

Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R084BY171TX
Loamy Sand 29-33" PZ
Last updated: 9/21/2023
Accessed: 04/26/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
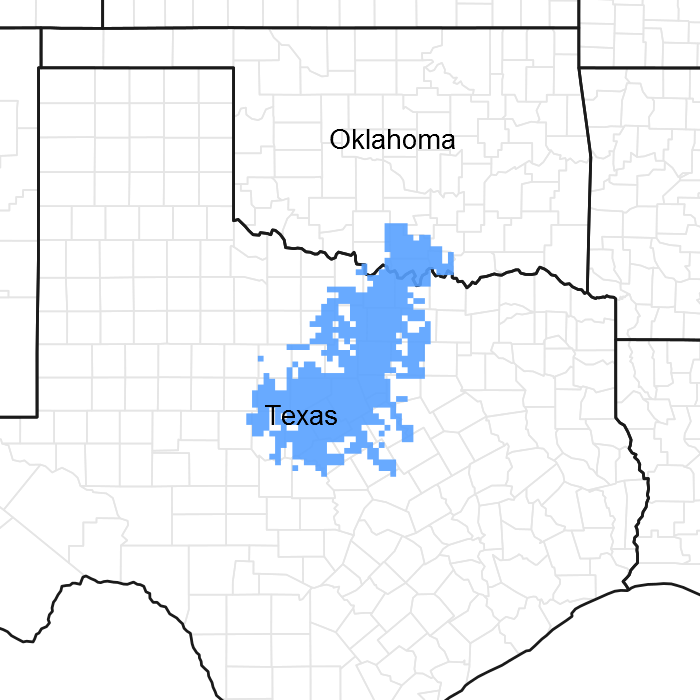
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 084B–West Cross Timbers
MLRA 84B is characterized by nearly level to strongly sloping, dissected plains with narrow valleys that deepen eastward. Soils are generally deep and formed in sediments of Cretaceous age. Average annual precipitation is 25 to 35 inches, and elevation ranges from 1000 to 1300 feet.
Classification relationships
This ecological site is correlated to soil components at the Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) level which is further described in USDA Ag Handbook 296.
Ecological site concept
These sites occur on deep loamy sand soils on uplands. The reference vegetation includes native tallgrasses with forbs, other grasses and scattered oaks. Without fire or brush management, woody species may increase and dominate the plant community. This site is similar to both the Sandy and Sandy Loam. The Loamy Sand site has higher production potential than the Sandy but lower than Sandy Loam.
Associated sites
| R084BY172TX |
Sandy 29-33" PZ Sandy soils. Lower production. |
|---|---|
| R084BY174TX |
Sandy Loam 29-33" PZ Sandy loam soils. Higher production. |
| R084BY169TX |
Deep Sand 29-33" PZ Deep and very deep sandy soils |
Similar sites
| R084BY174TX |
Sandy Loam 29-33" PZ Sandy loam soils. Higher production. |
|---|---|
| R084BY172TX |
Sandy 29-33" PZ Sandy soils. Lower production. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus stellata |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Sorghastrum nutans |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on treads and risers of stream terraces and paleoterraces, as well as base slopes, side slopes, and interfluves of low ridges and hillslopes in the West Cross Timbers. Slopes are typically less than 12 percent.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Alluvial plain
> Stream terrace
(2) Hills > Ridge (3) Alluvial plain remnant > Paleoterrace (4) Hills > Hillslope |
|---|---|
| Runoff class | Negligible to high |
| Elevation | 183 – 640 m |
| Slope | 0 – 12% |
| Water table depth | 51 cm |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
The climate is subtropical. Precipitation varies from an average of 33 inches in the eastern part of the Cross Timbers to 29 inches in the western part. Winters are dry and summers are hot and humid. Tropical maritime air masses control the weather during the spring, summer and fall. Large variations in temperature sometimes accompany polar air masses in winter.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 193-200 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | 220-225 days |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 787-838 mm |
| Frost-free period (actual range) | 192-204 days |
| Freeze-free period (actual range) | 216-226 days |
| Precipitation total (actual range) | 711-864 mm |
| Frost-free period (average) | 197 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | 222 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 813 mm |
Figure 2. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 3. Monthly minimum temperature range
Figure 4. Monthly maximum temperature range
Figure 5. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 6. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 7. Annual average temperature pattern
Climate stations used
-
(1) PUTNAM [USC00417327], Baird, TX
-
(2) RISING STAR 1S [USC00417633], Rising Star, TX
-
(3) PROCTOR RSVR [USC00417300], Comanche, TX
-
(4) MINERAL WELLS AP [USW00093985], Millsap, TX
-
(5) BRIDGEPORT [USC00411063], Bridgeport, TX
Influencing water features
This site may receive water from adjacent sites and/or shed water to lower areas. The presence of a good cover of deep rooted tallgrasses can help facilitate infiltration of water into the soil profile. These sites are not associated with wetlands.
Wetland description
NA
Figure 8.
Soil features
Representative soil components for this ecological site include: Bastrop, Chaney, Cisco, Decordova, Duffau, Pedernales, Silawa, Selden, and Windthorst
The site is characterized by deep soils with a high infiltration rate.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Alluvium
–
sandstone
(2) Slope alluvium – sandstone (3) Residuum – sandstone |
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Loamy fine sand |
| Drainage class | Moderately well drained to well drained |
| Permeability class | Moderately slow to moderately rapid |
| Soil depth | 102 – 183 cm |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 0 – 10% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 0 – 10% |
| Available water capacity (0-101.6cm) |
15.24 – 33.02 cm |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-101.6cm) |
0 – 10% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-101.6cm) |
0 – 2 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-101.6cm) |
0 – 2 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-101.6cm) |
5.1 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
0 – 10% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
0 – 10% |
Ecological dynamics
The reference plant community for the Loamy Sand site is a post oak, blackjack oak savanna with tall and midgrass understory. The grasses are primarily little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), Indiangrass (Sorghastrum nutans), big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii) and sand lovegrass (Eragrostis trichodes). Little bluestem and Indiangrass are the most commonly occurring grass species. Smaller amounts of big bluestem, switchgrass (Panicum virgatum), sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), purpletop tridens (Tridens flavus) and sand lovegrass occur as well. Shrubs and trees consist of post oak (Quercus stellata), blackjack oak (Quercus marilandica), elms (Ulmus spp), plums (Prunus spp), hawthorns (Crataegus spp), greenbriar (Smilax spp), grapes (Vitis spp), coralberry (Symphoricarpos orbiculatus), hackberry (Celtis occidentalis) and bumelia (Sideroxylon spp.). Most woody plants tended to be more confined to areas along drainages and other areas where native wildlife tended to concentrate. Switchgrass and big bluestem tended to occur more in the low drainages. Woody plants have increased on virtually all of the loamy sand sites over the past 100 to 150 years. Where the site was once cultivated mesquite (Prosopis glandulosa) tends to be one of the first woody plants to appear. Where there is a seed source close by, juniper (Juniperus ashei and Juniperus virginiana) will invade the site. In certain areas juniper has become a significant problem species along with mesquite. The production potential of the site is moderate; however, it is significantly lower than the Sandy Loam ecological site. Pre-settlement grazers included bison and deer. The grasses are fairly palatable and nutritious and the site provides year round grazing. The most limiting soil factor is erodibility followed by fertility. In very dry periods, the soils can appear rather droughty. When good rainfall is received, the site produces well.
