Later in the 19th century, cattle, sheep, goats, mules, and hogs were introduced. The pristine rangeland appeared to provide unlimited forage but as the ranges were fenced and overstocked they were degraded. The productivity of the rangeland began to decline, carrying capacity was reduced, and periodic die-offs of livestock occurred. Generally, the mid and taller grasses were replaced by shortgrasses and perennial grasses, and forbs were replaced by annuals. These changes not only reduced production but also in many instances caused permanent alteration of the ecological sites due to soil erosion, organic matter loss, compaction, moisture regime change, and other factors which altered many soil and hydrologic processes. This often precluded their recovery to pre-European conditions (Smith 1899, Smeins, Fuhlendorf and Taylor 1997). Not only did livestock overgraze the forage, but they also contributed to seed dispersal of some woody plants, particularly honey mesquite, which exacerbated its increase on the rangelands.
Historical accounts prior to the 1800s also identify grazing by herds of wild horses, followed by heavy grazing by sheep and cattle as settlement progressed. Grazing on early ranches changed natural graze-rest cycles to continuous grazing and stocking rates exceeded the carrying capacity. By the early 1800s cattle, sheep, and goat numbers appear to have been quite high in the Central Basin, resulting in heavy, year-round grazing (Lehman 1969). Sheep numbers peaked at 10.8 million head in 1943 and stood at about 1.2 million in 2000. Goat numbers in Texas around 1900 were around 100,000. They peaked in 1965 at 4.6 million and were 345,000 in 2000 (Texas Online). The Central Basin and Edwards Plateau region, because of its climate and diverse vegetation, was the mainstay of the Texas sheep and goat industry.
Today, beef cattle and horses are the primary grazers in the area. Goats used primarily for meat production are locally important, and their numbers have increased. Sheep remain a minor but still important part of livestock grazing in the Central Basin. White-tailed deer, wild turkey, bobwhite quail, and doves are major commercial wildlife species, and hunting leases are a major source of income for many landowners. While the Central Basin ecological sites have changed in many ways since settlement, opportunities exist to produce products and provide income while conserving and sustaining the long-term stability and productivity of the area.
Homesteads and communities developed along with ranching, and many ecological sites within MLRA 82 were converted to cropland for wheat (Triticum spp.), oats (Avena spp.), forage, and peanuts (Arachis hypogaea), and other products needed for local consumption or for cash crops. This conversion effectively eliminated the native plant communities due to land clearing and the harvest of larger trees, used for building construction among other uses.
Over time, as many of the croplands became degraded, and along with the rangeland that had been overused, introduced forages were brought in to assist with soil and water conservation and to increase productivity. Coastal bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon), Kleingrass (Panicum coloratum), Wilman lovegrass (Eragrostis superba) and King Ranch bluestem were widely planted on many acres of old cropland and in areas with deeper soils. The latter, while effective as a soil stabilizer, has become invasive in many areas where it is unwanted and is difficult to control.
In the 1940s, mechanical and herbicide treatments began to replace fire as a control of increasing density of woody plants on the rangeland. This activity was common practice for several decades until the 1980s, when these treatments became less cost-effective. It was clear that brush management practices were treating symptoms rather than underlying problems in addition to their undesirable environmental and wildlife consequences. Sites cleared of brush regenerated rapidly and often formed thickets that were denser and of lower diversity than the original stands. This realization coupled with the fact that brush management treatments were typically expensive and short-lived, lead to the development of Integrated Brush Management Systems (Scifres et al. 1985). This approach takes a holistic, large-scale, long-term, socioeconomic, ecosystem-based approach to brush management and recognizes multiple-use options for rangeland resources including alternate classes of livestock, lease hunting, exotic game ranching, carbon credits and ecotourism.
Grazing and fire are two factors that critically influence the relative abundance of grasses and woody plants through time. The resulting reduction in abundance of late seral grasses lead to a decline in soil organic matter, a reduction in fire frequency/intensity (due to lack of fine fuels), and a shift in dominance from midgrasses (little bluestem and sideoats grama) to shortgrasses (hooded windmillgrass (Chloris cucullata) and buffalograss) and forbs (Mexican sagewort (Artemisia ludoviciana ssp. mexicana) and croton (Croton spp.)). These changes would have favored woody plants, most of which are unpalatable to livestock, and enabled them to establish and maintain dominance.
Mesquite, whitebrush, juniper, lotebush, algerita, persimmon, prickly pear, and lime pricklyash (Zanthoxylum fagar) now dominate much of the Central Basin. These woody plants are not ‘new arrivals’ but rather, are native to the region and have increased in size and abundance within their historic ranges. Factors promoting their increase in abundance since European settlement are the subject of active debate. Such factors may involve an interactive combination of changes in climate, intensification of grazing, follow up brush management and reductions in fire frequency/intensity accompanied by increases in atmospheric CO2 concentrations and nitrogen deposition since the industrial revolution (Archer 1994).
Rangeland Health Reference Worksheets have been posted for this site on the Texas NRCS website (www.tx.nrcs.usda.gov) in Section II of the eFOTG under (F) Ecological Site Descriptions (ESD’s).
State and Transition Model:
A State and Transition Model for the Granite Gravel Ecological Site (R082AY365TX) is depicted in Figure 1. Thorough descriptions of each state, transition, plant community, and pathway follow the model. Experts base this model on available experimental research, field observations, professional consensus, and interpretations. It is likely to change as knowledge increases.
Plant communities will differ across the MLRA due to the naturally occurring variability in weather, soils, and aspect. The Savannah State is the reference state for this site. It is not necessarily the management goal but can be. Other vegetative states may be desired plant communities as long as the Range Health assessments are in the moderate and above category. The biological processes on this site are complex. Therefore, representative values are presented in a land management context. The species lists are representative and are not botanical descriptions of all species occurring, or potentially occurring, on this site. They are not intended to cover every situation or the full range of conditions, species, and responses for the site.
Both percent species composition by weight and percent canopy cover are used in this ESD. Most observers find it easier to visualize or estimate percent canopy for woody species (trees and shrubs). Canopy cover drives the transitions between communities and states because of the influence of shade and interception of rainfall. Species composition by dry weight is used for describing the herbaceous community and the community as a whole. Woody species are included in species composition for the site. Calculating similarity index requires the use of species composition by dry weight.
The following diagram suggests some pathways that the vegetation on this site might take. There may be other states not shown in the diagram. This information is intended to show what might happen in a given set of circumstances; it does not mean that this would happen the same way in every instance. Local professional guidance should always be sought before pursuing a treatment scenario.
