Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site XA232X01Y222
Boreal Graminoid Loamy Terrace Depressions
Last updated: 5/18/2020
Accessed: 02/12/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 232X–Yukon Flats Lowlands
The Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA is an expansive basin characterized by numerous levels of flood plains and terraces that are separated by minimal breaks in elevation. This MLRA is in Interior Alaska and is adjacent to the middle reaches of the Yukon River. Numerous tributaries of the Yukon River are within the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. The largest are Beaver Creek, Birch Creek, Black River, Chandalar River, Christian River, Dall River, Hadweenzic River, Hodzana River, Porcupine River, and Sheenjek River. The MLRA has two distinct LRU—lowlands and marginal uplands. The lowlands have minimal local relief and are approximately 9,000 square miles in size (Williams 1962). Landforms associated with the lowlands are flood plains and stream terraces. The marginal uplands consist of rolling and dissected plains that are a transitional area between the lowlands and adjacent mountain systems. The marginal uplands are approximately 4,700 square miles in size (Williams 1962).
This MLRA is bounded by the Yukon-Tanana Plateau to the south, Hodzana Highlands to the west, Porcupine Plateau to the east, and southern foothills of the Brooks Range to the north (Williams 1962). These surrounding hills and mountains partially isolate the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA from weather systems affecting other MLRAs of Interior Alaska. As a result, temperatures are generally warmer in summer and colder in winter than is characteristic in other areas at comparable latitude. There is a moisture and temperature gradient in which the lowlands region tends to be drier and colder and the surrounding marginal uplands region tends to be moister and warmer (PRISM Climate Group 2006).
The Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA is mostly undeveloped lands that are sparsely populated and not accessible by a road system. A number of villages, including Beaver, Birch Creek, Chalkyitsik, Circle, Fort Yukon, Stevens Village, and Venetie, are adjacent to the Yukon River or one of its major tributaries. The largest village is Fort Yukon, which according to the 2010 U.S. Census has 583 residents that are dominantly Gwich’in Alaska Natives.