Fire played a role in the ecology of the site as is true for most of the grasslands. The main effect of fire on this site was to hold woody shrubs and cactus in check. The grass species such as little bluestem and Indiangrass are considered fire neutral as far as their response to fire. Climate and soils are the most important and limiting factors affecting grass vegetation on the site. Fire will usually not produce much mortality in older woody plants. After brush has been controlled with herbicides or mechanically, fire can sometimes be used effectively to suppress regrowth. Small juniper can be killed by fire. Fuel loads are often the most limiting factor for the effective use of prescribed fire on this site. In general, the uses of fire on mature (larger) or dense stands of woody plants does not result in the same positive effects that burning has in tall/midgrass communities.
With abusive grazing practices, the vigorous Indiangrass and big bluestem will become lower in vigor while little bluestem will increase then secondary successional species such as sand dropseed (Sporobolus cryptandrus), and silver bluestem (Bothriochloa laguroides) will begin to increase along with an increase of woody plants. The little bluestem is a tough, resistant species is tolerant of some fairly heavy grazing for long periods, but at some point, a threshold is crossed and the ground cover is opened up resulting in bare places where weedy species can establish. Western ragweed (Ambrosia psilostachya), crotons (Croton setigerus), and cool-season annuals will quickly invade if the principal species are in a weakened condition. Mesquite may occupy the site when severe erosion has occurred and most of the topsoil (sand) is no longer present. The greatest contributor to the increase of mesquite is the domestic cow. The seed is consumed by animals after the seed pods ripen in late summer and when passed through the digestive system and excreted in the manure, the seed finds an excellent seedbed complete with moisture and nutrients. Some wildlife species rely heavily on mesquite beans and juniper berries for food and contribute to the spread of these species. It is possible for mesquite beans to lay dormant in the soil for many years and then germinate when ideal conditions occur. Grazing management probably has minimal effect on the proliferation of woody plants, but a good cover of perennial grasses likely minimizes the seed to soil contact the needed to establish. Prescribed fire where it can be safely carried out provides a much better method to control the spread of woody plants. Selective individual removal of woody plants is easy and economical when a few plants begin to show up on the site, but the increase may be fairly rapid and the number of woody plants per acre will soon become too numerous for individual control to be feasible. Prescribed grazing with a reasonable stocking rate can sustain the grass species composition and production at a near reference level until the brush canopy is so dense that the shade starts to interfere with photosynthesis. The loamy sand site can be abused to the point that the perennial warm season grasses thin out and lower succession grasses along with annual forbs begin to dominate. This process of degradation usually takes many years and is further exacerbated by summer drought and above average winter moisture.
Long-term droughts that occur only three to four times in a century can effect some change in plant communities. Short-term droughts are common and usually do not have a lasting effect in changing stable plant communities, although production will be affected. When a brush canopy becomes established which shades the ground sufficiently it tends to favor cool-season annual species. Once a state of brush and cool-season annuals is reached, recovery to a good perennial grass cover is unlikely without major input with brush management and reseeding. In summary, the change in states of vegetation depend on the type of grazing management applied over many years, and the rate of invasion and establishment of woody species. After the site crosses the threshold to a lower ecological condition, the effects of seasonal moisture and short-term dry spells become more pronounced. Plant communities that consist of warm season perennial grasses such as little bluestem are able to persist and withstand climatic extremes with only minor shifts in the overall plant community.
This site was inhabited by grassland wildlife species such as bison, grassland birds and small mammals. Over the years, as the site has changed to a more mixed grass and shrub community, more wildlife species have come to utilize it for habitat. Woody plants provide cover for white-tailed deer and bob-white quail. These wildlife species have both increased along with the brushy plants due to the cover that these plants provide. More forbs are needed to meet these species food requirements and woody plants for browse are important for deer. It is often the objective of many land owners to strike a balance in plant community so that these wildlife species can exist along with domestic livestock. This can be accomplished by a carefully thought out grazing and brush management program. It must be realized that managing at a lower successional level may meet some wildlife species requirements very well, but may not be nearly as productive for grazing purposes, and may not be as capable of satisfying functions such as nutrient cycling, hydrologic protection, plant community stability or soil protection. A proper balance can be achieved with careful planning that considers all resources.
Hydrologically, the site contributes runoff to the various draws, creeks, and streams that are common in the MLRA. If the perennial grass cover is maintained in good vigor, then maximum infiltration occurs and runoff is reduced. More water getting into the ground means a healthier, more productive plant community. If infiltration is minimal, then the effect is an artificially shallow soil with plant roots retreating to near the soil surface. More perennial grass cover means less runoff may result but the runoff that does occur is less laden with sediment. Overall watershed protection is enhanced by a healthy grassland community, as is nutrient cycling.
State and Transitional Pathways: Narrative
The following diagram suggests some pathways that the vegetation on this site might take in response to various treatment or natural stimuli over time. There may be other states that are not shown on this diagram. This information is to show that changes in plant community do occur as a result of management and natural factors; and can be changed by implementing certain practices. The plant communities described are commonly observed on this site. Before making plans for plant community manipulation for specific purposes, consult local professionals.
As a site changes in plant community makeup, the changes may be due to many factors. Change may occur slowly or in some cases, fairly rapidly. As vegetative changes occur, certain thresholds are crossed. This means that once a certain point is reached during the transition of one community to another, a return to the first state may not be possible without the input of some form of energy. This often means intervention with practices that are not part of natural processes. An example might be the application of herbicide to control some woody species in order to reduce its population and encourage more grass and forbs growth. Merely adjusting grazing practices would probably not accomplish any significant change in plant community once certain thresholds are crossed. The amount of energy required to effect change in community would depend on the present vegetative state and the desired change.
