Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F113XY907IL
Fragic Till Plain Woodland
Last updated: 5/17/2024
Accessed: 02/26/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 113X–Central Claypan Areas
The eastern Illinois portion of the Central Claypan Areas MLRA is in the Till Plains Section of the Central Lowland Province of the Interior Plains (USDA-NRCS, 2006) and includes the Southern Till Plain Natural Division of the natural divisions of Illinois (Schwegman, 1973; 1997; IDNR, 2018) in south-central Illinois. South-central Illinois is a dissected Illinoisan till plain south of the terminal Wisconsin moraine. This region consists of nearly level to gently sloping, old till plains. Stream valleys are shallow and generally are narrow. Elevation is about 660 feet (200 meters), increasing gradually from south to north. Local relief is generally low on the broad, flat till plains and flood plains and high on the dissected hills bordering rivers or drainage systems. The Kaskaskia, Little Muddy, Little Wabash, Embarras, and Skillet Fork rivers are part of this area. This region is covered with loess, which overlies old glacial drift (Illinoisan till) that has a high content of clay. Fragipans are also present. Pennsylvanian limestone and shale bedrock underlay the glacial till. The dominant soil orders in this region are Alfisol and Mollisol. The soils in the area predominantly have a mesic soil temperature regime, an aquic or udic soil moisture regime, and mixed or smectitic mineralogy. They generally are very deep, well drained to poorly drained, and loamy or clayey. (USDA-NRCS, 2006).
Classification relationships
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) (USDA-NRCS, 2006):
113 – Central Claypan Areas, Eastern Part
U.S. Forest Service Ecoregions (Cleland et al. 2007):
Domain: Humid Temperate Domain
Division: Hot Continental Division
Province: Eastern Broadleaf Forest (Continental)
Province Code: 222
Section: Central Till Plains, Oak-Hickory Section
Section Code: 222G
Ecological site concept
This woodland community type is found throughout the Central Claypan Areas MLRA in south-central Illinois. Fragic Till Plain Woodland ecological sites are found on convex ridges, knolls and gentle side slopes of drainageways on till plains. They formed in loess and the underlying silty or loamy deposits that overlie a strongly developed paleosol with a shallow to moderately deep fragipan.
The historic reference plant community was a woodland dominated by drought and fire-tolerant post oak (Quercus stellata Wangenh.*) and hickory species (Carya spp.), including shagbark hickory (Carya ovata (Mill.) K. Koch), mockernut hickory (Carya tomentosa (Lam.) Nutt.) along with a dense ground flora. Post oak and associated trees may be stunted due to the unfavorable soil conditions. Soils contain a subsurface hardpan (fragipan) that is impermeable or nearly impermeable, causing a shallowly perched water table. The soil moisture fluctuates widely throughout the growing season. A fragipan layer leads to 'xerohydric' conditions. The canopy is typically strongly dominated by post oak, but may include white oak (Quercus alba L.), swamp white oak (Quercus bicolor Willd.), southern red oak (Quercus falcata Michx.), and/or blackjack oak (Quercus marilandica Münchh.). The shrub and woody vine strata may contain Virgina creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia (L.) Planch.), Carolina rose (Rosa carolina L.), blackberry (Rubus spp.), and poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans (L.) Kuntze.). The herbaceous layer can be fairly dissimilar from one stand to the next. Some stands can be dominated by sweet woodreed (Cinna arundinacea L.), Indian woodoats (Chasmanthium latifolium (Michx.) Yates.) and slender spikerush (Eleocharis tenuis var. verrucosa (Svens.) Svens.). Plants more typical of dry and dry-mesic soil grow on slight rises, including fescue sedge (Carex festucacea Schkuhr ex Willd.), Pennsylvania sedge (Carex pensylvanica Lam.), poverty oatgrass (Danthonia spicata (L.) P. Beauv. ex Roem. & Schult.), woodland sunflower (Helianthus divaricatus L.), and others (Taft et al. 1994, 1995; NatureServe 2017).
Woodlands were distinguished from forest, by their relatively open understory, and the presence of sun-loving ground flora species (White, 1994). Fire was the primary disturbance factor that maintained this ecological site, while drought, windthrow, and grazing were secondary factors (LANDFIRE 2009).
* All plant common and scientific names in this document were obtained from the U.S. Department of Agriculture – Natural Resources Conservation Service National PLANTS Database (USDA NRCS, 2018).
