Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F114XA404IN
Outwash Upland Forest
Last updated: 9/26/2024
Accessed: 11/21/2024
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 114X–Southern Illinois and Indiana Thin Loess and Till Plain
MLRA 114 makes up about 4,550 square miles (11,795 square kilometers. The three parts of this MRLA are mostly in the Till Plains Section of the Central Lowland Province of the Interior Plains. The western third of the western part is in the Highland Rim Section of the Interior Low Plateaus Province of the Interior Plains. The eastern half of the eastern part is in the Kanawha Section of the Appalachian Plateaus Province of the Appalachian Highlands. Both large and small tributaries of the Ohio River dissect the nearly level to very steep glaciated uplands in this area. The major streams and rivers have well defined valleys with broad flood plains and numerous stream terraces. The flood plains along the smaller streams are narrow. Broad summits are nearly level to gently sloping. Elevation ranges from 320 feet (100 meters) on the southernmost flood plain along the Ohio River to 1,250 feet (380 meters) on the highest ridges. Local relief is mainly 10 to 50 feet (3 to 15 meters), but it can be 50 to 100 feet (15 to 30 meters) along drainageways and streams. Also, the Ohio River bluffs are as much as 300 feet (90 meters) above the river valley floor.
Classification relationships
USFS: 222 Eastern Broadleaf Forest (Continental) Province
Homoya's Natural Regions of Indiana: Bluegrass Region
The following NatureServe Explorer Ecological System has a high level of probability to match the ecological site found on these soils. Field verification is needed prior to using this information for conservation planning and/or restoration initiatives:
Ecological site concept
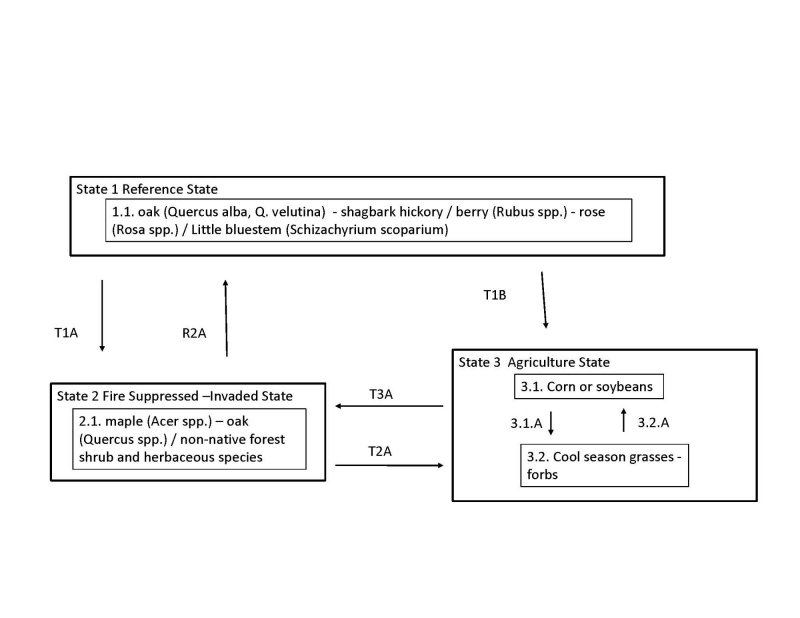
The Outwash Upland Forest site is that of a dry oak-hickory forest. The forest canopy is dominated by black oak, white oak and shagbark hickory. Associate canopy species include included black cherry, sassafras, and pignut hickory. Fire played an important role in maintaining an open understory, so brambles and native roses were common in the understory. A frequent fire regime allowed prairie species such as Pennsylvania sedge and big bluestem to exist on sites. Low severity surface fires maintained the dominance of oak and hickory trees. An increase in the fire return interval will move this state to more fire sensitive, shade tolerant species such as sugar maple and American beech. Currently, the majority of the site is in agricultural production, with the majority being used for growing corn and soybeans.
Associated sites
| F114XA502IN |
Till Uplands Till Upland sites may be associated with Outwash Upland Forest sites. |
|---|
Similar sites
| F114XA103IN |
Sloping Lacustrine Forest Similar tree species (oak, hickory, maple.) may be found on Sloping Lacustrine Forest sites. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Rubus |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Schizachyrium |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
| T1A | - | Fire free intervals in excess of approximately 40 years or more. |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Clearing site; tillage; seeding; weed control; agricultural management |
| R2A | - | Long-term restoration inputs including brush control, weed control, timber stand improvement projects, planting of desired species and prescribed burning. |
| T2A | - | Clearing site; tillage; seeding; weed control; agricultural management |
| T3A | - | Abandonment; no management inputs |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
| 3.1A | - | Seeding; weed control, grassland management |
|---|---|---|
| 3.2A | - | Tillage; site preparation; seeding; row crop management |