State and transition model
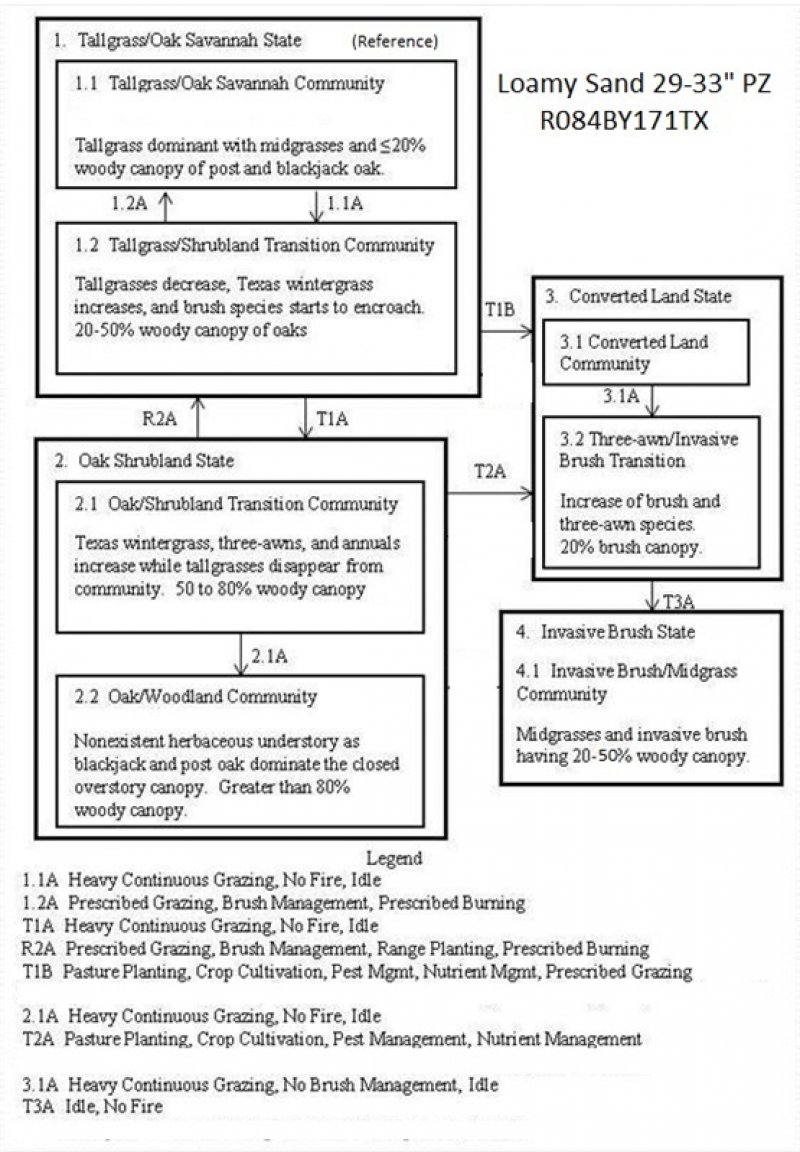
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 4 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Tallgrass/Oak Savannah State - Reference
The interpretive plant community for this site is the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah (1.1). The community is dominated by warm-season perennial tallgrasses with post oak and blackjack oak. The major perennial grass species are well dispersed through the community. Perennial forbs and shrubs are well represented throughout the community. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Tree canopy is less than 20 percent. The Tallgrass/Shrubland Transition Community occurs when post oak, blackjack oak and elm starts regeneration and the tallgrasses will start to disappear from the plant community. Invader brush (mesquite, juniper, yaupon, etc) appears and becomes established. Cedar elm, bumelia, and hackberry also start to increase. Texas wintergrass and purpletop tridens increases as brush canopy increases. The plant community consists of about a 20 to 50 percent canopy of mature trees with an understory canopy of shrubs and young oaks, elm and pecan. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Grasses account for 55% of species composition and shrubs/trees account for 30% of species composition.
Dominant plant species
-
post oak (Quercus stellata), tree
-
blackjack oak (Quercus marilandica), tree
-
Indiangrass (Sorghastrum nutans), grass
Community 1.1
Tallgrass/Oak Savannah Community
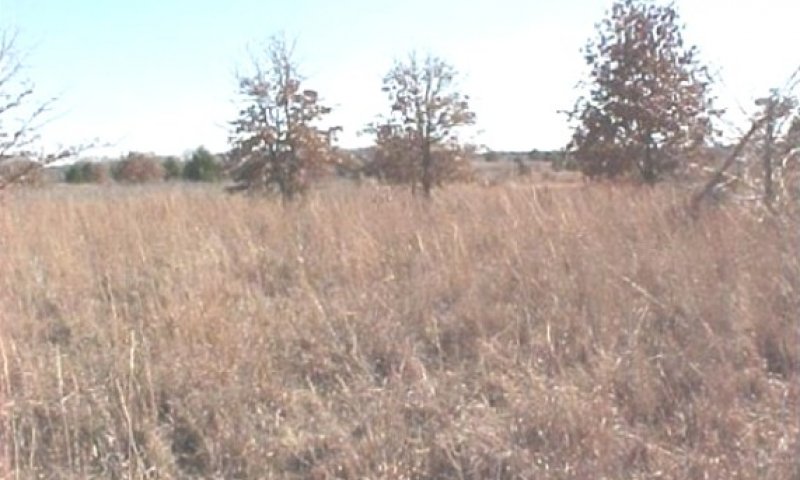

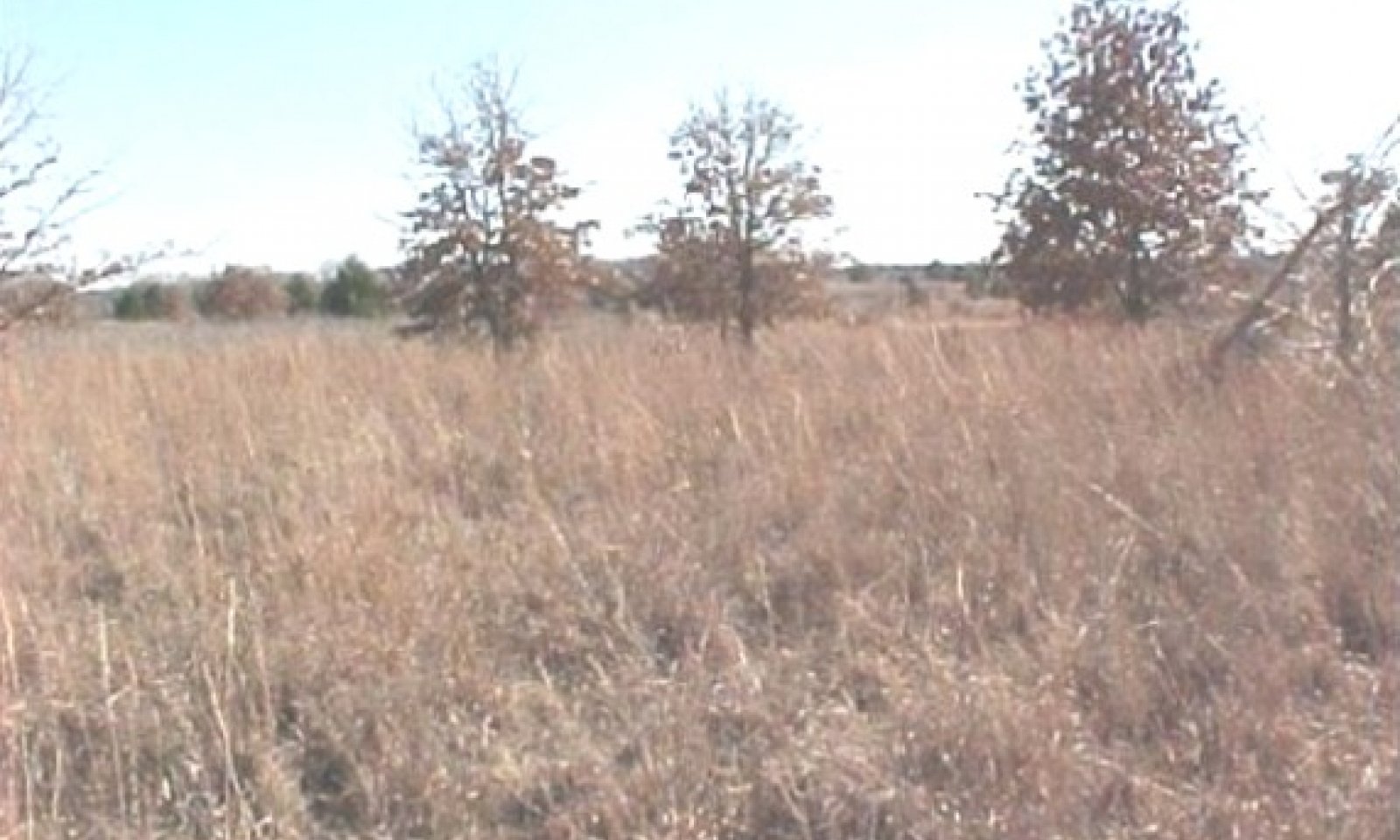
Figure 9. 1.1 Tallgrass/Oak Savannah Community
The interpretive plant community for this site is the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah (1.1). The community is dominated by warm-season perennial tallgrasses with post oak and blackjack oak. The major perennial grass species are well dispersed through the community. Perennial forbs and shrubs are well represented throughout the community. This plant community evolved with a short duration of heavy use by large herbivores followed by long rest periods due to herd migration along with occasional fire. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre.
Figure 10. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 2242 | 3138 | 4035 |
| Forb | 420 | 588 | 757 |
| Tree | 84 | 118 | 151 |
| Shrub/Vine | 56 | 78 | 101 |
| Total | 2802 | 3922 | 5044 |