Associated sites
| F113XY905IL |
Wet Upland Woodland The Fragic Till Plain Woodland ecological sites are in a drainage sequence with Wet Upland Woodlands that are on nearly level summits and broad till plains. |
|---|---|
| F113XY911IL |
Loamy Till Backslope Forest A backslope forest ecological site, that is often downslope, on loamy till soils. Fragipans are absent. |
| F113XY910IL |
Fragic Backslope Woodland Fragic Backslope ecological sites are on steeper downslopes that also support oak-hickory woodlands with fragic horizons. |
Similar sites
| F113XY910IL |
Fragic Backslope Woodland Fragic Backslope Woodland ecological sites are on steeper downslopes that also support oak-hickory woodlands with fragic horizons. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus stellata |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Rosa carolina |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Schizachyrium scoparium |
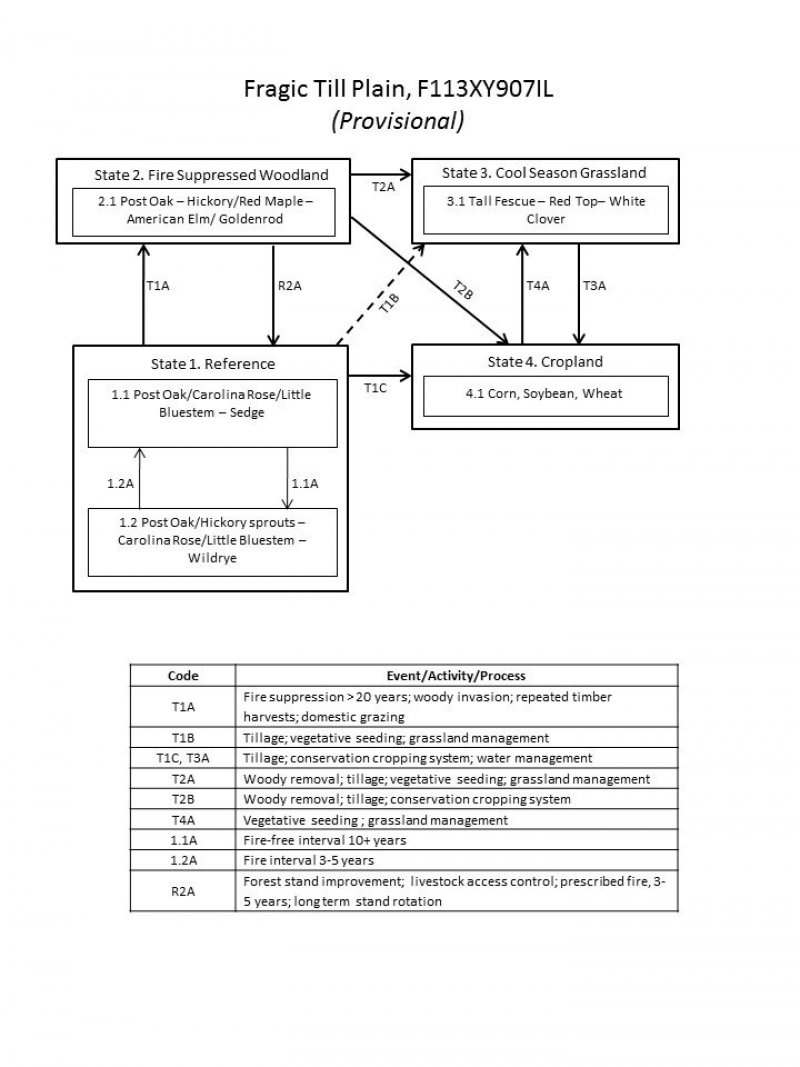
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
| T1A | - | Fire suppression > 20 years; woody invasion; repeated timber harvests; domestic grazing. |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Tillage; vegetative seeding; grassland management |
| T1C | - | Tillage; conservation cropping system; water management |
| R2A | - | Forest stand improvement; livestock access control; prescribed fire, 3-5 years; long term stand rotation |
| T2A | - | Woody removal; tillage; vegetative seeding; grassland management |
| T2B | - | Woody removal; tillage; conservation cropping system |
| T3A | - | Tillage; conservation cropping system; water management |
| T4A | - | Vegetative seeding; grassland management |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Fire interval greater than 10 years |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Fire interval 3-5 years |