Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R220XY349AK
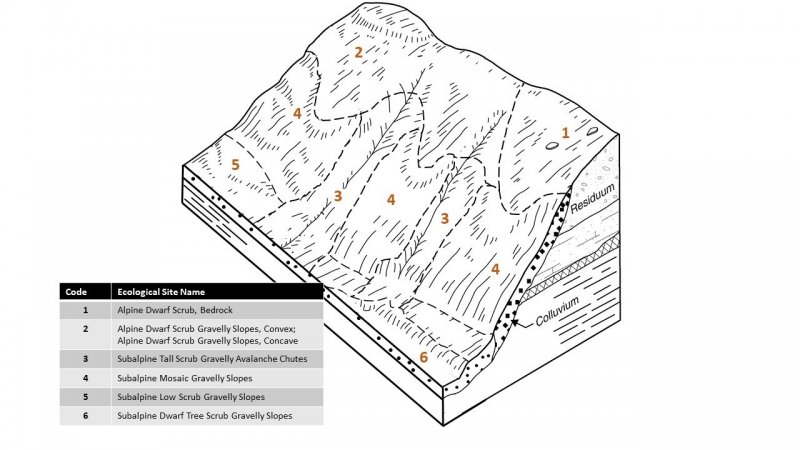
Subalpine Scrub Gravelly Dry Chutes
Last updated: 6/05/2025
Accessed: 03/14/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 220X–Alexander Archipelago-Gulf of Alaska Coast
The Alexander Archipelago-Gulf of Alaska Coast area consists of a narrow arc of islands and lower elevation coastal mountains in the Southern Alaska Region. This area spans from the Alexander Archipelago in southeastern Alaska, north and west along the coast of the Gulf of Alaska and Prince William Sound, and further west to the southern tip of the Kenai Peninsula and the northeastern islands of the Kodiak Archipelago. The area makes up about 27,435 square miles (USDA 2006). The terrain primarily consists of low to moderate relief mountains that are deeply incised. Throughout the area glaciers, rivers, and streams have cut deep, narrow to broad valleys. The broader valleys have nearly level to strongly sloping flood plains and stream terraces. Alluvial and colluvial fans and short footslopes are common in the valleys along the base of the mountains. Rocky headlands, sea cliffs, estuaries, and beaches are common along the coast.
During the late Pleistocene epoch, the entire area was covered with glacial ice. The numerous fjords of the Alexander Archipelago and Prince William Sound were formed chiefly as a result of glacial scouring and deepening of preglacial river valleys. Most glacial deposits have been eroded away or buried by mountain colluvium and alluvium, which cover about 90 percent of the present landscape. The remaining glacial and glaciofluvial deposits are generally restricted to coastal areas. During the Holocene epoch, volcanic activity within and adjacent to this area deposited a layer of volcanic ash of varying thickness on much of the landscape in the southeastern and northwestern parts of the area. Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Lower Tertiary stratified sedimentary rocks and Cretaceous and Tertiary intrusive rocks underlie much of the area and are exposed on steep mountain
slopes and ridges (USDA 2006).
The dominant soil orders in this MLRA are Spodosols, Histosols, and Entisols. Soils in the area typically have a cryic soil temperature regime, an udic moisture regime, and have mixed minerology. Spodosols are common on mountains and hills having been formed in gravelly or cobbly colluvium, glacial till, and varying amounts of silty volcanic ash. These Spodosols commonly range from shallow to deep, are well to somewhat poorly drained, and typically classify as Humicryods or Haplocryods. Histosols that are poorly to very poorly drained occur on footslopes, discharge slopes, and valley floors. These wet histosols commonly classify as Cryosaprists, Cryohemists, and Cryofibrists. Histosols that are well drained occur on steep mountainsides. These dry Histosols commonly classify as Cryofolists. Entisols are common on flood plains, stream terraces, and outwash plains having been formed in silty, sandy, and gravelly to cobbly alluvium. These Entisols are generally deep, range from well to somewhat poorly drained, and commonly classify as Cryaquents and Cryofluvents. Miscellaneous (nonsoil) areas make up about 23 percent of this MLRA. The most common miscellaneous areas are chutes, rock outcrop, rubble land, beaches, riverwash, and water.
This area represents the Northern extent of the Pacific temperate rainforest and is characterized by productive stands of conifers. Western hemlock and Sitka spruce are the dominant trees on mountains and hills at lower elevations. Due to warmer temperatures, western red cedar and Alaska cedar are more prevalent in the southern portion of this area. Black cottonwood and mixed forest types occur on flood plains. Areas of peat and other sites that are too wet for forest growth support sedge-grass meadows and low scrub. As elevation increases, mountain hemlock becomes the dominant tree in forested stands, which marks the transition to subalpine vegetation. The subalpine life zone typically occurs at elevations between 1500 to 3000 feet (Boggs et al. 2010, Carstensen 2007, Martin et al. 1995). Other common subalpine plant communities include tall alder scrub and bluejoint-forb meadows. Alpine vegetation occurs at even higher elevations, which marks the transition to the Southern Alaska Coastal Mountains Area (MLRA 222).