LRU notes
Alaska has no officially recognized LRU. However, there appear to be two distinct LRU in the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. These LRU are thought to have differing climatic regimes, landforms, and soil types (STATSGO and Jorgensen and Meidinger 2015). The two LRU were previously discussed in the MLRA notes section above and are termed the lowlands LRU and the marginal uplands LRU.
This ecological site is associated with the lowlands LRU.
Classification relationships
Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA.
Ecological site concept
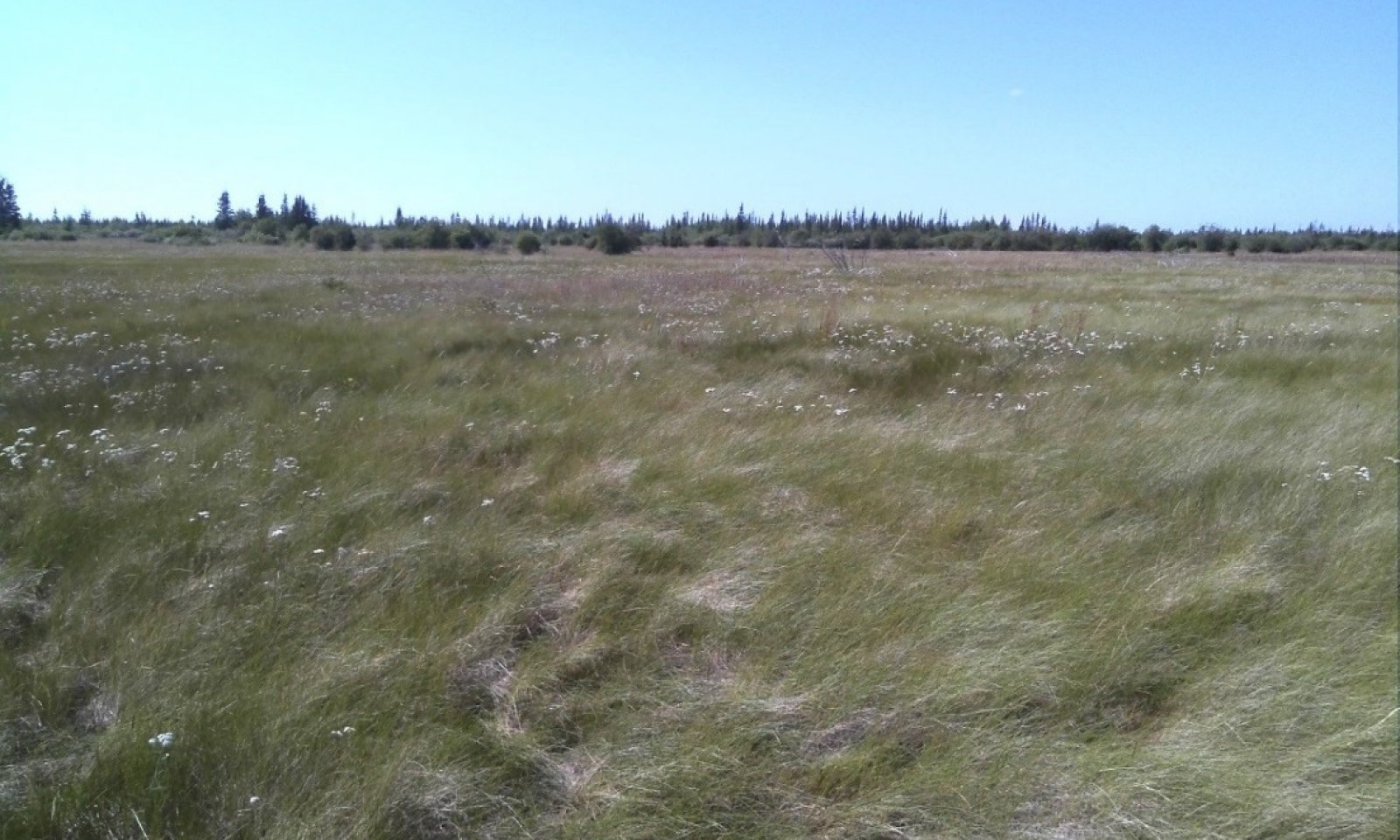
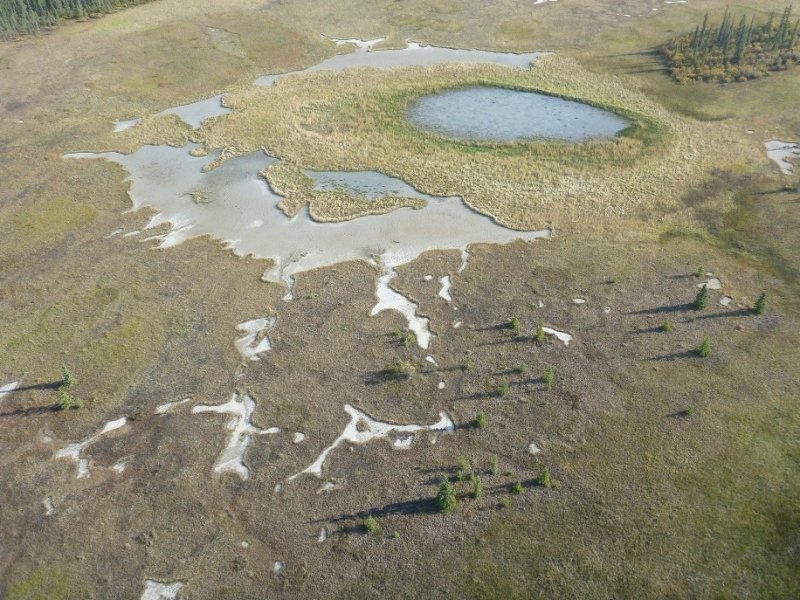
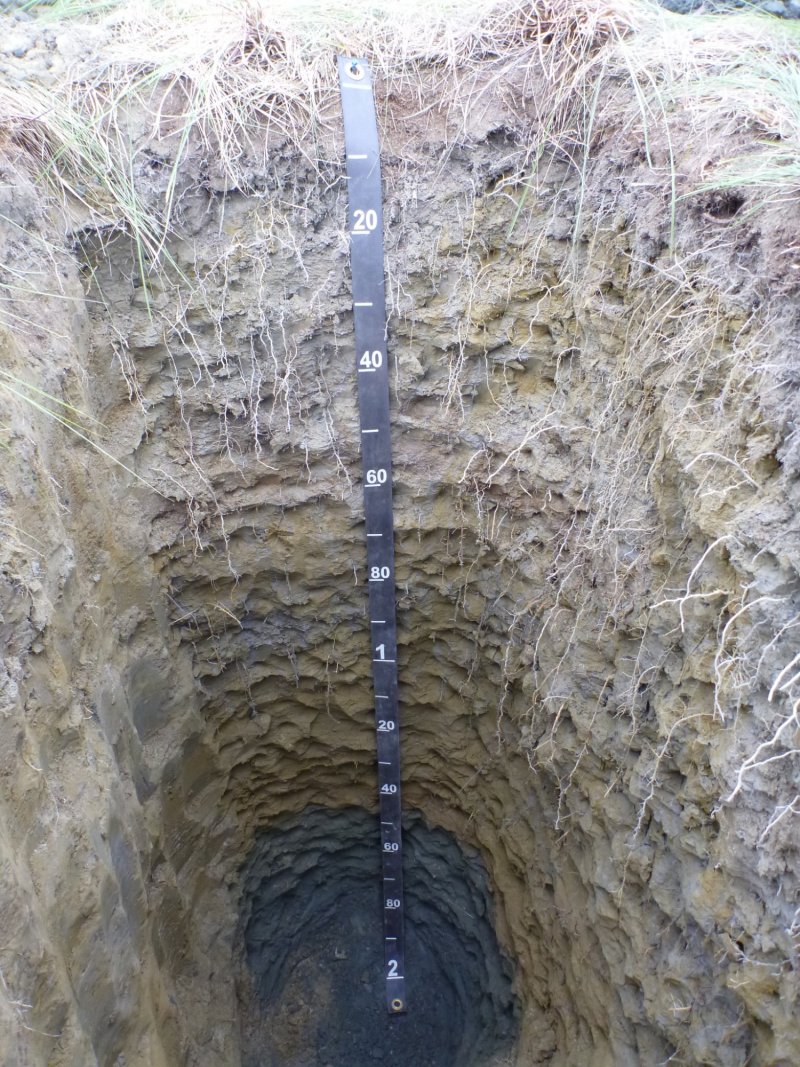
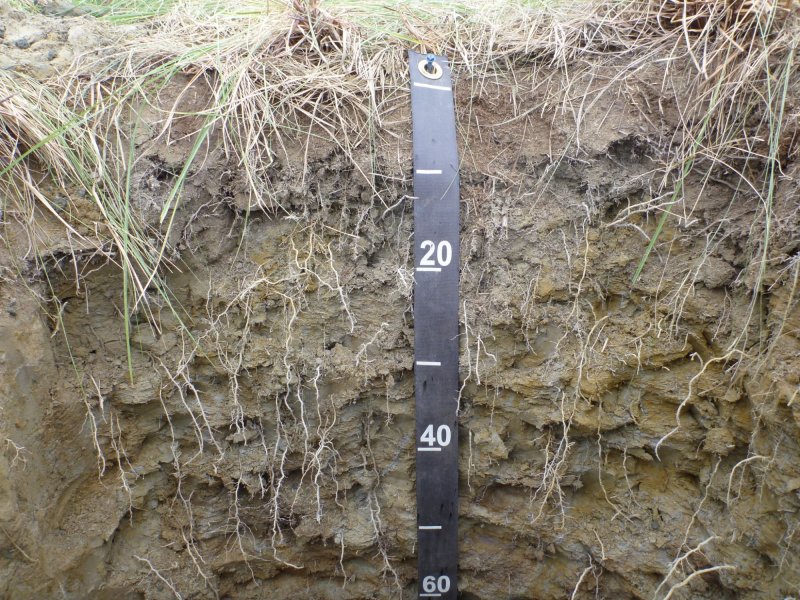
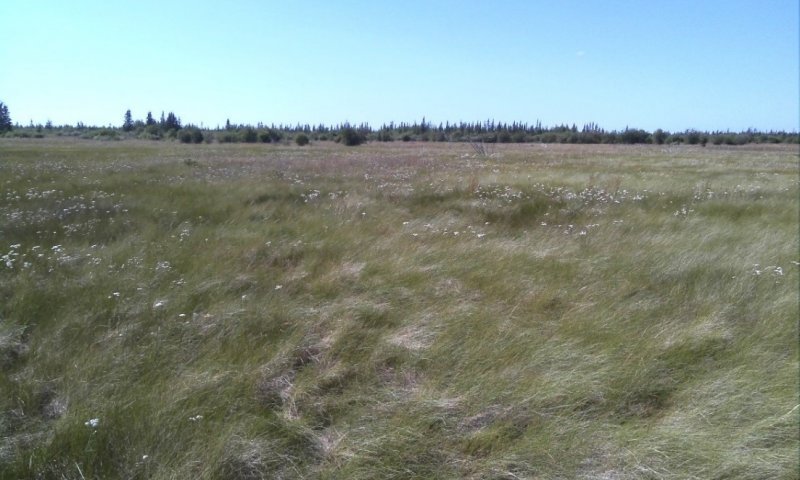
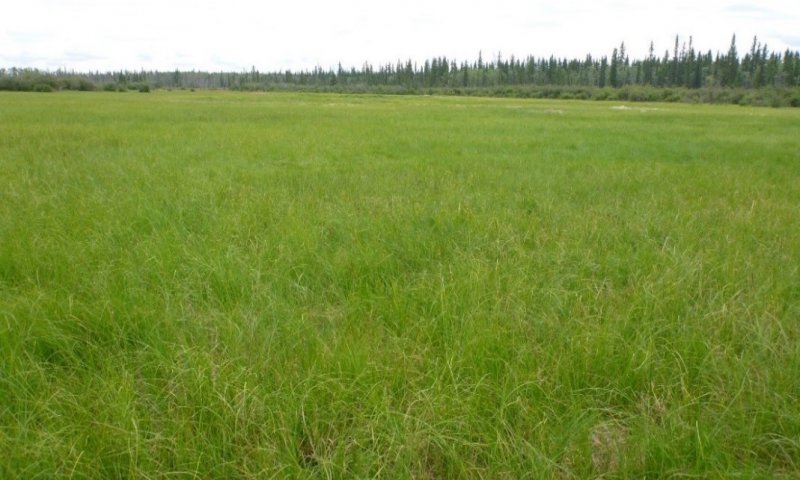
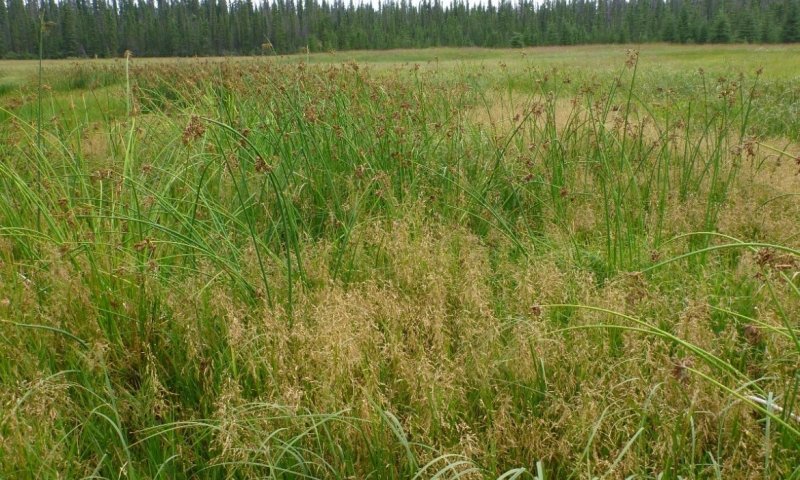
This ecological site is associated with closed depressions of stream terraces that support a reference state with multiple graminoid-dominant communities. These depressions are considered closed because they are not associated with a flood regime and have limited, if any, groundwater flow or recharge. The presumed hydrological inputs for this ecological