Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F120AY003KY
Loess Uplands
Last updated: 10/01/2024
Accessed: 02/27/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 120A–Kentucky and Indiana Sandstone and Shale Hills and Valleys, Southern Part
120A—Kentucky and Indiana Sandstone and Shale Hills and Valleys, Southern Part
This area is primarily in Kentucky (83 percent) and Illinois (17 percent). A very small part is in Indiana. The area makes up about 8,905 square miles.
Physiography:
This area is in the Highland Rim Section of the Interior Low Plateaus Province of the Interior Plains. Tributaries of the Ohio River dissect the nearly level to very steep uplands. The major streams and rivers have well defined valleys with broad flood plains and numerous stream terraces. The flood plains along the smaller streams are narrow. Elevation ranges from 345 feet (105 meters) on the flood plain along the Ohio River to about 950 feet (290 meters) on the highest ridges. Local relief varies widely within the area.
Soils:
Most of the soils are Udalfs. Most of the soils have a mesic soil temperature regime, a udic soil moisture regime, and mixed mineralogy. The soils in the area formed in loess or in sandstone, shale, siltstone, or limestone residuum. Fragiudalfs (Hosmer, Loring, and Zanesville series) and Fraglossudalfs (Sadler and Grenada series), which have a fragipan, and Hapludalfs (Wellston and Frondorf series) are the dominant soils on ridgetops and side slopes. Fragiudults (Tilsit series) and Hapludults (Gilpin and Shelocta series) are in the northern part of the area. Hapludolls (Huntington series), Eutrudepts (Nolin, Lindside, and Chagrin series), and Endoaquepts (Melvin and Newark series) are loamy soils on flood plains along the major streams. Endoaquepts and Epiaqualfs (Karnak and McGary series) are clayey soils in slackwater areas along the major rivers. Dystrudepts (Cuba and Steff series), Eutrudepts (Haymond and Wilbur series), Fluvaquents (Wakeland series), and Endoaquepts (Stendal series) are loamy soils on flood plains of local origin. Hapludalfs (Wheeling and Elk series) and Fragiudalfs (Otwood and Lawrence series) are loamy soils on terraces along the major streams.
Classification relationships
Landfire Biophysical Setting Model 4713050, Southern Interior Low Plateau Dry-Mesic Oak Forest.
Acidic Mesophytic forest (Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission. Natural Communities of Kentucky, 2009)
Ecological site concept
This ecological site is characterized by loess soils within hilly terrain on slopes typically less than 10%. Representative soils include: Alford, Baxter, Menfro, Muren.
The communities described in this provisional document reflect plant communities that are likely to be found on these soils and have not been field verified. This PES describes hypotheses based on available data of many different scales and sources and has not been developed utilizing site-specific ecological field monitoring. This PES does not encompass the entire complexity or diversity of these sites. Field studies would be required to develop a comprehensive and science-based native plant restoration plan for these sites.
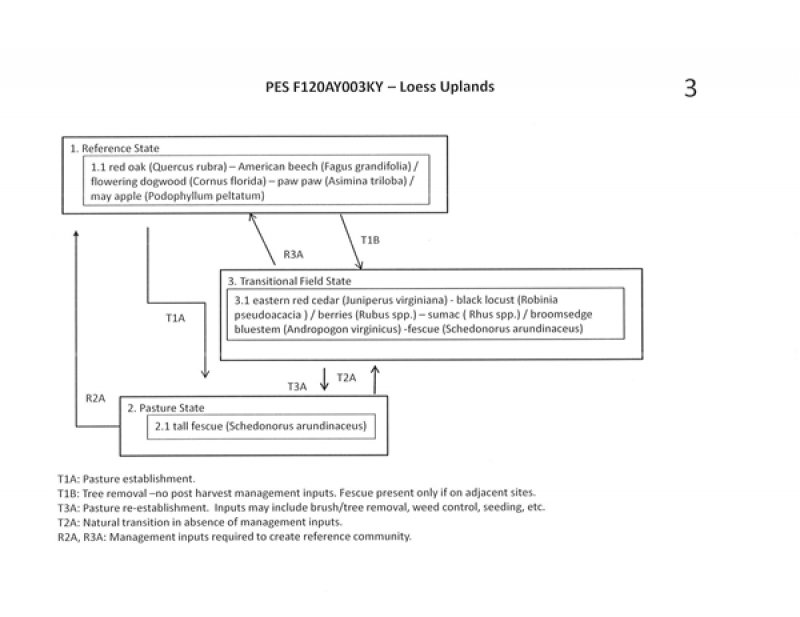
State 1, Phase 1.1. red oak (Quercus rubra) – American beech (Fagus grandifolia) / flowering dogwood (Cornus florida) – paw paw (Asimina triloba) / may apple (Podophyllum peltatum)
State 2, Phase 2.1: Pasture. Plant species dominants: Schedonorus arundinaceus (tall fescue. Species present are dependent upon seeding and management. State: 3. Transitional (Abandoned) Field
State 3, Phase 3.1: eastern red cedar (Juniperus virginiana) - black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia )/ berries (Rubus spp.) – sumac ( Rhus spp.) / broomsedge bluestem (Andropogon virginicus) -fescue (Schedonorus arundinaceus)
This phase is best described as an old field habitat with a mixture of native and introduced grasses and a variety of native and non-native herbs, forbs, seedlings, and saplings.
All mapunits in this project have slopes 12% or above so cropland was not included as a major state in this ecological model.
Restoration of states to the reference community would require long-term, intensive management inputs.
Associated sites
| F120AY001KY |
Deep Loess Deep Loess |
|---|
Similar sites
| F120AY001KY |
Deep Loess Deep Loess |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Quercus rubra |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Asimina triloba |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Podophyllum peltatum |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.