Figure 11. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX5514, Post oak/Blackjack Oak Savannah. Post oak and blackjack oak savannah with tall grasses..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 2 | 2 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 23 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 2 |
Community 1.2
Tallgrass/Shrubland Transition Community
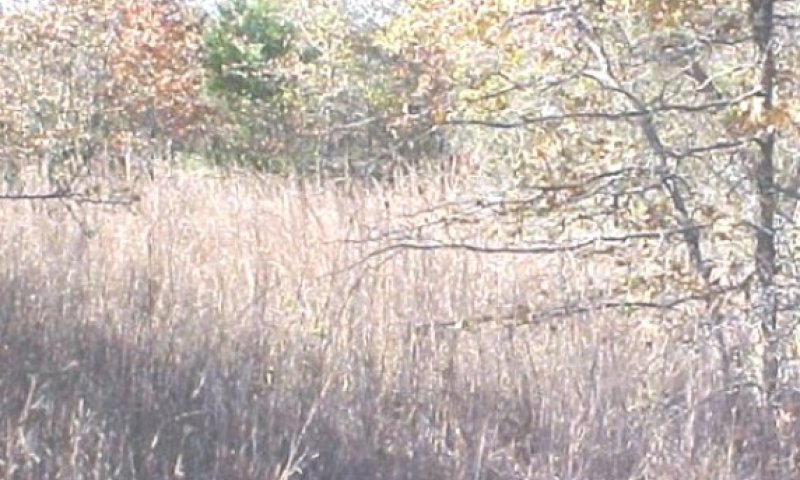

Figure 12. 1.2 Tallgrass/Shrubland Transition Community
This transition community occurs without fire or brush management. Postoak, blackjack oak and elm starts regeneration and the tallgrasses will start to disappear from the plant community. Invader brush (mesquite, juniper, yaupon, etc) appears and becomes established. Cedar elm, bumelia, and hackberry also start to increase. Texas wintergrass and purpletop tridens increases as brush canopy increases. The plant community consists of about a 20 to 50 percent canopy of mature trees with an understory canopy of shrubs and young oaks, elm and pecan. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Grasses account for 55% of species composition and shrubs/trees account for 30% of species composition. This transition community can revert back to the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah with prescribed burning and/or prescribed grazing. Without prescribed burning and/or prescribed grazing, this transition state will continue to shift toward the Oak Shrubland State (2).
Figure 13. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 6. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 1255 | 2197 | 3133 |
| Forb | 426 | 538 | 656 |
| Shrub/Vine | 560 | 594 | 628 |
| Tree | 560 | 594 | 628 |
| Total | 2801 | 3923 | 5045 |
Figure 14. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX5511, Shrubland Transition. Increasing percentage of shrubs invading site (20-50 % canopy).
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 30 | 25 | 8 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 1 |
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2


With heavy continuous grazing, no fire, and land in idle, the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah Community will shift to the Tallgrass/Shrubland Transition Community.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1


The Tallgrass/Shrubland Transition Community can shift back to the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah Community with the use of Prescribed Grazing, Brush Management, and Prescribed Burning conservation practices.
