
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F098XB031IN
Kankakee Acidic Interdunes
Last updated: 1/12/2024
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
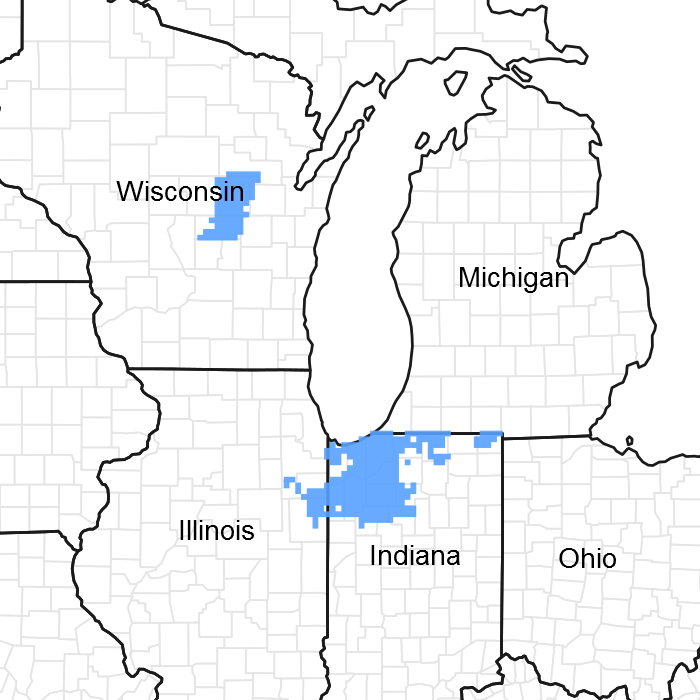
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 098X–Southern Michigan and Northern Indiana Drift Plains
"This area is in the Eastern Lake Section of the Central Lowland Province of the Interior Plains. It is a broad glaciated plain that is deeply mantled by till in the north and outwash to the south. Much of the area is nearly level to gently rolling. Elevation ranges from 183 to 391 m (600 to 1285 ft). Local topographic relief averages 9 m and ranges up to 74 m (30 to 245 ft). Highest relief occurs adjacent to river valleys eroded through moraines. Topography is more subdued south of the Atlantic/Gulf drainage divide near the Michigan/Indiana state line, elevations ranging from 185 to 280 m (605 to 920 ft). Local topographic relief in the south averages 4 m and ranges up to 49 m (10 to 160 ft).
The surface of this area is covered by 30 to 150 m (100 to 500 ft) of glacial drift in most areas. At the northern edge of the area, the drift is more than 100 meters (300 ft) thick. From the Grand River basin northward, most of the drift consists of till from the Saginaw Lobe of the Wisconsin Ice Sheet. From the Kalamazoo River basin southward, there are significant deposits of unconsolidated sand and gravel outwash formed between major lobes of the receding Wisconsin Ice Sheet. The outwash deposits are reworked as sand dunes in the Kankakee River basin.
The bedrock beneath the glacial deposits in this area is deformed in the shape of a basin. The center of this basin is in the north-central part of the area. Pennsylvanian-age sandstone are in the center of the basin, and Mississippian-age sandstone and shale beds form the outer rings of the basin. In a few areas the drift deposits are less than 2 m (6 ft) thick, where glacial outwash channels have eroded to limestone bedrock in Grand Rapids, and where sandstone bedrock cuestas peak in elevation in near Hillsdale, Michigan. A sandstone cliff < 15 m high (<50 ft) occurs along a short stretch of the Grand River in Grand Ledge, Michigan.
Most of the rivers in this area are short because of their proximity to the Great Lakes east and west of the area. The largest watersheds, the St. Joseph River, Grand River, and Kalamazoo River drain into Lake Michigan. The southern extent of the MLRA is drained by the Kankakee River of the Mississippi River watershed."
Classification relationships
Among the USFS ecoregional framework (Cleland et al., 2007), most of MLRA 98 is represented by the Humid Temperate Domain (200), Hot Continental Division (220), Midwest Broadleaf Forest Province (222), South Central Great Lakes Section (222J), subsections 222Jc, 222Jg, 222Jh, and 222Jf. Similar sites within the portion of MLRA 98 that overlap the Prairie Division (250) and Prairie Parkland Province
(251) are treated as separate ecological sites. MLRA 98 recently was adjusted to exclude portions of Warm Continental Division (210), Laurentian Mixed Forest Province (212) to the north, and subsections 222Ja and 222Jb to the northwest.
Among the EPA ecoregional framework (Omernik and Griffith, 2014), most of MLRA 98 falls within Eastern Temperate Forests (Level I: 8), Mixed Wood Plains (Level II: 8.1), Southern Michigan/Northern Indiana Drift Plains (Level III: 56), and Level IV: 56b, 56g, and 56h. Similar sites within the portion of MLRA 98 that overlap the Central USA Plains (Level II: 8.2) and Central Corn Belt Plains (Level III: 54) are treated as separate ecological sites. MLRA 98 recently was adjusted to exclude portions of Northern Forests (Level I: 5), Mixed Wood Shield (Level II: 5.2), Northern Lakes and Forests (Level III: 50) to the north, and level IV: 56d and 56f to the northwest.
Ecological site concept
The central concept of the Kankakee Acidic Interdunes is deep sands (>70% sands >100 cm deep) with low base saturation (pHs <5.5 and/or Spodosols) and high seasonal water tables intermediate in wetness between wetland and uplands (somewhat poorly drained). Such sites support vegetation composed of both upland and wetland species which tolerate low nutrient conditions. Characteristic species include pin oak (Quercus palustris) and black gum (Nyssa sylvatica) in forested sites with ferns and heaths (Ericaceae) in the understory. Open sites tend to have various warm season grasses, sedges, rushes and forbs with Atlantic-Gulf Coastal Plain affinities.
Associated sites
| F098XB030IN |
Kankakee Sand Dunes |
|---|---|
| F098XB032IN |
Kankakee Wet Acidic Interdunes |
| R098XB033IN |
Kankakee Moist Drift Flats |
Similar sites
| F098XA017MI |
Moist Acidic Drift Flats |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus palustris |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Rhexia virginica |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.