Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R222XY352AK
Alpine Dwarf Scrub Dry Organic Slopes
Last updated: 2/18/2025
Accessed: 03/06/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
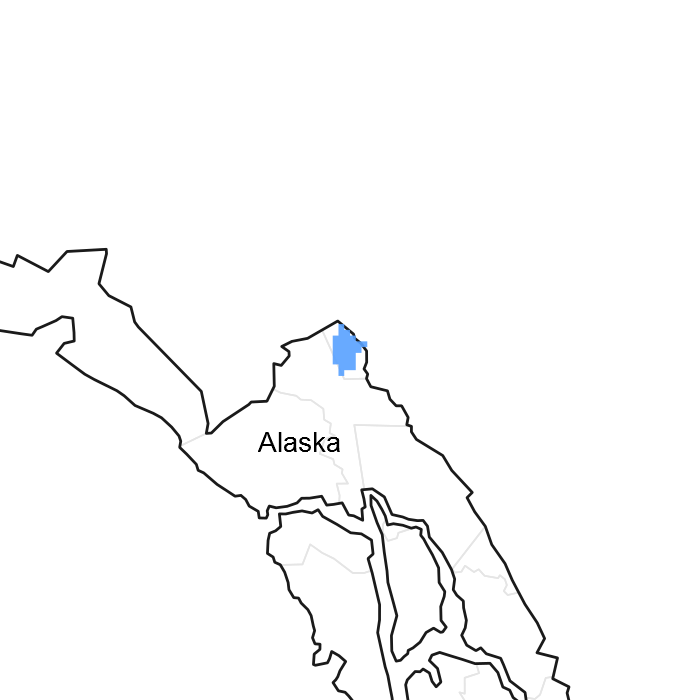
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 222X–Southern Alaska Coastal Mountains
This area is in the Southern Alaska Region and includes the higher elevations of the Coast, St. Elias, Chugach, and Kenai Mountains. The area makes up about 26,335 square miles. The terrain consists of steep, rugged, high-relief mountains. Glaciers and ice fields make up about 54 percent of the area. Unglaciated portions of the area are deeply incised with narrow to broad valleys. Flood plains and stream terraces on valley floors rapidly give rise to steep alluvial fans and mountain footslopes. Elevation ranges from sea level at the base of tidewater glaciers and ice fields to 18,008 feet at the summit of Mt. St. Elias (USDA 2006).
During the Pleistocene epoch, the area was covered with glacial ice. As the glacial ice melted, sediments were deposited by the melting ice. However, most of the original glacial deposits have eroded away or have been buried by colluvium and slope alluvium, which covers more than 90 percent of the present unglaciated landscape. The remaining glacial and glaciofluvial deposits and recent fluvial deposits are generally restricted to the bottoms of the larger valleys. Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Lower Tertiary stratified sedimentary rocks, and occasionally Paleozoic intrusive rocks, underlie much of the area and are exposed on steep mountain slopes and ridges (USDA 2006).
Miscellaneous (non-soil) areas make up more than 90 percent of this MLRA. The most common miscellaneous areas are rock outcrop, rubble land, avalanche chutes, and glaciers. The dominant soil orders in this area are Spodosols and Histosols. The soils in the area have a cryic soil temperature regime or a subgelic soil temperature class, a udic or aquic soil moisture regime, and mixed or amorphic mineralogy (USDA 2006).