Conservation practices
| Brush Management | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Burning | |
| Prescribed Grazing |
State 2
Oak Shrubland State
The Oak/Shrubland Transition Community (2.1) consists of 50 to 80% canopy of woody plants. As the shrubland community ages, oak matures and the invader species increase. Warm-season perennial tallgrasses such as Indiangrass and switchgrass have all but disappeared. In the early stages of this transition stage little bluestem tends to dominate the grasses; however, as brush canopy continues to increase, Texas wintergrass, three-awns and annuals continue to increase while the little bluestem decreases. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Grasses make up 30% species composition while shrubs/trees make up 35% species composition. The Oak/Woodland Community is a closed overstory (greater than 80% canopy) woodland dominated by postoak and blackjack oak. The herbaceous understory is almost nonexistent except for remnants of shade-tolerant species. Small isolated clearings will contain little bluestem, perennial three-awns, Texas wintergrass and small amounts of other grasses. Continuous grazing by domestic livestock has accelerated the shift. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Species composition for grasses is 5% while shrubs/trees reach 90%.
Dominant plant species
-
post oak (Quercus stellata), tree
-
elm (Ulmus), tree
-
Ashe's juniper (Juniperus ashei), tree
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
-
Texas wintergrass (Nassella leucotricha), grass
Community 2.1
Oak/Shrubland Transition Community
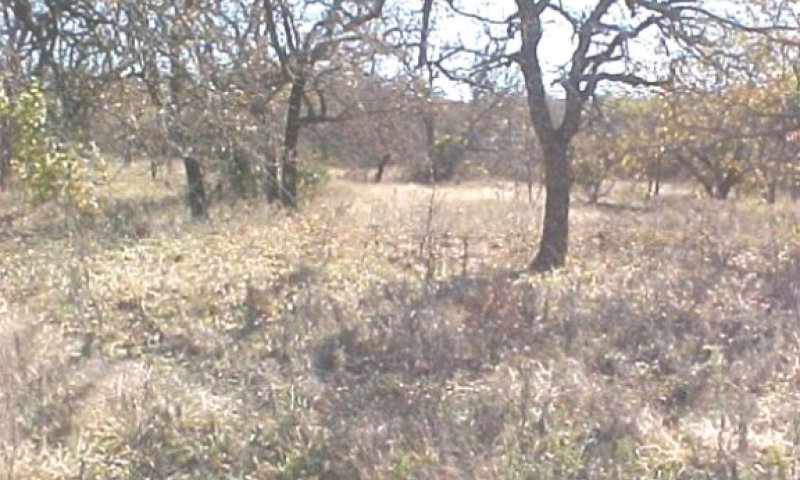

Figure 15. 2.1 Oak/Shrubland Transition Community
The Oak/Shrubland Transition Community (2.1) consists of 50 to 80% canopy of woody plants. As the shrubland community ages, oak matures and the invader species increase. Warm-season perennial tallgrasses such as Indiangrass and switchgrass have all but disappeared. In the early stages of this transition stage little bluestem tends to dominate the grasses; however, as brush canopy continues to increase, Texas wintergrass, three-awns and annuals continue to increase while the little bluestem decreases. Where severe erosion has occurred or cropland has been abandoned mesquite and/or juniper may dominate the site. Continuous grazing by domestic livestock has accelerated the shift. The shift to this state has occurred due to the absence of fire or other means of brush suppression. Where this state has been reached from cropland or pasture, mesquite and/or juniper dominate the woody vegetation, but postoak and blackjack oak are beginning to occur. The grass species that dominate the site are splitbeard bluestem (Andropogon ternarius), silver bluestem (Bothriochloa laguroides), Texas wintergrass and three-awns along with the seeded introduced grass species. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Grasses make up 30% species composition while shrubs/trees make up 35% species composition. This state can be reverted back to near reference condition by some means of brush suppression and good grazing management. Without this treatment the site will continue to shift toward the Oak/Woodland Community (2.2).
Figure 16. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 7. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forb | 790 | 1278 | 1768 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 790 | 1278 | 1760 |
| Shrub/Vine | 594 | 706 | 791 |
| Tree | 628 | 673 | 725 |
| Total | 2802 | 3935 | 5044 |
Figure 17. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX3999, Oak - Shrubland Transition. Oak/Shrubland Transition with increase of wintergrass and annuals..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
Community 2.2
Oak/Woodland Community
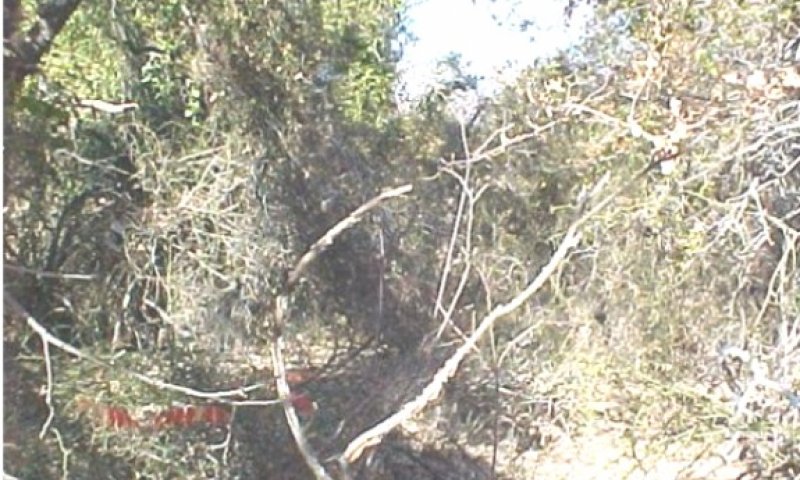

Figure 18. 2.2 Oak/Woodland Community
This plant community is a closed overstory (greater than 80% canopy) woodland dominated by postoak and blackjack oak. Other species present in small amounts are cedar elm, hackberry, bois d àrc (Maclura pomifera). Understory shrubs and sub-shrubs include yaupon, hawthorns, and American beautyberry (Callicarpa americana). Woody vines are also present and include greenbriars, poisonoak (Toxicodendron spp), Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia) and grapes. The herbaceous understory is almost nonexistent. Shade tolerant species such as purpletop tridens (Tridens flavus) and Canada wildrye (Elymus canadensis) occur in small amounts. Small isolated clearings will contain little bluestem, perennial three-awns, Texas wintergrass and small amounts of other grasses. Continuous grazing by domestic livestock has accelerated the shift. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Species composition for grasses is 5% while shrubs/trees reach 90%. This Oak/Woodland Community (2.2) has developed due to the absence of fire (or some other method of brush suppression). Livestock grazing yearlong accelerates the shift. The Tallgrass/Oak Savannah (1.1) can be restored by prescribed burning but will require many years of burning due to light fuel load of fine fuel and the absence of a seed source for the tallgrasses. Chemical control alone is usually not a good option for treatment on a large scale due to the resistance of some of the woody plant species to herbicides. Mechanical treatment of this site along with seeding is generally the best method for conversion back to a tallgrass savannah. The cost of doing this type of treatment is usually so expensive as to be not economically feasible so in most instances it is planted to introduced grass species and converted to pastureland. The soils of this site are very sensitive to erosion. During the transition states from the Reference State due to the reduction of grass litter, sheet and rill erosion and in some instances wind erosion has accelerated and by the time it has reached the Woodland State the topsoil depth is greatly reduced. This in turn has reduced the soils natural fertility. While in the transition stages, the organic matter in the soil is also reduced and may never be what was present in the tallgrass prairie. In the Oak/Woodland Community (2.2), the amount of litter cover is similar to the Reference State but this cover is now mostly leaves. The leaves of the trees and underbrush intercept rainfall from lighter intensity rainfall which evaporates before reaching the ground resulting in less water reaching the soil surface. When runoff does occur there are more tendencies for the litter to drift until it catches on the stems of dense underbrush or what little grass is present. When the woodland is grazed the amount of litter decreases along with a decrease of surface vegetation which increases the drifting of the litter with runoff. Due to the presence of shade the amount of grass cover is greatly reduced which in turn reduces forage production from the reference state. When this state is reached following abandonment of cropland or pastureland of introduced plants quite often severe erosion has occurred. The absence of topsoil has greatly decreased water infiltration which in turn increases runoff.