site are primarily thaw of the annual active soil layer and/or permafrost, snowmelt runoff, and precipitation. This hydrologic regime coupled with the areas parent material results in the development of sodic soil properties.
Sodic soils have electrical conductivity of less than 4 dS/m, pH of greater than 8.5, and exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) greater than 15 (Ogle and John 2010). Since these depressions are closed, soil water is drawn upward through the soil during summer months via evapotranspiration. This causes accumulation of salts in the soil profile and is a feature commonly observed in arid or semi-arid basin soils of the continental United States. Salt compounds in the soils are calcite, dolomite, gypsum, halite, and trona (Clautice and Mowatt 1981). Certain plant species are better adapted to the physiological stress associated with sodic soils than others, which likely leads to the unique plant communities observed in the reference state for this ecological site.
Associated sites
| XA232X01Y218 |
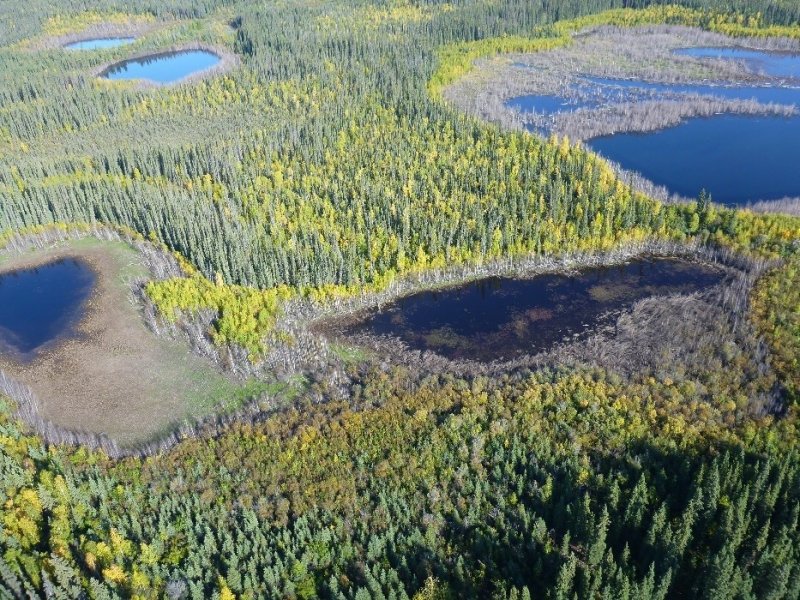