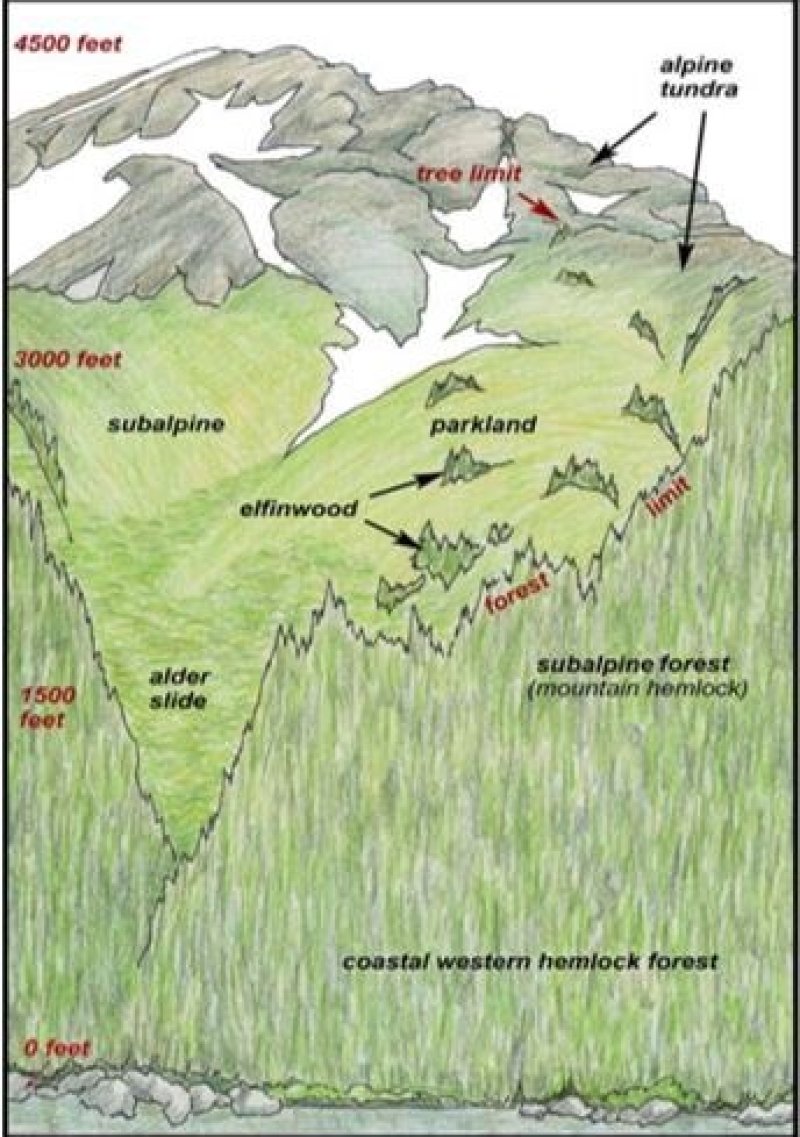
Alpine plant communities characterize the vegetation in this area. Alpine vegetation consists of a variety of dwarf scrub and herbaceous communities. Low willow scrub is common in drainages. Lichens, scattered herbs, and dwarf shrubs dominate bedrock exposures and very shallow soils. In general, there is little or no plant growth at elevations above about 7,500 feet (USDA 2006). At lower elevations, subalpine vegetation consists of a variety of mountain hemlock and tall scrub communities. These subalpine plant communities typically occur at elevations between 1500 to 3000 feet (Boggs et al. 2010, Carstensen 2007, Jaques 1983; Martin et al. 1995) and are associated with the Alexander Archipelago-Gulf of Alaska Coast area (MLRA 220X).
The area is almost entirely undeveloped wild land. Remote wild-land recreation is the principal land use in this area. The rugged, high mountains, extensive glaciers and ice fields, and wilderness qualities of the area attract visitors from around the world. Small rural communities along the road system are the only permanent settlements. Part of the Wrangell-St. Elias Bay National Park and Preserve, the Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve, the Misty Fjords National Monument, the Chugach National Forest, and the Tongass National Forest are in this MLRA.