Figure 19. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 8. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | 1267 | 1715 | 2275 |
| Shrub/Vine | 1255 | 1765 | 2270 |
| Forb | 146 | 202 | 263 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 135 | 191 | 235 |
| Total | 2803 | 3873 | 5043 |
Figure 20. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX5513, Postoak Woodland. Postoak dominated closed overstory with over 80 percent canopy cover..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 50 | 14 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
Pathway 2.1A
Community 2.1 to 2.2


The Oak/Shrubland Transition Community shifts to the Oak/Woodland Community when heavy continuous grazing, no fires, and land in idle occur.
State 3
Converted Land State
Conversion of the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah (1.1) to Converted Land Community (3.1) (mainly for cotton production) occurred from first settlement by European settlers during the middle 1800’s and continued until early 1900’s. Some remains in cropland today. This site is often planted to introduced grasses following crop production or brush control. Typical species planted include Bermudagrass varieties and yellow bluestems. Many of these species may become invasive and once established they are difficult to remove and hinders the establishment of native species. In the Threeawn/Invasive Brush Transition Community, the plant community will move toward a transition of invasive brush species such as mesquite and/or cacti without the annual application of the cultural practices, especially fertilization. The introduced grass species will start to disappear and be replaced by three-awns and annuals. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Grasses comprise of 30% and shrubs/trees comprise of 40% species composition.
Dominant plant species
-
Bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon), grass
Community 3.1
Converted Land Community
Conversion of the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah (1.1) to Converted Land Community (3.1) (mainly for cotton production) occurred from first settlement by European settlers during the middle 1800’s and continued until early 1900’s. Some remains in cropland today. The early cropping with little regard for erosion control leads to severe erosion by water. Erosion changes fertility, soil structure and moisture holding capacity of the soil. While restoration of this site to some semblance of the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah (1.1) is possible with seeding, prescribed grazing and prescribed burning; a complete restoration of the reference plant community in a reasonable time is very unlikely. In recent years if cropping is abandoned, the land is usually planted to introduced grass and managed as pastureland. Refer to cropland capability classes for production potentials and limitations. This site is often planted to introduced grasses following crop production or brush control. These grasses are planted mostly for livestock grazing and some hay production. Typical species planted include Bermudagrass varieties and yellow bluestems. Many of these species may become invasive and once established they are difficult to remove and hinders the establishment of native species. The establishment and maintenance of these species requires fertilization, weed control and prescribed grazing management. Without the annual application of these cultural practices the plant community will move toward a transition of invasive brush species such as mesquite and/or juniper, silver bluestem, three-awns, tridens species, western ragweed and other various herbaceous plant species. Refer to pastureland suitability groups for species suitability, production potentials and limitations.
Figure 21. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX5520, Pastureland. Coastal Bermudagrass or Introduced Species..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 21 | 22 | 10 | 5 | 14 | 10 | 8 | 0 |
Community 3.2
Three-awn/Invasive Brush Transition Community
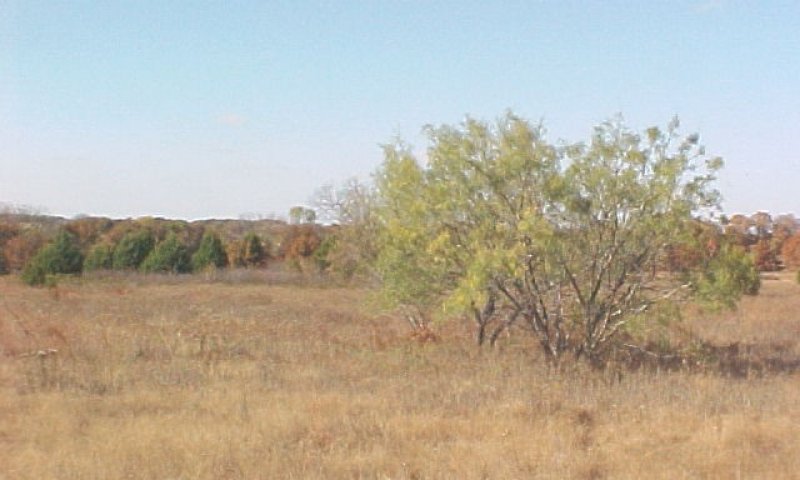

Figure 22. 3.2 Three-awn/Invasive Brush Transition Community
Without the annual application of the cultural practices, especially fertilizer, the plant community will move toward a transition of invasive brush species such as mesquite (Prosopis spp.) and/or cactus (Opuntia spp.). The introduced grass species will start to disappear and be replaced by three-awns (Aristida spp.) and annuals.