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Absence of disturbance, natural regeneration over time, and prolonged excessive grazing pressure |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Loss of vegetative cover and/or extensive soil disturbance resulting in active soil erosion |
| R2A | - | Removal of woody canopy and reintroduction of historic disturbance return intervals |
| T2A | - | Loss of vegetative cover and/or extensive soil disturbance resulting in active soil erosion |
| T3A | - | Soil stabilization and rangeland seeding. Probability of success is low. |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Savannah State
The Savannah State consists of two communities: the Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1) and the Oak Savannah Community (1.2). The Midgrass Savannah Community occurred on this ecological site in a dynamically shifting mosaic over time with the Oak Savannah Community. The majority of production occurs in late spring and early summer when temperatures and moisture are typically most suitable for growth. As conditions become warmer and drier, grasses become dormant and substantial litter accumulation occurs, making the site prone to fire. Recurrent fire (less than 10 years intervals) favors the dominant grasses and suppresses woody plants. In years without fire, leaf litter decomposes and adds organic matter to the soil, thus enhancing its fertility and water holding capacity. Prescribed grazing accelerates the process. The dominant grasses are productive below ground and are deeply rooted. Extensive root systems bind the soil to minimize erosion while enabling the dominant grasses to access stored soil moisture. Prior to settlement, Granite Gravel sites had a savannah appearance with open areas dominated by midgrasses (little bluestem and sideoats grama) interspersed with scattered mottes dominated by oaks. The Midgrass Savannah (1.1) may have up to 20 percent canopy cover while the Oak Woodland will have more than 20 percent woody canopy. Relatively frequent fires (7-12 year mean fire return interval) (Frost 1998) maintained the open areas by killing shrubs that were not yet to a fire resistant height. Mature hardwoods found in the mottes were long-lived and resistant to ground fires. Fires may have been natural or human-induced. When fires were frequent on the savannah, most fires burned only the understory and pruning, leaving mottes of trees. Even with proper grazing and favorable climate conditions, lack of fire for 8-15 years will allow trees and shrubs to increase in canopy to reach the 20 percent level that indicates the shift to the Oak Savannah Community (1.2). This transition is not dependent on degradation of the herbaceous community, but on the lack of some form of brush control. Shrub species would increase within the grassland portion of the savannah and within the understory of the mottes following fire. Fine fuels were continuous and of sufficient quantity to allow fire to slow the establishment of young brush and trees but not of sufficient quantity to create crown fires that would scorch mature trees. Therefore, the savannah would be relatively open for a short period following a fire, shrubs would begin to reestablish reducing the savannah appearance, fire would return in 10 years or less, this fire would slow the growth of young shrubs and trees without reducing the cover of mature trees. This allows for returning the savannah appearance and shifting species composition back to dominance by little bluestem and other grasses. Occasionally a site would not burn for a period long enough for trees to grow to a fire resistant stage within the grassland portion of the savannah. As these trees matured, the fine fuel understory would decrease, reducing the ability of fires to grow large enough (and hot enough) to reduce the cover of mature trees. This long-term lack of fire (25 - 50 years) would allow large trees to fill in open areas shifting the site to a woodland appearance. Once the site had dense tree cover, the site is resistant to fires and a very resilient woodland community would develop. The absence of fire, the Oak Savannah Community (1.2) dominated the site with a near closed canopy stand of hardwoods, including oak (Quercus spp.) and pecan (Carya spp.). The two communities in the Savannah State shifted between one another depending on the frequency and intensity of fire, grazing, and drought. The primary influence on the understory is grazing management and the primary influence on the overstory is fire. This allows the understory and overstory to react independently, i.e., trees can increase to the point where they dominate a site even if the understory component remains vigorous and intact. Grazing management alone cannot maintain the site in the Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1). It was rare that a dense woodland community would shift to a grassland or savannah community. A die-off could occur due to disease or to a very hot fire that spread to the tree crowns and killed mature trees, events that typically only occur every 300 to 1,000 years. Following a severe fire, the site would have a grassland appearance for a few years as shrubs and trees resprouted or grew from seed. Shrubs and trees comprise a portion of both plant communities in the Savannah State (1.0), hence woody propagules are present. The Savannah State always has the potential for shrub dominance without fire. Mann (2004) discussed the importance of human-caused fire as an important factor in maintaining open grasslands before European settlement. The relationship between the two communities in the Savannah State remains similar post-settlement. However, natural fires become less frequent and less widespread as human population density increases. “Cool”, slow-burning natural fires have become basically non-existent, because they are relatively easy to put out using modern firefighting equipment and techniques. Without fire, the reference savannah community becomes less resilient. Unless managers practice some method of brush control, shrub species will increase in the grassland portion of the savannah and in the understory of the oak mottes. Brush control can play the role that natural fires played pre-settlement. However, it is difficult to manage in an ecological and economic matter on a small scale, as this site is rapidly repopulated by shrubs and trees without fire or brush management. Brush control may be prescribed fire, mechanical, chemical, or targeted grazing (generally by goats, although some instances exist in the Central Basin where exotic wildlife species or overpopulated white-tailed deer reduce woody cover). The savannah is more often observed with mowing or haying than with grazing management. There are examples of this site being maintained as a savannah with introduced hay fields and mottes of trees.
Dominant plant species
-
post oak (Quercus stellata), tree
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
-
sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), grass
Community 1.1
Midgrass Savannah Community
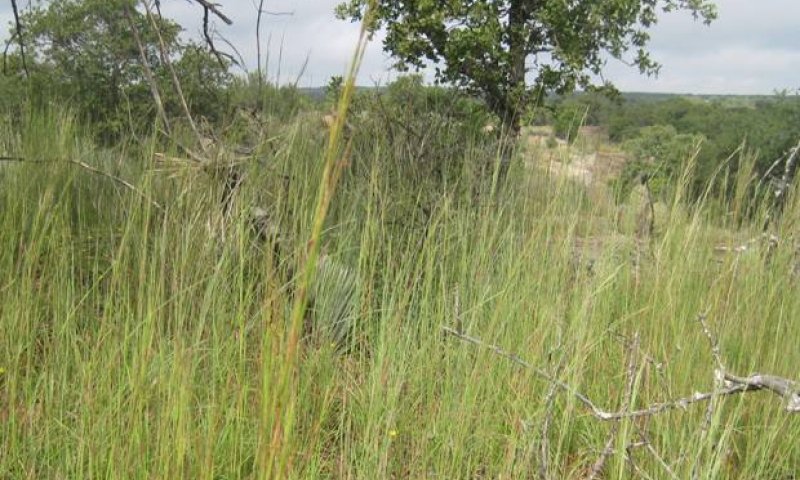

Figure 9. 1.1 Midgrass Savannah Community
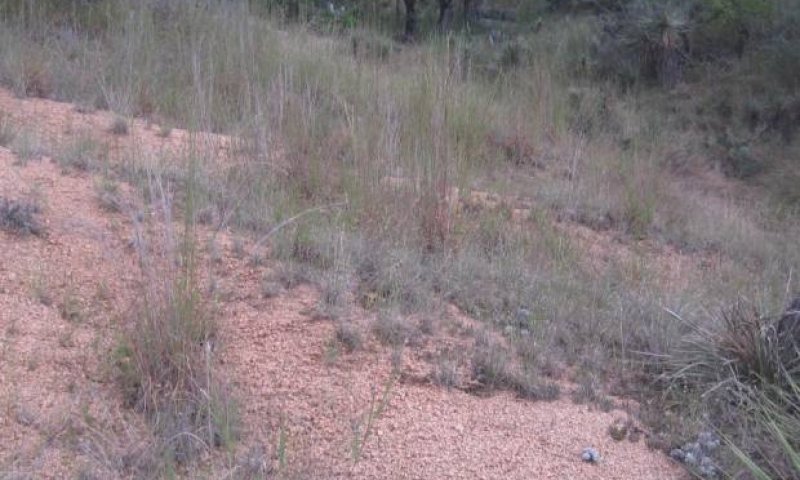

Figure 10. 1.1 Midgrass Savannah Community (2)
The Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1), or reference community, is an open savannah characterized by expanses of grassland (dominated by little bluestem and sideoats grama) interspersed with scattered mottes dominated by mature oak trees. This community requires relatively frequent fire and/or brush control (every 5 to 10 years) to maintain the savannah appearance. Without fire, shrubs will begin to dominate the open areas eventually resulting in a nearly closed canopy of shrubs and trees. The Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1) remains the presumed reference community. It is possible to have a reference community understory with a savannah appearance but the woody portion of the savannah is populated by shrub and tree species other than the native hardwoods. The community can be maintained through the implementation of fire and brush management, combined with properly managed grazing that provides adequate growing season deferment to allow establishment of midgrass propagules and/or the recovery of vigor of stressed plants. Little bluestem, sideoats grama, meadow dropseed, vine mesquite, and plains lovegrass dominate the herbaceous component of the site. Forbs commonly found on the site include Mexican sagewort, bundleflower, Engelmann’s daisy, western ragweed, orange zexmenia, and sensitive briar. Shrub and tree species found in the Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1) include species of oaks, whitebrush, pricklypear, and honey mesquite. Shrubs continually increase in the open areas of the savannah and in the understory of the mottes. This pressure to move towards a woodland or shrubland community if further increased when aggressive, invasive shrubs become a part of the community. Although large, land-clearing crown fires are relatively rare, similar impacts to the mature hardwoods occur when trees are cleared from the site by logging, chaining, or spraying. If a manager combines woodland removal with proper grazing management and ongoing, maintenance level brush control, a woodland community could shift to a grassland community, mimicking the natural shift that occurred with large land-clearing fires. Maintaining the grassland would require diligent brush control. There are examples where intensive targeted grazing with goats has maintained a grassland or savannah community on this site. The grassland and open savannah communities have proven to be difficult to manage on this site. This is due to the difficulty in combining effective brush management with grazing management that provides for grazing events of proper intensity and sufficient periods of deferment. Due to the difficulty of managing native species in the savannah community, many times this site was seeded with introduced grass species.