Boreal Woodland Loamy Frozen Terraces This ecological site is associated with wet soils on the tread of stream terraces in Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. Soils generally have permafrost at moderate depth (20 to 40 inches) and pond occasionally for long durations of time. The reference plant community is characterized as a needleleaf woodland (10 to 25 percent cover; Viereck et al. 1992) composed of black spruce (Picea mariana) and white spruce (Picea glauca). |
|---|---|
| XA232X01Y219 |
Boreal Forest Loamy Terraces Moist This ecological site is associated with somewhat poorly to moderately well drained soils on the treads of stream terraces in the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. Flooding frequency ranges from rare to none. The reference plant community is characterized as an open needleleaf forest (25 to 60 percent cover) primarily composed of mature white spruce (Picea glauca). |
| XA232X01Y223 |
Boreal Scrub Loamy Frozen Terrace Depressions This shrubby ecological site occurs in the transitional area between the forested tread of a stream terrace and the graminoid-dominant communities associated with closed, terrace depressions (ecological site XA232X01Y222). This site typically occurs between the outer third and lip of these closed depressions. The reference plant community for ecological site is characterized as an open tall scrubland (Viereck et al. 1992) and those shrubs are primarily an assortment of willow (Salix spp.). |
| XA232X01Y229 |
Boreal Scrub Loamy Terrace Swales This ecological site is associated with swales on stream terraces in lowlands region of the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. Associated soils are considered very poorly drained. The reference plant community is characterized as open tall scrub (Viereck et al. 1992) and the dominant shrubs are willow (Salix spp.) and shrub birch (Betula glandulosa). |
| XA232X01Y212 |
Boreal Sedge Peat Terrace Depressions This ecological site is associated with drainageways on stream terraces in the lowlands region of the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. Associated drainageways are very poorly drained with a water table that remains above the soil surface for the entire growing season. The reference plant community phase is characterized as subarctic lowland sedge wet meadow (Viereck et al. 1992) and is composed primarily of water sedge (Carex aquatilis). |
| XA232X01Y221 |