Figure 23. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 9. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forb | 841 | 1121 | 1401 |
| Grass/Grasslike | 841 | 1121 | 1401 |
| Shrub/Vine | 560 | 841 | 1121 |
| Tree | 560 | 841 | 1121 |
| Total | 2802 | 3924 | 5044 |
Figure 24. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX5517, Threeawn/Invasive Shrubs Community. Threeawns and Invasive Shrub dominant community. Converted from old cropland into threeawn shrub community..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 2 | 2 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 23 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 2 |
Pathway 3.1A
Community 3.1 to 3.2
The Converted Land Community will shift to the Three-awn/Invasive Brush Transition Community with the use of heavy continuous grazing, no brush management, and land being abandoned.
State 4
Invasive Brush State
The Invasive Brush/Midgrass Community occurs due to continued absence of added fertility the plant community will continue change toward a brushy condition. The shrubs will continue to thicken especially mesquite. At this state the introduced grasses have almost disappeared. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Grasses make up 30% species composition and trees/shrubs make up 40%.
Community 4.1
Invasive Brush/Midgrasses Community
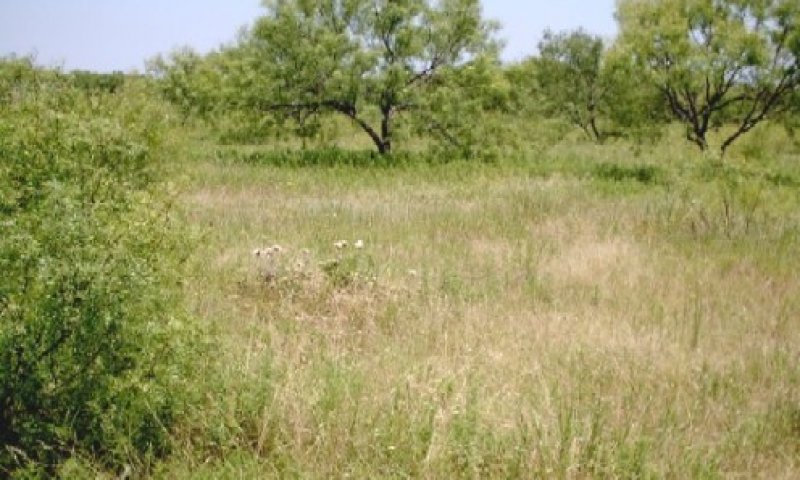

Figure 25. 4.1 Invasive Brush/Midgrasses Community
Without added fertility and brush management, the plant community will continue change toward a brushy condition. The shrubs will continue to thicken especially mesquite and as the brush ages the historic hardwoods start to appear. The grass changes toward more perennials, where the fertility is especially low splitbeard bluestem appears and may dominate the grasses. At this state the introduced grasses have almost disappeared. Annual production ranges from 2500 to 4500 pounds per acre. Grasses make up 30% species composition and trees/shrubs make up 40%.
Figure 26. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 10. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 841 | 1205 | 1569 |
| Forb | 729 | 1037 | 1345 |
| Tree | 673 | 897 | 1121 |
| Shrub/Vine | 560 | 785 | 1009 |
| Total | 2803 | 3924 | 5044 |
Figure 27. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). TX5523, Midgrass & Invasive Brush Community. old cropland field dominated by plant community consisting of midgrasses and invasive brush..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 2 | 2 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 23 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 2 |
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
The Tallgrass/Oak Savannah State will transition into the Oak Shrubland State due to continuous heavy grazing, no fires, and land not in use.
Transition T1B
State 1 to 3
The Tallgrass/Oak Savannah State will transition into the Converted Land State with the application of various conservation practices including Pasture/Hay Planting, Crop Cultivation, Pest Management, Nutrient Management, and Prescribed Grazing.
Restoration pathway R2A
State 2 to 1
With the use of Prescribed Grazing, Brush Management, Range Planting, and Prescribed Burning conservation practices, the Oak Shrubland State can be restored into the Tallgrass/Oak Savannah State.
Conservation practices
| Brush Management | |
|---|---|
| Conservation Crop Rotation | |
| Prescribed Burning | |
| Prescribed Grazing | |
| Range Planting |
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
The Oak Shrubland State will transition into the Converted Land State with the use of various conservation practices including Pasture/Hay Planting, Crop Cultivation, Pest Management, and Nutrient Management.
Transition T3A
State 3 to 4
The Converted Land State will transition into the Invasive Brush State due to land being abandoned from land conversion such as cropland and pastureland as well as no fires.
Additional community tables
Table 11. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Tallgrass | 841–1513 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 841–1513 | – | ||
| 2 | Tallgrasses | 280–504 | ||||
| big bluestem | ANGE | Andropogon gerardii | 0–252 | – | ||
| Indiangrass | SONU2 | Sorghastrum nutans | 0–252 | – | ||
| 3 | Midgrass | 140–252 | ||||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 140–252 | – | ||
| 4 | Midgrass | 140–252 | ||||
| silver beardgrass | BOLAT | Bothriochloa laguroides ssp. torreyana | 140–252 | – | ||
| 5 | Cool-season Grass | 140–252 | ||||
| Texas bluegrass | POAR | Poa arachnifera | 140–252 | – | ||
| 6 | Midgrass | 140–252 | ||||
| purpletop tridens | TRFL2 | Tridens flavus | 140–252 | – | ||
| 7 | Midgrass | 280–504 | ||||
| sand lovegrass | ERTR3 | Eragrostis trichodes | 280–504 | – | ||
| 8 | Midgrass | 140–252 | ||||
| composite dropseed | SPCOC2 | Sporobolus compositus var. compositus | 0–129 | – | ||
| sand dropseed | SPCR | Sporobolus cryptandrus | 0–129 | – | ||
| 9 | Mid/Shortgrasses | 140–252 | ||||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 0–62 | – | ||
| Canada wildrye | ELCA4 | Elymus canadensis | 0–62 | – | ||
| plains lovegrass | ERIN | Eragrostis intermedia | 0–62 | – | ||
| Texas wintergrass | NALE3 | Nassella leucotricha | 0–62 | – | ||
| crowngrass | PASPA2 | Paspalum | 0–62 | – | ||
| switchgrass | PAVI2 | Panicum virgatum | 0–62 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 10 | Perennial Forbs | 140–252 | ||||
| Cuman ragweed | AMPS | Ambrosia psilostachya | 0–62 | – | ||
| sagebrush | ARTEM | Artemisia | 0–62 | – | ||
| sensitive partridge pea | CHNI2 | Chamaecrista nictitans | 0–62 | – | ||
| whitemouth dayflower | COER | Commelina erecta | 0–62 | – | ||
| prairie clover | DALEA | Dalea | 0–62 | – | ||
| Engelmann's daisy | ENGEL | Engelmannia | 0–62 | – | ||
| singlestem buckwheat | ERAC3 | Eriogonum acaule | 0–62 | – | ||
| beeblossom | GAURA | Gaura | 0–62 | – | ||
| Maximilian sunflower | HEMA2 | Helianthus maximiliani | 0–62 | – | ||
| lespedeza | LESPE | Lespedeza | 0–62 | – | ||
| dotted blazing star | LIPU | Liatris punctata | 0–62 | – | ||
| Nuttall's sensitive-briar | MINU6 | Mimosa nuttallii | 0–62 | – | ||
| yellow puff | NELU2 | Neptunia lutea | 0–62 | – | ||
| evening primrose | OENOT | Oenothera | 0–62 | – | ||
| amberique-bean | STHE9 | Strophostyles helvola | 0–62 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 11 | Shrubs | 140–252 | ||||
| sumac | RHUS | Rhus | 0–62 | – | ||
| blackberry | RUBUS | Rubus | 0–62 | – | ||
| roundleaf greenbrier | SMRO | Smilax rotundifolia | 0–62 | – | ||
| grape | VITIS | Vitis | 0–62 | – | ||
|