Figure 11. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 960 | 1200 | 1440 |
| Forb | 120 | 150 | 180 |
| Tree | 95 | 120 | 145 |
| Shrub/Vine | 25 | 30 | 35 |
| Total | 1200 | 1500 | 1800 |
Figure 12. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX4410, Mid/Tallgrass Oak Savannah with <5% Woody Canopy. Mid and tallgrasses with oak savannah having less than 5% woody canopy cover..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 2 | 3 | 5 | 13 | 23 | 15 | 4 | 5 | 15 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
Community 1.2
Oak Savannah Community
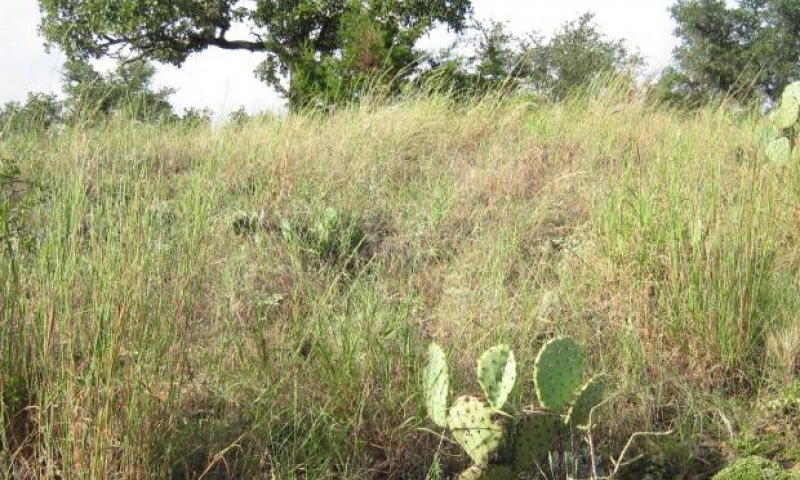

Figure 13. 1.2 Oak Savannah Community
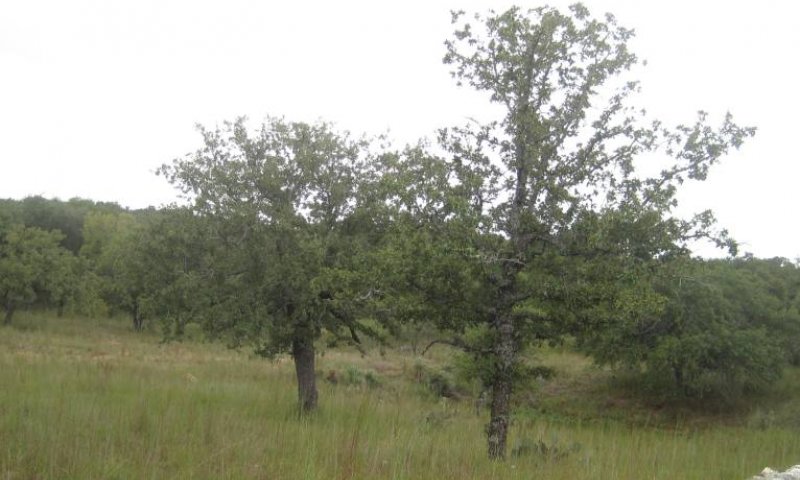

Figure 14. 1.2 Oak Savannah Community (2)
The Oak Savannah Community (1.2) is presumed to have historically covered a substantial minority of this ecological site. Over time the oak mottes would expand while mature trees and shrubs increased in canopy cover. The understory vegetation in the openings between trees would remain similar in composition to that of the Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1). As tree density increased, cool-season grasses and forbs would increase in species composition. Cool-season species increase as the distance to drainages decreases due to increased tree cover and shade near drainages. Dominant species in the Oak Woodland Community are similar to those found in the Midgrass Savannah Community, but species composition shifts to dominance by trees and shrubs. There is also an increase in cool-season grasses and forbs. Texas wintergrass and Canada wildrye increase in production. There also tends to be an increase in the number of shrubs growing in the understory of the hardwoods and in the open areas of the savannah.
Figure 15. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 6. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 600 | 750 | 900 |
| Tree | 300 | 375 | 450 |
| Shrub/Vine | 180 | 225 | 270 |
| Forb | 120 | 150 | 180 |
| Total | 1200 | 1500 | 1800 |
Figure 16. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX4411, Midgrass Savannah with Woody Encroachment. Midgrass Savannah with Woody Encroachment..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 13 | 22 | 15 | 5 | 3 | 15 | 7 | 5 | 4 |
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2


The driver for community shift 1.1A is lack of fire and/or brush control to maintain the woody component as mottes of mature oak and other hardwoods. Native woody species canopy exceeding 20 percent indicates a shift to the Oak Woodland Community (1.2). The Midgrass Savannah Community requires fire and/or brush control to maintain the savannah appearance with woody species cover below 20 percent. Regardless of the composition and vigor of the herbaceous component, this community will shift to the Oak Savannah Community without effective brush control. This shift can occur even with proper grazing management and if the herbaceous component remains vigorous. Brown and Archer (1999) concluded that even with a healthy and dense stand of grasses, woody species would populate the site and eventually dominate the community. Because the woody species that dominate in the Oak Savannah Community (1.2) are native species that occur as part of the reference community, the shift to the Oak Savannah Community is a linear process with shrubs increasing soon after fire or brush control ceases. This is a continual process. There is a 5- or 10-year window before shrubs begin to increase followed by a rapid transition to the Oak Savannah Community. The drivers of the transition (lack of fire and lack of brush control) constantly pressure the system toward the Oak Woodland Community.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1


Fire/brush control and proper grazing management drive community shift 1.2A.The shift from Oak Savannah Community (1.2) to Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1) is thought to have been infrequent historically, as large, crowning fires would be required to remove mature trees found in the Oak Savannah Community. Smaller repeated fires over long periods of time would result in some bark damage to older oaks and subsequent introduction of disease to the tree, resulting in hollow or dead trees. The Oak Savannah Community can return to the Midgrass Savannah Community with fire and/or brush management combined with proper grazing management that provides sufficient critical growing season deferment in combination with proper grazing intensity. Favorable moisture conditions will facilitate or accelerate this transition.
Conservation practices
| Brush Management | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Burning | |
| Prescribed Grazing |
State 2
Shrubland State
The Shrubland State is characterized by trees, a significant shrub cover, and a shortgrass- understory. Two communities represent this state and are distinguished by the amount of shrubs present. The Shortgrass Savannah Community (2.1) is characterized by having less than 25% canopy cover by woody species. The Shrubland Community (2.2) is characterized by having more than 25% woody canopy cover. The understory may be similar in both. Both communities in the Shrubland State have typically lost the savannah appearance. The hardwoods that made up a portion of the plant community in the Savannah State (1.0) may or may not be present in the Shrubland State (2.0). The transition to the Shrubland State will not cause a decrease in the number of hardwoods. However, the Shrubland State often occurs on lands that have been cleared of brush and trees at some point in the past. Trees were removed for lumber or firewood, in some cases to clear the land for pasture or farming. Rootplowing had the same effect as tillage, converting the site to a grassland immediately following plowing but leaving the site subject to rapid invasion by fast-growing shrub species. This transition may respond like agricultural conversion and may have been accompanied by shifts in soil chemistry and structure. Rootplowing is likely to shift the community to the Oak Savannah Community (2.2). Once invasive woody species begin to establish, returning fully to the native community is difficult, but it is possible to return to a similar plant community. The understory of the Shrubland State tends to be dominated by shortgrasses and lower-palatability forbs. The communities in the Shrubland State have a degraded herbaceous community when compared to the Savannah State. This is generally a result of long-term improper grazing management. One factor that leads to overgrazing on this site is the failure to reduce the stocking rate as woody cover increases (loss of grazeable acres). Increased woody cover results in less forage being available. Unless stocking rates are reduced, the stocking pressure on the remaining forage increases, which increases the likelihood of palatable plants being overgrazed, losing vigor, and being grazed out of the community. At the same time, less palatable plants gain a comparative advantage and increase their representation in species composition.