Classification relationships
National Vegetation Classification – Ecological Systems: Alaskan Pacific Maritime Alpine Sparse Shrub and Fell-Field (CES204.318) (NatureServe 2015)
Biophysical Settings: Alaskan Pacific Maritime Herbaceous Dwarf Shrubland (BpS 7816430) (LANDFIRE 2009)
Ecological site concept
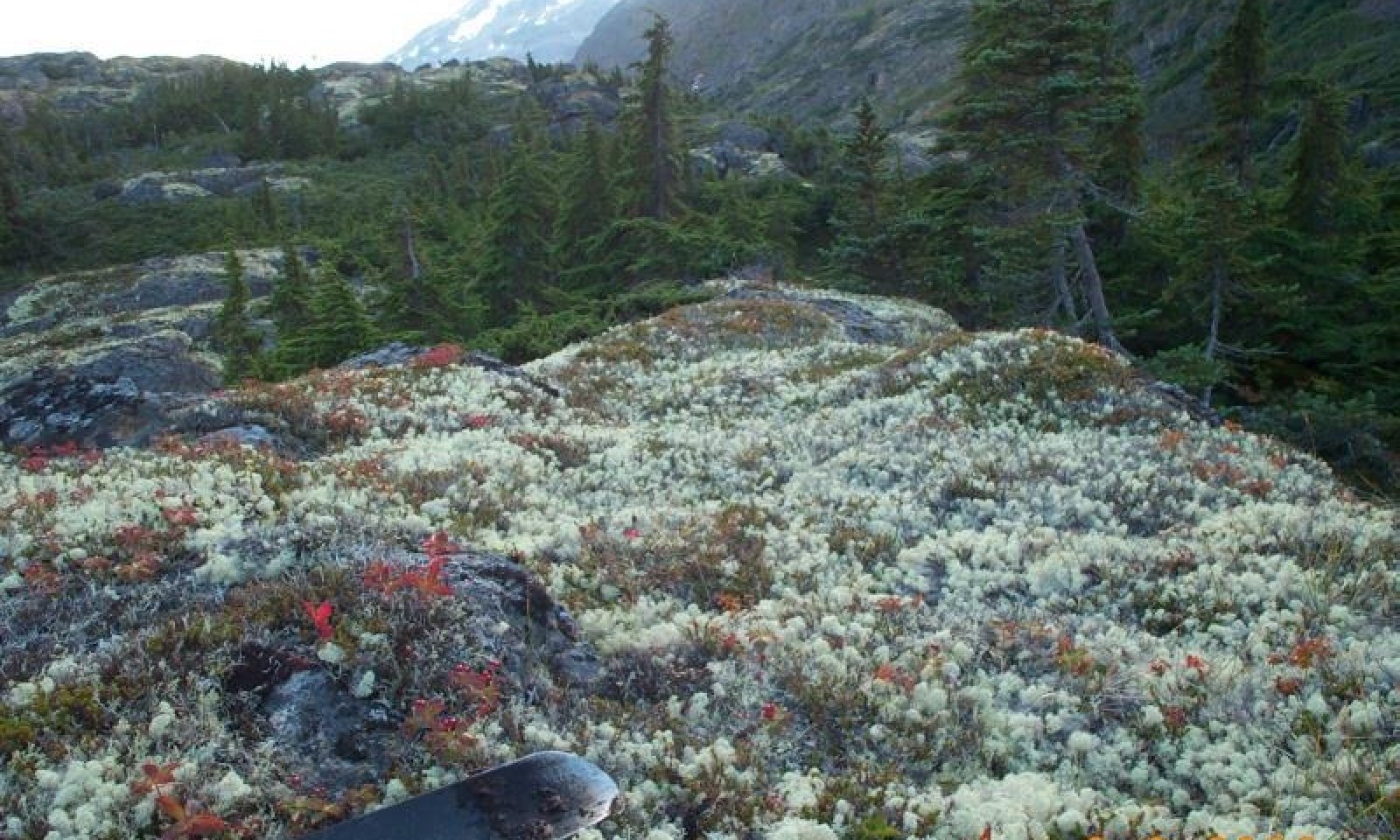
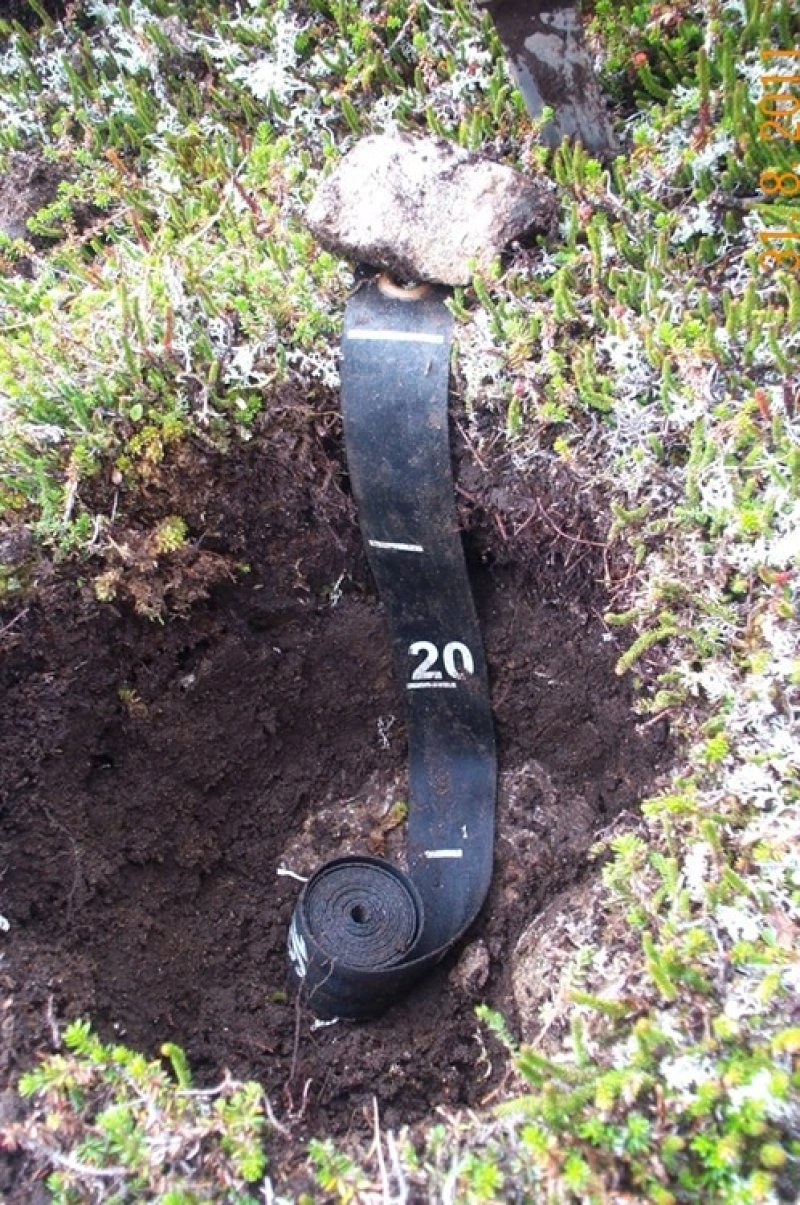
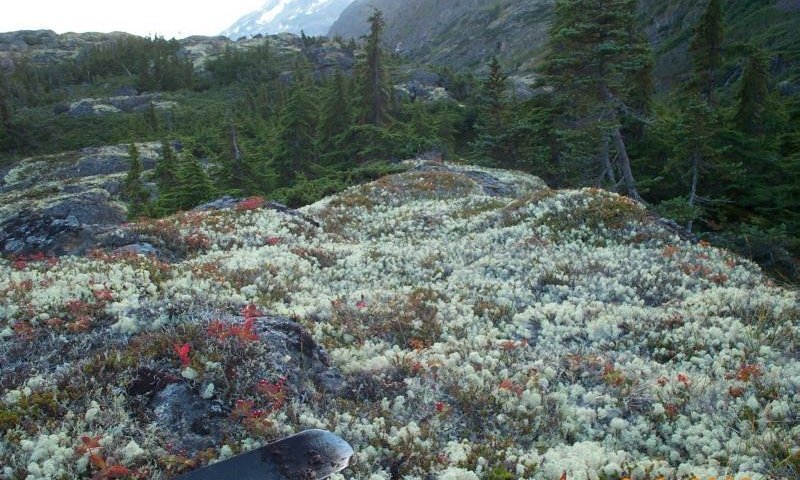
This high-elevation site has shallow, organic soils and is associated with a harsh alpine climate. The alpine is characterized as having very short growing seasons, cold temperatures, and high-winds. The soils are a dry organic mat over bedrock typically at or below 10 inches. The harsh alpine climate and shallow, organic soils combine to prevent the growth and dominance of common subalpine species like mountain hemlock.
The reference plant community is ericaceous dwarf scrub. Common species include black crowberry, bog blueberry, alpine sweetgrass, star reindeer lichen, greygreen reindeer lichen, and bunchberry dogwood. The primary disturbance processes that maintain this plant community are exposure to cold temperatures, wind, and avalanches (NatureServe 2018).
Associated sites
| R222XY357AK |
Alpine Dwarf Scrub Moist Gravelly Slopes Occurs in the alpine in protected areas with persistent snowpack, resulting in wet mineral soils with a shortened growing season. |
|---|---|
| R222XY356AK |
Alpine Dwarf Scrub Dry Gravelly Slopes Occurs on alpine exposed slopes with 10 to 20 inches of mineral soil over bedrock. |
| R222XY360AK |
Alpine Herbaceous Wet Organic Depressions Both sites occur in the alpine where organic matter accumulates, however, site 360 is saturated organic matter over bedrock. |
Similar sites
| R222XY356AK |
Alpine Dwarf Scrub Dry Gravelly Slopes Both sites support ericaceous dwarf scrub plant communities. Site 352 typically has more lichen cover and occurs on soils less than 10 inches deep, whereas site 356 occurs on soils 10-20 inches deep on convex shapedexposed slopes. |
|---|---|
| R222XY360AK |
Alpine Herbaceous Wet Organic Depressions Both sites occur in the alpine where organic matter accumulates; however, site 360 is saturated organic matter over bedrock. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Empetrum nigrum |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Cladina stellaris |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.