Boreal Forest Loamy Terraces This ecological site is associated with moderately well to well drained soils on the tread of stream terraces in the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. Flooding frequency ranges from rare to none. The reference plant community is characterized as an open needleleaf forest (25 to 60 percent cover) primarily composed of mature white spruce (Picea glauca). |
| XA232X01Y262 |
Boreal Woodland Gravelly Terraces This ecological site is associated with wet soils on the tread of gravelly stream terraces in the lowlands region of the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. Gravelly horizons range from very shallow to shallow depths (0 to 20 inches) and soils lack permafrost at depth. The pH of soil horizons commonly range from neutral to moderately alkaline, which leads to diverse species assemblages. The reference plant community phase is characterized as a needleleaf woodland (10 to 25 percent cover; Viereck et al. 1992) composed primarily of black spruce (Picea mariana) and white spruce (Picea glauca). |
| XA232X01Y209 |
Boreal Tussock Loamy Frozen Terraces This ecological site occurs on stream terraces in the lowlands region of the Yukon Flats Lowlands MLRA. Soils commonly have permafrost at moderate depth (20 to 40 inches) and pond frequently for very long durations. The reference plant community is characterized as open low mixed shrub-sedge tussock bog (Viereck et al. 1992). |
Similar sites
| XA232X01Y205 |
Boreal Grass Loamy Flood Plain Depressions Ecological site XA232X01Y205 supports a similar graminoid-dominant reference state and plant communities. XA232X01Y205 occurs in depressions of flood plains, is associated with a flood regime, and is associated with soils that do not have sodic parent materials. These differences in landform position, disturbance regime, and soil type result in similar, but unique, plant communities for each ecological site. |
|---|
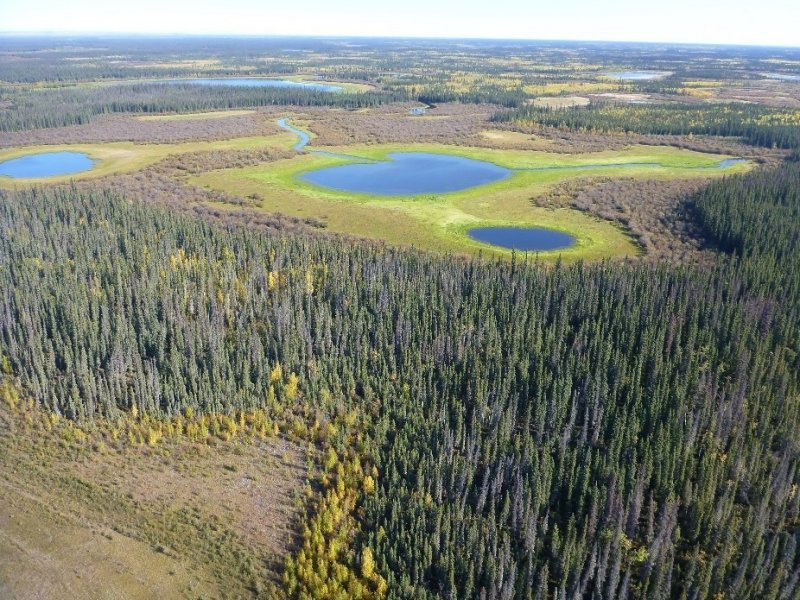

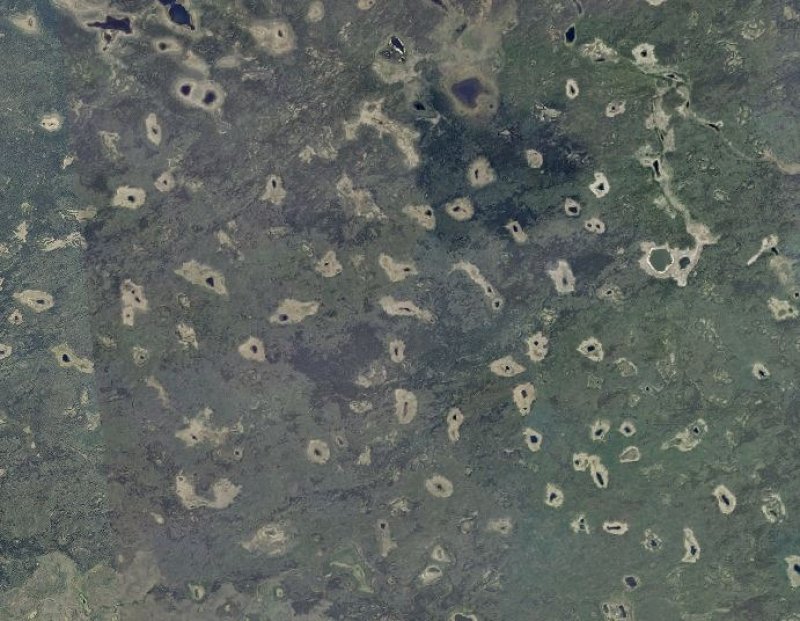
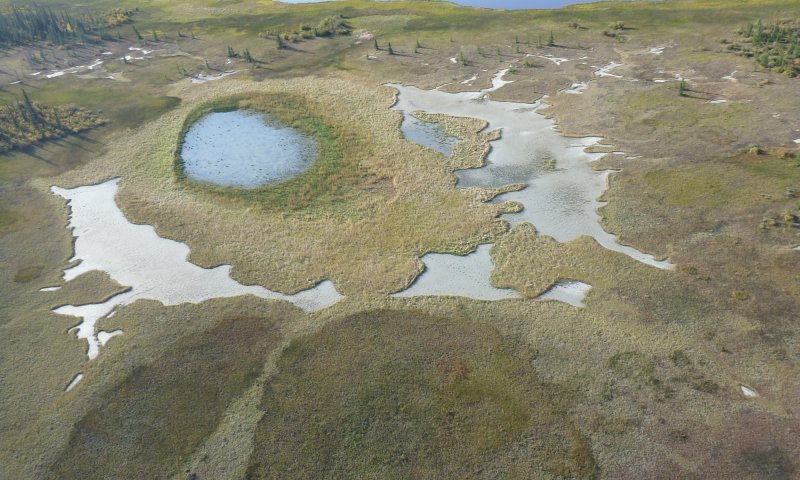
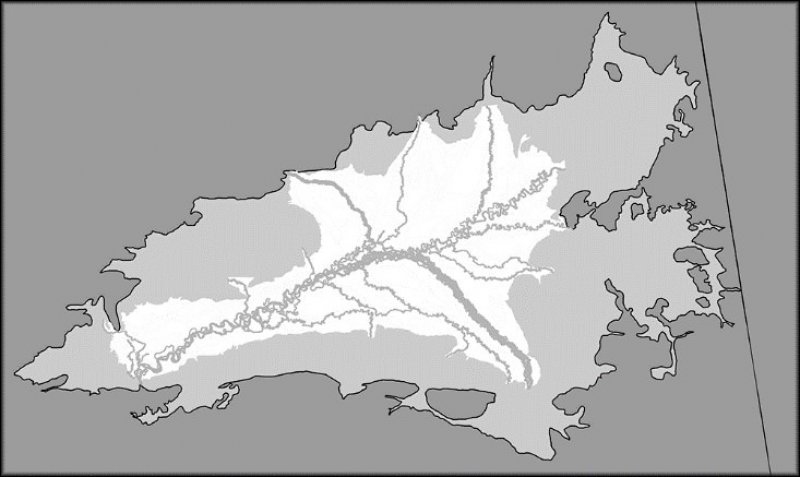
Figure 1. Aerial photograph of closed depressions in the Yukon Flats Lowlands. The outer third, or lip, of these depressions commonly supports willow dominant plant communities (XA232X01Y223).
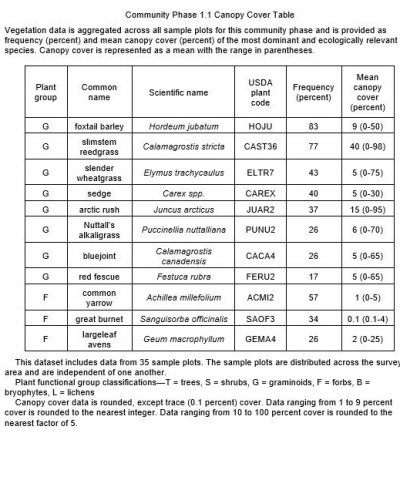
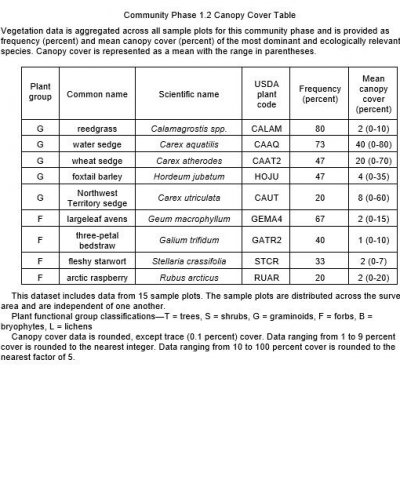
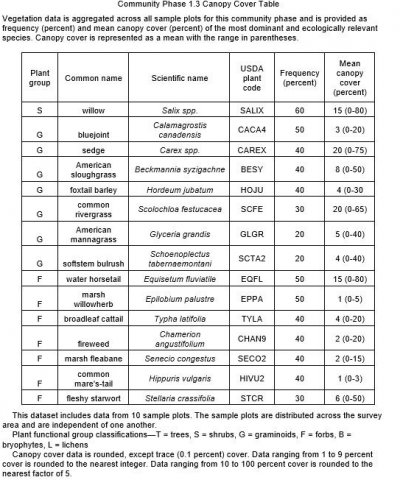
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Calamagrostis stricta |
Legacy ID
R232XY222AK
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.