Dominant plant species
-
mesquite (Prosopis), shrub
-
juniper (Juniperus), shrub
-
red grama (Bouteloua trifida), grass
-
hairy grama (Bouteloua hirsuta), grass
Community 2.1
Shortgrass Savannah Community
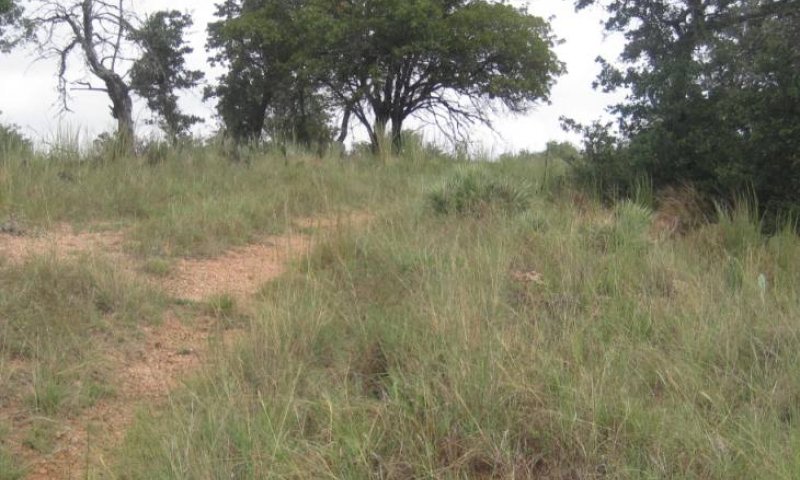

Figure 17. 2.1 Shortgrass Savannah Community
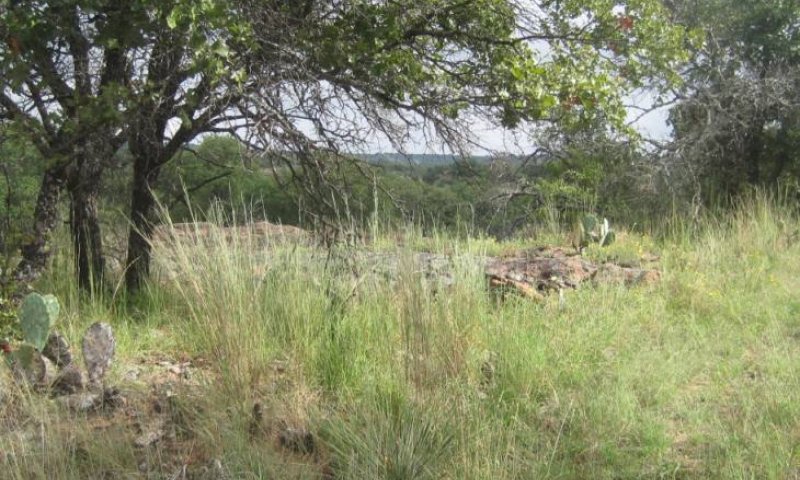

Figure 18. 2.1 Shortgrass Savannah Community (2)
The Shortgrass Savannah Community (2.1) typically results from improper livestock grazing management over a long period of time combined with a lack of brush control. This site is characterized by a degraded herbaceous community with shrub and tree canopy cover less than 25 percent. Woody species increase on the site regardless of grazing management (except for goats). Growing-season stress, usually from overgrazing, causes reduction in vigor and survival of palatable midgrasses, which allows less palatable midgrasses and forbs, along with shortgrasses to increase in the herbaceous community. However, lack of fire and/or brush management allows for an increase in woody canopy cover between 20-50 percent of mesquite, juniper, persimmon, and whitebrush. Midgrasses such as Arizona cottontop and other desirable midgrasses will dominate this site. With the advent of heavy, continuous grazing, mid-height grasses give way to shortgrasses such as buffalograss and hooded windmillgrass. Perennial forbs such as orange zexmenia (Wedelia texana) increase in relative abundance. With continued grazing, these give way to red grama (Bouteloua trifida), hairy grama (Bouteloua hirsuta), hairy tridens (Erioneuron pilosum), three-awn, slim tridens (Tridens muticus), and annual forbs. Drought interacts with grazing to trigger the transition. Heavy, continuous grazing will reduce plant cover, litter, and mulch. Bare ground will increase and expose the soil to erosion. Litter and mulch will move off-site as plant cover declines. This community requires brush management to maintain. But like the Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1), there will be constant pressure for the shrubs to increase past the 25 percent canopy layer that indicates the shift to the Shrubland Community (2.2). To control woody species populations, prescribed grazing, browsing, and fire can be used to control smaller shrubs and trees, while mechanical removal of larger shrubs and trees may be necessary in older stands. A prescribed fire will help control shrubs not yet of reproductive capacity but is questionable for use because of the lack of grass fuel to carry the fire. This will help in preventing the site from transitioning to a Shrubland Community (2.2). Fire may be required every 3-5 years to maintain the woody canopy cover. Winter and/or summer fires can benefit this plant community. A winter prescribed fire will help to kill shorter brush, while summer fires tend to burn hotter and open the canopy layer. When conducting a summer prescribed fire, more risk is associated than a winter prescribed fire. Care must be taken when conducting both a winter and summer prescribed fire.
Figure 19. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 7. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrub/Vine | 225 | 280 | 335 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 190 | 240 | 290 |
| Tree | 130 | 160 | 190 |
| Forb | 95 | 120 | 145 |
| Total | 640 | 800 | 960 |
Figure 20. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX4412, Shortgrass/Mixed-brush Community. Shortgrass dominant with mixed-brush species..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 13 | 22 | 15 | 5 | 3 | 15 | 7 | 5 | 4 |
Community 2.2
Shrubland Community
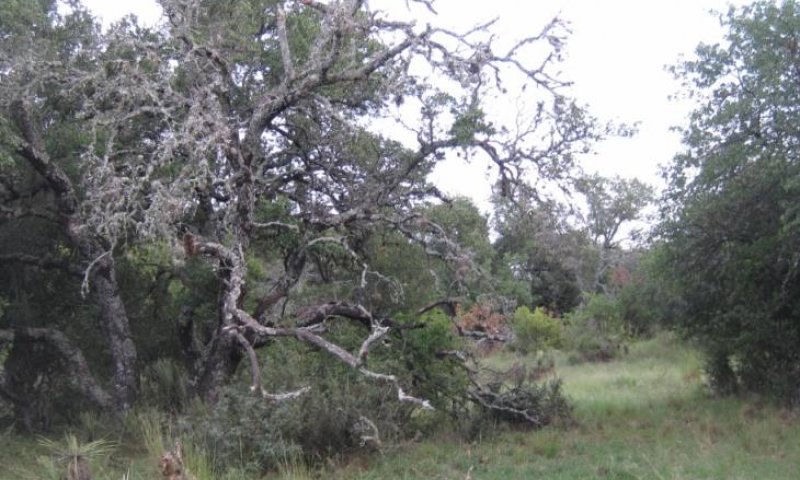

Figure 21. 2.2 Shrubland Community
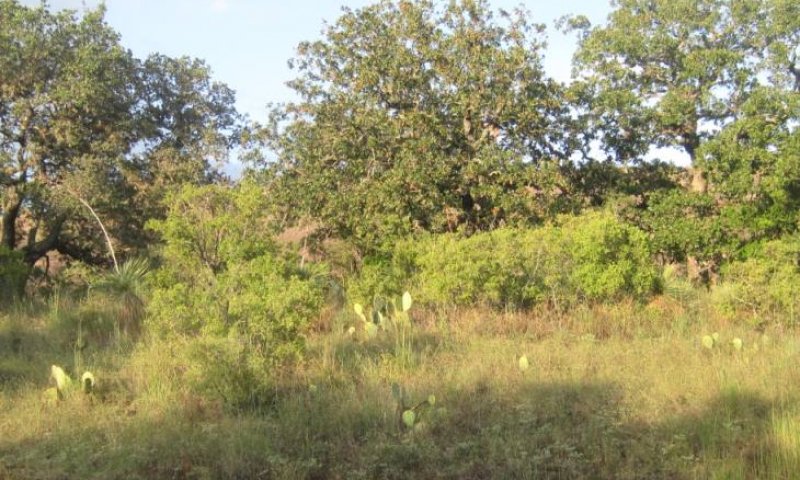

Figure 22. 2.2 Shrubland Community (2)
The Shrubland Community (2.1) has over 25 percent woody plant canopy, dominated by woody species. The community loses its savannah appearance as shrubs begin to fill the open grassland portion of the savannah. Shade from overstory is the driving factor. This community results from the lack of effective brush control. Production of the overstory canopy has increased by a similar amount to the decrease in herbaceous production. Unpalatable woody species have increased in size and density. The Shrubland Community typically has multiple shrub species: Texas persimmon, mesquite, whitebrush, catclaw, yucca, and/or juniper. Texas wintergrass (Nassella leucotricha), three-awns (Aristida spp.) and annuals increase in the shade of the trees. Plant vigor and productivity of grass species is reduced due to shade. Shade is a driving factor for the understory plant community. Without brush control, tree canopy will continue to increase until canopy cover approaches 80 percent. The Shrubland Community is common on Granite Gravel sites. Unless managers practice effective, ongoing brush control this community will remain or reestablish. In the absence of fire and brush management, a highly stable and resilient Woodland Community (2.2) develops as woody patches increase in abundance and coalesce with each other. Shrubs mix with oaks to create a canopy cover of greater than 30 percent. Ground cover and herbaceous production beneath shrub canopies is minimal, but soil organic carbon and nitrogen levels are enhanced. A sparsely vegetated community is not stable on this site. Shrubs, undesirable grasses and forbs reestablish relatively quickly following disturbance. Because of the availability of invasives with low palatability, this site rarely stays barren. There are examples that are degraded but not dominated by brush but these examples tend to be quickly reinvaded by brush. In this plant community, annual production is dominated by woody species. Goats and deer can find fair food value if browse plants have not been grazed excessively. Forage quantity and quality for cattle is low. Intensive treatment is required to affect restoration back to the Savannah State (1.0). Prescribed burning may not be possible until woody cover is reduced by herbicides or mechanical treatments to the point that grasses (fine fuels) can establish. Brush treatment tends to be short-lived. Observation shows that even effective treatment will require constant maintenance to suppress brush reestablishment. Without maintenance, canopy cover may exceed 30 percent in 3 to 5 years.