This area includes the Municipality of Juneau, Alaska's capital, and a number of smaller coastal towns and villages. Federally administered lands within this MLRA include Admiralty Island National Monument and part of Misty Fjords National Monument, Tongass National Forest, Chugach National Forest, and Glacier Bay, Wrangell-St. Elias, and Kenai Fjords National Parks and Preserves. The southern terminus of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline is in Valdez.
For many decades, logging, commercial fishing, and mining have been the primary industrial land uses throughout much of the area. In recent years, changes in public interests, land use policies, and timber economics have contributed to a significant decline in the timber industry. Commercial fishing continues to be an important industry and most communities support a fleet of boats and fishing related facilities. A number of mines operate in the area and others have been prospected and proposed. Tourism and wildland recreation are becoming increasingly important within the area. Subsistence hunting, fishing, and gathering provide food and a variety of other resources to local residents and remain the principal economy for residents of remote villages.
Classification relationships
USFS Ecoregion Province: Marine Mountains (M240), Forest-Meadow High (M242b) (Bailey 2007)
U.S. EPA Level III Ecoregion: Pacific Coastal Mountains (119) (Gallant et al. 2010)
National Vegetation Classification – Ecological Systems: Alaskan Pacific Maritime Alder-Salmonberry Shrubland (CES204.152) (NatureServe 2015)
Biophysical Settings: Alaskan Pacific Maritime Alder-Salmonberry Shrubland (BpS 7816520) (LANDFIRE 2009)
Alaska Natural Heritage Program Landcover Class: Low-Tall Shrub: Alder-Salmonberry (Boggs et al. 2016)
Alaskan Vegetation Classification: Tall Alder Scrub (Viereck et al. 1992)
Ecological site concept
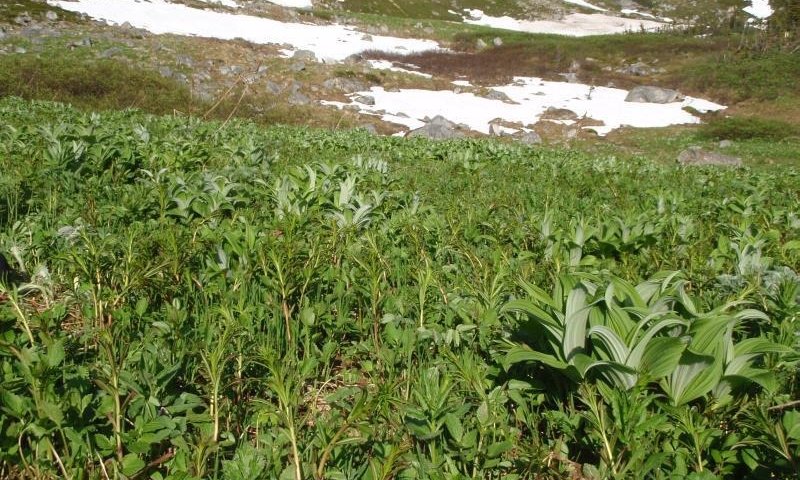
This subalpine site occurs on avalanche chutes. Avalanche chutes are typically not forested and support fast growing shrub species and an assortment of grasses and forbs. While an avalanche chute can go from the alpine to sea-level, this site covers the portion of an avalanche chute in the subalpine life zone. The soils are dry for much of the growing season and are considered moderately well to well drained. Soils are gravelly and composed of a mixture of colluvium and residuum. Bedrock typically occurs within 20 inches.
The reference plant community is closed tall scrub dominated by Sitka alder and salmonberry. Areas where avalanche remove this tall scrub community support highly diverse herbaceous meadows (Landfire 2009; Boggs et al. 2008).
Associated sites
| F220XY200AK |
Subalpine Forest Gravelly Dry Slopes Occurs on similar bands of elevation on dry soils that support forested communities. |
|---|---|
| F220XY338AK |
Subalpine Forests Dry Organic Slopes Occurs on similar bands of elevation on dry organic soils that support forested communities. |
| F220XY204AK |
Subalpine Forests Organic Wet Slopes Occurs on similar bands of elevation on wet organic soils that support forested communities. |
Similar sites
| R220XY358AK |
Subalpine Scrub Gravelly Dry Slopes Both sites have tall scrub plant communities. R220XY358AK does not occur in avalanche chutes. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Alnus viridis ssp. sinuata |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Avalanche destroys and removes woody vegetation |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Time and recovery after an avalanche. |