Tree
|
||||||
| 12 | Tree | 191–370 | ||||
| blackjack oak | QUMA3 | Quercus marilandica | 0–168 | – | ||
| post oak | QUST | Quercus stellata | 0–168 | – | ||
| 13 | Tree | 90–168 | ||||
| hackberry | CELTI | Celtis | 0–39 | – | ||
| plum | PRUNU | Prunus | 0–39 | – | ||
| gum bully | SILA20 | Sideroxylon lanuginosum | 0–39 | – | ||
| Hercules' club | ZACL | Zanthoxylum clava-herculis | 0–39 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
The historic Postoak-tallgrass savannah was habitat to migratory bison herds, deer, turkey, migratory birds and large predators such as wolves, coyotes, mountain lions and black bear. White-tail deer, turkey, bobcats and coyotes along with resident and migratory birds and small mammals find suitable habitat today. Domestic livestock and white-tail deer are the dominant grazers and browsers of the site. As the savannah changes through the various vegetative states towards the Postoak Woodland, the quality of the habitat may improve for some species and decline for others. Management must be applied to maintain a vegetative state in optimum habitat quality for the desired animal species.
Hydrological functions
Peak rainfall periods occur in April, May, June, September and October. Rainfall amounts may be high (3 to 10 inches per event) and events may be intense. The soil of this site are very susceptible to erosion and severe erosion occurs where adequate herbaceous cover is not maintained and on heavy use areas such as roads and livestock trails. Periods of 60 plus days of little or no rainfall during the growing season are common. The hydrology of this site may be manipulated with management to yield higher runoff volumes or greater infiltration to groundwater. Management for less herbaceous cover will favor higher surface runoff while dense herbaceous cover favors ground water recharge. Potential movement of soil (erosion), pesticides and both organic and inorganic nutrients(fertilizer) should always be considered when managing for higher volumes of surface runoff.
Recreational uses
Hunting, hiking, camping, equestrian, bird watching and off road vehicle use.
Wood products
Oaks and mesquite are used for firewood. Mesquite is also used for barbecue wood.
Other products
None.
Other information
None.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented here has been derived from limited NRCS clipping data and field observations of range trained personnel: Lemuel Creswell RMS, Comanche; Earl V. Hogan RMS, James Luton RMS, Montague; William Donham, Agron, Granbury; Kent Ferguson RMS, Weatherford.
References
-
. 2021 (Date accessed). USDA PLANTS Database. http://plants.usda.gov.
Other references
White-tailed Deer, Their Foods and Management in the Cross Timbers By Kenneth L. Gee, Michael D Porter, Steve Demarais, Fred C. Bryant, and Gary Van Vreede. A Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation Publication, 1991
Technical Review:
Homer Sanchez, State Rangeland Management Specialist, NRCS, Temple, Texas
Mark Moseley, State Rangeland Management Specialist, NRCS, Stillwater, Oklahoma
Kent Ferguson, Zone Rangeland Management Specialist, NRCS, Weatherford, Texas
Dr. Jack Eckroat, Grazing Lands Specialist, NRCS, Stillwater, Oklahoma
Justin Clary, Rangeland Management Specialist, NRCS, Temple, Texas
Contributors
Earl Hogan
PES edits by Colin Walden, Stillwater Soil Survey Office
Approval
Bryan Christensen, 9/21/2023
Acknowledgments
Site Development and Testing Plan:
Future work, as described in a Project Plan, to validate the information in this Provisional Ecological Site Description is needed. This will include field activities to collect low, medium and high intensity sampling, soil correlations, and analysis of that data. Annual field reviews should be done by soil scientists and vegetation specialists. A final field review, peer review, quality control, and quality assurance reviews of the ESD will be needed to produce the final document. Annual reviews of the Project Plan are to be conducted by the Ecological Site Technical Team.
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | Colin Walden, Range Management Specialist, Soil Survey Region 9. |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | colin.walden@ok.usda.gov |
| Date | 01/26/2018 |
| Approved by | Bryan Christensen |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
Minimal evidence of current or past rill formation. -
Presence of water flow patterns:
Few water flow patterns on steep areas. Short and stable, not incising. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
No pedestals terracettes present. -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
Bare ground less than 10 percent. Bare areas small and not connected. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
No gullies present. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
No wind scoured areas. -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Litter movement less than 3 feet. Vegetative cover should restrict litter movement over long distances. Only herbaceous litter less than .25 inches expected to move. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Soil stability scores of 5 or greater expected. -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
Chaney - A--0 to 4 inches; dark grayish brown (10YR 4/2) loamy sand, very dark grayish brown (10YR 3/2) moist; weak fine granular structure;
-
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
Presence of perennial tall and midgrasses help to facilitate percolation into the soil. Some
runoff expected on steeper slopes during moderate precipitation events. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
No compaction under reference conditions. Beware texture change of Bt horizon not product of compaction. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Native Tallgrasses (groups 1,2)Sub-dominant:
Forbs (10)
Oaks (12)Other:
All other groupsAdditional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Possible mortality only during prolonged drought. Less than 5%. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Litter expected to be at 75% cover at average .25 inch depth. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
Annual production 3500 lb/acre. Ranging from 2500 - 4500 lbs. -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
Juniper(ashe juniper/eastern redcedar) most common invader. Also greenbriar, poison ivy, and other woodies will increase
without fire. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
Plants should be capable of reproducing every year with exception of prolonged growing season drought.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.