Figure 23. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 8. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrub/Vine | 480 | 600 | 720 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 240 | 300 | 360 |
| Tree | 145 | 180 | 215 |
| Forb | 95 | 120 | 145 |
| Total | 960 | 1200 | 1440 |
Figure 24. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX4413, Shortgrass/Annuals Woodland Community. Woodland community with shortgrasses and annuals..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 3 | 3 | 7 | 13 | 20 | 15 | 7 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 5 |
Pathway 2.1A
Community 2.1 to 2.2


The driver for community phase pathway 2.1A is lack of fire and/or brush control, and improper grazing management. Without brush control (including fire), the Shortgrass Savannah Community (2.1) will shift to the Shrubland Community (2.2). Shrubs will continue to increase until they reach 25 percent canopy cover. Once shrubs have more than 25 percent canopy cover, management back to the Altered Savannah Community becomes more difficult due to the amount of energy required to remove dense brush. Overgrazing and/or long-term drought (or other growing season stress) will accelerate this shift from the Altered Savannah Community (2.1) to a Shrubland Community (2.2). Increasing growing season stress will reduce the density and vigor of the herbaceous component, which will allow additional opportunity for shrubs to establish. The understory may be a mix of shortgrasses and cool-season grasses. Even with proper grazing, in the absence of fire, the woody component will increase to the point that the herbaceous component will decline in production and shift in composition toward sedges, short grasses, cool-season grasses, and forbs suited to grow in shaded conditions with reduced available soil moisture.
Pathway 2.2A
Community 2.2 to 2.1


The driver for community shift 2.2A is fire and/or brush control, with proper grazing management. Extensive and selective brush management can reduce the woody component of the Shrubland Community (2.2) below the community shift level of 25 percent woody canopy cover. It may be difficult to shift back to the Shortgrass Savannah Community (2.1) with fire alone due to the lack of fuel provided by the understory and height of the canopy cover. Fire can reduce seedlings of brush species if the seedling is younger than 2 years or the budding zone has not transitioned below the soil surface (Kramp, et. al. 1999). Fire and/or brush management will be required to maintain woody canopy cover below the 25 percent level. The limitations with fire are amplified if the understory transitions to cool-season grasses. If the herbaceous component has transitioned to shortgrasses and low forbs, proper grazing management (combined with favorable moisture conditions and adequate seed source) will be necessary to facilitate the shift of the understory component in the Shrubland Community (2.2) to the Shortgrass Savannah Plant Community (2.1).
Conservation practices
| Brush Management | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Burning | |
| Prescribed Grazing | |
| Grazing Land Mechanical Treatment | |
| Planned Grazing System | |
| Native Plant Community Restoration and Management |
State 3
Eroded State
This state is characterized by a single community, the Eroded Community (3.1). The Eroded State has the potential to be a terminal state. Due to the relatively high risk of severe soil erosion of the soil type, this site can erode to the point where there is a loss of soil functionality. When this level of erosion occurs, the site loses soil structure, soil fertility, organic matter, and/or soil microflora. There are examples of the loss of the A and B horizons and some with the soil eroded to bedrock. Once the site loses soil horizons or soil functions, it is very difficult or impossible to return the site to one of the other States, resulting in State 3 being a terminal state. Steeper portions of this site are subject to severe erosion when the plant cover is disturbed. Some examples of the site have eroded to the granite bedrock.
Dominant plant species
-
mesquite (Prosopis), shrub
-
sumac (Rhus), shrub
-
whitebrush (Aloysia gratissima), shrub
Community 3.1
Eroded Community
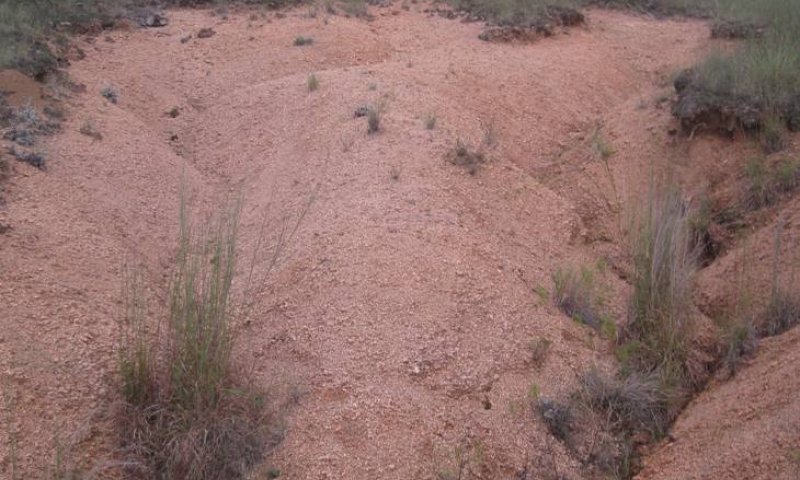

Figure 25. 3.1 Eroded Community
The Eroded Community (3.1) is characterized by a variety of thick shrubs and a small component of the herbaceous community with few palatable perennial species present. The shrubs may be dense in areas where shrubs can find adequate moisture in the eroded soils. This community occurs only where significant loss of soil depth, function, or fertility has occurred. Due to their aggressive nature, invasive shrubs, grasses, and forbs reestablish relatively quickly following disturbance if there is adequate soil left. This community is frequently associated with significant soil erosion and/or disturbance. Erosion creates a loss of soil structure and fertility and in severe conditions may expose bedrock. Exposed granite outcrops may be present in areas with steep slopes. When slopes exceed 10 percent, areas erode easily due to the lack of herbaceous vegetative cover. Soils may erode to the point that they can no longer be managed back to any of the other states.
Figure 26. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 9. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrub/Vine | 155 | 190 | 225 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 75 | 95 | 115 |
| Forb | 70 | 90 | 110 |
| Tree | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Total | 300 | 375 | 451 |
Figure 27. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX4418, Eroded Community. Eroded Community with <15% herbaceous canopy cover..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 13 | 22 | 15 | 5 | 3 | 15 | 7 | 5 | 4 |
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
The driver for Transition T1A is a lack of fire or brush management coupled with overgrazing. Overgrazing, lack of fire, and/or improper brush management will result in the site crossing a threshold to the Shrubland State (2.0) characterized by shortgrasses, unpalatable grasses and forbs, annual grasses and forbs, and shrubby species. Bare ground, erosion, and water flow patterns will increase, and forage production will decline. Without regular fire, woody species will increase in size, density, and canopy cover, reducing production from herbaceous species. Woody species composition may vary greatly depending largely on management. Trees will be present if they were not historically removed. More frequently, the woody component is made up of many species of widely scattered shrubs. Overgrazing causes a loss of dominant midgrasses and forbs from the savannah. This transition is indicated by a decrease of little bluestem and sideoats grama to less than 10 percent of species composition of the herbaceous community. Once these species are lost from the community or present only in trace amounts (typically with low vigor), grazing management alone cannot create a shift back to the reference community. At this point, a threshold has been crossed indicating a change in state. Degradation of the herbaceous community combined with the aggressive nature of shrubs creates a loss in the savannah structure on the site. The grassland portion is reduced and the trees exist in competition with aggressive shrubs. This competition limits the ability of trees to reproduce and increase. The aggressive nature of shrubs keeps the Savannah State (1.0) at high risk of transition to the Shrubland State (2.0). The possible exception would be the skilled use of goats to target and suppress the shrubs. The trigger for this transition comes when shrubs reach reproductive capacity. Overgrazing, prolonged drought, no fire, and lack of brush management and a warming climate will provide a competitive advantage to shrubs.
Transition T1B
State 1 to 3
When the Granite Gravel site is subjected to inappropriate management, the effects may be seen in a loss of vegetative cover followed by a loss of soil. In some cases, this erosion can be extreme enough to result in the loss of the A (and even B) horizons. Severe soil degradation can be caused by abusive grazing, mismanaged brush control, or other soil-disturbing activities including rock harvest or gravel mining. Long-term drought may also trigger this transition from the Savannah State or exacerbate the effects of inappropriate grazing management on the Granite Gravel site. This loss of soil accompanies the loss of the vegetative cover associated with this site.
Restoration pathway R2A
State 2 to 1
The driver for Restoration Pathway R2A is fire and/or brush control combined with natural restoration of the herbaceous community or active management of the herbaceous restoration process (range seeding). Restoration may require aggressive treatment of invader species. Restoration of the Shrubland State to the Savannah State (R2A) requires substantial energy input. An integrated approach of biological, mechanical and chemical brush control in combination with prescribed fire, proper grazing, and favorable growing conditions is the most economical means of creating and maintaining the desired plant community. A long-term prescribed fire program may sufficiently reduce brush density to a level below the threshold of the Savannah State (1.0). However, the fire program will have to be aggressive because many of the woody species on this site are resprouters following fire and fuel loading is marginal. Establishment of native grasses is difficult and dependent upon natural seeding from remnant patches and seed banks. If remnant populations of midgrasses and desirable forbs are not present at sufficient levels, range planting will be necessary to restore a desirable herbaceous plant community. Proper grazing management and stocking rates maintain the herbaceous layer in this state. With proper grazing management, midgrasses can regain dominance on the site and undesirable trends in soil organic matter, fertility, temperature, and erosion can be arrested and reversed. Re-growth of established woody plants will slow and it will become more difficult for new plants to establish. The extent to which the original Midgrass/Oak Savannah Community (1.1) can be re-established will depend on the extent to which soil physical and chemical properties were altered during retrogression (Heitschmidt and Stuth 1991).
Conservation practices
| Brush Management | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Burning | |
| Prescribed Grazing | |
| Grazing Land Mechanical Treatment |
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
The driver for this transition is non-selective brush control through chaining, root plowing, or broadcast herbicides. This action removes the trees. Contributing drivers include heavy browsing by wildlife, sheep, and goats and overgrazing by cattle. The resprouting shrubs are generally not palatable forage. Severe soil degradation can result. A loss of vegetative cover can be followed by a loss of soil. In some cases, this erosion can be extreme enough to result in the loss of the A (and even B) horizons. Mottes of trees may or may not survive this transition. Severe soil degradation can be caused by abusive grazing, mismanaged brush control, poor farming techniques or other soil-disturbing activities including rock harvest. Trails from livestock or wildlife easily contribute to the erosion of this state. This loss of soil results in or accompanies the loss of the vegetative cover associated with this site. Long-term drought may also trigger this transition from the Shrubland State or exacerbate the effects of inappropriate grazing management on the Granite Gravel site.
Transition T3A
State 3 to 2
The Eroded State is frequently a terminal state unless range restoration processes are put in place. Restorations to the Shrubland State (2.0) are uncommon due to the pronounced loss of soil chemistry and structure and the decline of native plant communities. Severe loss of soil and soil properties will make restoration difficult and expensive, as it may require seedbed preparation and seeding of native grass and forb species.
Conservation practices
| Brush Management | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Burning | |
| Prescribed Grazing | |
| Grazing Land Mechanical Treatment | |
| Range Planting | |
| Planned Grazing System | |
| Native Plant Community Restoration and Management |
Additional community tables
Table 10. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Warm-season Mid/Tallgrasses | 840–1260 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 750–1260 | – | ||
| green sprangletop | LEDU | Leptochloa dubia | 350–500 | – | ||
| silver beardgrass | BOLAT | Bothriochloa laguroides ssp. torreyana | 200–400 | – | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 150–300 | – | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 200–300 | – | ||
| sand lovegrass | ERTR3 | Eragrostis trichodes | 100–200 | – | ||
| vine mesquite | PAOB | Panicum obtusum | 100–200 | – | ||
| plains bristlegrass | SEVU2 | Setaria vulpiseta | 100–200 | – | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 100–200 | – | ||
| composite dropseed | SPCO16 | Sporobolus compositus | 100–200 | – | ||
| Indiangrass | SONU2 | Sorghastrum nutans | 75–150 | – | ||
| Arizona cottontop | DICA8 | Digitaria californica | 75–150 | – | ||
| purpletop tridens | TRFL2 | Tridens flavus | 50–100 | – | ||
| switchgrass | PAVI2 | Panicum virgatum | 0–50 | – | ||
| 2 | Warm-season shortgrasses | 60–90 | ||||
| threeawn | ARIST | Aristida | 60–90 | – | ||
| buffalograss | BODA2 | Bouteloua dactyloides | 60–90 | – | ||
| hairy grama | BOHI2 | Bouteloua hirsuta | 60–90 | – | ||
| red grama | BOTR2 | Bouteloua trifida | 60–90 | – | ||
| hooded windmill grass | CHCU2 | Chloris cucullata | 60–90 | – | ||
| fall witchgrass | DICO6 | Digitaria cognata | 60–90 | – | ||
| curly-mesquite | HIBE | Hilaria belangeri | 60–90 | – | ||
| Hall's panicgrass | PAHA | Panicum hallii | 60–90 | – | ||
| 3 | Cool-season grasses | 35–55 | ||||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 35–55 | – | ||
| Canada wildrye | ELCA4 | Elymus canadensis | 35–55 | – | ||
| Texas wintergrass | NALE3 | Nassella leucotricha | 35–55 | – | ||
| 4 | Grass-likes | 25–35 | ||||
| sedge | CAREX | Carex | 25–35 | – | ||
| flatsedge | CYPER | Cyperus | 25–35 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 5 | Forbs | 120–180 | ||||
| Forb, annual | 2FA | Forb, annual | 75–125 | – | ||
| Cuman ragweed | AMPS | Ambrosia psilostachya | 75–125 | – | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLUM2 | Artemisia ludoviciana ssp. mexicana | 75–125 | – | ||
| croton | CROTO | Croton | 75–125 | – | ||
| bundleflower | DESMA | Desmanthus | 75–125 | – | ||
| Engelmann's daisy | ENPE4 | Engelmannia peristenia | 75–125 | – | ||
| lespedeza | LESPE | Lespedeza | 75–125 | – | ||
| sensitive plant | MIMOS | Mimosa | 75–125 | – | ||
| awnless bushsunflower | SICA7 | Simsia calva | 75–125 | – | ||
| white heath aster | SYERE | Symphyotrichum ericoides var. ericoides | 75–125 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 6 | Shrubs/Vines | 25–35 | ||||
| whitebrush | ALGR2 | Aloysia gratissima | 25–30 | – | ||
| Texas persimmon | DITE3 | Diospyros texana | 25–30 | – | ||
| Texas kidneywood | EYTE | Eysenhardtia texana | 25–30 | – | ||
| algerita | MATR3 | Mahonia trifoliolata | 25–30 | – | ||
| pricklypear | OPUNT | Opuntia | 25–30 | – | ||
| honey mesquite | PRGL2 | Prosopis glandulosa | 25–30 | – | ||
| sumac | RHUS | Rhus | 25–30 | – | ||
| blackberry | RUBUS | Rubus | 25–30 | – | ||
| western soapberry | SASAD | Sapindus saponaria var. drummondii | 25–30 | – | ||
| bully | SIDER2 | Sideroxylon | 25–30 | – | ||
|
Tree
|
||||||
| 7 | Trees | 95–145 | ||||
| pecan | CAIL2 | Carya illinoinensis | 50–125 | – | ||
| hybrid hickory | CARYA | Carya | 50–125 | – | ||
| blackjack oak | QUMA3 | Quercus marilandica | 50–125 | – | ||
| post oak | QUST | Quercus stellata | 50–125 | – | ||
| live oak | QUVI | Quercus virginiana | 50–125 | – | ||
| elm | ULMUS | Ulmus | 50–125 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
The Granite Gravel site provides at least a portion of the habitat for many species of reptiles, birds, mammals, and insects. Game birds, songbirds, and birds of prey were indigenous or frequent users, and most are still plentiful. Quail and doves frequent this site depending upon the vegetative community. Small mammals that use the site include armadillos, opossum, raccoons, rodents, jackrabbits, cottontail rabbits, and skunks. Its use by deer is limited by browse and cover in reference condition. As ecological state shifts and woody plants increase and invade, it becomes more habitable for deer. Deer prefer many of the forbs and legumes that grow on the site.
Feral hogs (Sus scrofa) can be found on most Ecological Sites in Texas. Damage is caused by feral hogs each year including, crop damage by rutting up crops, destroyed fences, livestock watering areas, and predation on native wildlife, domestic livestock (small calves, goats, and sheep) and ground-nesting birds. Feral hogs have no natural predators other than humans, thus allowing their population to grow to high numbers (Cearley 2009 & Mapston 2004). Feral hogs have naturalized to rangelands across the state.
Predators including bobcats, coyotes, foxes, and mountain lions can also be found on the site.
The site is suitable for the production of livestock, including cattle, sheep and goats. In the reference state, the site is very suited to primary grass eaters such as cattle. As retrogression occurs and woody plants invade, the Oak Savannah (1.2) and Shortgrass Savannah (2.1) plant communities become a good habitat for sheep, goats, deer and other wildlife because of the desirable browse and cool season grasses. Cattle, sheep and goats should be stocked in proportion to the available grass, forb and browse forage, keeping deer competition for forbs and browse in mind. Deer populations must also be kept within limits of the habitat sustainability even if the site is managed exclusively for deer. If the animal numbers are not kept in balance with herbage and browse production through prescribed grazing management and good wildlife population management, the Shrubland Community (2.2) will have little to offer as habitat except cover.
Plant Preference by Animal Kind:
This rating system provides general guidance as to animal preference for plant species. It also indicates possible competition between kinds of herbivores for various plants. Grazing preference changes from time to time, especially between seasons, and between animal kinds and classes. Grazing preference does not necessarily reflect the ecological status of the plant within the plant community. For wildlife, plant preferences for food and plant suitability for cover are rated. Refer to habitat guides for a more complete description of a species habitat needs.
Legend: P=Preferred D=Desirable U=Undesirable N=Not Consumed T=Toxic X=Used, but degree of utilization unknown
Preferred – Percentage of plant in animal diet is greater than it occurs on the land
Desirable – Percentage of plant in animal diet is similar to the percentage composition on the land
Undesirable – Percentage of plant in animal diet is less than it occurs on the land
Not Consumed – Plant would not be eaten under normal conditions. It is only consumed when other forages not available. This can also include plants that are unavailable during parts of the year.
Toxic – Rare occurrence in diet and, if consumed in any tangible amounts results in death or severe illness in animal (Hart, 2003). (Note: many plants can be good forage but toxic at certain doses or at certain times of the year. Animals in poor condition are most susceptible.)
Hydrological functions
Granite Gravel sites tend to be well vegetated with high levels of canopy cover and low level of bare ground in all communities. Therefore, most examples are functioning hydrologically. Abusive management can create bare soils (particularly in the case of mismanaged brush control or misguided attempts at farming. Bare soils are subject to erosion. Once the organic layer erodes in the A horizon, soils function less well hydrologically and the risk of further erosion increases.
Soils on this site are well drained and water movement to underground layers is moderately high. This contributes to the recharge of aquifers and sustained stream flow. Soils drain well and make almost 100 percent of soil water available to plants. However, sandy soils drain quickly and have soil moisture available for less of the growing season.
The Midgrass Savannah (1.1) and Oak Savannah (1.2) Communities tend to retain a highly functioning water cycle. As long as the understory remains intact, bare ground remains very low. Rapid rainfall infiltration and good porosity create a cycle where water is highly available in the soil profile with little runoff. Availability is limited to the period soon after rain. Surface runoff quality will be high and erosion and sedimentation rates will be low. High rates of infiltration will allow water to move below the rooting zone during periods of heavy rainfall.
A shift to the Shortgrass Savannah Community (2.1) may reduce canopy cover and increase bare ground. If bare ground stays low, the water cycle is expected to function similarly to the Midgrass Savannah Community (1.1). If bare ground increases, infiltration will decrease and runoff will increase due to reduced ground cover, rainfall splash, soil capping, reduced organic matter, and poor structure. With a combination of a sparse ground cover and intensive rainfall, this site can contribute to an increased frequency and severity of flooding within a watershed.
Domination of the site by woody species may degrade the water cycle in the Shrubland Community (2.2). Interception of rainfall by tree canopies increases, which reduces the amount of rainfall reaching the surface and being available to understory plants. Increased stem flow, due to the funneling effect of the canopy, increases soil moisture at the base of trees, especially on mesquite. Evergreen species, such as live oak, create increased transpiration which provides less water for deep percolation. Increases in woody canopy create declines in grass cover, which creates similar causes impacts as those described for overgrazing above. Under the dense canopy of the shrubland, leaf litter builds up. This increases soil organic matter, builds structure, improves infiltration, and reduces surface erosion. These conditions improve the function of the water cycle compared to lower levels of canopy cover.
The Eroded State (3.0) tends to have poor hydrologic function. Runoff is high and infiltration low. This state is caused by loss of soil which creates conditions that increase the risk of the remaining soil eroding. With a combination of a sparse ground cover and intensive rainfall, this site can contribute to an increased frequency and severity of flooding within a watershed. Soil erosion is accelerated, quality of surface runoff is poor and sedimentation increases.
Recreational uses
Recreational uses include recreational hunting, hiking, camping, equestrian, and bird watching.
Wood products
Mesquite and some oak are used for firewood, charcoal, and other specialty wood products.
Other products
Seeds are harvested from many plants for commercial sale. Many grasses and forbs are harvested by the dried-plant industry for sale in dried flower arrangements. Honeybees are utilized to harvest honey from many flowering plants, such as honey mesquite.
Other information
NA.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented was derived from the revised Granite Gravel Range Site, literature, limited NRCS clipping data (417s), field observations and personal contacts with range-trained personnel.
Other references
Reviewers:
Joe Franklin, ZRMS, NRCS, San Angelo, Texas
Kent Ferguson, StRMS, NRCS, Temple, Texas
Justin Clary, RMS, NRCS, Temple, Texas
Mark Moseley, ESI Specialist, NRCS, Boerne, Texas
References:
1. AgriLife. Wildlife. "Managing Feral Hogs Not a One-shot Endeavor." Press release. AgNews. 01 Jan. 2009. Texas Cooperative Extension. 23 Apr. 2009 http://agnews.tamu.edu/showstory.php?id=903
2. Appel, D. N. 1995. The Oak Wilt Enigma: Perspective from the Texas Epidemic. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 33:103-118.
3. Archer, S. 1994. Woody plant encroachment into southwestern grasslands and savannas: rates, patterns and proximate causes. In: Ecological implications of livestock herbivory in the West, pp. 13-68. Edited by M. Vavra, W. Laycock, R. Pieper. Society for Range Management Publication, Denver, CO.
4. Archer, S. and F. Smeins. 1991. Ecosystem-Level Processes. Pp. 109-139, In Grazing Management: An Ecological Perspective. Edited by R.K. Heitschmidt and J.W. Stuth. Timber Press, Inc., Portland. 259p.
5. Bestelmeyer, B.T., J.R. Brown, K.M. Havstad, R. Alexander, G. Chavez and J.E. Hedrick. 2003. Development and Use of State-and-Transition Models for Rangelands. J. Range Manage. 56: 114-126.
6. Bomar, G.W. 1983. Texas Weather. Univ. Tex. Press, Austin. 265p.
7. Brown, J.R. and S. Archer. 1999. Shrub invasion of grassland: recruitment is continuous and not regulated by herbaceous biomass or density. Ecology 80(7): 2385-2396.
8. Bureau of Economic Geology. 1981. Geologic Atlas of Texas, Llano Sheet. Bur. Econ. Geol., Univ. Tex. Austin.
9. Bushland, R.C. 1985. Eradication program in the southwestern United States. Symposium on eradication of the screwworm from the United States and Mexico. Misc. Pub. Entomol. Soc. Am., 62:12-15.
10. Carr, J.T. 1969. The Climate and Physiography of Texas. Tex. Water Devel. Bd. Rep. No. 53. 27p.
11. Eidson, J.A. and F.E. Smeins. 1999. Texas blackland prairies. 305–307. in Terrestrial ecoregions of North America: a conservation assessment. Ricketts, T., E. Dinerstein, and D. Olson. editors. Island Press. Washington, D.C.
12. Everitt, J.H., D.L. Drawe, and R.I. Lonard. 1999. Field Guide to the Broad-Leaved Herbaceous Plants of South Texas. Lubbock, Texas: Texas Tech University Press.
13. Everitt, J.H., D.L. Drawe, and R.I. Lonard. 2002. Trees, Shrubs, and Cacti of South Texas. Lubbock, Texas: Texas Tech University Press.
14. Foster, J.H. 1917. Pre-settlement fire frequency regions of the United States: a first approximation. Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference Proceedings No. 20.
15. Foster, J.H. 1917. The Spread of Timbered Areas in Central Texas. J. For. 15:442-445.
16. Frost, C. C. 1995. Presettlement fire regimes in southeastern marshes, peatlands, and swamps. In: Proceedings, 19th Tall Timbers fire ecology conference. Tallahassee, FL: Tall Timbers Research Station pp. 39-60.
17. Frost, C. C. 1998. Pre-settlement fire frequency regions of the United States: A first approximation. Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference Proceedings No. 20.
18. Fuhlendorf, S. D. and D. M. Engle. 2001. Restoring Heterogeneity on Rangelands: Ecosystem Management Based on Evolutionary Grazing Patterns. Bioscience. 51:625-632.
19. Fulbright, T. E., J. A. Ortega-Santos, A. Lozano-Cavazos, and L. E. Ramírez-Yánez. 2006. Establishing vegetation on migrating inland sand dunes in Texas. Rangeland Ecology and Management 59:549-556.
20. Goerdel, A.R. 2000. Soil Survey of Llano County. USDA, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington, D.C.
21. Gould, F.W. 1975. The Grasses of Texas. Texas A&M University Press, College Station, TX. 653p.
22. Grace, J. B., L. K. Allain, H. Q. Baldwin, A. G. Billock, W. R. Eddleman, A. M. Given, C. W. Jeske, and R. Moss. 2005. Effects of prescribed fire in the coastal prairies of Texas. USGS Open File Report 2005-1287.
23. Hart, C. R. t. Garland, A. C. Barr, B. B. Carpenter and J. C. Reagor. 2003. Toxic Plants of Texas. Texas Cooperative Extension Bulletin B-6103 11-03.
24. Knapp, A.K., et al. 1999. The Keystone Role of Bison in North American Tallgrass Prairie. Bioscience 49: 39-50.
25. Kneuper, C.L., C.B. Scott, and W.E. Pinchak. 2003. Consumption and Dispersion of Mesquite Seeds by Ruminants. Journal of Range Management. 56:255-259.
26. Kramp, B, R, Ansley, and D. Jones. 1999. The effect of prescribed fire on mesquite seedlings. Vernon Center Technical report.
27. Mann, C. 2004. 1491. New Revelations of the Americas before Columbus.
28. Mapston, Mark E. Feral Hogs in Texas. Rep. Texas Cooperative Extension. 23 Apr. 2009 http://icwdm.org/Publications/pdf/Feral%20Pig/Txferalhogs.pdf
29. Riskind, D.H. and D.D. Diamond. 1988. An Introduction to Environment and Vegetation. Pp. 1-15, In Edwards Plateau Vegetation: Plant Ecological Studies in Central Texas. Edited by B.B. Amos and F.R. Gehlbach. Baylor University Press, Waco, TX.
30. Scifres, C.J. and W.T. Hamilton. 1993. Prescribed Burning for Brush Management: The South Texas Example. Texas A&M University Press, College Station, TX. 245 p.
31. Scifres, C.J., H.T. Hamilton, J.R. Conner, J.M Inglis, G.A. Rasumssen, R.P. Smith, J.W. Stuth, T.G. Welch (eds.) 1985. Integrated brush management Systems for South Texas: Development and implementation. Tex. Ag. Exp. Stat. B-1493. 71 p.
32. Smeins, F., S. Fuhlendorf, and C. Taylor, Jr. 1997. Environmental and Land Use Changes: A Long Term Perspective. Chapter 1 in: Juniper Symposium 1997, pp. 1-21. Texas Agricultural Experiment Station.
33. Smith, J.G. 1899. Grazing Problems in the Southwest and How To Meet Them. U.S. Dep. Agr. Div. Agron. Bull. No. 16. 47p.
34. Stringham, T.K., W.C. Krueger, and P.L. Shaver. 2001. State and transition modeling: an ecological process approach. J. Range Management. 56(2):106-113.
35. Teer, J.G., J.W. Thomas and E.A. Walker. 1965. Ecology and Management of White-tailed Deer in the Llano Basin of Texas. Wildlife Monographs 10: 1-62.
36. Texas A&M Research and Extension Center. 2000. Native Plants of South Texas (http://uvalde.tamu.edu/herbarium/index.html).
37. Texas Agriculture Experiment Station. 2007. Benny Simpson’s Texas Native Trees (http://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/ornamentals/natives/).
38. Texas Online. http://www.tshaonline.org/handbook/online/articles/asw02
39. Texas Parks and Wildlife Dept. 2007. List of White-tailed Deer Browse and Ratings. District 8.
40. Thurow, T.L. 1991. Hydrology and Erosion. Chapter 6 in: Grazing Management: An Ecological Perspective. Edited by R.K. Heitschmidt and J.W. Stuth. Timber Press, Portland, OR.
41. TR 1737-15 (1998) Riparian Area Management – a User’s Guide to Assessing Proper Functioning Condition and the Supporting Science for Lotic Areas. Bureau of Land Management, US Forest Service, Natural Resources Conservation Service.
42. USDA, NRCS. 1997. National Range and Pasture Handbook.
43. USDA, NRCS. 2007. The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov). National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA 70874-4490 USA.
44. USDA/NRCS Soil Survey Manuals for appropriate counties within MLRA 86A.
45. Vines, R.A. 1977. Trees of Eastern Texas. University of Texas Press, Austin, TX. 538 p.
46. Vines, R.A. 1984. Trees of Central Texas. University of Texas Press, Austin, TX.
47. Wade, D. D., B. L. Brock, P. H. Brose, J. B. Grace, G. A. Hoch, and W. A. Patterson III. 2000. Fire in Eastern ecosystems. In: Brown, J.K., and J. Kaplers, eds. Wildland fire in ecosystems: effects of fire on flora. Gen. Tech. Rep. RMRS-GTR-42-vol. 2. Ogden, UT: United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station 257 p.
48. Weniger, D. 1984. The Explorers’ Texas: The Land and Waters. Eakin Press, Austin. 224 p.
49. Whitehouse, E. 1933. Plant Succession on Central Texas Granite. Ecol. 14: 391-404.
50. Wright, H.A. and A.W. Bailey. 1982. Fire Ecology: United States and Southern Canada. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
51. Wright, B.D., R.K. Lyons, J.C. Cathey, and S. Cooper. 2002. White-tailed Deer Browse Preferences for South Texas and the Edwards Plateau. Texas Cooperative Extension Bulletin B-6130.
Contributors
Jack Alexander, Synergy Resource Solutions, Inc., Dr. Fred Smeins, Texas A&M University (Phase 1)
Mark Moseley
Edits by Travis Waiser, MLRA Leader, NRCS, Kerrville, TX
Approval
Bryan Christensen, 9/19/2023
Acknowledgments
Site Development and Testing Plan:
Future work, as described in a Project Plan, to validate the information in this Provisional Ecological Site Description is needed. This will include field activities to collect low, medium and high intensity sampling, soil correlations, and analysis of that data. Annual field reviews should be done by soil scientists and vegetation specialists. A final field review, peer review, quality control, and quality assurance reviews of the ESD will be needed to produce the final document. Annual reviews of the Project Plan are to be conducted by the Ecological Site Technical Team.
QC/QA completed by:
Bryan Christensen, SRESS, NRCS, Temple, TX
Erin Hourihan, ESDQS, NRCS, Temple, TX
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | Synergy Resource Solutions, Belgrade, Montana |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | Zone Rangeland Management Specialist, NRCS, San Angelo, Texas 325-944-0147 |
| Date | 03/08/2011 |
| Approved by | Bryan Christensen |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
None. -
Presence of water flow patterns:
None, except following extremely high intensity storms when short flow patterns may appear. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
None. -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
0 to 10 percent bare ground. Very small (<1 square foot) and non-connected areas. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
None. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
Essentially none. -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Very little litter movement under normal rainfall intensity. Litter is well distributed and stays in place. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
High (Soil stability score of 4+). -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
0-28 inches thick, sandy, sandy loam, coarse sandy loam, fine sandy loam, brown, weak fine and very fine subangular blocky structure. SOM 0-3%. Soil surface is very stable (average soil stability values of > 4). -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
High canopy, basal cover and density with small interspaces should make rainfall impact negligible. This site has well drained soils, deep with level to gently sloping (0 to 3 percent slopes) which produces negligible runoff and erosion. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
None. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Warm-season midgrasses >>Sub-dominant:
Warm-season shortgrasses >Other:
Cool-season grasses > Forbs > Shrubs > Trees > Warm-season tallgrassesAdditional:
Forbs make up 5 percent of species composition, shrubs and trees compose up to 5 percent species composition. -
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Grasses due to their growth habit will exhibit some mortality and decadence, though very slight. Little mortality evident on woody species. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Tree litter may be up to 6 inches deep. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
Representative value for production = 1500 lbs/ac. -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
Mesquite,cacti, ashe juniper, whitebrush are primary invaders. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
All species should be capable of reproducing except for periods of prolonged drought conditions, heavy natural herbivory and fires.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Absence of disturbance, natural regeneration over time, and prolonged excessive grazing pressure |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Loss of vegetative cover and/or extensive soil disturbance resulting in active soil erosion |
| R2A | - | Removal of woody canopy and reintroduction of historic disturbance return intervals |
| T2A | - | Loss of vegetative cover and/or extensive soil disturbance resulting in active soil erosion |
| T3A | - | Soil stabilization and rangeland seeding. Probability of success is low. |